Geog of Korea part 2
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
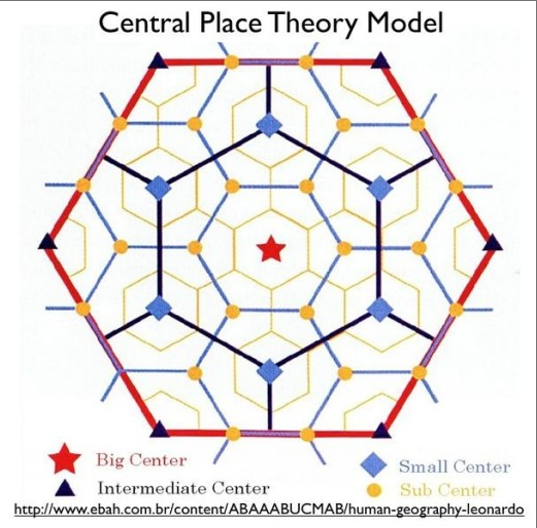
Central Place Theory Model
It suggests that settlements are arranged in a hexagonal pattern to efficiently serve consumers, with larger cities offering specialized goods and services that require a larger market area.
Andong Hahoe Folk Village
is a traditional village in South Korea known for its well-preserved historic architecture and cultural heritage, illustrating rural settlement patterns.
Rural Area Type Farming
Agglomerated Settlement
Rural Area Type Fishing
Around Harbor
Rural Area Type: Mountain
Dry-Field, stock farming and forestry
Percent of urbanization of Korea
90%
Slow City Movement
returning to the farm
Japanese occupation
Growth on coast and manufacturing town
1950 urban development
Immigration from North Korea, overpopulation, slums
1960 urban development
Urbanization in Seoul/Busan by Economic Development Policy
1970 urban development
More urban than ruraal population, larger provincial cities, export oriented cities
Provincial Cities (1970)
Kwangju, Daejon
Export Oriented cities
(Pohand, Ulsan, Changwon)
1980 Urban Develpment
Growth of satellite cities, suburbanization, urban rural integration cities
Satellite Cities
Seongnam, Ansan, Goyang
Example of high urban hierarchy
Seoul
Example of low urban hierarchy
Donghae
Who created Central Place Theory
Walter Christaller
When was Central Place Theory created
1933
What shape does the central place theory model use
overlapping hexagons
What is at the center of each hexagonal market area
central place
Size of market area is proportional to
number of goods and services offered from the place
Primate City
Seoul. high population, growth of satellite cities around seoul
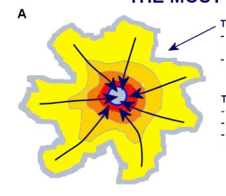
Classic Monocentric Model
High density center, people move from outside in
Urban Village Model
People live next to their place of employment, walk/cycle to work, exists only in the mind of planners, not real
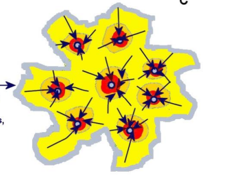
Polycentric Model
No dominant center, amenities distriuted evenly, random people movement
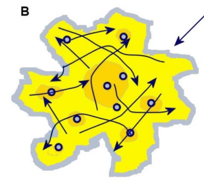
Composite Model
Dominant center, some subcenters, both radial and random movement
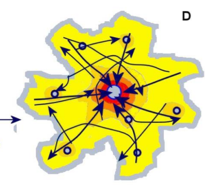
Regional Differentiation
Urban area’s regional specialization due to the growth and functional diversification
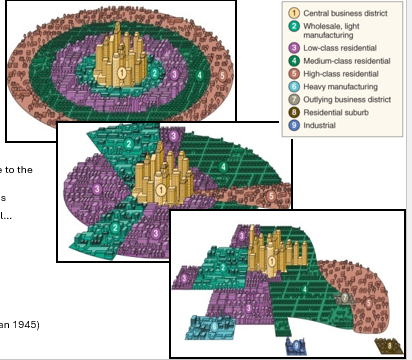
Concentric Zone Model (Burgess 1925)
Concentric Circle City Model, Central Business District → factory→low class residential→med class residential → high class residential → commuter zone
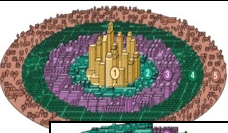
Sector Model (Hoyt 1939)
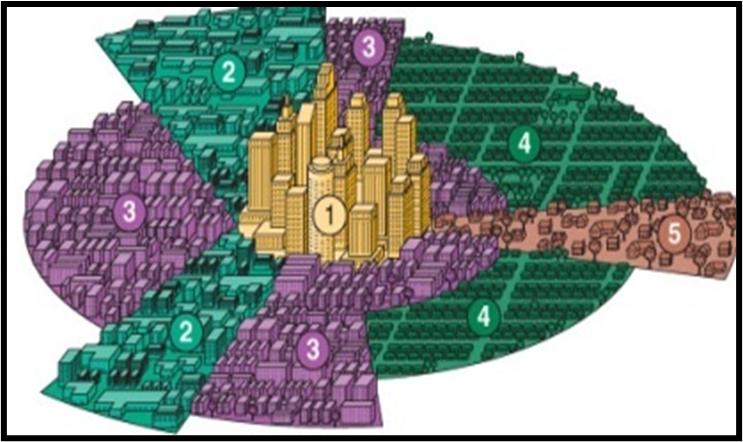
Multiple-Nuclei Model (Harris and Ullman 1945)
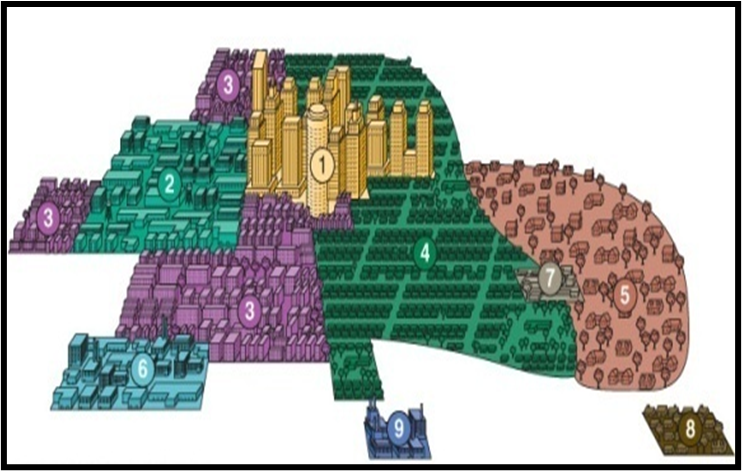
Metropolitan Peripheral Model
Revised Multple Nuclei model with a surrounding beltway and peripheral areas
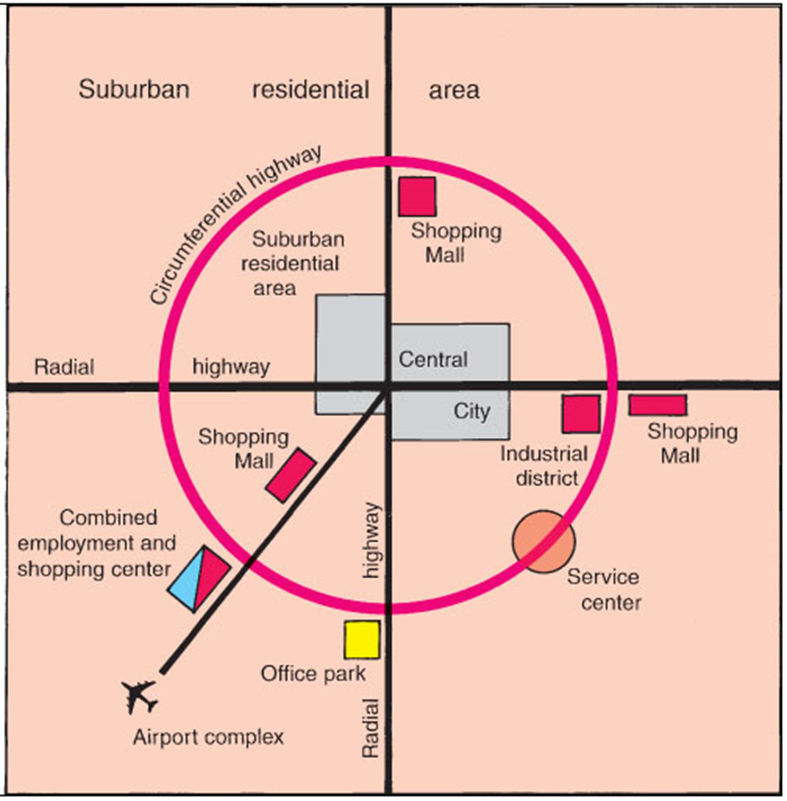
Central Business District (CBD)
A single point at which the maximum possible interchange could be achieved
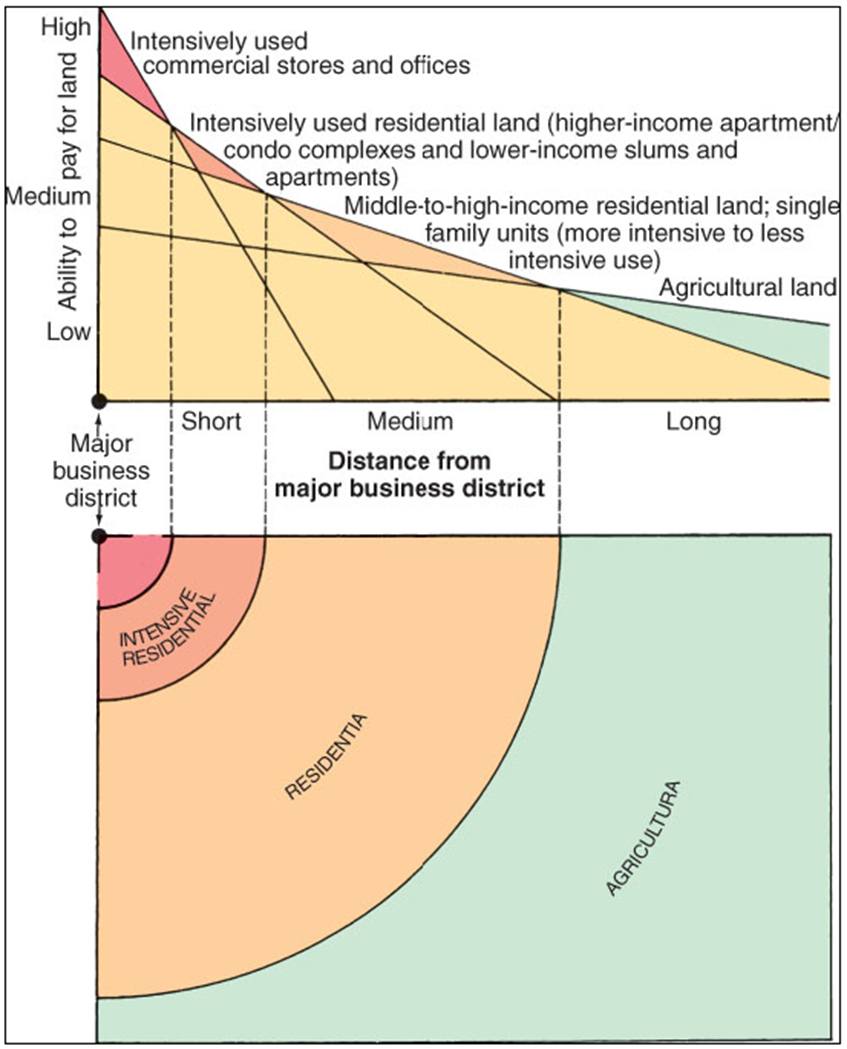
Central City
the principal core of a larger urban area
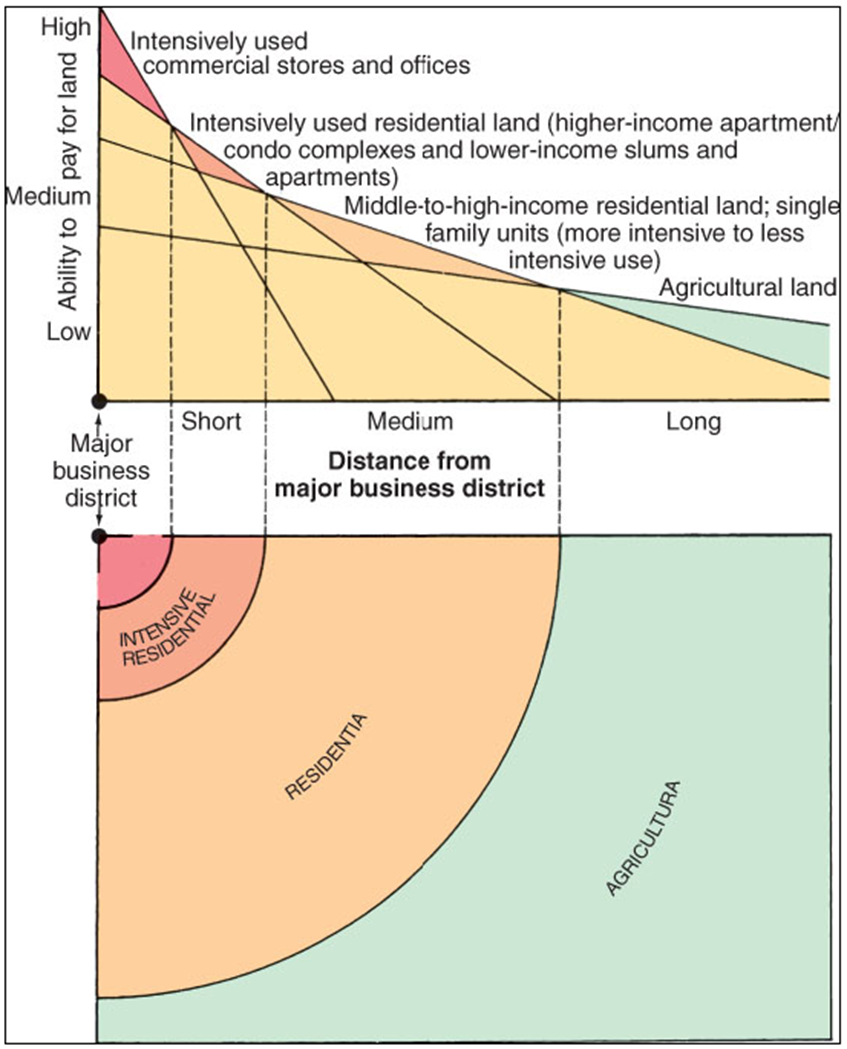
urbanized area
A continuously built-up landscape defined by population densities with no reference to political boundaries
Suburban
Beyond a city border
Metropolitan Area
Suburban and urban area coimbined
Urban Dichotomy
Separated rural and urban (see photo)
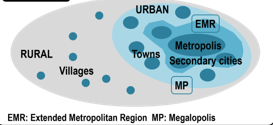
Urban Continuum
Several steps between urban and rural
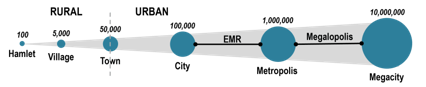
Mega City Population
10 million or more
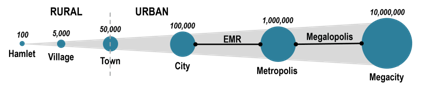
Metropolis
1 million or more
Influenced Zone of Central City
Lack of urban landscape, but affected by central city in the context of transportation and land use
Rural Hinterland
•Maximum distance for commuting
•Commercial horticulture
Adams Model
describes urban growth
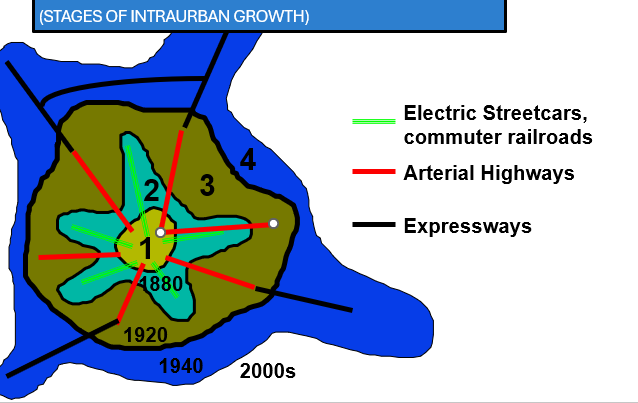
Adams Model stage a
Walking and horsecar era

Adams Model stage B
Electric Streetcar Era Adds suburb towns and railways, reshapes CBD

Adams Model Stage C
Recreational Auto Era, Adds roads and suburban area
Adams Model Stage D
Freeway Era Adds main roads and more suburbs
Adams Model Stage E
Adds highways, additional centers
United States Development Walking – Horse car Era
-1888
US Development Electric streetcar era
1888-1920
US Development Recreational Auto Era
1920-1945
US Development Freeway era
1945 onward
Urban Sprawl from Seoul goes to
Gyungi-Do and Incheon
Seoul Urban Spawl era
1980 and on
Spatial changes in seoul metropolitan
large scale apartments, agriculture to shopping and logistics, agitourism and rec
Poverty Regions in Seoul
South east of city center
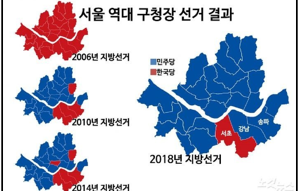
Urban planning and development are important to mitigate
flooding, low birth rate, high prices, high crime, traffic,