PFISTER APUSH final review
1/157
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
158 Terms
Encomienda System
A system whereby the Spanish crown granted the conquerors the right to forcibly employ groups of Indians; it was a disguised form of slavery.
Great Plains Native Americans
-Either wandering Hunters or stationary farming people
-Nomadic hunters used tepees (easy to move)
-Relied heavily on the buffalo
-Used horses (after introduction by Europeans) = easy to travel and hunt
Bacon's Rebellion
1676 rebellion of landless former servants in Virginia; Exposed the weakness of the indentured servant system to the ruling planter oligarchy, who thereafter relied more and more on African slaves
First Great Awakening
Religious revival in the colonies in 1730s and 1740s; led by George Whitefield and Jonathan Edwards; The movement attempted to combat the growing secularism and rationalism of mid-eighteenth century America. Religious splits in the colonies became deeper
House of Burgesses
The first elected legislative assembly in the New World established in the Colony of Virginia in 1619
Indentured Servants
Colonists who received free passage to North America in exchange for working without pay for a certain number of years; most common in the Chesapeake region
Jamestown (1607)
The first permanent English settlement in North America, found in East Virginia in 1607
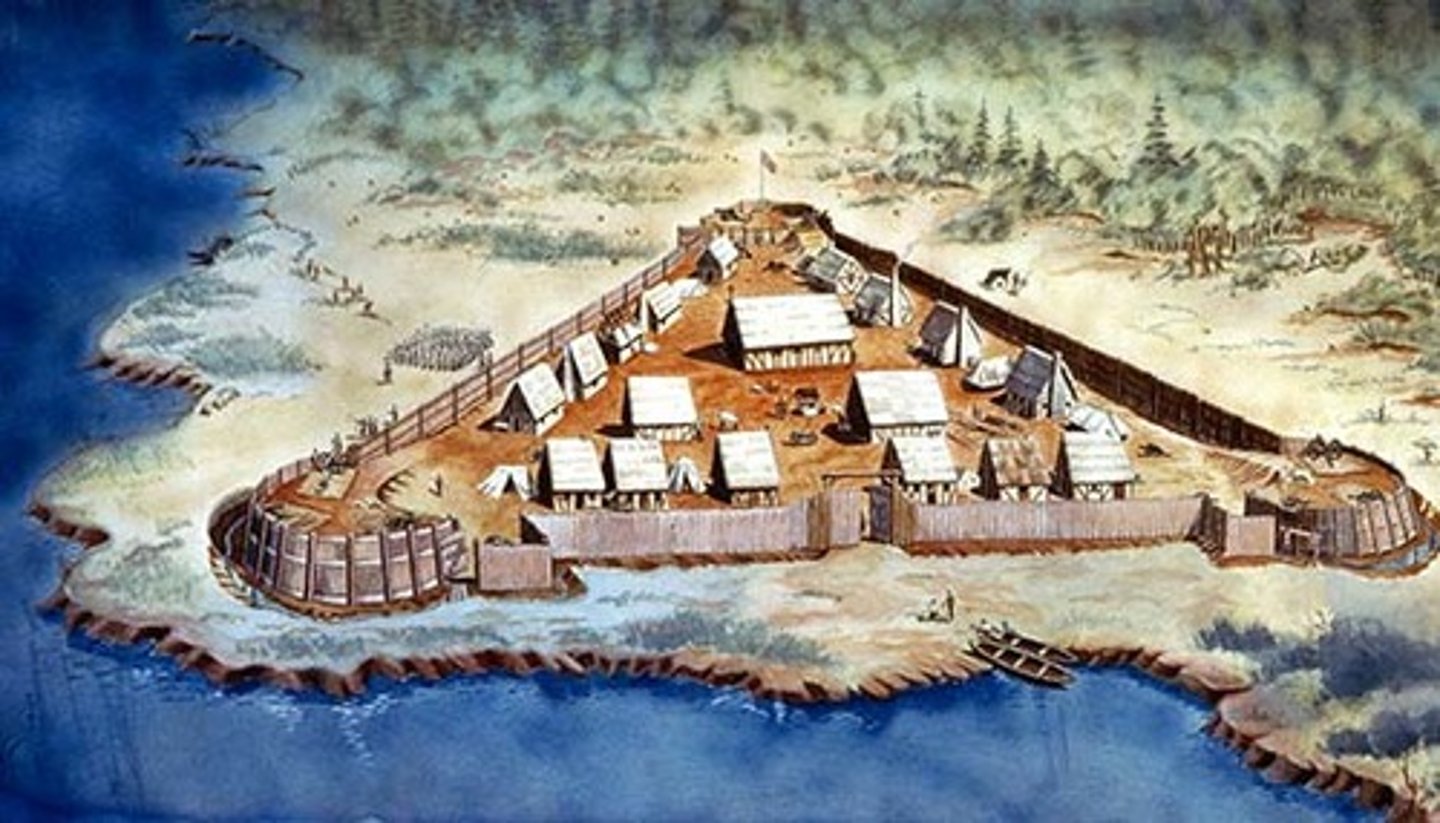
John Smith
Helped found and govern Jamestown. His leadership and strict discipline helped the Virginia colony get through the difficult first winter
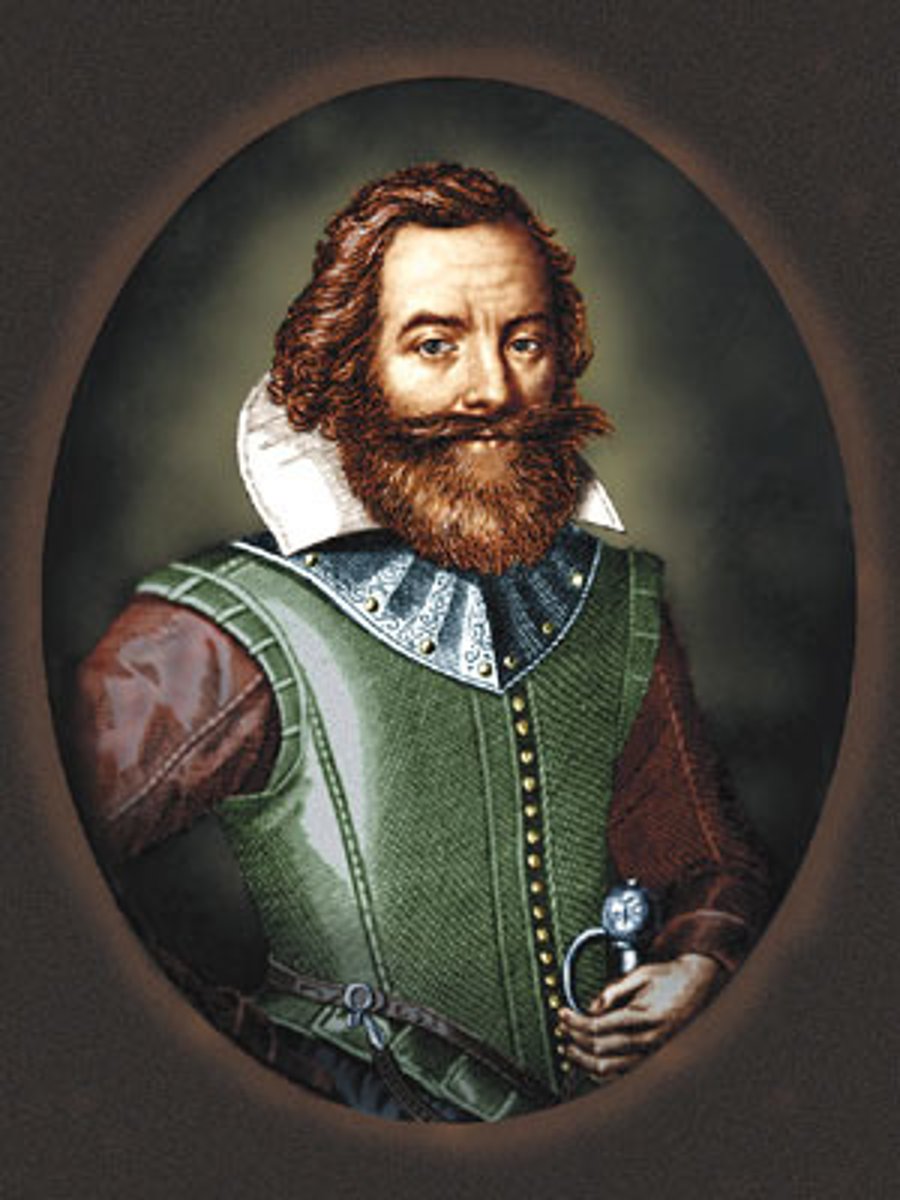

John Winthrop
Puritan leader of the Great Puritan Migration who became the long-serving governor of the Massachusetts Bay Colony

"City Upon a Hill"
Bay Colony coined by Winthrop to describe how their colony should serve as a model of excellence for future generations
Mayflower Compact
1620 - The first agreement for self-government in America. It was signed by the 41 men on the Mayflower and set up a government for the Plymouth colony
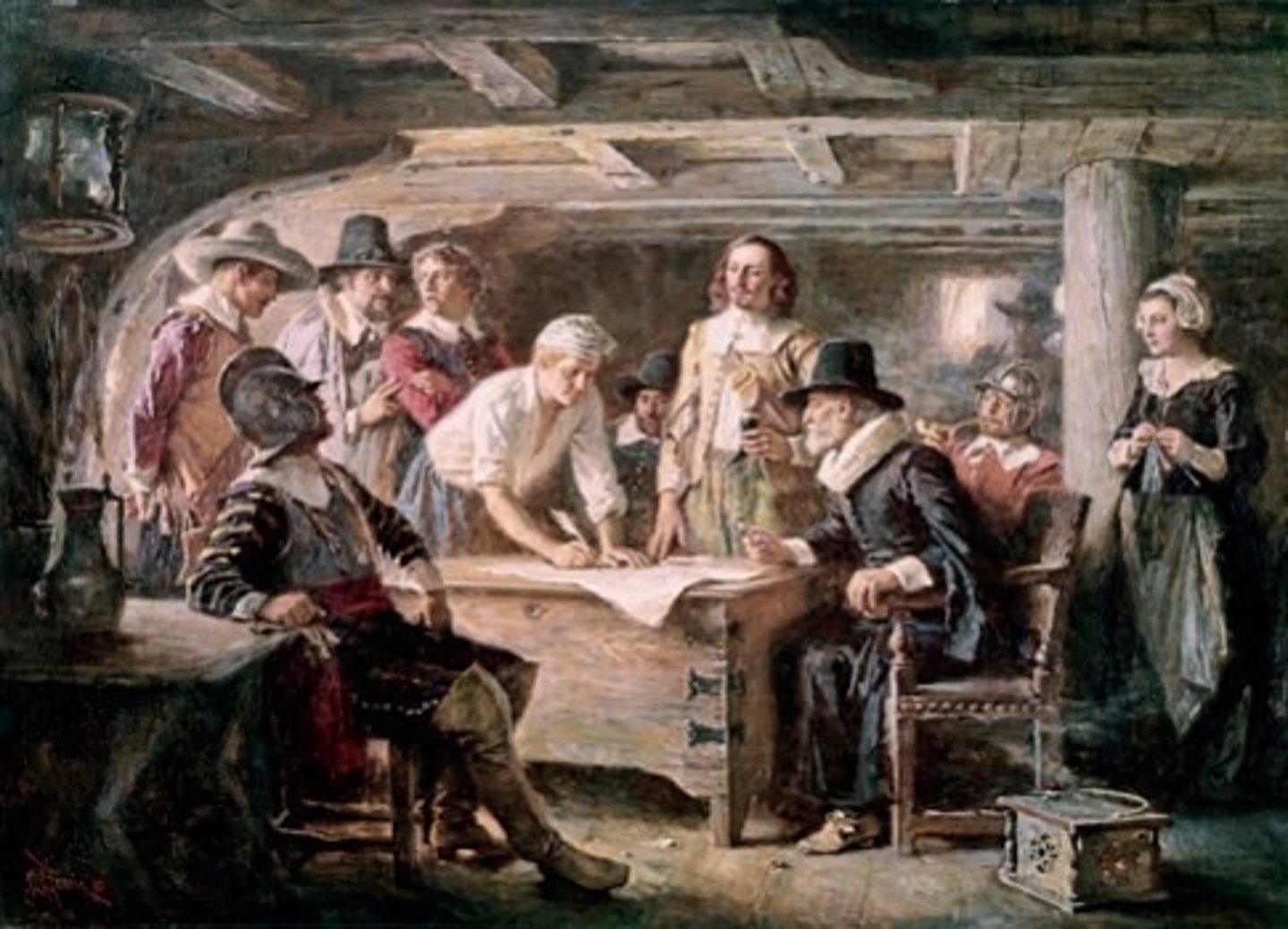

Pilgrims (Separatists)
Group of English Protestant separatists who established Plymouth Colony in Massachusetts in 1620 to seek religious freedom
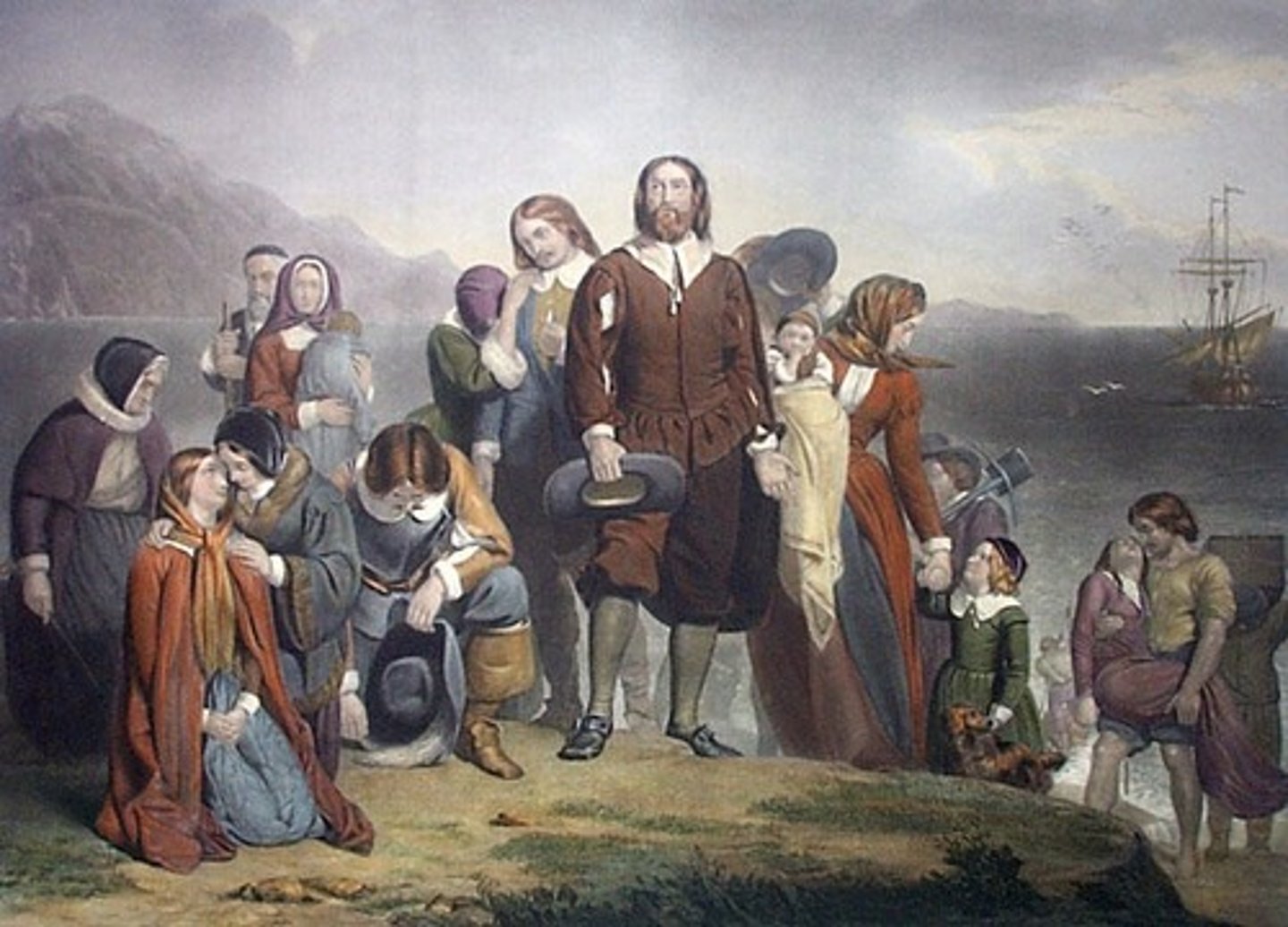

Plymouth
Colony settled by the Pilgrims in 1620
Pueblo Revolt
1680, revolt of indigenous laborers led by Pope'; killed colonists and priests and got Spanish out of modern-day New Mexico for 12 years
Puritans
Protestant sect in England hoping to "purify" the Anglican church of Roman Catholic traces in practice and organization; founded Massachusetts Bay colony in 1630
John Rolfe
Jamestown colonist who introduced a variety of tobacco that could be grown successfully in Virginia

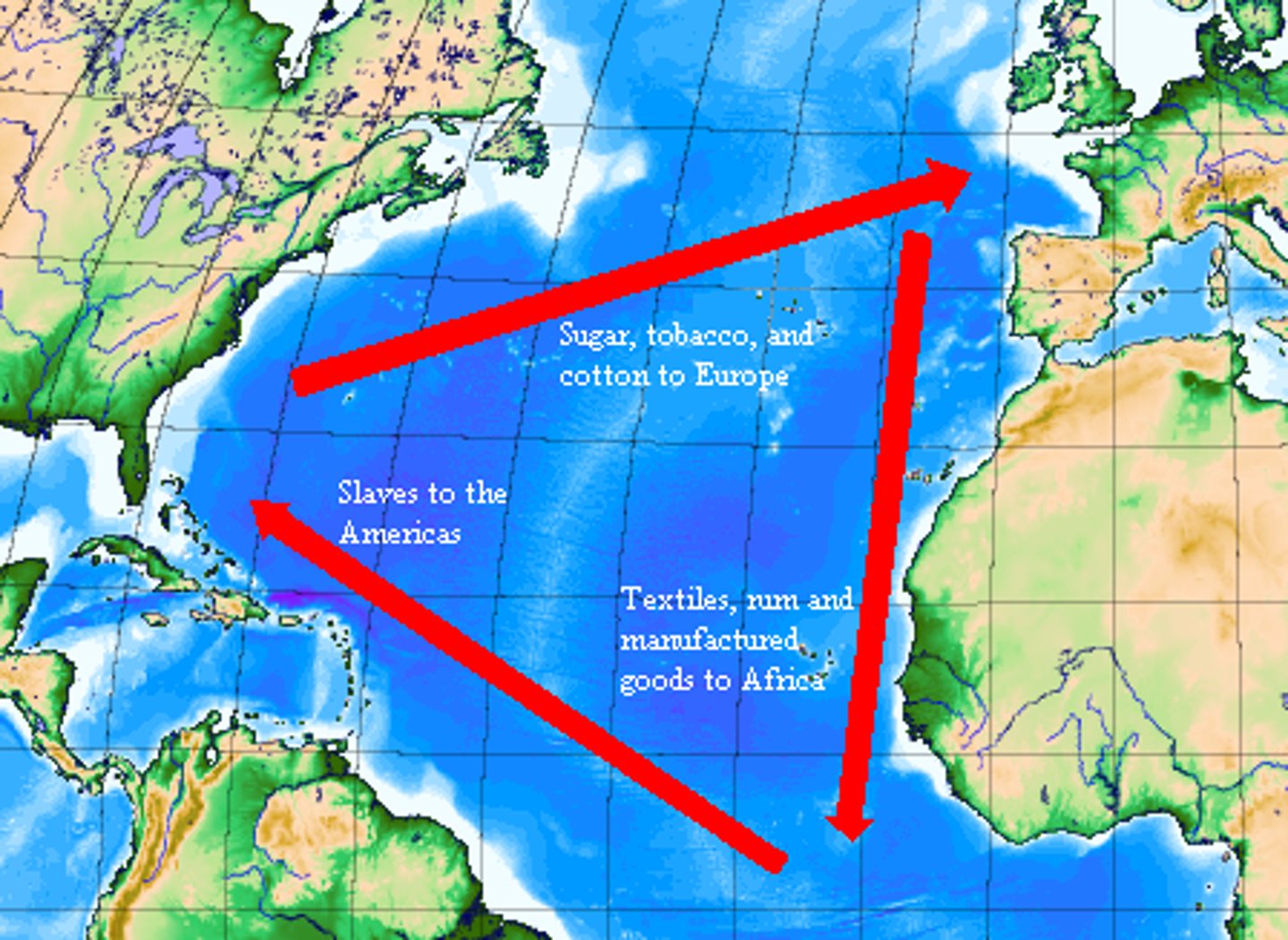
Triangular Trade
A three way system of trade during 1600-1800s: Africa sent slaves to America, America sent Raw Materials to Europe, and Europe sent Guns and Rum to Africa
3/5 Compromise (1787)
The decision at the Constitutional convention to count slaves as fraction of a person for the purposes of representation in Congress and taxation
Alexander Hamilton
1789-1795; First Secretary of the Treasury. He advocated creation of a national bank, assumption of state debts by the federal government, and a tariff system to pay off the national debt

Battle of Saratoga
American victory over British troops in 1777 that was a turning point in the American Revolution because it led to French assistance
Bill of Rights
First 10 amendments to the Constitution; added to placate the anti-federalists
Boston Massacre
The first bloodshed of the American Revolution (1770), as British guards at the Boston Customs House opened fire on a crowd killing five Americans
Constitutional Convention
A meeting in Philadelphia in 1787 that produced a new constitution
Second Continental Congress
Convened in the wake of the bloodshed at Lexington and Concord; issued both the Olive Branch Petition and the Declaration of Independence
Declaration of Independence
The document recording the proclamation of the second Continental Congress (4 July 1776) asserting the independence of the colonies from Great Britain
Federalist Papers
A collection of 85 articles written by Alexander Hamilton, John Jay, and James Madison to defend the Constitution during the ratification debates
Federalists (political party)
Political Party led by Hamilton - pro-British; supported by the wealthy; pro-merchants and trade; Favored the National Bank; loose interpretation
French and Indian War
(1754-1763) War fought in the colonies for possession of the Ohio Valley area; led to the end of Salutary Neglect
Intolerable Acts
A series of laws passed in 1774 to punish Boston for the Tea Party
James Madison
"Father of the Constitution," Federalist leader, and fourth President of the United States

John Adams
Revolutionary leader in Boston who became America's first Vice-President and second President

Kentucky and Virginia Resolutions
Republican documents that argued that the Alien and Sedition Acts were unconstitutional
Lexington and Concord
The first battle of the American Revolution (April 19, 1775)
"No taxation without representation"
Expression that reflected the colonists' belief that they should not be taxed because they had no direct representatives in Parliament
Northwest Ordinance of 1787
A law that established a procedure for the admission of new states to the Union
Anti-Federalists
people who opposed the Constitution
Salutary Neglect
An English policy of not strictly enforcing laws in its colonies
Shays' Rebellion
A 1787 rebellion in which ex-Revolutionary War soldiers attempted to prevent foreclosures of farms in Massachusetts as a result of high interest rates and taxes; highlighted the weakness of the Articles of Confederation
Sons of Liberty
A radical organization for colonial independence formed to protest the Stamp Act; formed the Committees of Correspondence which spread information and promotted opposition to British policies; leaders included Samuel Adams and Paul Revere
Stamp Act
1765; law that taxed printed goods, including: playing cards, documents, newspapers, etc.
Thomas Paine
American Revolutionary leader and pamphleteer (born in England) who supported the American colonist's fight for independence and supported the French Revolution (1737-1809)
Common Sense
A pamphlet written by Thomas Paine that claimed the colonies had a right to be an independent nation, and placed blame on the king
Treaty of Paris 1763
Ended French and Indian War, France lost Canada, land east of the Mississippi, to British, New Orleans and west of Mississippi to Spain
Andrew Jackson
The seventh President of the United States (1829-1837), who as a general in the War of 1812 defeated the British at New Orleans (1815). As president he opposed the Bank of America, objected to the right of individual states to nullify disagreeable federal laws, and increased the presidential powers.
Battle of New Orleans
A battle in 1815 between American and British troops for control of the Mississippi River, ending in an American victory; was won after the treaty was signed
Eli Whitney
Inventor of the cotton gin and use of interchangeable parts

Hartford Convention
Meeting of Federalists near the end of the War of 1812 in which the party listed it's complaints against the ruling Republican Party. These actions were largley viewed as traitorous to the country and lost the Federalist much influence
Indian Removal Act
(1830) a congressional act that authorized the removal of Native Americans who lived east of the Mississippi River
Judicial Review
Allows the Supreme Court to determine the constitutionality of laws
Marbury v. Madison
Supreme Court case involving the Midnight Judges that established the power of Judicial Review
Louisiana Purchase
Territory in western United States purchased from France in 1803 for $15 million; nearly doubled the size of the United States
Missouri Compromise
An agreement in 1820 between pro-slavery and anti-slavery factions in the United States concerning the extension of slavery into new territories; Missouri joined the union as a slave state, Maine joined as a free state, and slavery was prohibited in all other areas north of the 36-30 line
Nulification
A state's refusal to recognize an act of Congress that it considers unconstitutional
Revolution of 1800
Jefferson's election changed the direction of the government from Federalist to Democratic- Republican, so it was called a "revolution."
Seneca Falls Convention
Took place in upstate New York in 1848; Women of all ages and even some men went to discuss the rights and conditions of women. There, they wrote the Declaration of Sentiments, which among other things, tried to get women the right to vote
Thomas Jefferson
3rd President of the United States
Battle of Tippecanoe
1811 battle in which Tecumseh and the Prophet's tribes are crushed by General Harrison when they try to unite multiple tribes for self-defense
Trail of Tears
The forced removal of Cherokees and other eastern tribes to lands west of the Mississippi River; 25% of the Natives died en route
Transcendentalism
A nineteenth-century movement which held that every individual can reach ultimate truths through spiritual intuition, which transcends reason and sensory experience
War of 1812
War between the U.S. and Great Britain caused by England's use of impressment, inciting the Native Americans, and the refusal of Red Coats to leave the United States; ended with a renewed sense of American nationalism
War Hawks
Southern and Westerners during Madison's presidency who pressed for war with Britain
William Lloyd Garrison
Prominent American abolitionist, journalist and social reformer. Editor of radical abolitionist newspaper "The Liberator," and one of the founders of the American Anti-Slavery Society.
Worchester v. Georgia
Supreme Court ruling that the Cherokee nation was a distinct community in which the laws of Georgia had no force
13th Amendment
Abolished slavery
Battle of Antietam
Civil War battle in which the North succeeded in halting Lee's Confederate forces in Maryland. Was the bloodiest battle of the war resulting in 25,000 casualties; one of the bloodiest days in US history
Civil War
A war between the Union and Confederacy between 1861-1865
Compromise of 1850
(1) California admitted as a free state, (2) popular sovereignty allowed in Utah and New Mexico, (3) resolution of Texas-New Mexico boundaries and debt, (4) slave trade abolished in DC, and (5) new fugitive slave law; advocated by Henry Clay and Stephen A. Douglas
Union
Term for the North during the US Civil War
Confederacy
Term for the South during the US Civil War
Dred Scott vs. Sanford
1857 Supreme Court case that decided the US Congress did not have the power to prohibit slavery in federal territories and slaves, as private property, could not be taken away without due process
Emancipation Proclamation
Presidential statement declaring that all slaves in the Confederate States would be free as a military necessity
Gettysburg Address
A 3-minute address by Abraham Lincoln at the dedication of a national cemetery on the site of the Battle of Gettysburg
Harriet B. Stowe
Wrote "Uncle Tom's Cabin" which depicted the horrors of slavery and is considered one of the causes of the Civil War
Homestead Act
1862 law that gave 160 acres of land to citizens willing to live on and cultivate it for five years; used to encourage settlement of the west
James K. Polk
11th president who wanted to settle the Oregon boundary, to acquire California, and incorporate Texas into the union
Kansas-Nebraska Act
A law that allowed voters in Kansas and Nebraska to choose whether to allow slavery; contradicted the Missouri Compromise
Mexican-American War
(1846-1848) The war between the United States and Mexico in which the United States acquired one half of the Mexican territory.
Paternalism
The practice of slave owners of restricting the freedom of their slaves and claiming their actions were in the slaves' best interest.
Reconstruction
The 12-year period after the Civil War when the southern states were restructured and readmitted to the Union
Robert E. Lee
Commander of the Confederate Army
Jim Crow Laws
Laws designed to enforce segregation of blacks from whites
Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo
Treaty that ended the Mexican War, granting the U.S. control of Texas to the Rio Grande, New Mexico, and California in exchange for $15 million
Ulysses S. Grant
The eighteenth President of the United States; he achieved international fame as the leading Union general in the American Civil War
Andrew Carnegie
A Scottish-born American industrialist and philanthropist who founded his steel company in 1892 and dominated the American steel industry within 10 years
Chinese Exclusion Act
1882 law that barred Chinese laborers from entering the United States; first immigration act targeting a single nationality
Dawes Act of 1887
Law designed to civilize Indians and make them more settled by giving them land to farm and refusing to recognize tribal authority, instead it harmed their native culture
Free Silver
Political issue involving the unlimited coinage of silver, supported by farmers and William Jennings Bryan
Gilded Age
A name for the late 1800s, coined by Mark Twain to describe the tremendous increase in wealth caused by the industrial age and the ostentatious lifestyles it allowed the very rich. The great industrial success of the U.S. and the fabulous lifestyles of the wealthy hid the many social problems of the time, including a high poverty rate, a high crime rate, and corruption in the government
Jane Addams
Leader of the Settlement House Movement and founder of Hull House. First American Woman to earn the Nobel Peace Prize in 1931
John D. Rockefeller
An American industrialist and first billionaire who revolutionized the oil industry and defined the structure of modern philanthropy. Most likely the wealthiest American ever
Knights of Labor
Labor union that sought to organize all workers regardless of skill level and focused on broad social reforms
Hull House
Settlement house founded by Progressive reformer Jane Addams in Chicago in 1889
Laissez-faire
Idea that government should play as small a role as possible in economic affairs; "hands off"
Plessy v. Ferguson
A 1896 Supreme Court decision which legalized state ordered segregation so long as the facilities for blacks and whites were equal
Populist Party
U.S. political party formed in 1892 representing mainly farmers, favoring free coinage of silver and government control of railroads and other monopolies
Transcontinental Railroad
Completed in 1869 at Promontory, Utah, it linked the eastern railroad system with California's railroad system, revolutionizing transportation in the west
W.E.B. DuBois
Co-founded the NAACP to help secure legal equality for minority citizens
"Cross of Gold" speech
An impassioned address by William Jennings Bryan at the 1896 Democratic Convention, in which he attacked the "gold bugs" who insisted that U.S. currency be backed only with gold
19th Amendment
Amendment to the U.S. Constitution (1920) extended the right to vote to women in federal or state elections.
The Influence of Sea Power on History
An influential treatise on naval warfare written in 1890 by Alfred Thayer Mahan; discusses the various factors needed to support a strong navy; encouraged imperialsim