Unit A 12 Phys, Diagram of a Contractile Myocardiocyte Action Potential
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
4
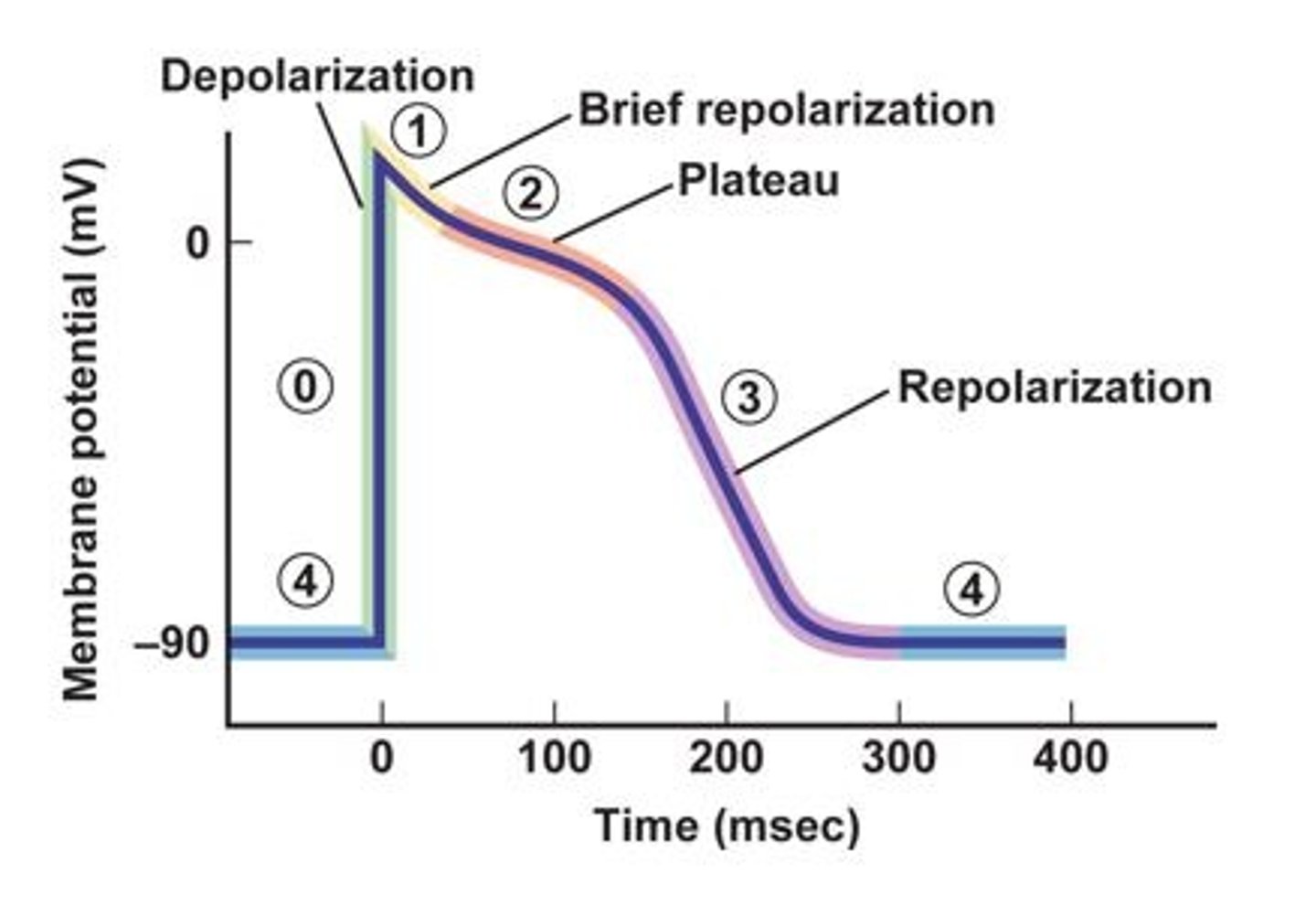
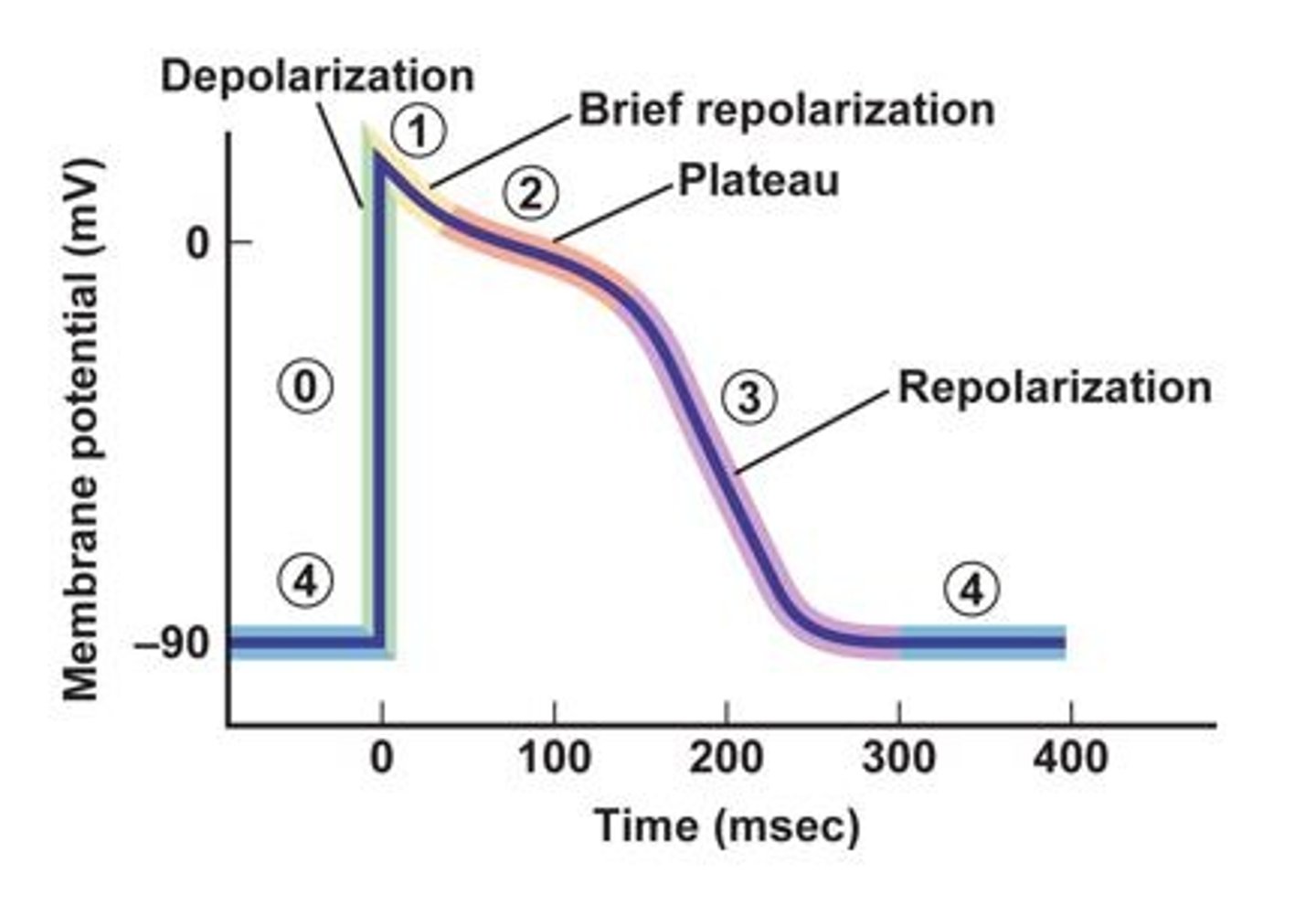
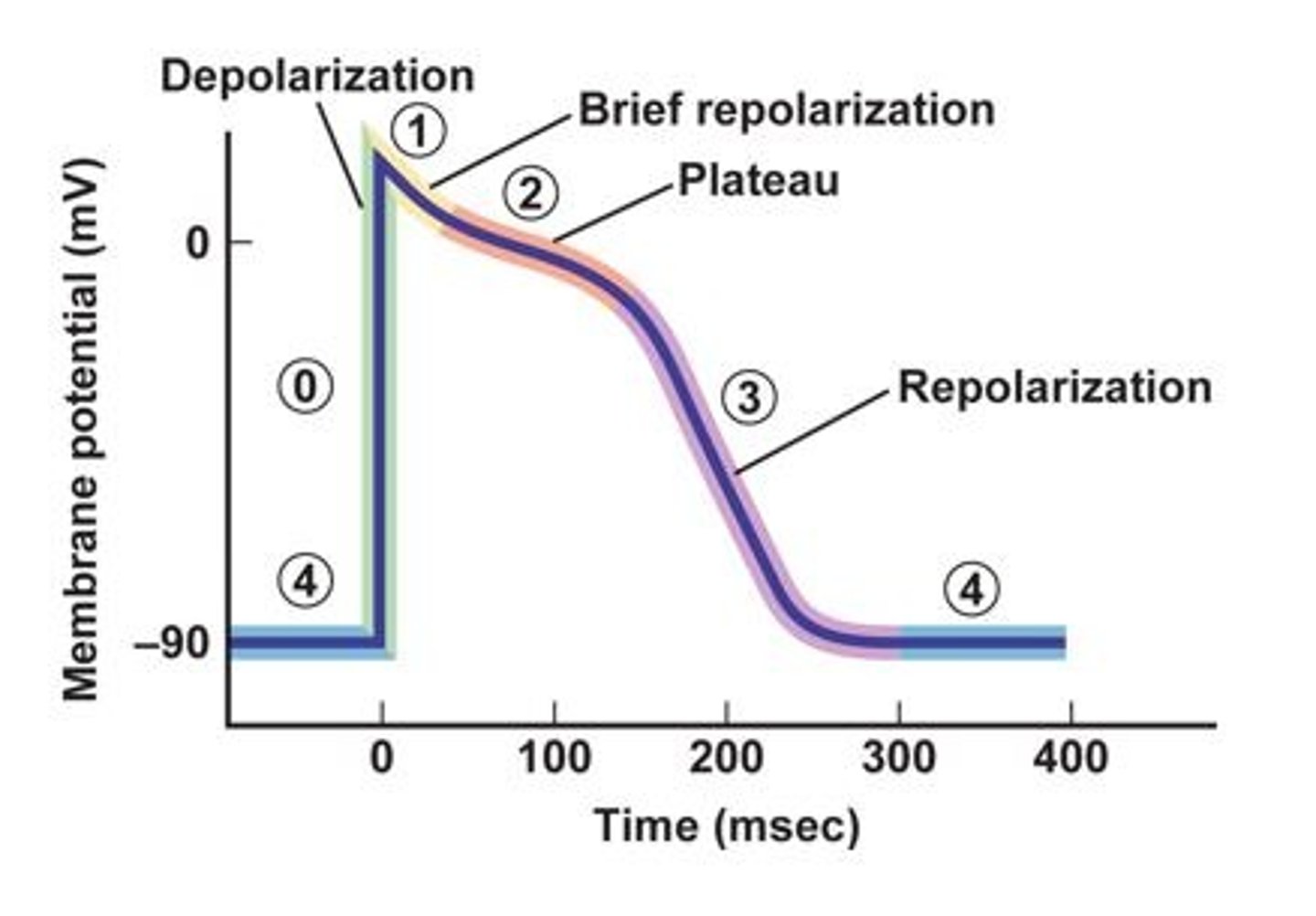
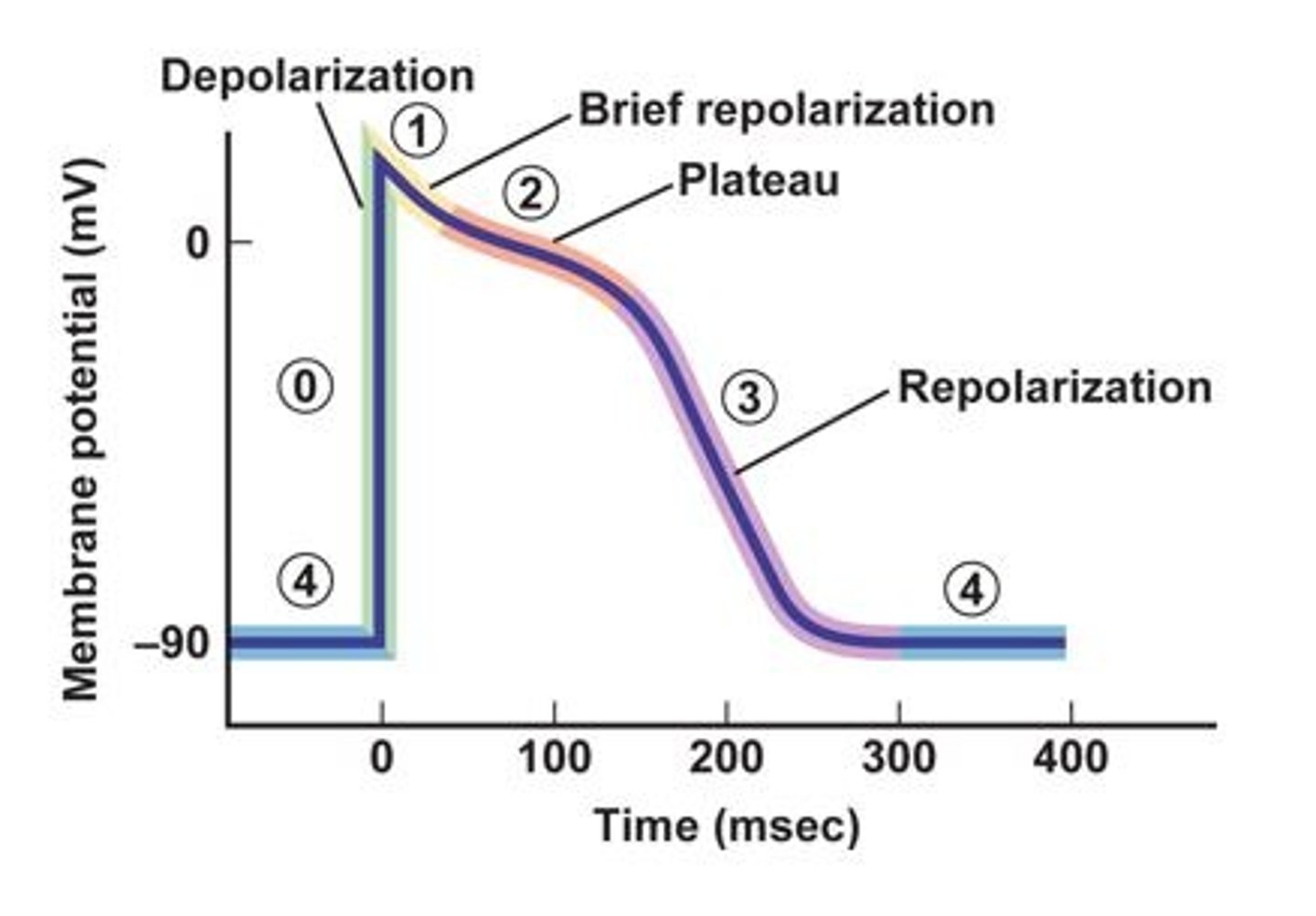
The resting membrane potential is represented by what number on the diagram?
0
What number on the diagram represents fast Voltage-gated Na+ channels opening causing a rapid depolarization as Na+ flows into the cell
1
What number on the diagram represents when fast voltage-gated Na+ channels close and the outward movement of K+ by potassium leak channels and slow voltage gated K+ channels, brings a brief, small repolarization as the membrane becomes slightly less positive.
2
What number on the diagram represents when the L-type voltage-gated Ca2+ channels open allowing Ca2+ to enter the cell balanced by the leaving of K+ out of K+ leak channels and slow voltage gated K+ channels. This depolarization is maintained for 200 to 300 msec before Ca2+ channels close and complete repolarization occurs.
3
What number on the diagram represents the closing of L-Type voltage-gated Ca2+ channels and the opening of rapid voltage-gated K+ channels which causes a rapid outward diffusion of K+. In addition, slow voltage gated K+ channels and leak channels are contributing to the outflow of K+.
Plateau phase
The term for the phase that results from a slow inward diffusion of Ca2+ through slow voltage gated (L-type) Ca2+ channels balanced by a slow outward movement (efflux) of K+ through K+ leak channels and slow voltage gated K+ channels.
-90 mV
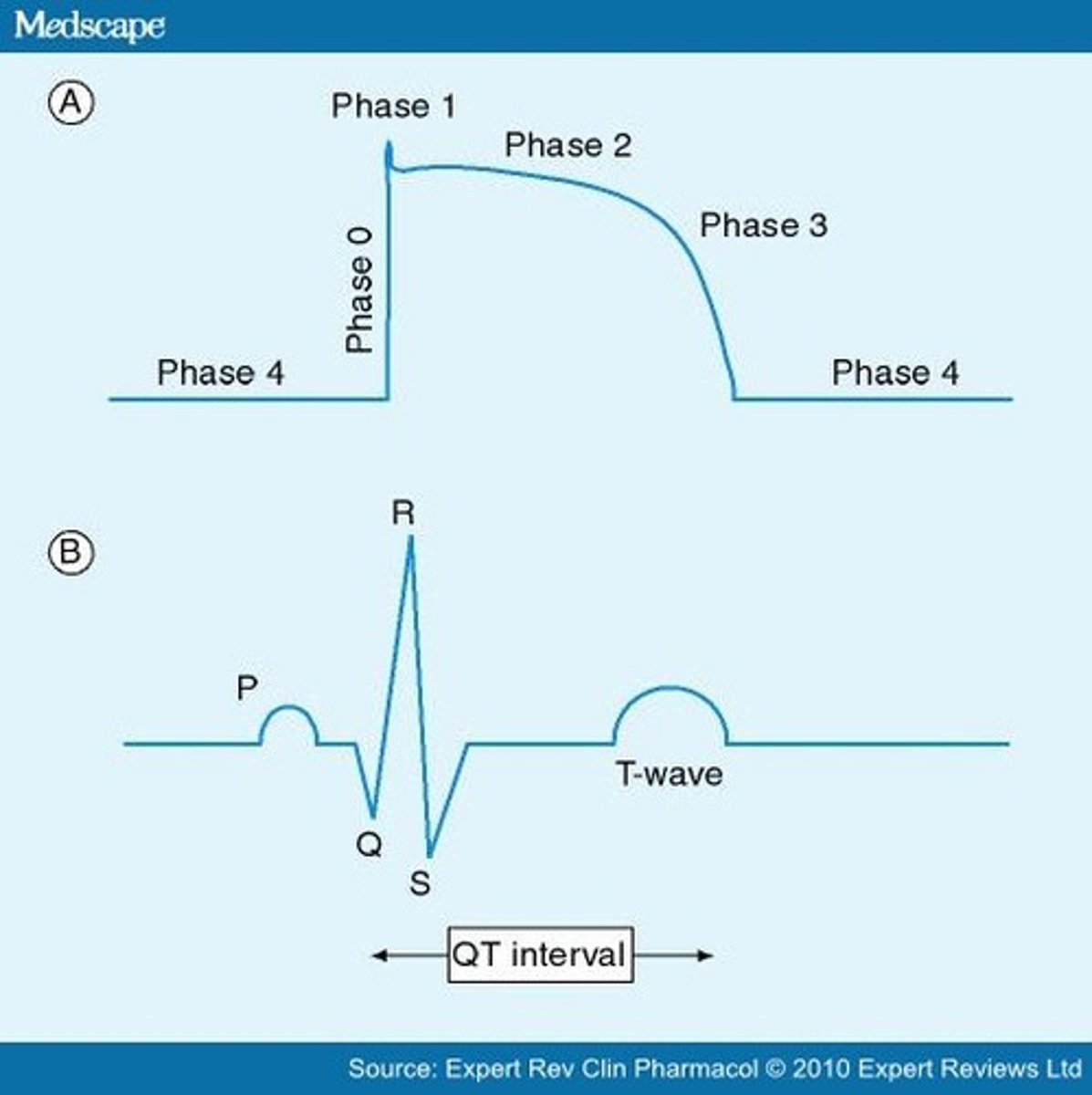
The myocardial contractile cells have a resting membrane potential of about ______ (-90, -85, -70) mV.
Threshold
Action potentials from pacemaker regions stimulate myocardial cells to depolarize to _______________ (resting membrane potential or threshold).
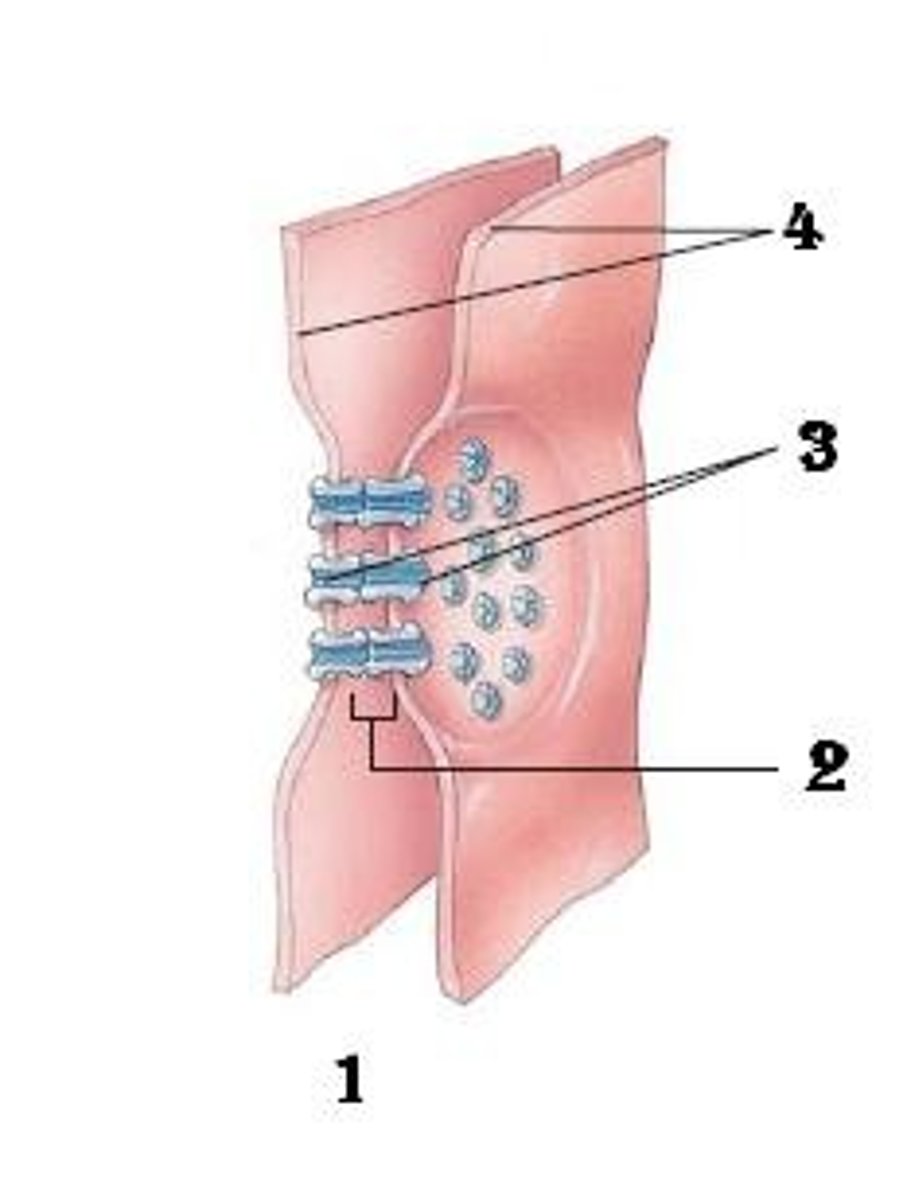
Gap junctions
Ions such as Na+ and Ca2+ move between autorhythmic cells and myocardiocytes through what specific type of junctions to raise the resting membrane potential to threshold.
Fast voltage gated sodium channels
Name the specific type of channels that are opening at Phase 0 on the Diagram.
Potassium
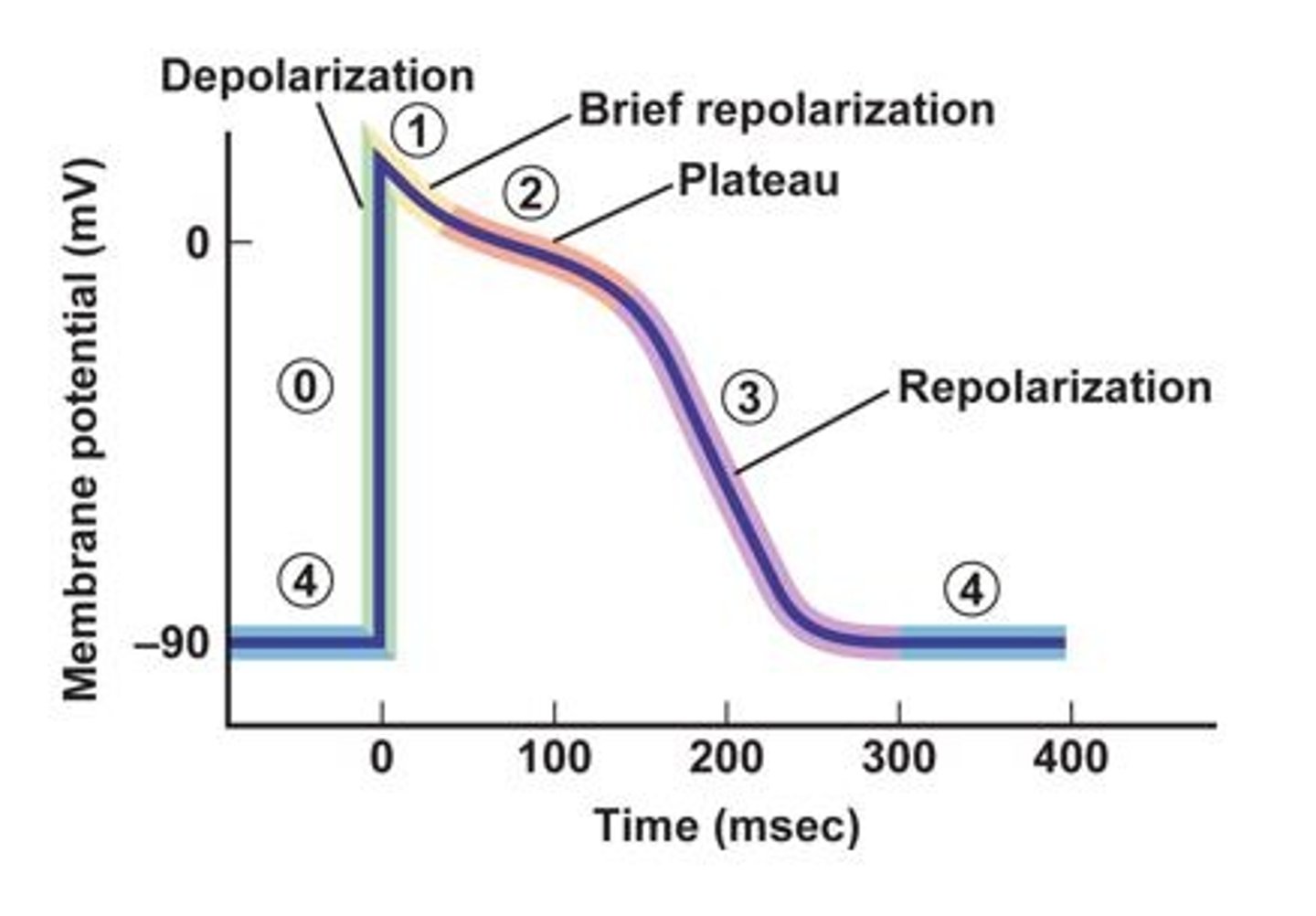
On phase 1 on the Diagram fast voltage-gated Na+ channels close and there is an outward movement of what ion resulting in a brief, small repolarization as the membrane becomes slightly less positive.
Enter
At phase 2 on the voltage-gated L-type Ca2+ channels open allowing Ca2+ to slowly _____(enter or leave) the cell.
Potasium
At phase 2 on the voltage-gated L-type Ca2+ channels open allowing Ca2+ to enter the cell balanced by what ion leaving the cell through leak channels and slow voltage gated channels?

Increase
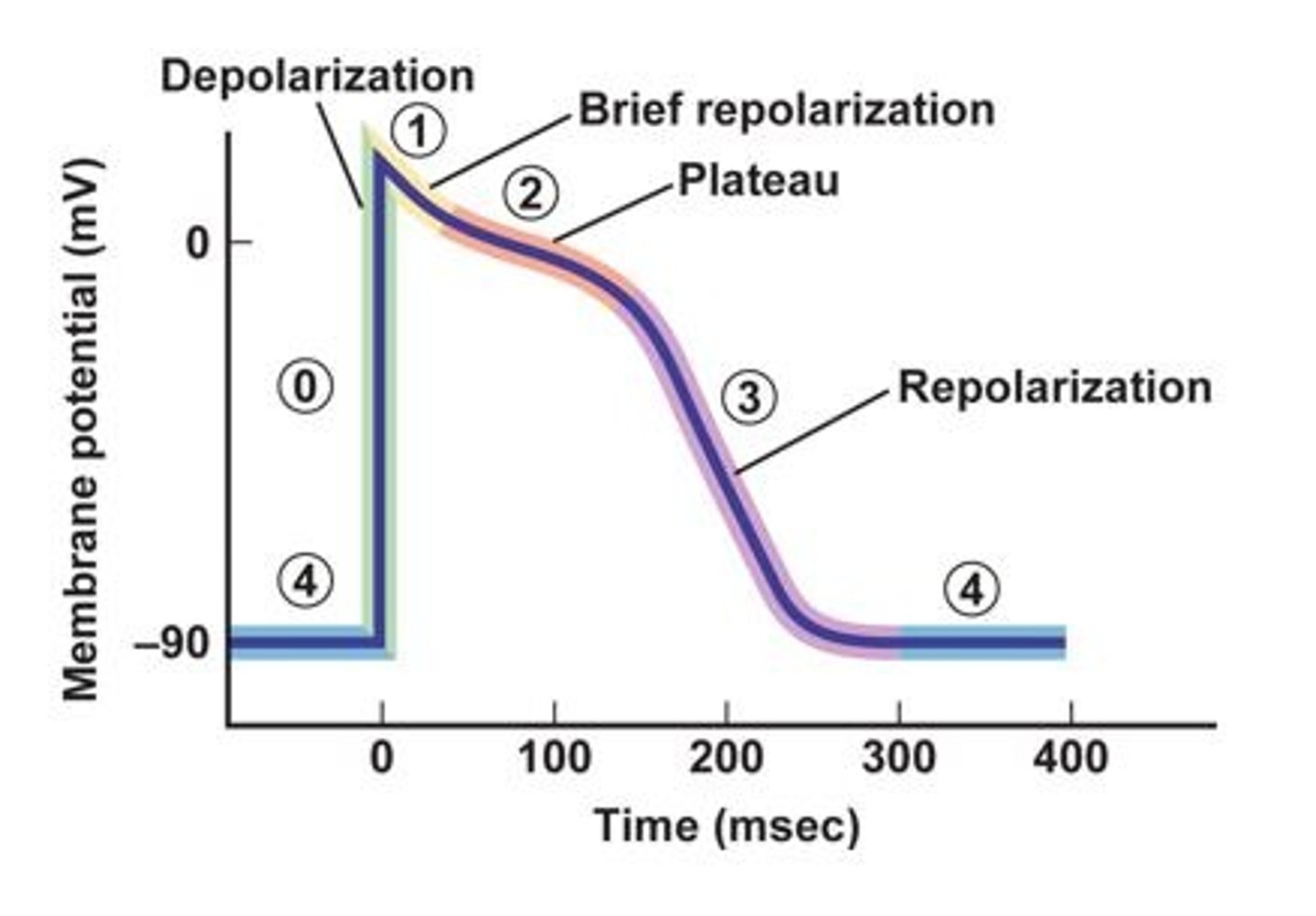
The prolonged plateau phase functions to _____________ (increase or decrease) cardiac contractile time to ensure adequate time and strength to eject the blood. The long refractory period that acts as a protective mechanism in the heart by preventing multiple action potentials from occurring.
Outward
In phase 3 on the Diagram the rapid repolarization at the end of the plateau phase is achieved by the closing of the voltage-gated L-type Ca2+, K+ channels and the opening of rapid voltage-gated K+ channels which causes a rapid ________ (inward or outward) diffusion of K+.