Adrenal Glands
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
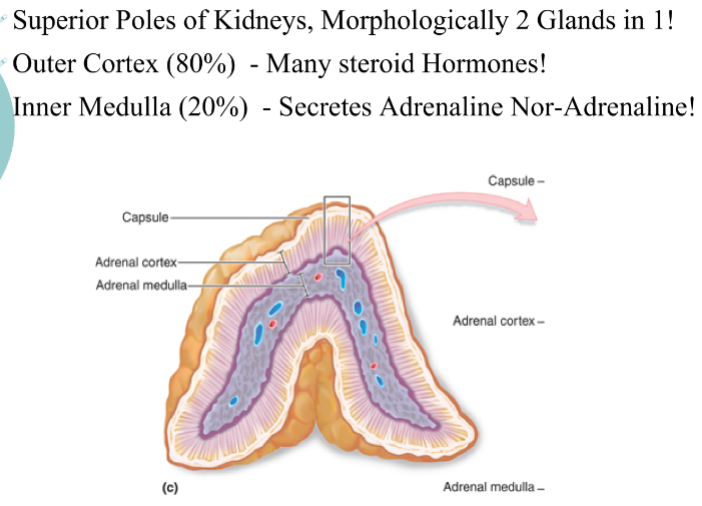
Where are adrenal glands found
Outer cortex (80%)
Inner Medulla (20%)
Location & structure of the adrenal glands
Hormones produced by medulla & % of each
Adrenaline (80%)
Nor-Adrenaline (20%)
Precursor of adrenaline
Tyrosine
As you produce adrenaline you also produce what other hormone
Dopamine
Blood conc. of adrenaline
10-10M
Effects of adrenal medulla hormones on the CVS

Effects of adrenal medulla hormones on the GIT
Decreased motility
Effects of adrenal medulla hormones on the skin
Increased sweating
Effects of adrenal medulla hormones on the skeletal muscle
Increased tension generation
Effects of adrenal medulla hormones on the nervous tissue
Increased brain arousal, reflex speed, aggression, anxiety
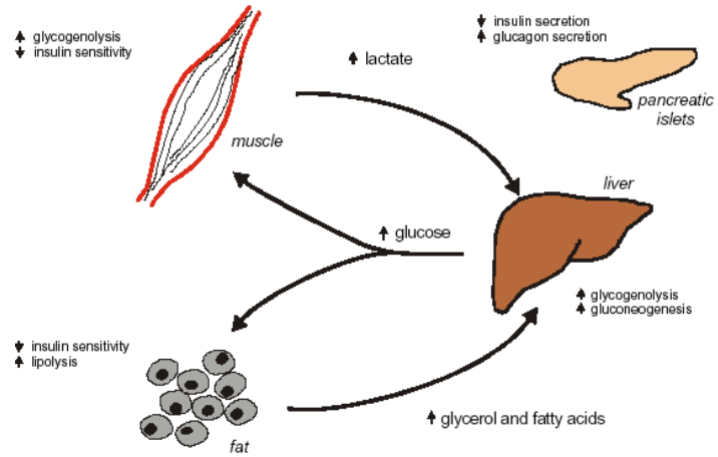
Metabolic effects of adrenal medulla hormones on muscle, pancreatic islets, liver & fat
What is pheochromocytoma
Rare catecholamine producing tumour
What do pheochromocytomas arise from
chromaffin cells of adrenal medulla or from sympathetic ganglia
Symptoms of pheochromocytomas
Pressure - sudden major increase in blood pressure
Pain - abrupt throbbing headache, chest, abdominal pain
Perspiration - generalized diffuse diaphoresis
Palpitations usually with true tachycardia often with feelings of panic or anxiety
Pallor of the skin from vasoconstriction
3 types of steroid hormones produced int he adrenal cortex
Mineralocorticoids
Glucocorticoids
Weak Androgens
Give an example of each type of steroid hormone produced int he adrenal cortex
Mineralocorticoids
Glucocorticoids
Weak Androgens
Mineralocorticoids - Aldosterone
Glucocorticoids - Cortisol
Weak Androgens - Weak Sex Steroids (Androstenedione & Dehydroepiandrosterone)
Mineralocorticoids
What are they derived from
Are they stored
Are they synthesised on command
Mineralocorticoids are:
Derived From Cholesterol
Not Stored
Synthesised on Demand
How are glucocorticoids found in the body
glucocorticoids are found bound to plasma
How are weak androgens found in the body
Bound to intracellular receptors in the cytoplasm / nucleus
Role of weak androgens
Alter gene activity
What are the layers from outside to inside in the adrenal gland
Capsule - Adrenal cortex (zona glomerulosa, zona fasciculata, zona reticularis) - Adrenal medulla
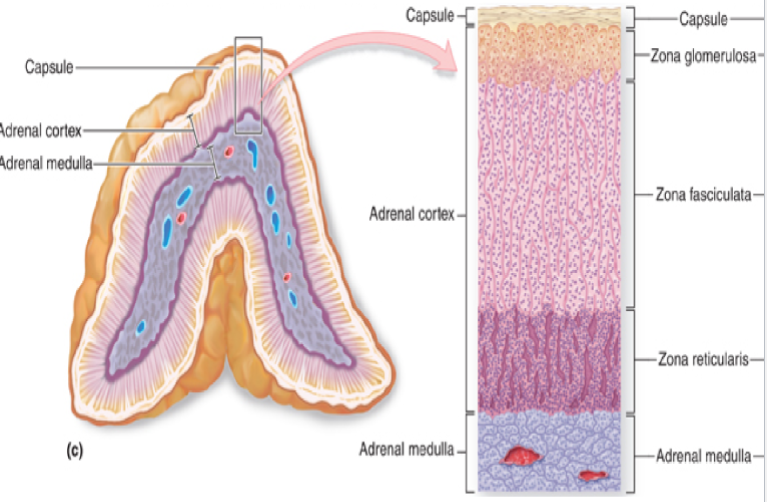
What will a problem in each of the zones present as
zona glomerulosa: sodium imbalance
zona fasciculata: cortisol imbalance (causes high/low blood sugar)
zona reticularis: androgenic effects (or deficiency)
Remembered as GFR - salt, sugar, sex!
A deficiency in cholesterol causes a deficiency in what types of steroid hormone (mineralocorticoids, glucocorticoids, androgens)
all 3: mineralocorticoids, glucocorticoids, androgens
A deficiency in progesterone causes a deficiency in what types of steroid hormone (mineralocorticoids, glucocorticoids, androgens)
mineralocorticoids
glucocorticoids
Some androgens - would have an effect on androstenedione production but not dehydroepiandrosterone
A deficiency in 17-hydroxypregnenolone causes a deficiency in what types of steroid hormone (mineralocorticoids, glucocorticoids, androgens)
glucocorticoids & androgens
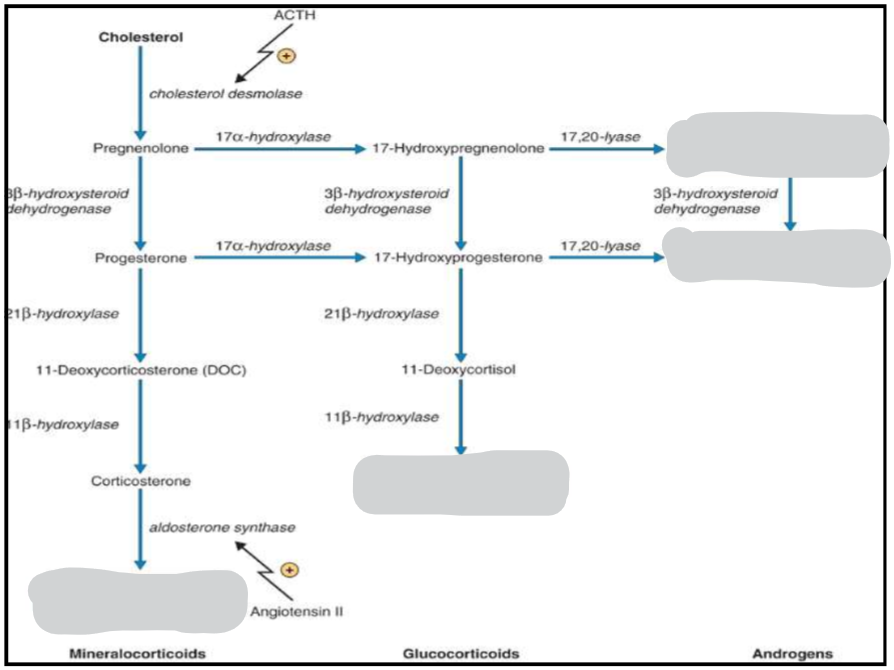
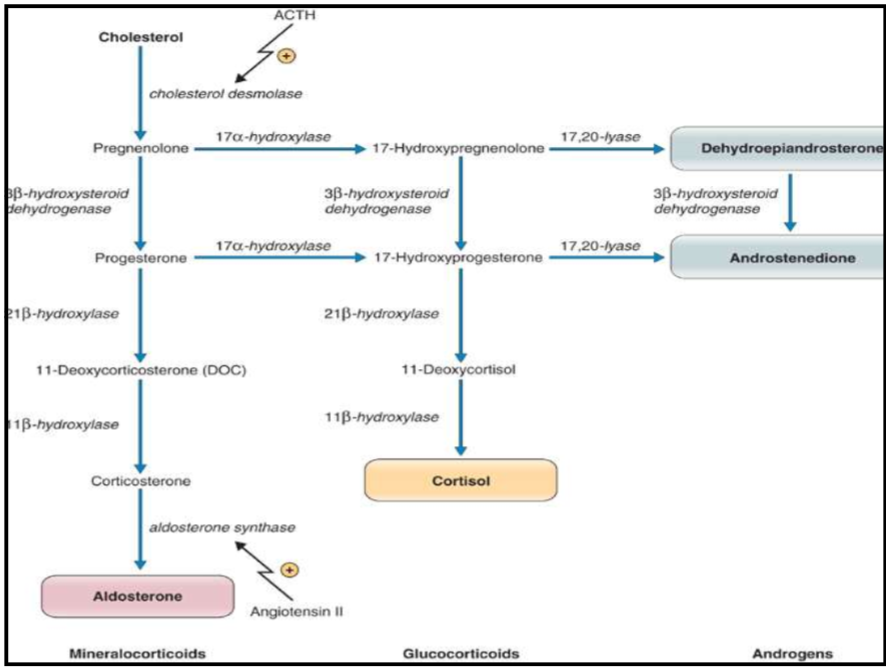
What zones in the adrenal gland secrete glucocorticoids
Zona Fasiculata and Reticularis
Most common glucocorticoid
Cortisol
Why is cortisone prescribed more than cortisol
Fewer side effects
Normal Cortisol Blood Concentration
5-25µg/100mls
In what zone of the adrenal gland is cortisol mainly produced
zona fasciculata (contains enzymes for cortisol synthesis)
(small amounts in zona reticularis)
What hormones are required for cortisol synthesis
Corticotropin-Releasing Hormone (CRH)
Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH)
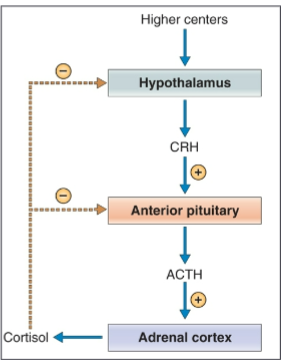
How is cortisol release regulated
Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal (HPA) Axis regulates cortisol release through a negative feedback loop
Hypothalamus releases CRH (Corticotropin-Releasing Hormone) → stimulates the pituitary.
Anterior Pituitary releases ACTH (Adrenocorticotropic Hormone) → stimulates the adrenal cortex.
Adrenal Cortex (Zona Fasciculata) releases Cortisol into the bloodstream.
Cortisol provides negative feedback to suppress CRH and ACTH production, preventing excess cortisol release.
What is the Dexamethasone Suppression Test (DST) used for
Diagnose the cause of hypercortisolemia (high cortisol levels)
Based on the negative feedback mechanism
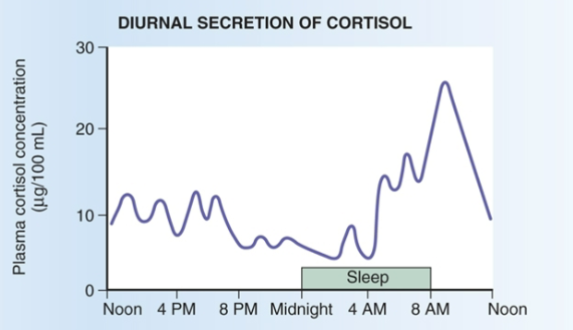
When is cortisol highest & lowest
Highest @ 8am
Lowest @ 2am
Is adrenocroticotrophin (ACTH) an anterior/posterior pituitary hormone
anterior
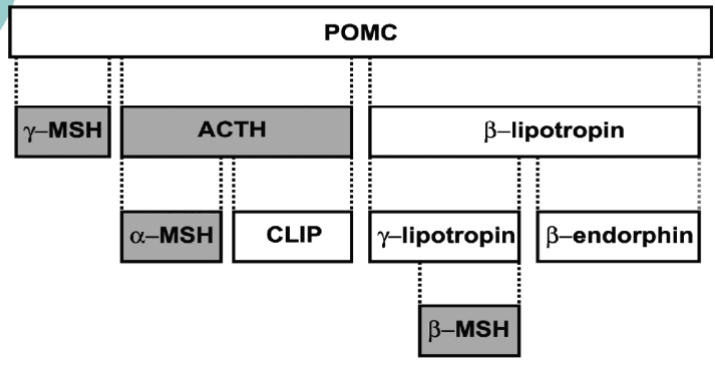
Precursor of adrenocroticotrophin (ACTH)
Pro-Opio-Melano-Corticotrophin (POMC)
What other hormones is Pro-Opio-Melano-Corticotrophin (POMC) a precursor for
MSH (Melanocyte-Stimulating Hormones)
Lipotropins
Endorphins
CLIP
How is cortisol transported
Mainly Bound in Plasma
How is cortisol transported
Mainly Bound in Plasma to transcortin
What synthesises transcortin
Liver
In the equilibrium between free & bound cortisol, what balance is there between the 2
Mostly bound, some free (active)
What influences free cortisol levels
Increased transcortin decreases free cortisol
Increased oestrogen (pregnancy / oral contraceptives) decreases free cortisol by increasing transcortin

Role of cortisol
Stabilise glucose between meals
Spares glucose
Promotes breakdown of protein & fat
(overall catabolic & diabetogenic)
What are the metabolic effects of cortisol on muscle, liver & fat
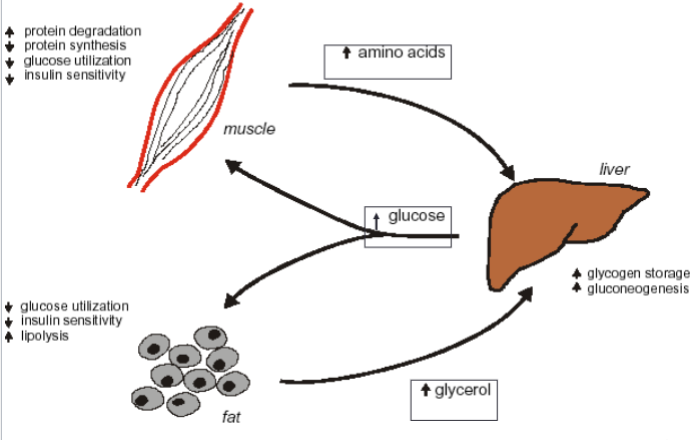
How do you tell if someone is having an excess of cortisol or glucagon
Cortisol promotes glycogen storage in the liver
Glucagon breaks down glycogen in the liver
Anti-inflammatory & immunosuppressive effects of cortisol
Cortisol inhibits every part of inflammation
Reduction in inflammation
Reduction in autoimmune reactions
Decreased healing
Decreased immune protection
(synthetic glucocorticoids are used to treat inflammatory disorders - eczema, asthma, prevent transplant rejection)

Effect of cortisol on cardiovascular system
Increases cardiac potential by making you more sensitive to adrenaline
Potentiates Effects of Adrenaline - increases β-adrenergic Sensitivity
Effect of cortisol on bones
Decreased osteoblast production and decreased Ca2+ production
(weakens bones)
Effect of cortisol on the liver
Increased Amino Acid Uptake by Liver
Increased Plasma Hepatic Proteins
What are the Mineralocorticoid Like Effects of Cortisol
Only Significant At Prolonged High Levels
Increased Sodium and Water Re-absorption, increased Potassium Excretion
Maintain Blood Volume in Dehydration, Hemorrhagic Stress
Cortisol effect on RBC production
Increases RBC production
Effect of cortisol & stress on metabolism
Increased energy substrates
Effect of cortisol & stress on mineralocorticoids
Dehydration
Haemorrhagic stress
Effect of cortisol & stress on cardiovascular system
Increased cardiac potential
Effect of cortisol & stress on hepatics
Slows tissue repair done by hepatic AA
Effect of cortisol & stress on immune response
Prevents over stimulation of the immune system
Effect of cortisol & stress on RBCs
Increases oxygen carriage
Effect of cortisol & stress on platelets
Prevents blood loss
What causes Cushing’s Syndrome
Caused by excess endogenous or exogenous glucocorticoids
Primarily at adrenal level
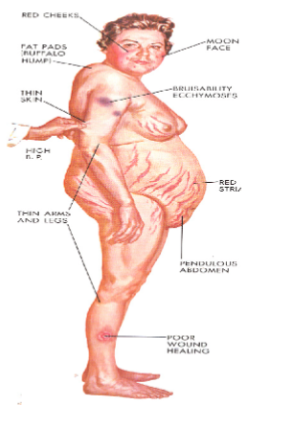
What causes Cushing’s disease
Overproduction of ACTH and cortisol
Metabolic symptoms of Cushing’s syndrome

What is Addison’s disease
Primary adrenocortical insufficiency
The adrenal cortex is destroyed
Insufficient production of cortisol, often accompanied by aldosterone and adrenal androgen deficiency
What causes Addison’s disease
The result of an infection (TB / autoimmune disease)
Can be caused by another treatment (e.g. chemo)
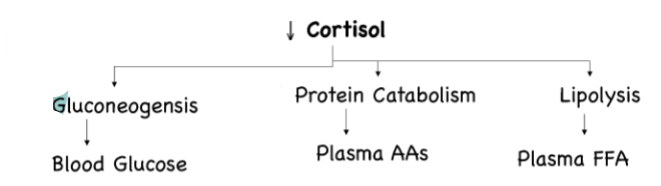
Effects of under secretion of cortisol (Addison’s disease) on each of these (arrow up/down)
& other effects of low cortisol
Leads to an inability to maintain blood glucose between meals
Inability to deal with stress
Susceptibility to inflammation & allergies
Increased pigmentation
Increased ACTH, POMC and MSH
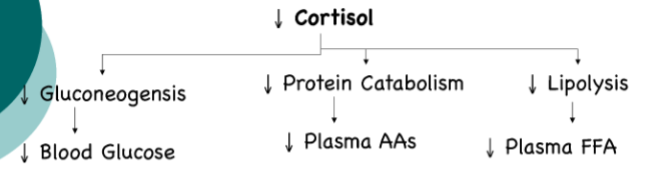
Which of these are affected by increased ACTH: Mineralocorticoids (aldosterone), glucocorticoids (cortisol), androgens (dehydroepiandrosterone & androstenedione)
What would the effect be
All
Increased production
Which of these are affected by a lack of 21 β-hydroxylase: Mineralocorticoids (aldosterone), glucocorticoids (cortisol), androgens (dehydroepiandrosterone & androstenedione)
What would the effect be
All
Mineral corticoids & Glucocorticoids production would decrease
Androgens production would increase due to a build up of its precursors
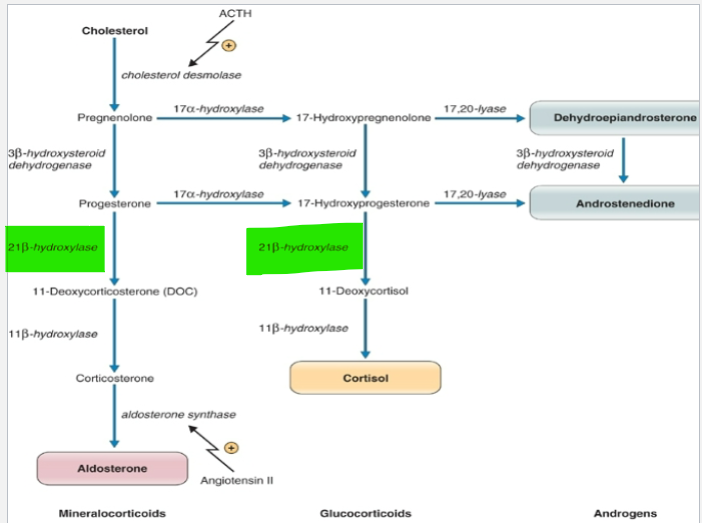
What causes 21 β-hydroxylase deficiency
Congenital abnormality
adrenogenital syndrome or congenital adrenal hyperplasia
What are the results of a 21 β-hydroxylase deficiency
Unable to produce mineralocorticoids or glucocorticoids
Produce adrenal androgens – virilisation of females
In utero – cause masculinisation of external genitalia
In children – increase growth, suppression of gonadal function
Which of these are affected by a lack of 17α-hydroxylase: Mineralocorticoids (aldosterone), glucocorticoids (cortisol), androgens (dehydroepiandrosterone & androstenedione)
What would the effect be
No glucocorticoids or adrenal androgens
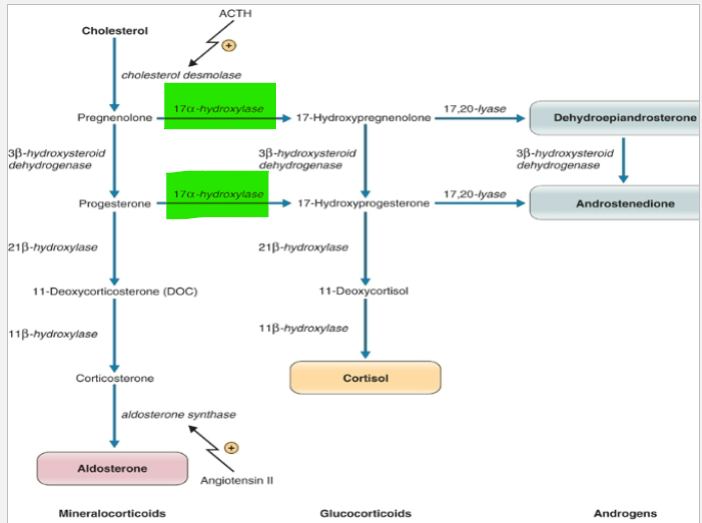
What is the result of a deficiency in 17α-hydroxylase
Overproduction of corticosterone but inhibits aldosterone levels
(inhibitory feedback)
Which is more common: 21 β-hydroxylase deficiency or deficiency in 17α-hydroxylase
21 β-hydroxylase deficiency