AP GOV ~ Unit #1, Unit 1: Foundations of American Democracy - AP Gov - WEEK 1, Unit 1: Foundations of American Democracy - AP Gov - WEEK 2, Unit 1: Foundations of American Democracy - AP Gov - WEEK 3, Unit 1: Foundations of American Democracy - AP Go…
1/118
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
119 Terms
What three British documents influenced the main idea of American democracy? (3)
-Magna Carta
-English Petition of Rights
-English Bill of Rights

What did the Magna Carta do?
Limited the power of the king

What did the English Petition of Rights do? (2)
-Protected the rights of the Parliament
-Protected Rule of Law

What is the "rule of law"?
No one is above the law

What is the British Parliament equivalent to in American gov?
Congress
What did the English Bill of Rights do? (2)
-Expanded the rights of Parliament
-The people limited the rights of the king (trial by jury)

What were the philosophical influences on the early American democracy? (4)
-Hobbes
-Locke
-Montesquieu
-Rousseau

Who was Hobbes and what did he believe? (3)
-Believed in absolutism
-All people have bad intentions
-Thought it was a "one way street"

Who was Locke and what did he believe? (5)
-More positive outlook than Hobbes
-HUGE fighter for natural rights (Life, Liberty, Property)
-Social Contract theory supporter!
-Inspired Thomas Jefferson
-The people have the right to overthrow the gov in the situation that their natural rights were violated; it is their duty as citizens to do so

What is the social contract theory?
Agreement by the citizens that they will surrender some extreme rights for protection from the gov as well as a more organized society as a whole

Who was Montesquieu and what did he believe? (2)
-Created 3 branches of government
-Separation of Powers / Checks + Balances

Who was Rousseau and what did he believe? (1)
-Majority Rule

What were the main influences in the Declaration of Independence? (4)
-Natural Rights
-Popular Sovereignty
-Republicanism
-Social Contract

How did Natural Rights' definition change from Locke to the DOI?
Life, Liberty, & Property -------> Life, Liberty, & PURSUIT OF HAPPINESS

What is popular sovereignty?
The idea that the authority of government comes from the people

What is Republicanism?
Large pops of people elect reps to make decisions on their behalf in gov
How is DOI split up and what do each part practically say?
-Preamble ("This relationship isn't working")
-The type of gov the Founding Fathers wanted ("This is the relationship we were expecting to have")
-Grievances ("It's not me, it's you")
-Problems w/ the British citizens
-Seperation ("We are never getting back together. Like ever.")

What are the theories of Democracy? (3)
-Participatory
-Pluralism
-Elitism

What is the Participatory theory?
Widespread political participation is needed for a dem. gov.
Ex) Voting, Jury Duty, Social Media, etc.

What is the Pluralist theory?
Theory that emphasizes the roles of interest/non-gov groups in the policymaking process
Ex) Voting, community volunteering, live streaming meetings

What is the Elitist theory?
Elites have a disproportionate amount of influence over the policymaking process
Ex) Testifying at hearings, creating media events, bundling campaign donations, presenting ideas for bills to lawmakers

What is totalitarianism?
Government has total control of a country

What is an authoritation government?
Suppress voices of the citizens to maintain power; may not have complete control over economic and social institutions
What is a constitutional republic?
A democratic system with elected representatives in which the Constitution is the supreme law

Who was James Madison?
Father of the Constitution

What is the constitution?
A document stating the rules under which a government will operate

What is a republic?
A government in which citizens rule through elected representatives

What were the Articles of Confederation?
Document that organized our government. (First national government in America)

What were weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation? (5)
-One vote per state
-Unicameral legislature
-No independent executive/judicial brand
-Lacked power to tax****
-States controlled trade

What caused the end of the AOC? (2)
-Annapolis Convention
-Shay's Rebellion

What was the Annapolis Convention?
Meeting of 12 delegates from 5 states to improve the Articles of Confederation -- it was quickly disassembled and moved to Pennsylvania because they saw they didn't have enough people

What was Shay's Rebellion?
A series of protests in 1786 and 1787 by American farmers against state and local enforcement of tax collections and judgments for debt.

Why would some Americans worry about replacing the AOC though most people believed it was ineffective? (3)
-Fear of super strong national gov
-Southern states feared that the gov would abolish slavery
-Small states were afraid of losing reps

What was called to draft a new governing doc for America?
The Constitutional Convention

What was the Constitutional Convention?
Meeting of delegates in 1787 to revise the Articles of Confederation, which produced the new U.S. Constitution

What were the men like at the Constitutional Convention? (5)
-White
-Educated
-Elite
-Had political experience
-1/3 were slave owners

Major People at the Constitutional Convention (4)
-James Madison
-George Washington
-Alex Hamilton
-Ben Franklin
What was the goal of the Constitutional Convention?
To create a strong and fiscal military state

What was the main issue the fathers were trying to tackle during the Constitutional Convention?
How to maintain rep and powers of the national gov while protecting individual rights?

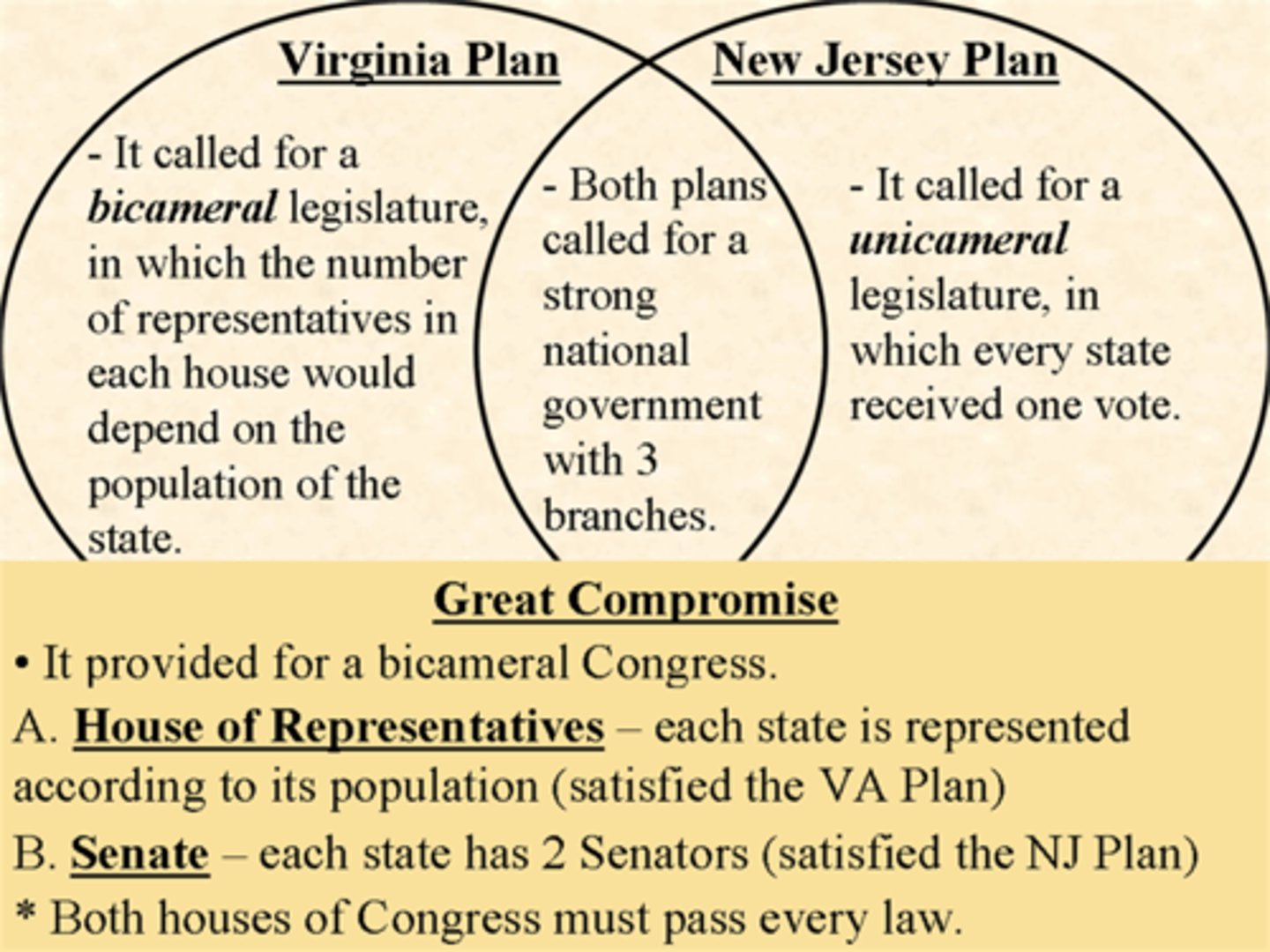
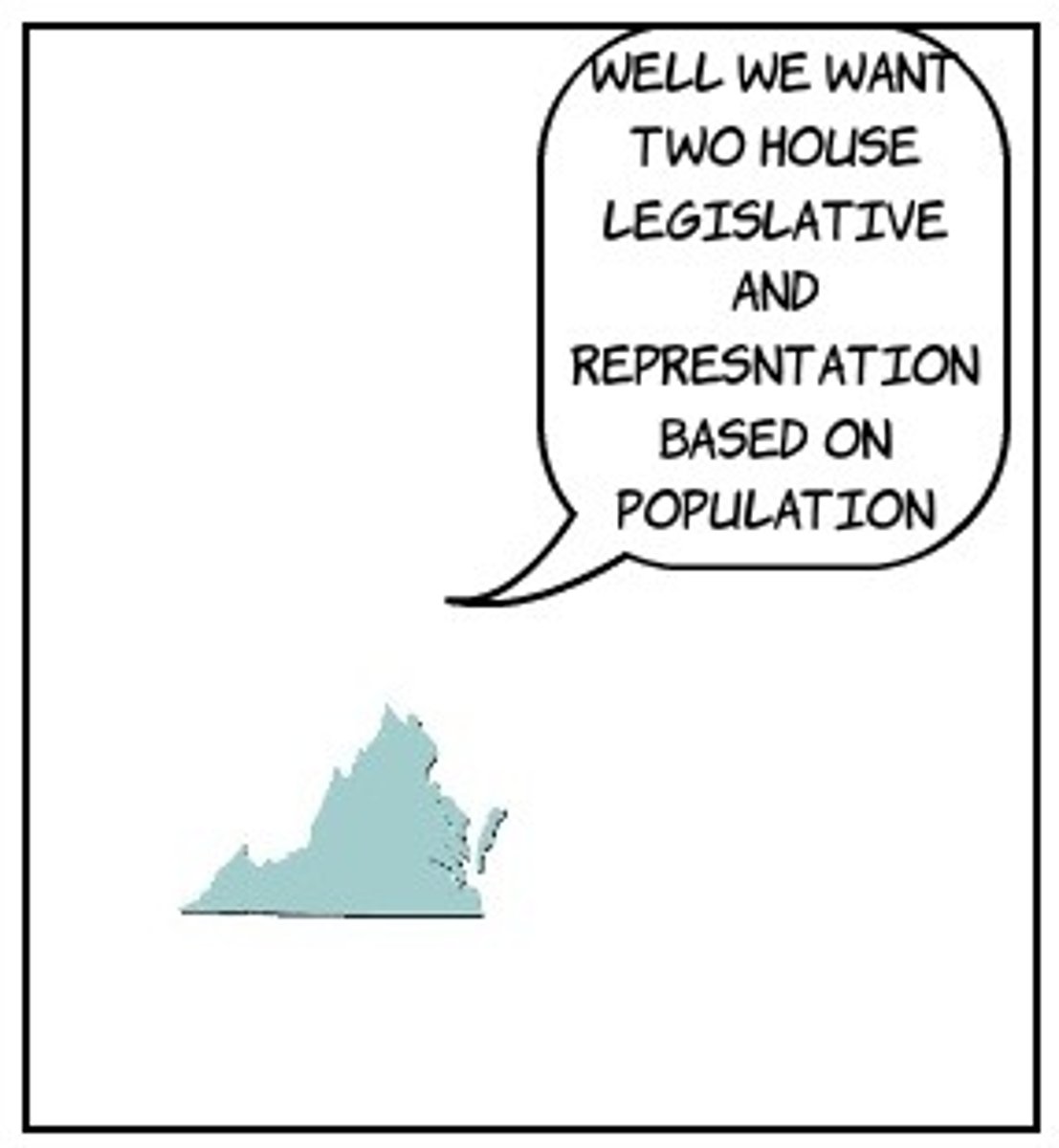
What was the Virginia Plan?
Each state had their delegates based on population (favored large states)
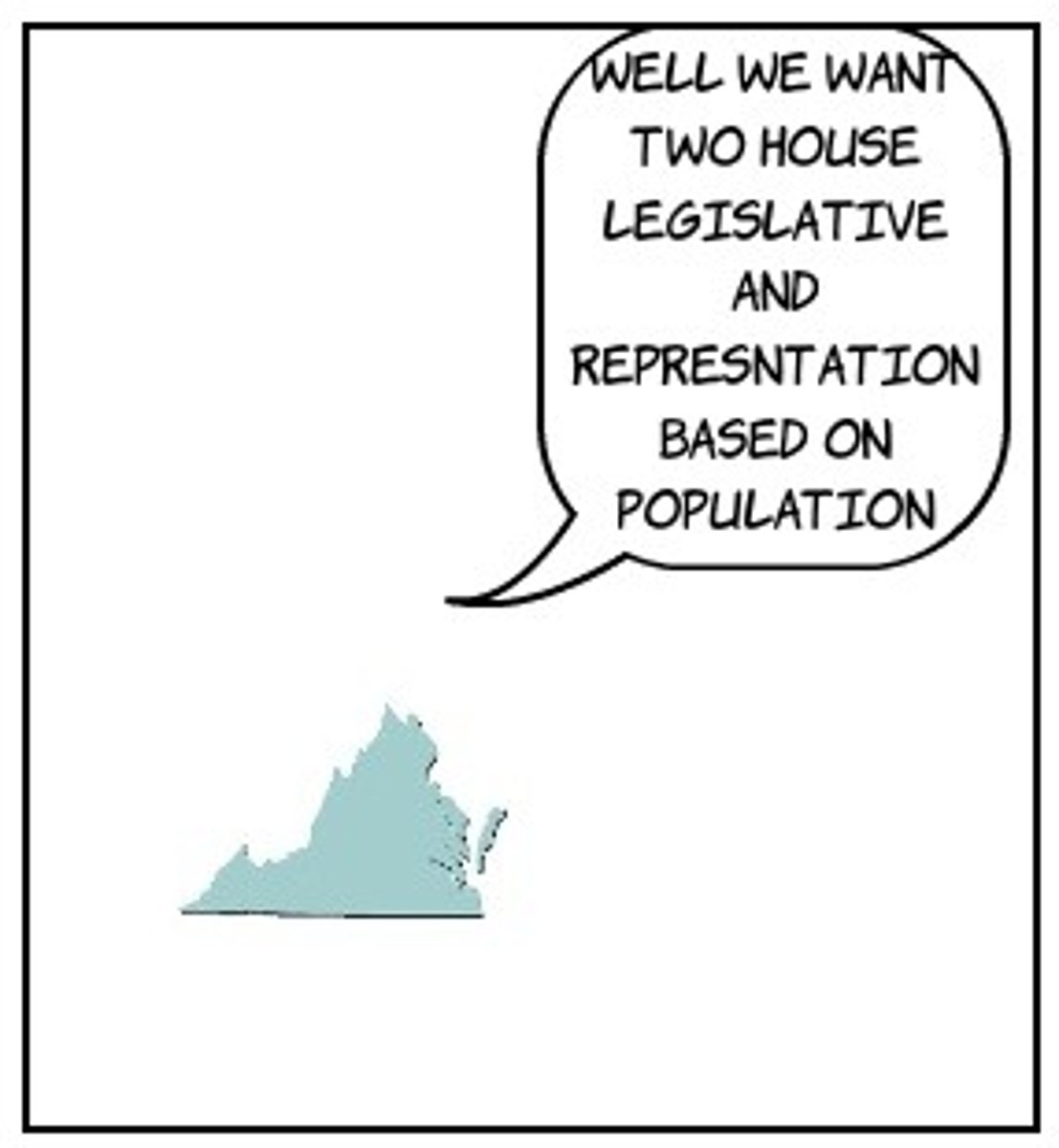
What was the New Jersey Plan?
Each state had the same amount of delegates so the size didnt matter (favored small states)

What was the Great Compromise?
Created a bicameral legislature (combined VA and NJ plans to create Congress) one house based on representation, one house has equal representation
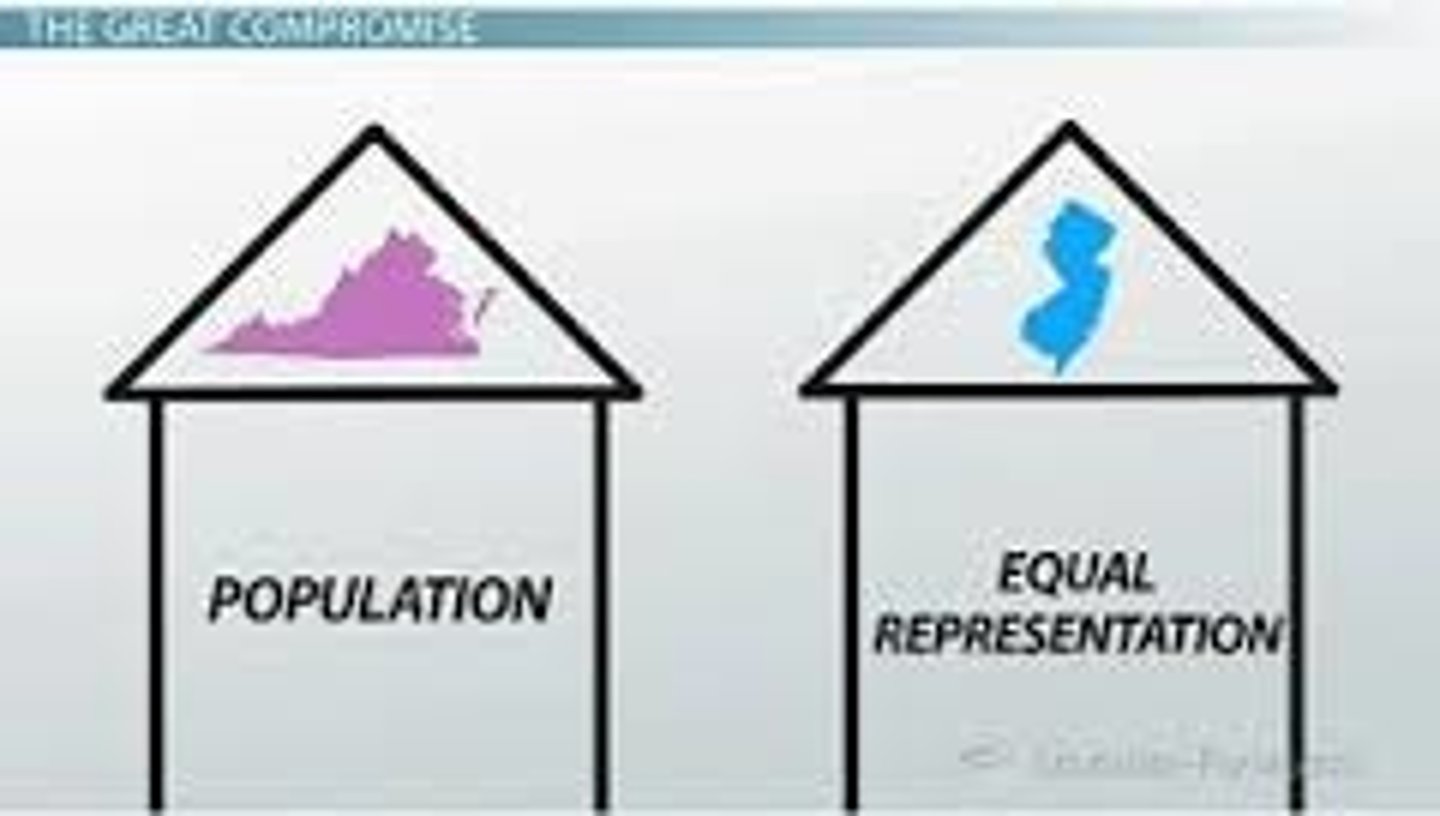
What is the Senate?
Upper house of the legislature, each state elects two

Who does the Senate benefit?
Smaller states
What is the House of Representatives?
The lower house of Congress, consisting of a different number of representatives from each state, depending on population

Who does the HOR benefit?
Larger States
What is the 3/5 compromise?
Slaves in the south would be counted as 3/5 for the house of representation and taxes

What is the Compromise on Importation?
Congress could not restrict the slave trade until 1808

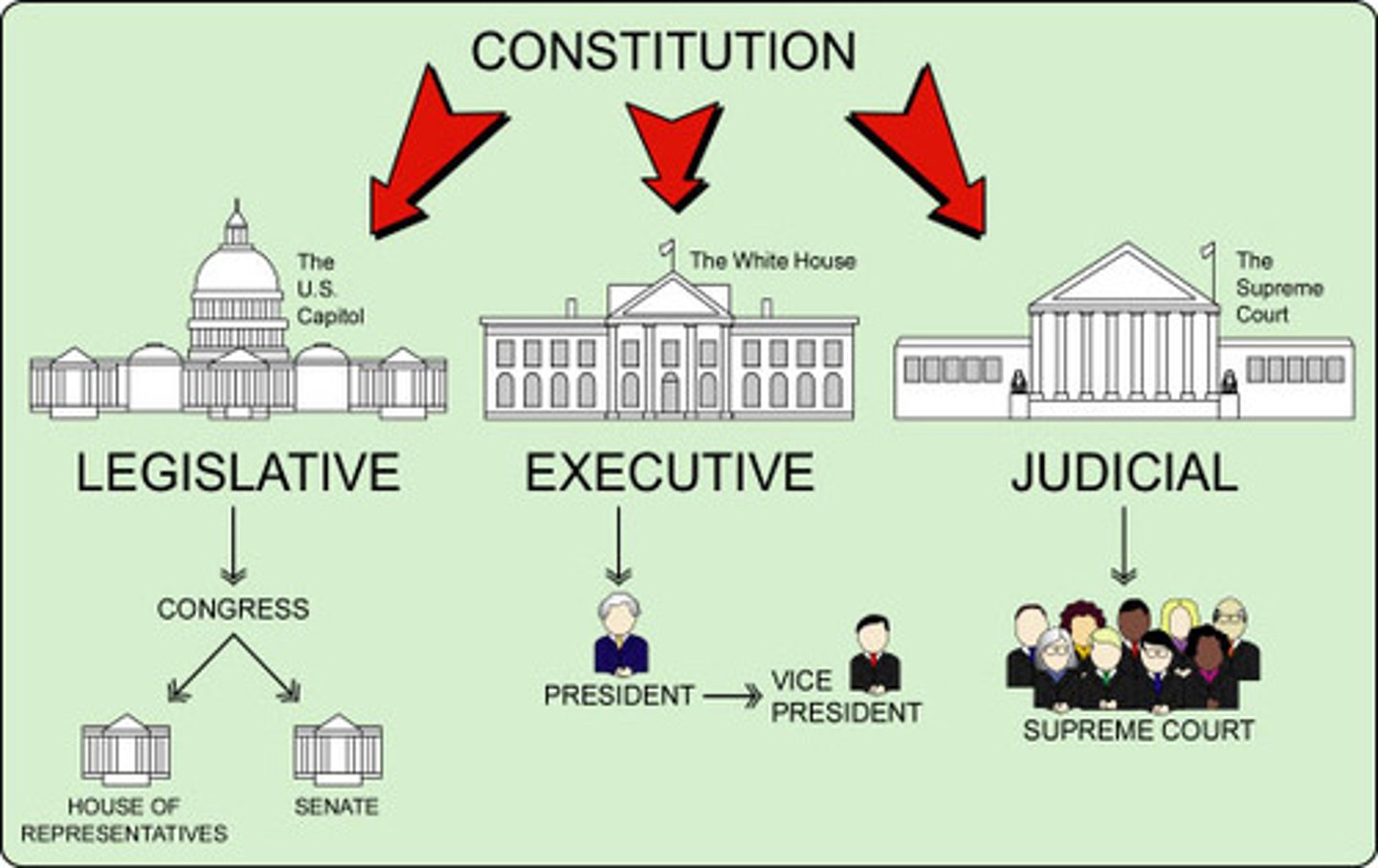
What are the 7 articles of the Constitution?
LEJRASR
Article 1: Legislative Branch
Article 2: Executive Branch
Article 3: Judicial Branch
Article 4: Relations of States (within and b/w fed)
Article 5: Amendment process
Article 6: Supremacy Clause
Article 7: Ratification

What are the main ideas in the Constitution? (8)
-Individual Rights
-Limited gov
-Popular Sovereignty
-Separation of Powers
-Checks and Balances
-Federalism
-Rule of Law
-Republicanism

What are the powers of the Legislative Branch?
makes the laws; declares war, levies taxes

What are the powers of the Executive Branch?
Commander in Chief, Pardons, Appointments, Treaties, Law enforcement

What are the powers of the Judicial Branch?
interprets the constitution and other laws, reviews lower-court decisions

Who are the Federalists?
supporters of the US Constitution

Who are the Anti-Federalists?
People who did not support the Constitution. They were complaining that the Constitution did not have the rights of the people and lacked Bill of Rights or basically a shield from doing harm.

What is the Federalist 51?
Federalist No. 51 addresses means by which appropriate checks and balances can be created in government and also advocates a separation of powers within the national government. The idea of checks and balances is a crucial part of the U.S. system of government.

What is Brutus 1?
Author: Anti-Federalist
Suspicion of Power (the country is too large to be governed as a republic and the constitution gives the fed gov too much power)
Excess of power

What is Federalist 10?
An essay composed by James Madison which argues that liberty is safest in a large republic because many interests (factions) exist. Such diversity makes tyranny by the majority more difficult since ruling coalitions will always be unstable.

What is Marbury v. Madison?
Supreme Court set up judicial review allowing courts to declare Congress' acts constitutional or unconstitutional.

What is McCulloch v. Maryland?
Established that the Constitution grants implied powers to Congress, and that state action may not obstruct valid constitutional power of the federal government

What is U.S v. Lopez?
Was the first United States Supreme Court case since the New Deal to set limits to Congress's power under the Commerce Clause

government
the rules and institutions that make up that system of policymaking

politics
the process of influencing the actions and policies of government

democracy
a system of government where power is held by the people

natural rights
the right to life, liberty, and property, which government cannot take away

social contract
people allow their governments to rule over them to ensure an orderly and functioning society

popular sovereignty
the idea that the government's right to rule comes from the people

republicanism
a system in which the government's authority comes from the people
pluralist theory
a theory of democracy that emphasizes the role of groups in the policymaking process
elitist theory
theory of democracy that the elites have a disproportionate amount of influence in the policymaking process

participatory democracy
the theory that widespread political participation is essential for democratic government

political institutions
the structure of government, including the executive, legislature, and judiciary
constitutional republic
a democratic system with elected representatives in which the Constitution is the supreme law

Articles of Confederation
a governing document that created a union of thirteen sovereign states in which the states, not the union, were supreme

unicameral
a one-house legislature

Shays's Rebellion
a popular uprising against the government of Massachusetts
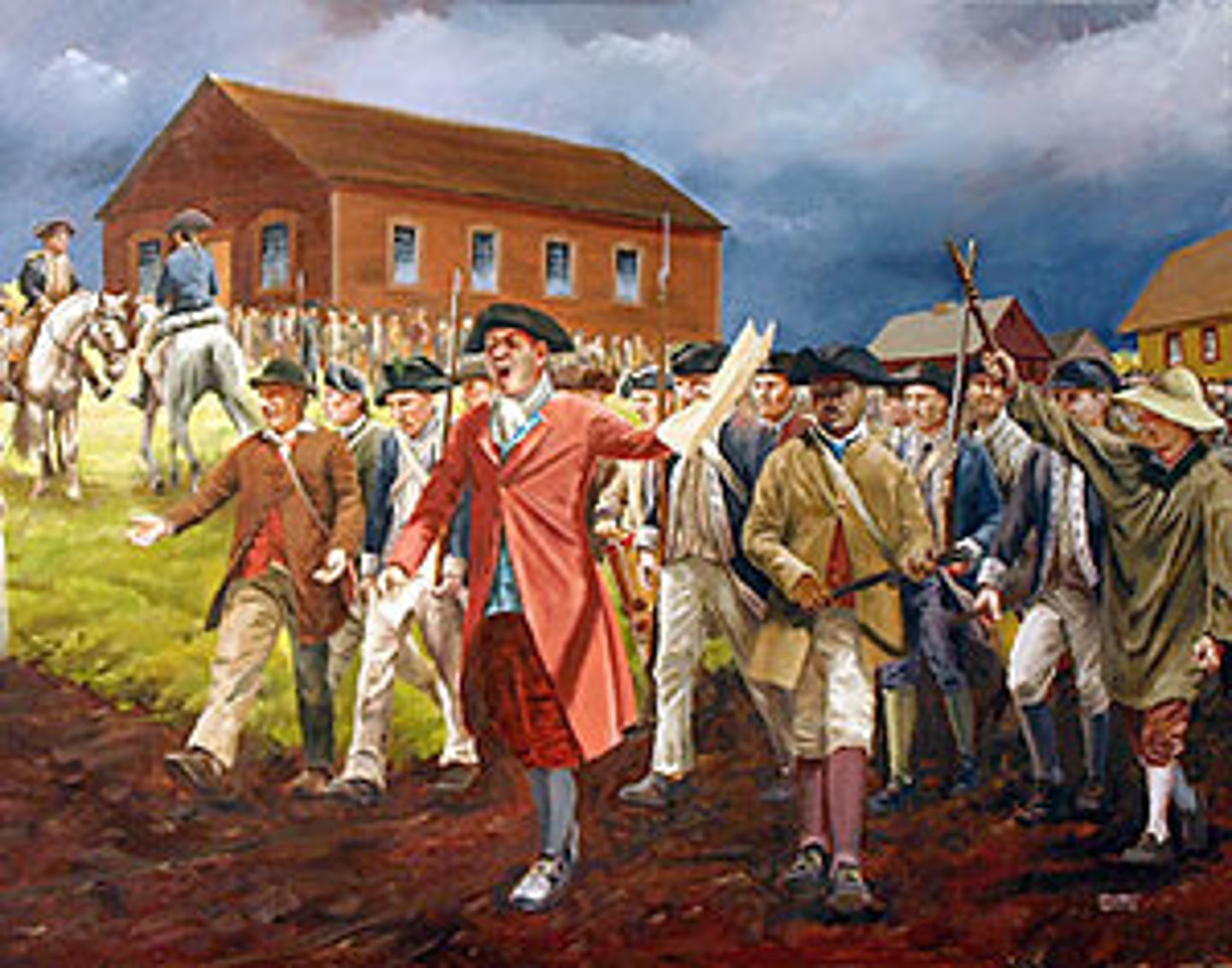

writ of habeas corpus
the right of people detained by the government to know the charges against them

bill of attainder
when the legislature declares someone guilty without a trial

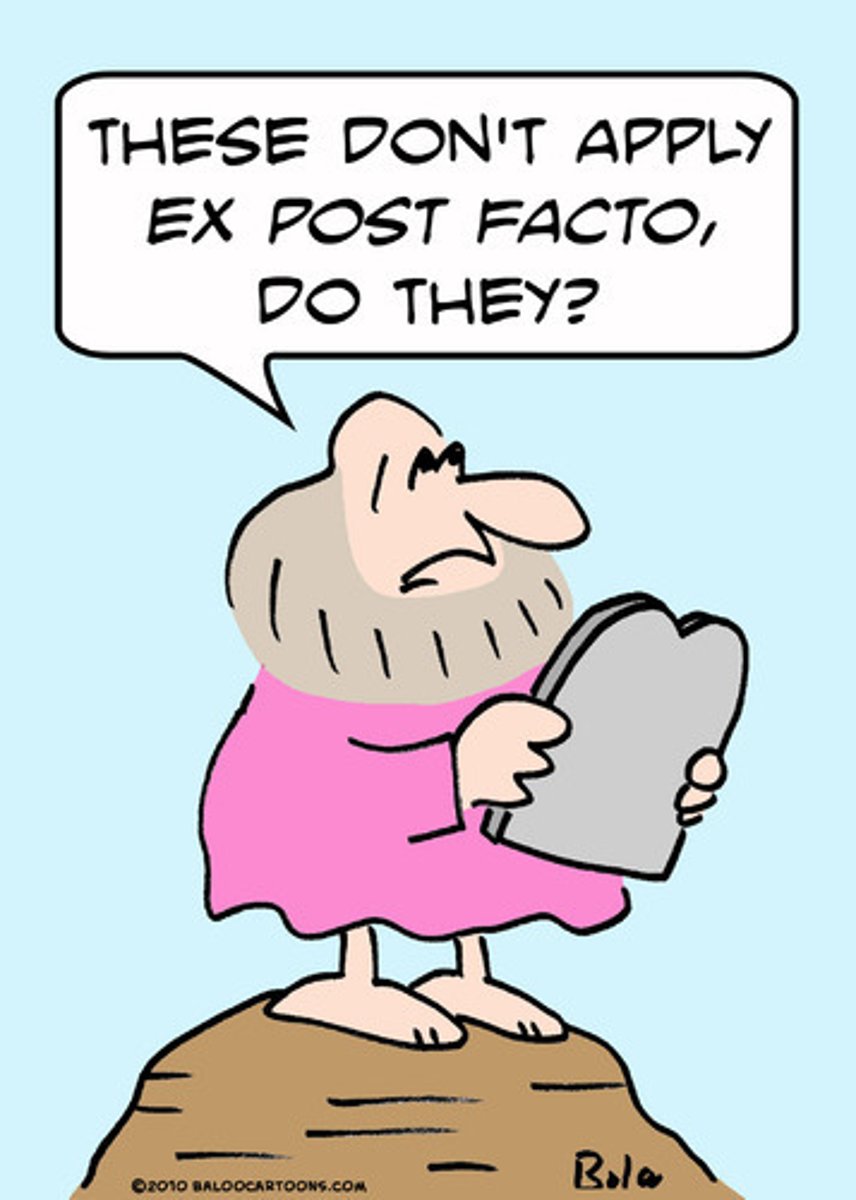
ex post facto law
a law punishing people for acts that were not crimes at the time they were committed

Virginia Plan
a plan of government calling for a three-branch government with a bicameral legislature, where more populous states would have more representation in Congress
New Jersey Plan
a plan of government that provided for a unicameral legislature with equal votes for each state

Great Compromise
an agreement for a plan of government that drew upon both the Virginia and New Jersey Plans; it settled issues of state representation by calling for a bicameral legislature with a House of Reps apportioned proportionately and a Senate apportioned equally
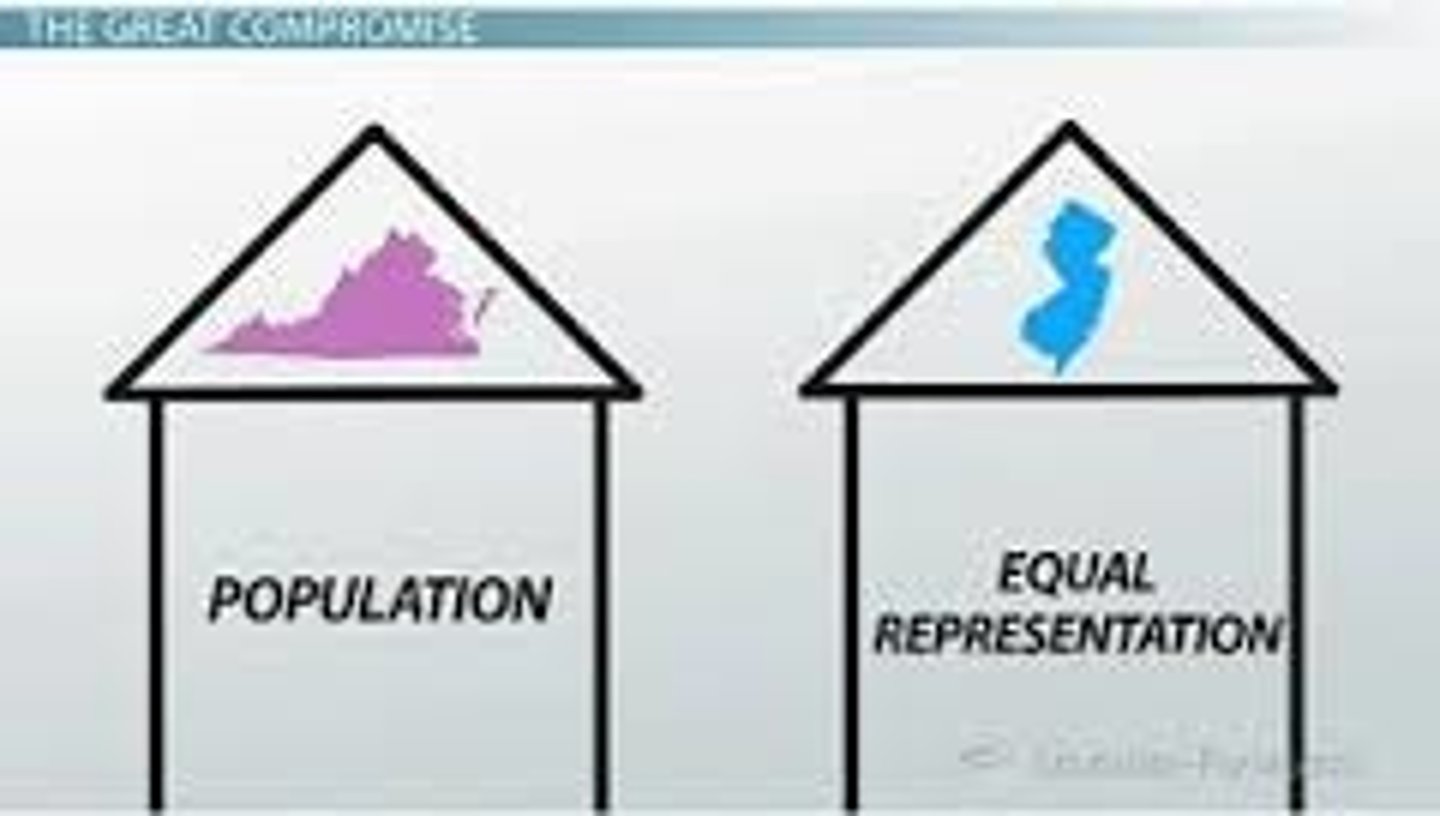
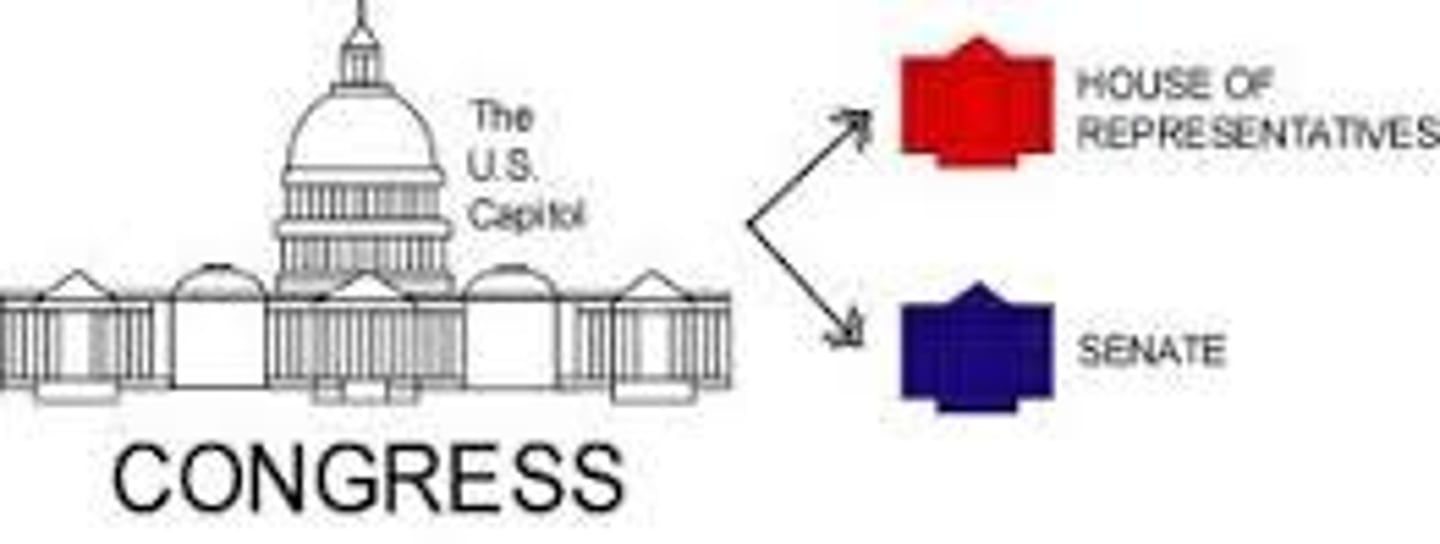
bicameral
a two-house legislature
3/5 Compromise
an agreement reached by delegates at the Constitutional Convention that a slave would count as three-fifths of a person in calculating a state's population
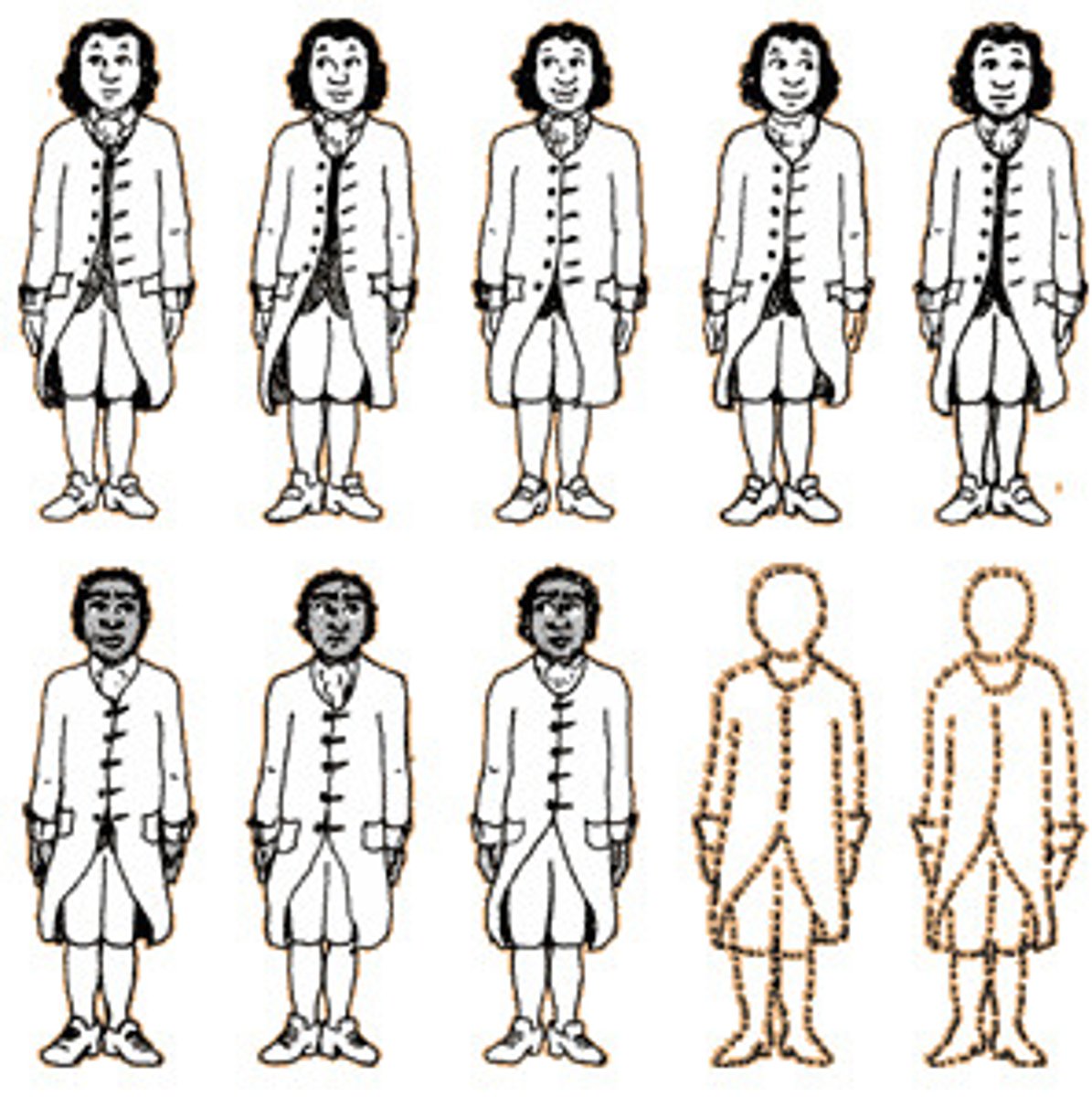

separation of powers
a design of government that distributes powers across institutions in order to avoid making one branch too powerful on its own
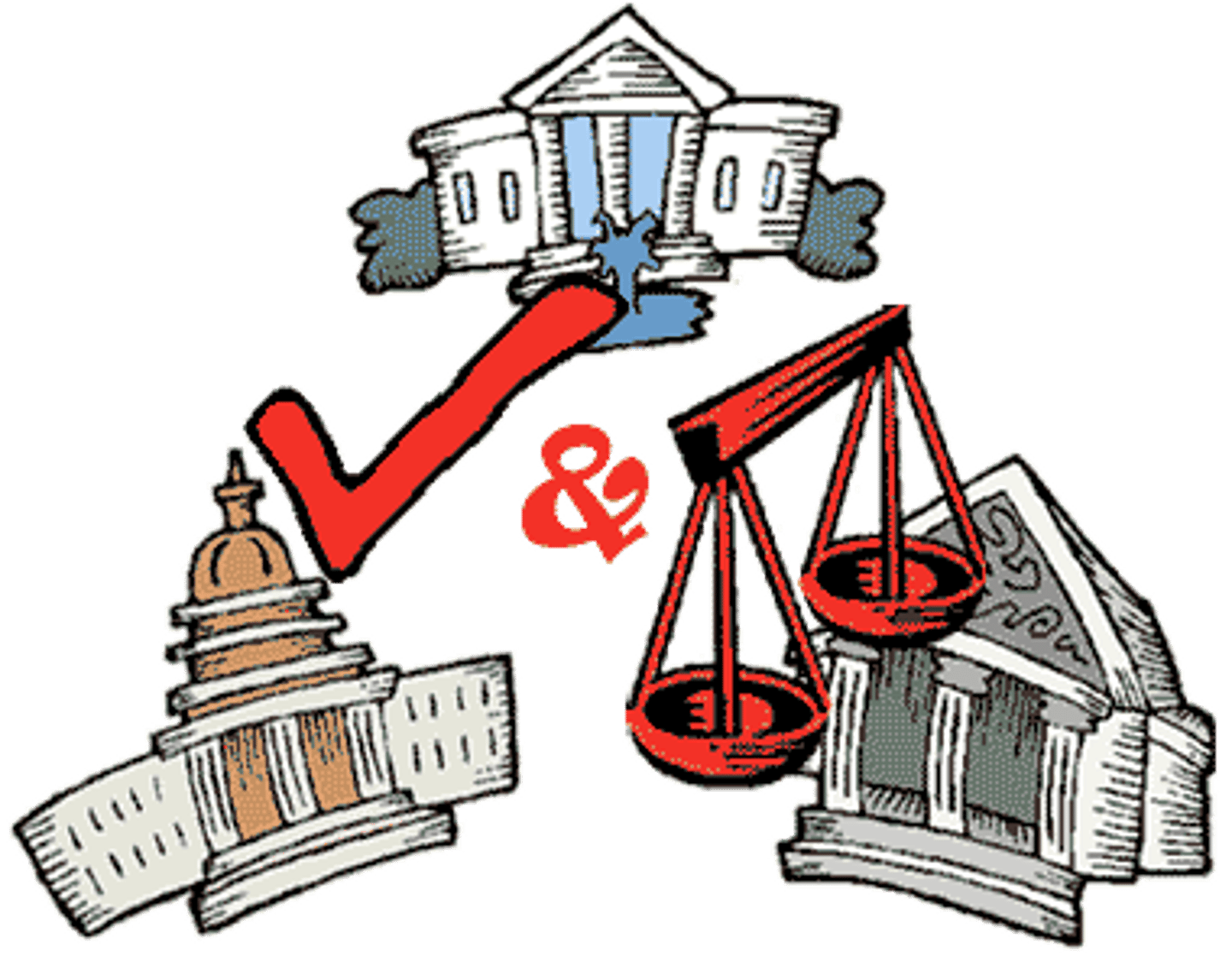
checks and balances
a design of government in which each branch has powers that can prevent the other branches from making policy
federalism
the sharing of power between the national government and the states
expressed or enumerated powers
authority specifically granted to a branch of government in the Constitution

necessary and proper clause
language in Article I, Section 8, granting Congress the powers necessary to carry out its enumerated powers

implied powers
authority of the federal government that goes beyond its expressed powers; powers not granted specifically to the national government but considered necessary to carry out the enumerated powers

supremacy clause
constitutional provision declaring the Constitution and all national laws and treaties are the supreme law of the land
amendment
a constitutional provision for a process by which changes may be made to the Constitution

Federalists
supporter of the proposed Constitution, who called for a strong national government

Anti-Federalists
a person who opposed to the proposed Constitution who favored stronger state governments
Federalist Papers
a series of eighty-five essays written by Alexander Hamilton, James Madison, and John Jay and published between 1787 and 1788 that lay out the theory behind the Constitution

faction
a group of self-interested people
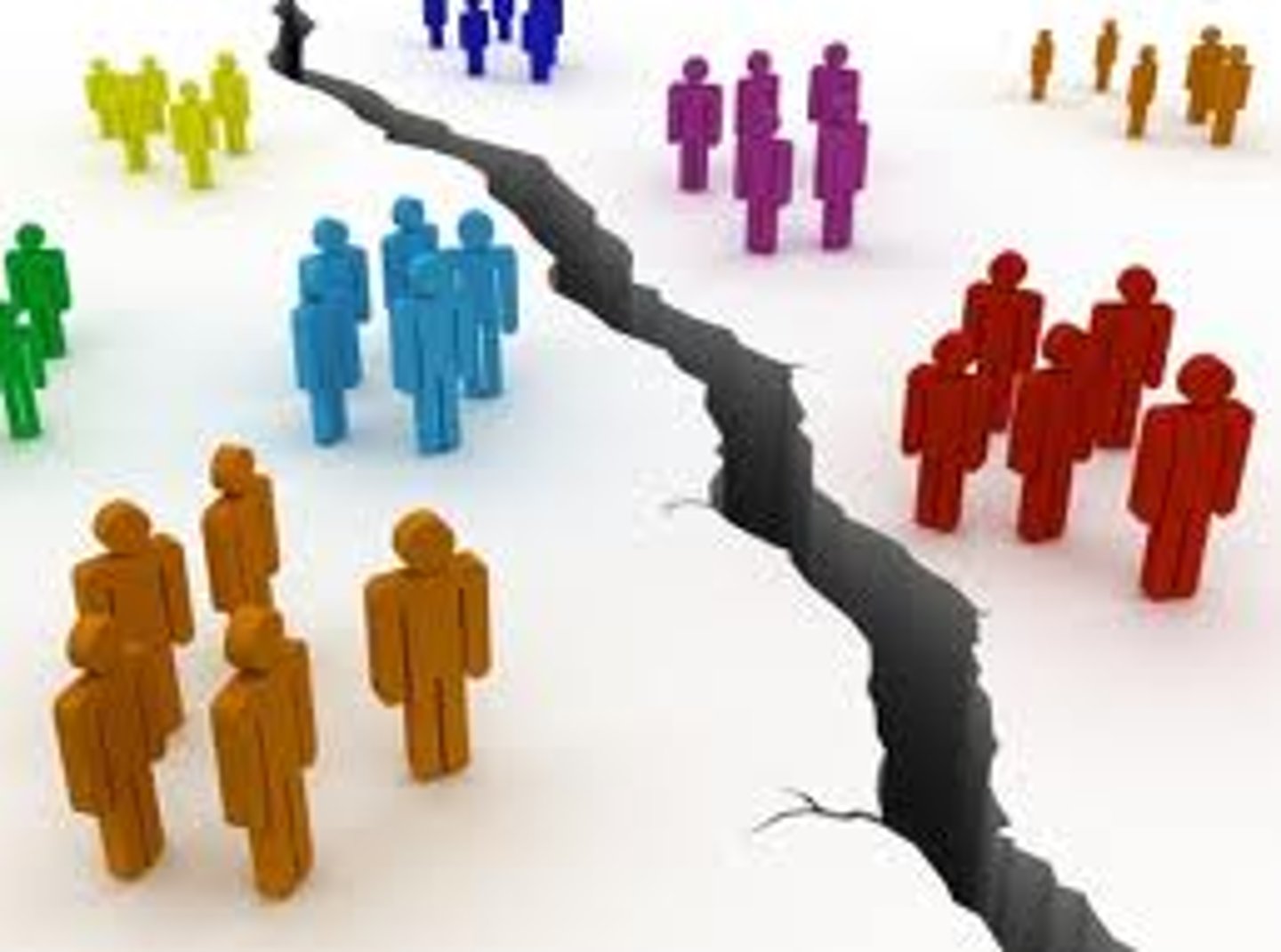

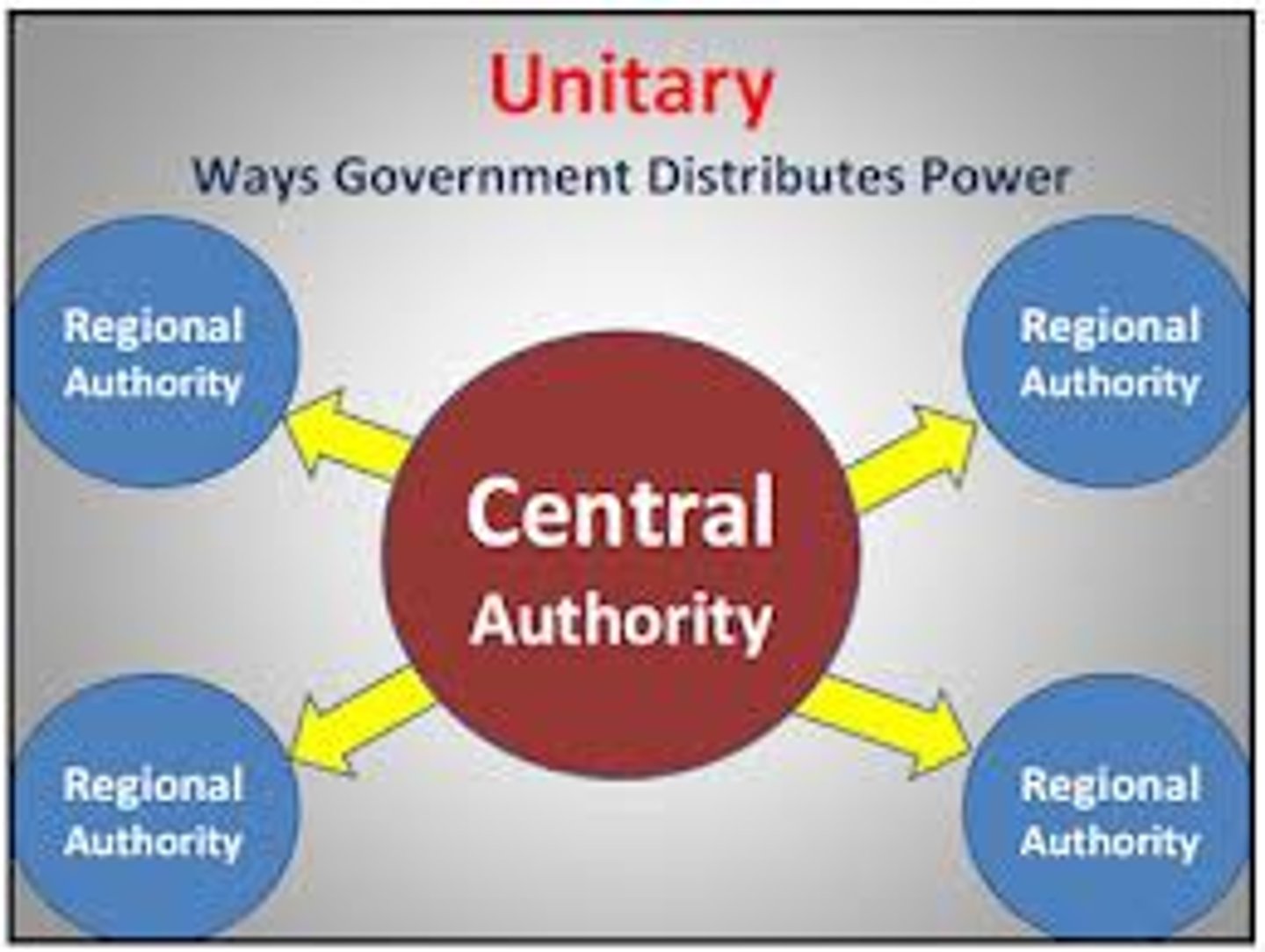
unitary system
a system where the central government has all of the power over subnational governments
confederal system
a system where the subnational governments have most of the power

federal system
a system where power is divided between the national and state governments
exclusive powers
powers only the national government may exercise
