Chapter 12: Food Production and the Environment
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
Food security
Every person in a given area has daily access to enough nutritious food to have an active and healthy life
Food insecurity
Living with chronic hunger and poor nutrition, which threatens one's ability to lead healthy and productive lives
Poverty
The root cause of food insecurity is...
Macronutrients
Ex) carbs, proteins, and fats
Micronutrients
Ex) vitamins, iron, iodine, and calcium
Chronic undernutrition
Occurs in people who cannot grow or buy enough food to meet their basic energy needs
Chronic malnutrition
Deficiencies of protein and other key nutrients
Iodine
Essential for proper functioning of the the thyroid gland, which produces hormones that control the body's rate of metabolism (deficiency causes goiter)
Famine
A severe shortage of food in an area accompanied by mass starvation, many deaths, economic chaos, and social disruption
Overnutrition
Occurs when food energy intake exceeds energy use and causes excess body fat
Underweight or overweight
People who have a lower life expectancy, greater susceptibility to disease and illness, and lower productivity and life quality
Croplands
Produce mostly grains and provide about 77% of the worlds food using 11% of its land area
Ranglands, pastures and feedlots
Produce meat and supply about 16% of the world's food using about 29% of its land area
Ocean fisheries and aquaculture
Produce 7% of the world's food
Industrialized or high-input agriculture
Uses heavy equipment and large amounts of financial capital, fossil fuel, water, commercial fertilizers and pesticides to produce single crops
Monocultures
Single crops
Yield
The amount of food produced per unit of land
Plantation agriculture
A form of industrialized agriculture used primarily in tropical developing countries; involves cash crops
Cash crops
crops grown especially for export and profit; ex. Bananas, soybeans, sugarcane, coffee, and palm oil
Hydroponics
A method whereby plants are grown with their roots in troughs of water inside a greenhouse
Traditional subsistence agriculture
Uses mostly human labor and draft animals to produce only enough crops for a farm family's survival, with little left over to sell or store as a reserve in hard times
Traditional intensive agriculture
Farmers increase their inputs of human and draft-animal labor, fertilizer, and water to obtain higher crop yields
Polyculture
Growing several crops on the same plot simultaneously
slash-and-burn agriculture
a type of polyculture; involves burning and clearing small plots in tropical forests, growing a variety of crops for a few years until the soil is deleted of nutrients, and then shifting to other plots.
O Horizon
Leaf litter
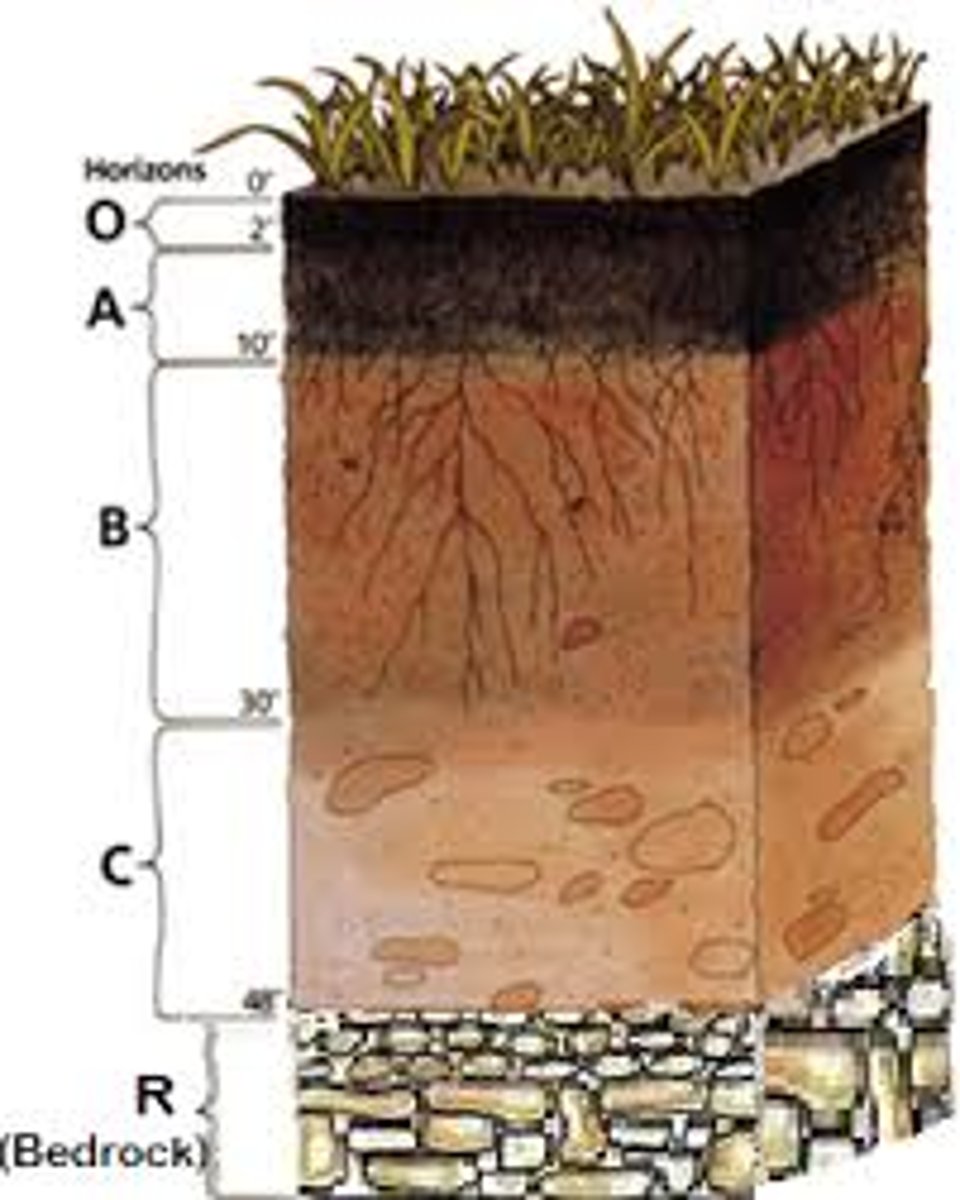
A Horizon
Topsoil
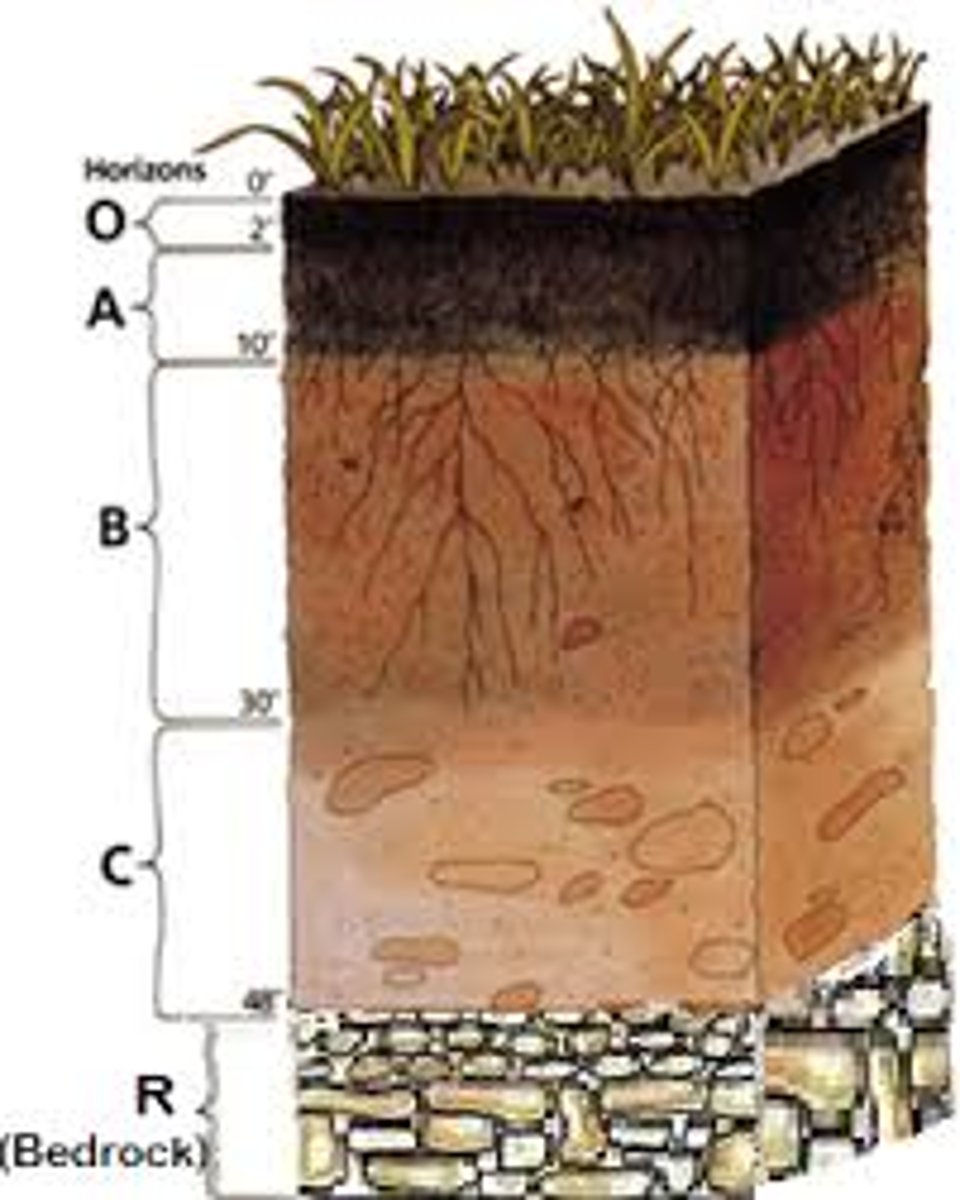
B Horizon
Subsoil
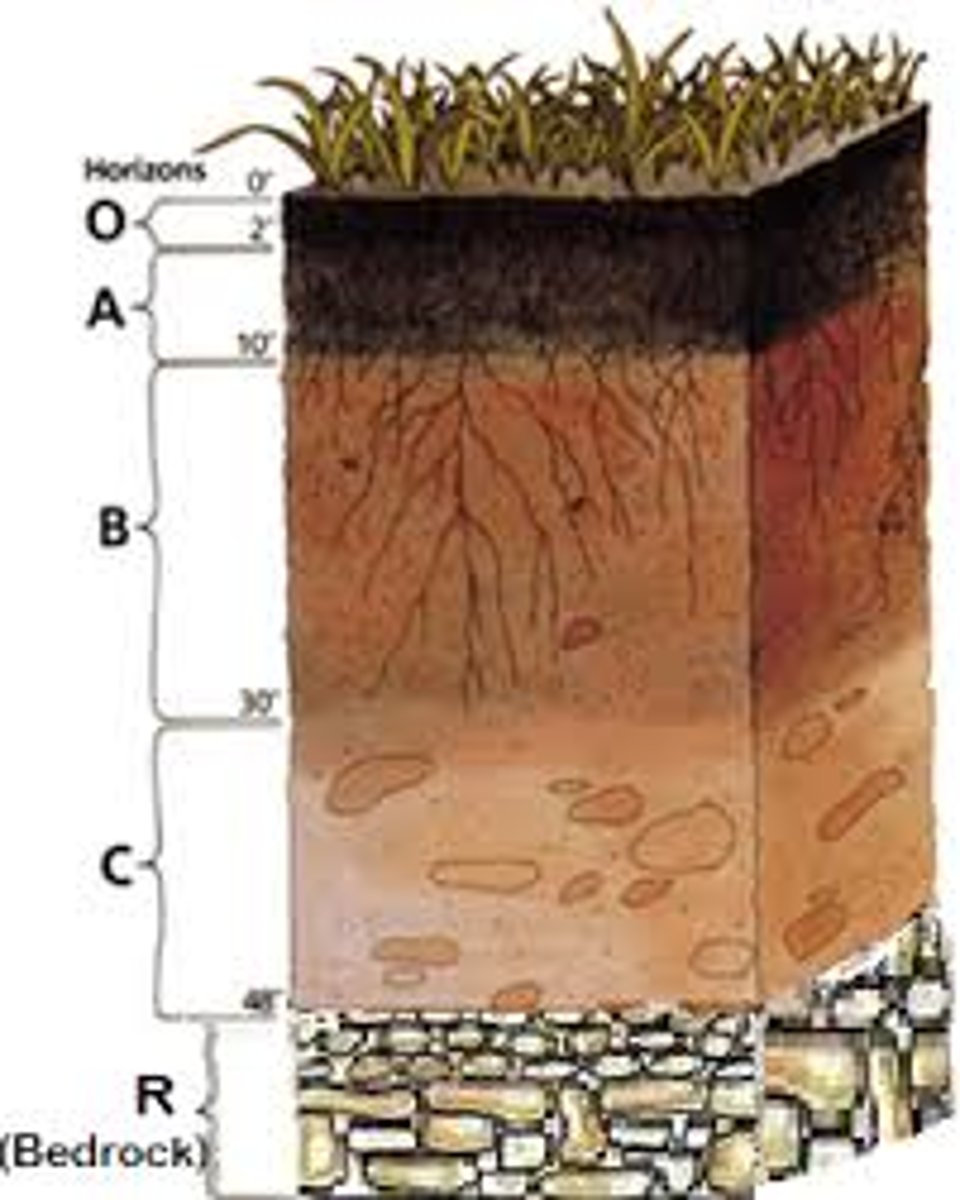
C Horizon
Parent material; often lies on bedrock
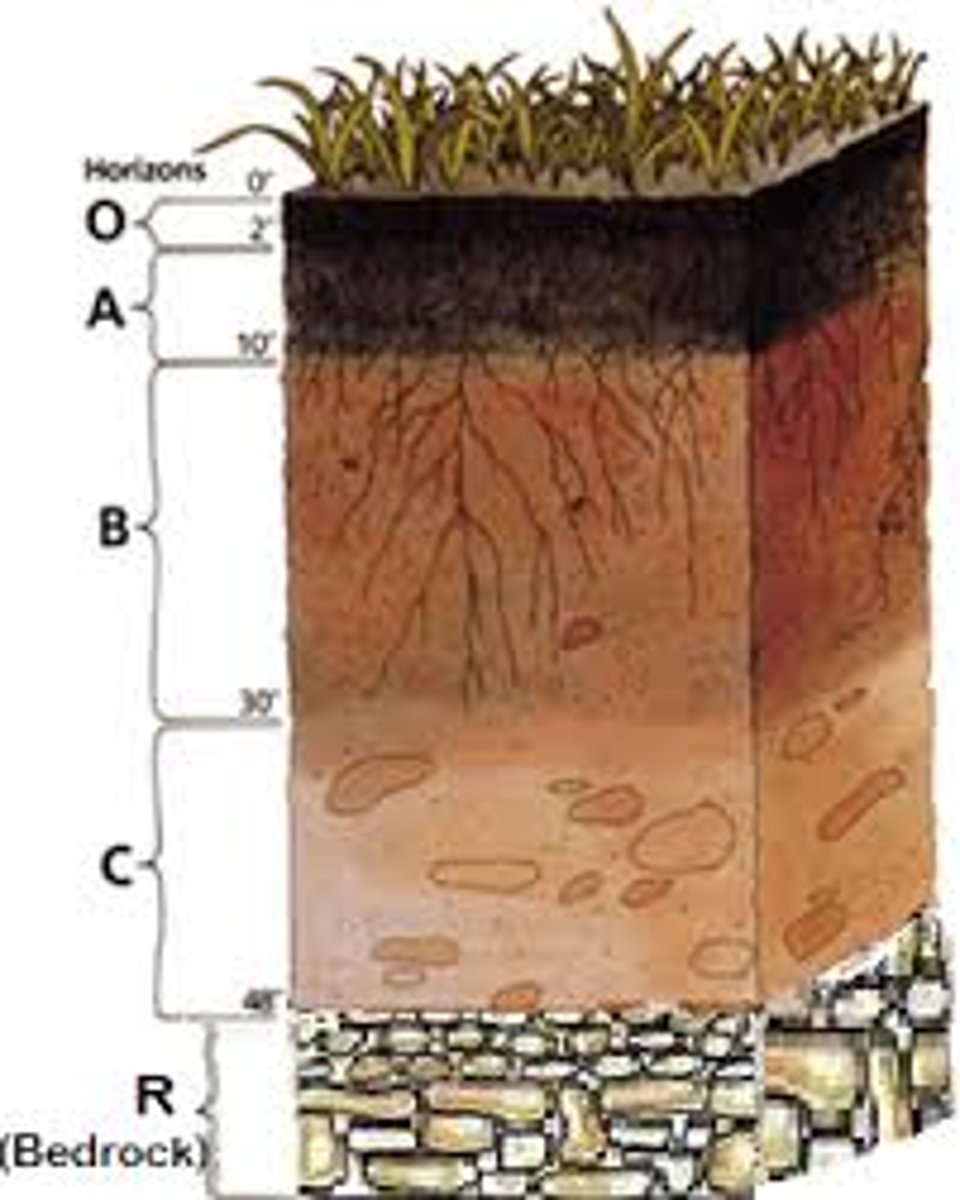
Humus
Porous mixture of the partially decomposed bodies of dead plants and animals
Low-input; high-input
measurements of the amount of chemicals and effort needed to accomplish a certain type of agriculture
agribusinesses
a small number of giant multinational corporations increasingly controlling the growing, processing, distribution, and sale of food in the United States and in the global marketplace
first gene revolution
involves cross breeding through artificial selection; typically takes 15 years
second gene revolution
involves genetic engineering; results in genetically modified organisms or transgenic organisms
advanced tissue culture
Using this method, scientists have altered citrus trees, which normally take 6 years to produce fruit, to yield fruit in only one year. Scientists hope to use this technique to mass-produce only orange juice sacs which would eliminate the need for citrus orchards altogether.
fishery
a concentration of particular aquatic species suitable for commercial harvesting in a given ocean area or inland body of water
aquaculture/fish-farming
raising marine and freshwater fish in ponds and underwater cages
blue revolution
nickname for aquaculture
soil erosion
the movement of soil components, especially surface litter and topsoil, from one place to another by the actions of wind and water
waterlogging
water accumulates underground and gradually raises the water table
marginal land
Land that is not well suited for growing crops
agrobiodiversity
the world's genetic variety of animals and plants used to provide food
pest
any species that interferes with human welfare by competing with us for food, invading lawns and gardens, destroying building materials, spreading disease, invading ecosystems, or simply being a nuisance
natural enemies
all the predators and parasites and even disease organisms that may feed on a given organism; used to control a specific pest through predation or parasitism
first-generation pesticides
mainly natural chemicals borrowed from plants
second-generation pesticides
synthetic organic compounds used to kill insects and other pests; started with the use of DDT in the 1940s
broad-spectrum agents
pesticides that are toxic to many pest and nonpest species; i.e. DDT, organophosphate compounds such as malathion and parathion
narrow-spectrum (selective) agents
pesticides that are effective against a narrowly defined group of organisms
boomerang effect (aka the circle of poison)
residues of banned or unapproved chemicals exported to other countries can return to the exporting countries on imported food
integrated pest management (IPM)
a variety of pest control methods that include repairs, traps, bait, poison, etc. to eliminate pests
soil conservation
involves using a variety of ways to reduce soil erosion and restore soil fertility, mostly by keeping the soil covered with vegetation
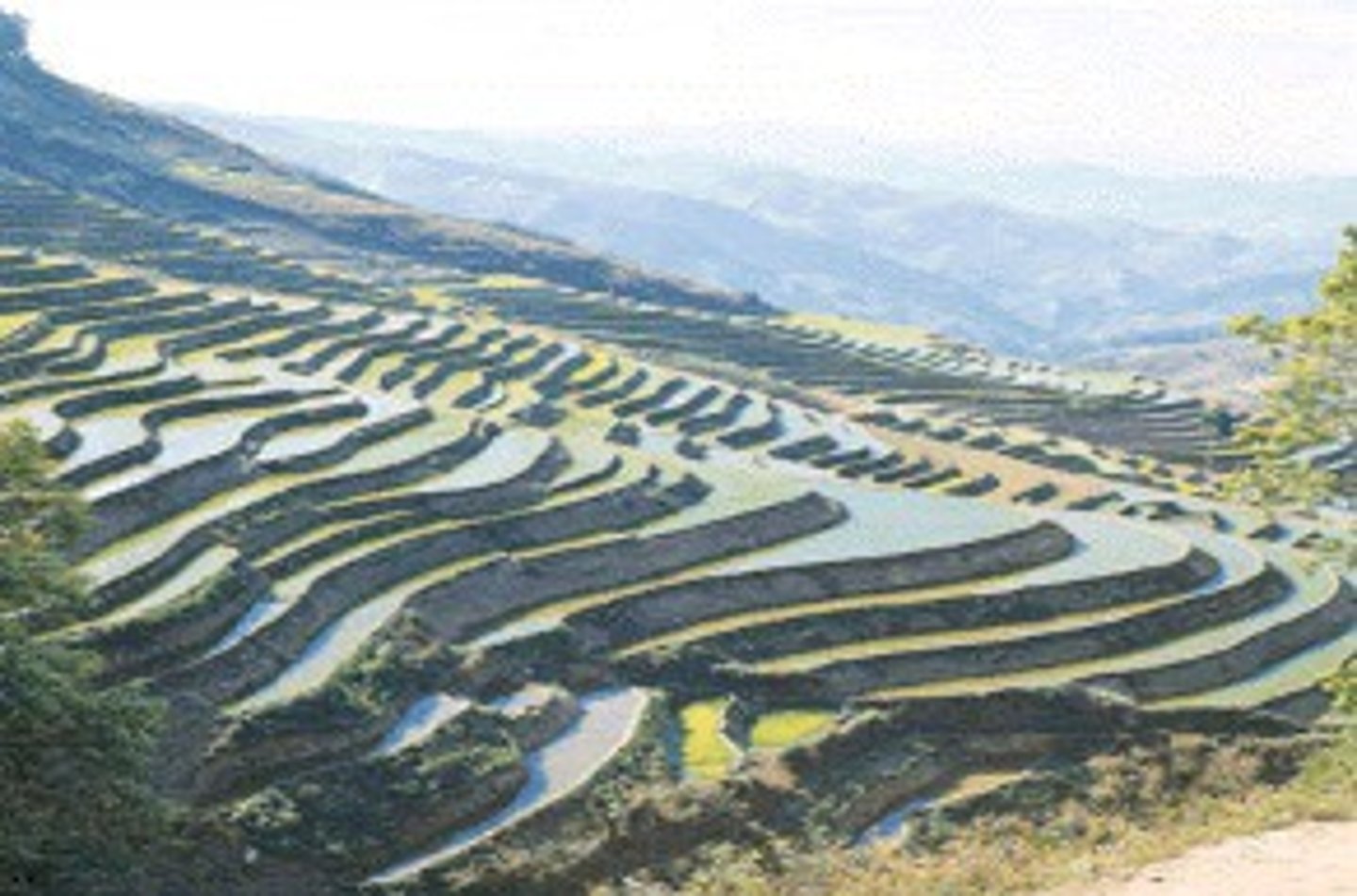
terracing
a way to grow food on steep slopes without depleting topsoil; it is done by converting steeply sloped land into a series of broad, nearly level terraces that run across the land's contours

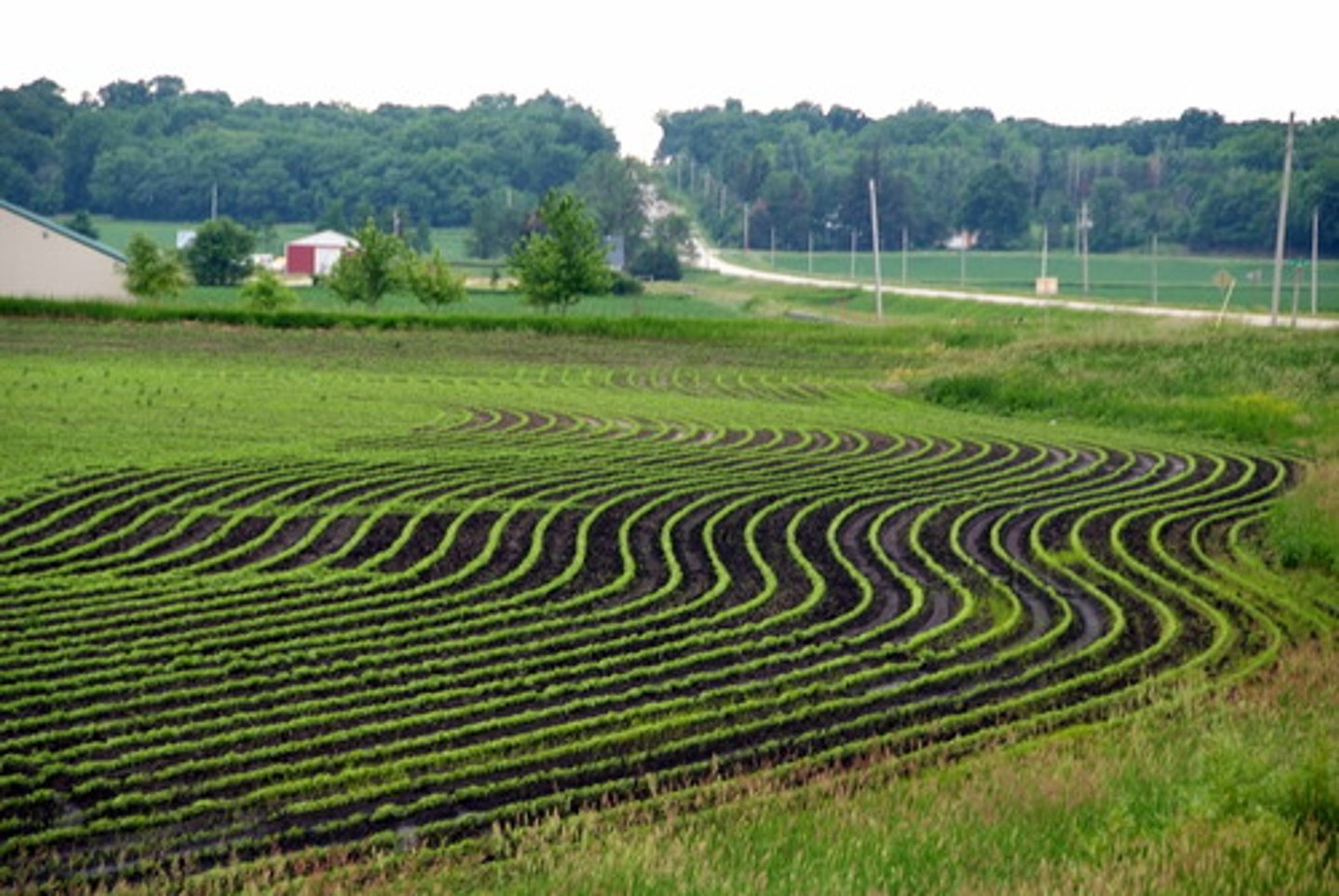
contour planting
involves plowing and planting crops in rows across the slope of the land rather than up and down

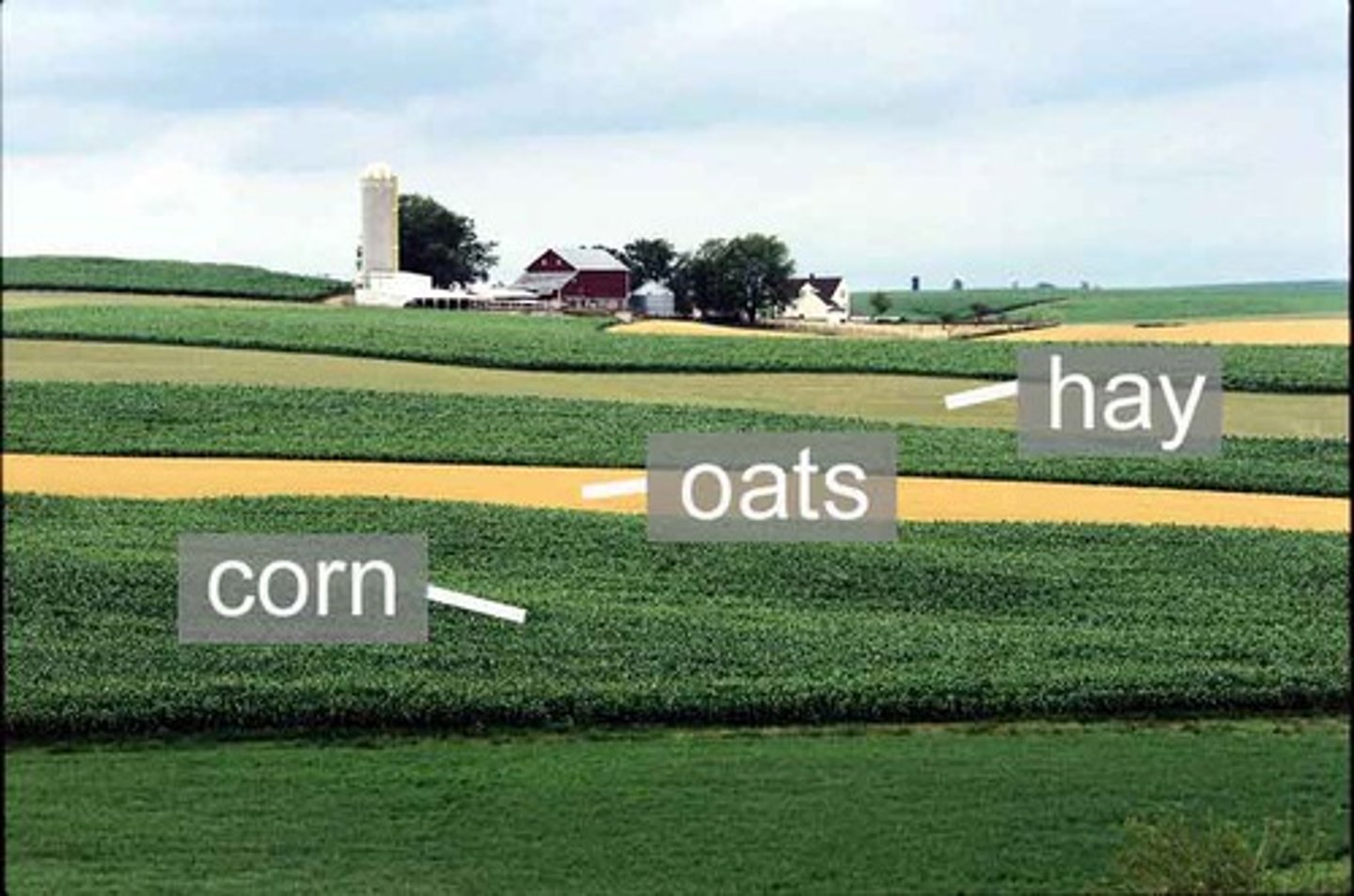
strip cropping
involves planting alternating strips of a row crop (i.e. corn or cotton) and another crop that completely covers the soil, called a cover crop (i.e. alfalfa, clover, rye)

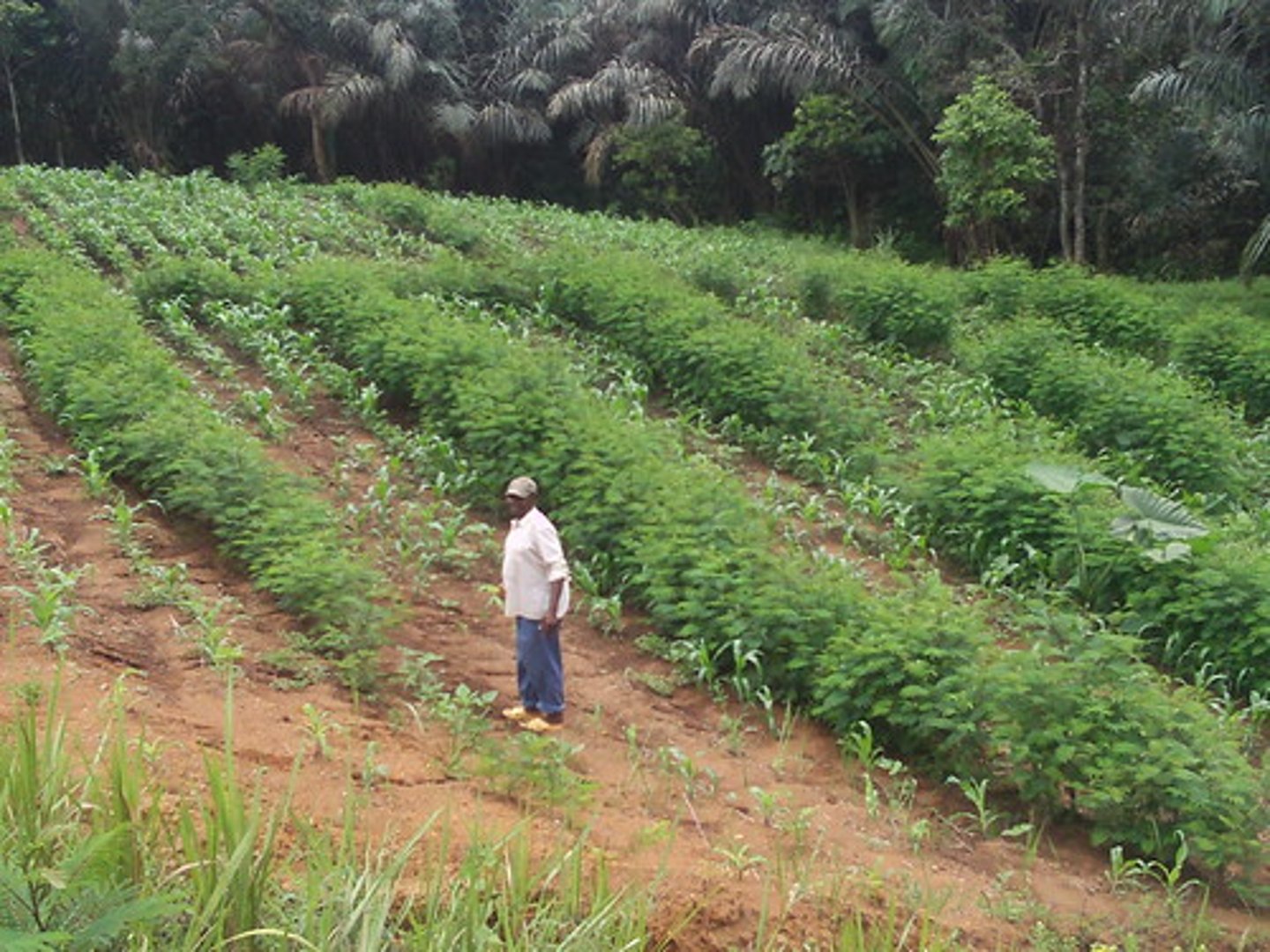
alley cropping or agroforestry
several crops are planted together in strips or alleys between trees and shrubs that can provide fruit or fuel wood

windbreaks/shelterbelts
trees around crop fields to reduce wind erosion
conservation-tillage farming
Crop cultivation in which the soil is disturbed little (minimum-tillage farming) or not at all (no-till farming) to reduce soil erosion, lower labor costs, and save energy
erosion hotspots
1/10 of the world's cropland that is highly erodible and accounts for the majority of the world's soil erosion
Soil Erosion Act
established the Soil Conservation Service as part of the USDA; soil districts were formed throughout the country
organic fertilizer
fertilizer made from plant and animal wastes
synthetic inorganic fertilizer
fertilizer produced from nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium and other minerals
green manure
consists of freshly cut or growing green vegetation that is plowed into the topsoil to increase the organic matter and humus available to the next crop
organic agriculture
agriculture in which crops are grown with the use of ecologically sound and sustainable methods and without the use of synthetic pesticides, synthetic inorganic fertilizers, and genetically engineered plants or animals.
CAFO
concentrated animal feeding operation-a very crowded form of livestock raising done in industrialized countries
topsoil
the fertile top layer of many soils
desertification
the process in which the productive potential of topsoil falls by 10% or more because of a combination of prolonged drought and human activities that expose topsoil to erosion.
soil salinization
caused by repeated applications of irrigation water in dry climates lead to the gradual accumulation of salts in the upper soil layers
pesticides
chemicals used to kill or control populations of organisms that we consider undesirable. (ex. herbicides, insecticides, rodenticides)
persistence
how long a chemical remains deadly in nature
animal manure
the dung and urine of cattle, horses, poultry, and other farm animals
compost
a material produced when microorganisms in topsoil break down organic matter such as leaves, crop residues, food wastes, paper, and wood in the presence of oxygen.
polyaquaculture
operations which raise fish or shrimp along with algae, seaweeds, and shellfish in coastal lagoons, ponds, and tanks.