So far FA
1/136
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
137 Terms
how many bones in the vertebrae
24 bones
how many bones in the cervical vertebrae
7 bones
how many bones in the thoracic vertebrae
12 bones
how many bones in the lumbar vertebrae
5
cervical image
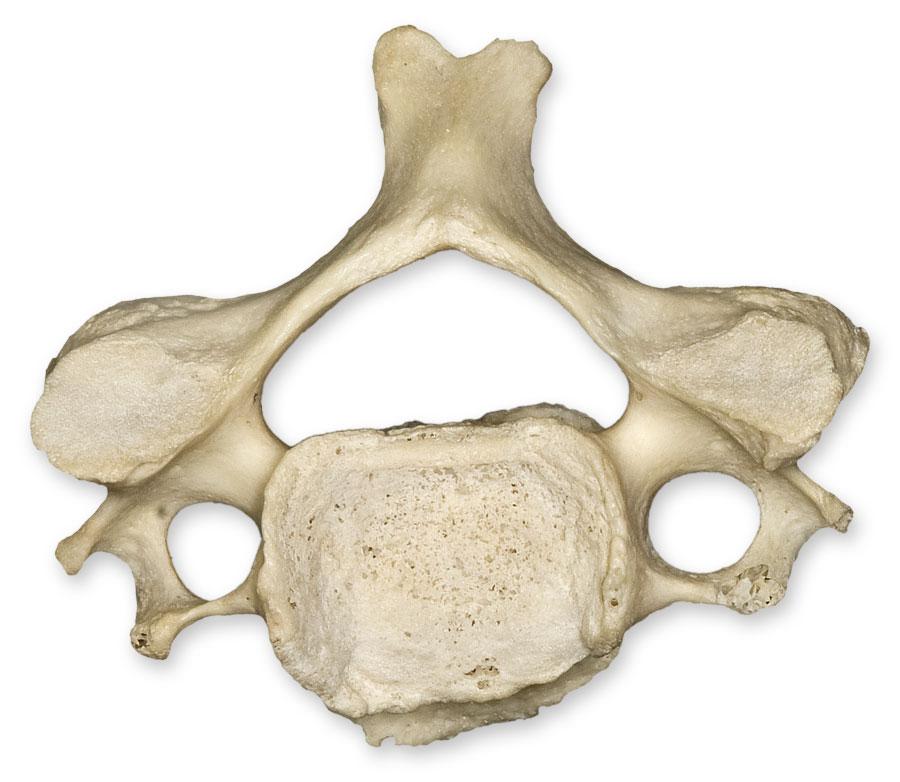
thoracic image
lumbar image

characteristics of the cervical vetrebrae
by transeverse foramina
characteristics of the thoracic vertebrae
long spinous process
articulations for ribs
characteristics of the lumbar vertebrae
by curved articular facets
sternum
“breastbone”
anterior portion of rib cage
articulates with ribs and clavicles
sternum image
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/sternum/GykQvBR1rfKsXp03AnEIWw_fzUqtGqMzjS1i5OGnwwWg_Sternum_02.png)
the rib cage
12 pairs of ribs - numbered superiorly to inferiorly
articulations
anteriorly- sternum
posteriorly-vertebrae
rib cage image

sternal end
part of rib that articulates with sternum
sternal end image

sacrum
inferior end of spine
posterior portion of pelvic girdle
sacrum image
:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/logos/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/learnable/anterior-sacroiliac-ligament/GxiyG7AzXz8OaNqGEJg67w_Anterior_sacroiliac_ligament.png)
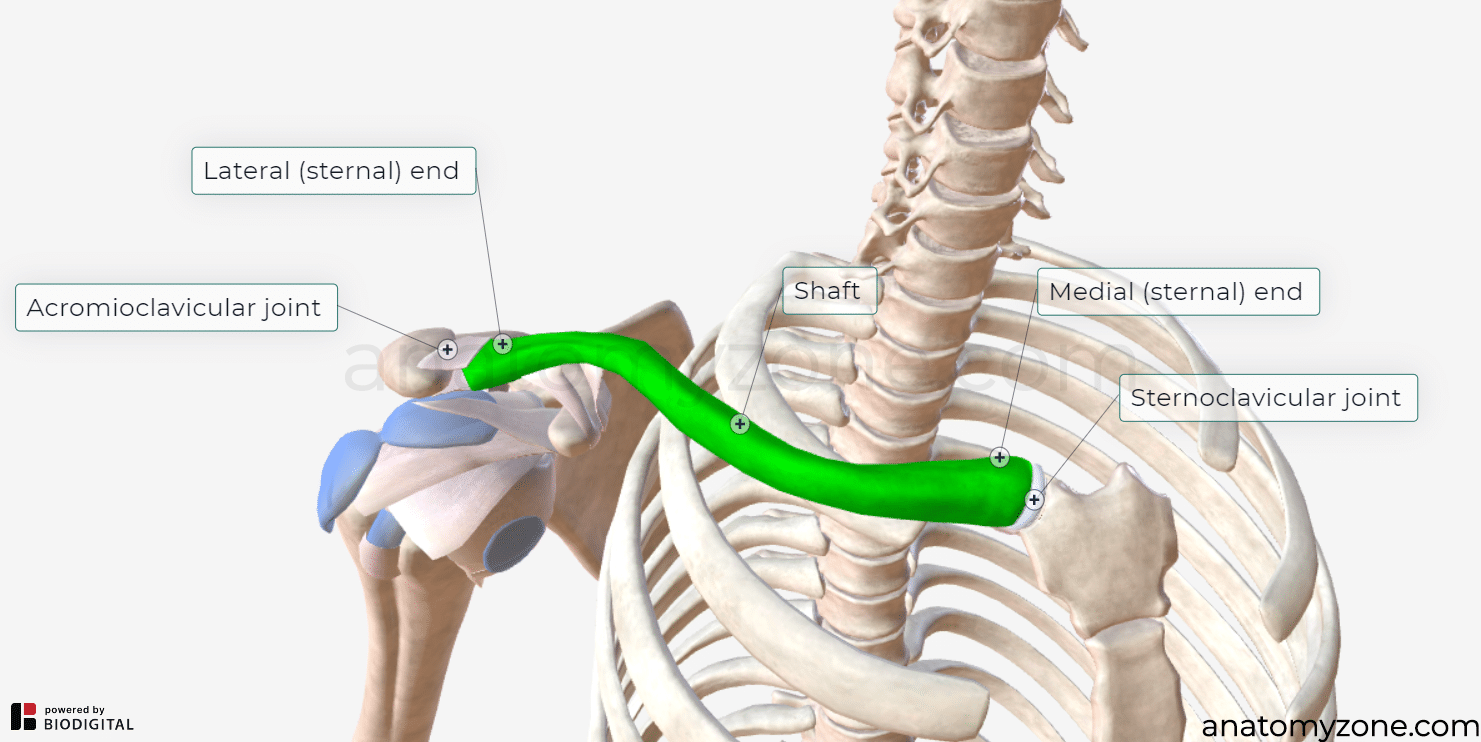
clavicle
“collarbone”
connects upper limb to axial skeleton
clavicle image
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/the-clavicle/laI4ltz7XFxESmitLKnd5g_clavicula_3_large_Gq8qvS5hSXwXBG70cLbW0w.png)
medial end
articulates with the sternum at the manubrium
medial end image
scapula
“shoulder blade”
posterior portion of the shoulder
scapula image
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/scapula/eY95lK2Mob0dRIR1f2Gw4Q_scapula_large_ac0mi5RXSTk9o39q93aWpg.png)
humerus
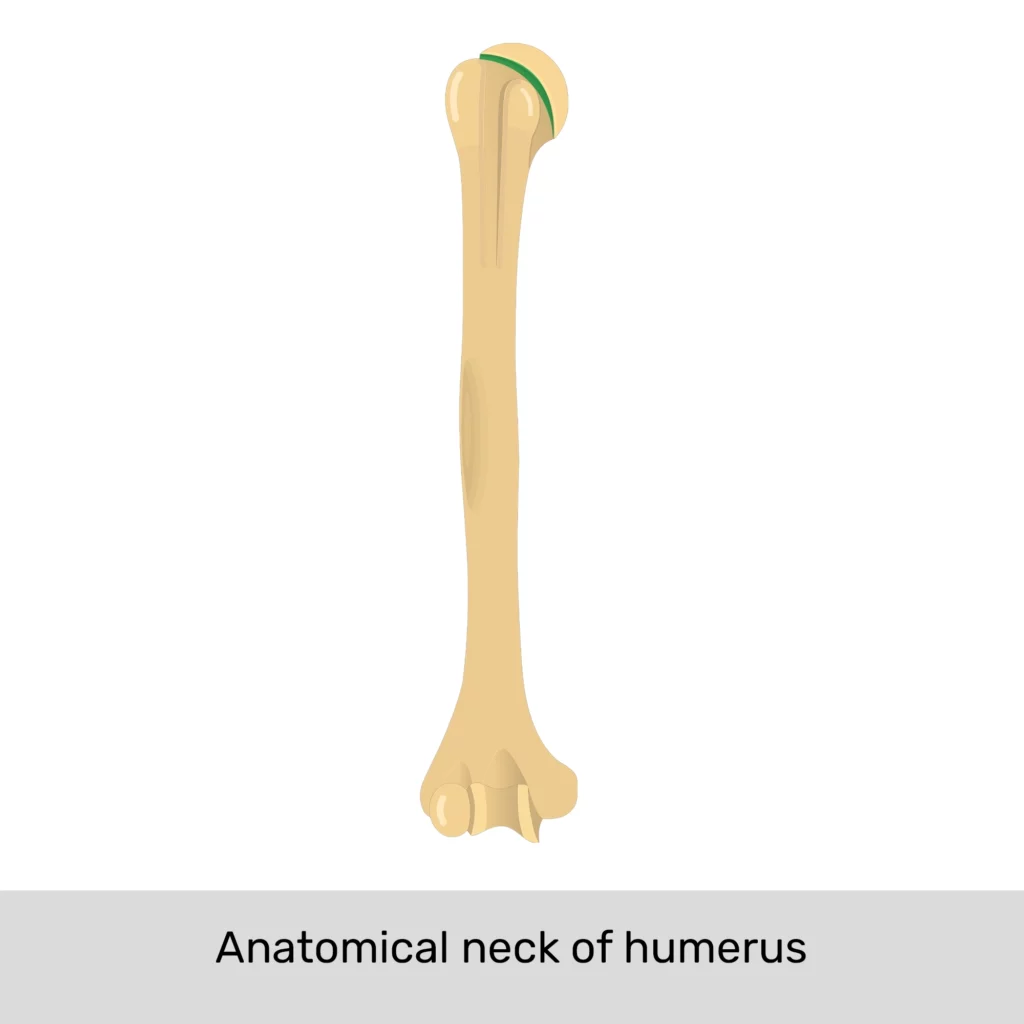
ulna (medial)

radius (lateral)

how many bones in carpals (wrist bones)
8 bones
how many bones in metacarpals (bones in palm)
5 bones
how many bones in phalanges (finger bones; singular= planax)
14 bones
Os coxae (innominate)
“hip bone”
lateral and anterior pelvic girdle
proximal lower limb
illium
blade of bone
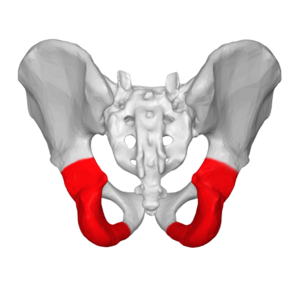
ischium
posterior and inferior part we sit on
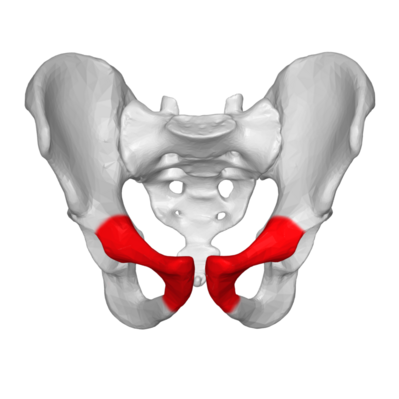
pubis
illium image
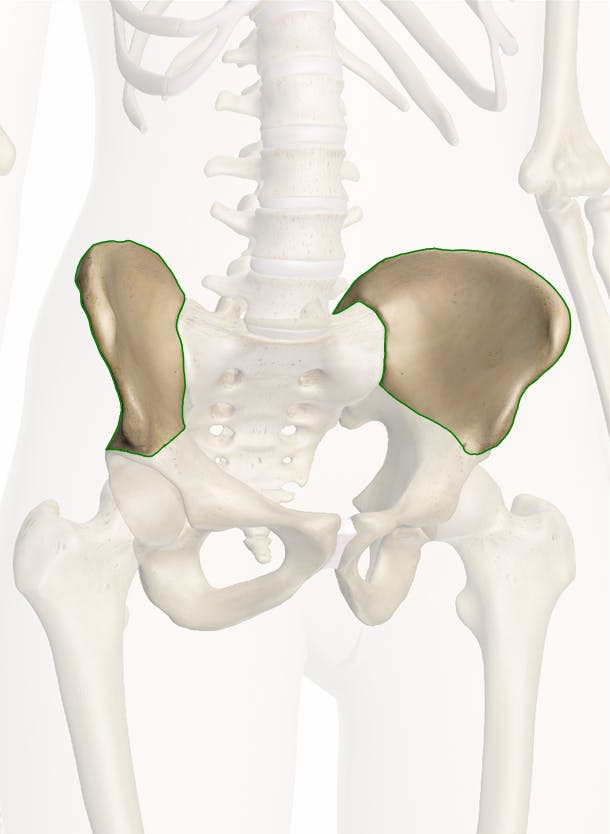
ischium image
pubis image
auricular surface
medial “ear shaped” surface that is articulation between os coxae and sacrum
greater sciatic notch
the wide notch just inferior to the posterior inferior iliac spine; pathway for performs muscle
auricular surface image
:watermark(/images/watermark_only_413.png,0,0,0):watermark(/logos/logo_url_sm.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/learnable/lunate-surface-of-the-acetabulum/rcbFSCuSUUpjdabAI04w_ESyMZz7r99_facies_lunata_2.png)
greater sciatic notch image

pubic symphysis
where the two pubic bones articulate
ischiopubic ramus
between ischium and pubis
pulic symphysis image

ischiopuvic ramus
:watermark(/images/watermark_only_413.png,0,0,0):watermark(/logos/logo_url_sm.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/learnable/superior-pubic-ramus-4/yAgxt753nbXomJzZ4LepnQ_Superior_ramus_of_pubis.png)
how many bones in tarsal (ankle bones) bones
7 bones
how many bones in metatarsals (bones in foot arches)
5 bones
how many bones in toe phalanges
14 bones
Mediolegal Death Investigator System
Responsible for
conducting death investigations
certifying cause, manner and circumstances of unnatural & unexplained deaths
Mechanisms of death
the immediate physiologic derangement resulting in death, which is not etiologically specific
hemorrhage
cardiac arrhythmic
sepsis
Death investigation
scene investigation
interviews with next-of-kin (family, friends)
review of recent medical history
examination of body
coroners
oversee death investigations within a particular jurisdiction
elected or appointed
common qualifications
registered voter
no felonies
training program
medical examiners
physician who investigates death that are sudden, unexpected, or violent
not required to be a forensic pathologist
most-need additional specialized training in forensic pathology or related field
forensic pathologists
medical specialists who determines cause and manner of death through a postmortem exam
conducts autopsies and other postmortem examinations
medical degree + residency + fellowship + certification
Medicolegal Death Investigators
first to examine the death scene
collection information and evidence
liaise with families and law enforcement
ensure proper handling of the body + chain of custody
what are the skeletal collection types that WCU has
archaeological
anatomical
donations
archaeological
provenience
often temporary possession
donations
grave robbing
criminals
1831 (MA) - Unclaimed individuals
1968- Uniform Anatomical Gift Act
anatomical
pre 1985 in India
1985-2008 in China
today are donations/high quality casts
what are the collections WCU
John A. Williams Documented Human Skeletal Collection
WCU Anatomical Collection
John A. Williams Documented Human Skeletal Collection
Associated with FOREST (est. 2003), which was the 2nd Outdoor Decomposition Facility in the US
about 130 individuals in the collection and which are self-donated and next-of-kin
less than 400 pre-donors (self donation)
WCU Anatomical Collection
legally acquired
old medical specimens
donated to wcu
what is forensic anthropology
the application of anthropological methods and theory
those related to the recovery and analysis of human remains that matters to legal concern
what are the skeletal biologists examples
human bone
human variation
what do forensic anthropology
hired as consultants on forensic cases
search and recovery
excavation of buried remains
skeletal analysis
trauma analysis
mass fatalities
identification
what are the types of cases
skeletonized
mummified
burned
decomposed
what are the three main periods
Formative Period (early 1800s-1938)
Consolidation Period (1939-1971)
Modern Period (1972- Present)
what happened during the Formative Period
Early 1800s
rise of anatomy
anthropometry
skull collections
studies of human variation
Parkman Murder (1849)
Harvard chemistry prof John W. Webster murdered this person over debt
dismembered segments in privy, furnace, and chest
Harvard anatomists were Drs. Jeffries Wyman and Oliver Wendell Holmes
had a fatal stab wound between ribs
Dr. Nathan Keep was a dentisted that found a mold of _____ mouth
Sausage Vat Murder (1897)
“____ King of Chicago” Adolph Luetgert killed his wife Louisa
disposed body in vat of potash (waster-soluble potassium bearing salts)
George A. Dorsey was the anthropologist who testified bones from human female
Thomas Dwight
Father of Forensic Anthropology
Physician, anatomist. professor at Harvard
the Identification of the Human Skeleton: A Medico-legal Study (1878)
Ales Hrdlicka
Father of Physical Anthropology
1903: Smithsonian
1918: American Journal of Physical Anthropology
1930: FBI cases
Earnest Hooton
Physical Anthropologist at Harvard
1943: Medico-Legal Aspects of Physical Anthropology
Students opened first doctoral programs
what are the establishments of skeletal research collections
Hamann-Todd Osteological Collection (AT Cleveland Ohio, Case Western)
>3000 (1893-1938)
Robert J. Terry Anatomical Collection
>1700 (1910-1967)
Frye Standard (1923)
evidence: established and generally accepted
researcher as expert
what period was WWII used in play and where is the facitly located
consolidation and Hawaii
Mildred Trotter
Anatomist, forensic anthropologist
1948: CILHI Director
Founding member of the American Association of Physical Anthropologists (1930)
T. Dale Stewart
1924-1927/1931-1971 – Smithsonian
1954: Director of US Army ID Lab, Japan
Essentials of Forensic Anthropology (1979)
____ Award
American Academy of Forensic Sciences
Daubert v. Merrell Dow Pharmaceuticals (1993)
Judge as “Gatekeeper”
Theory or technique:
Tested
Peer-reviewed
Known error rate
Standards for use
Generally accepted
2009 National Academy of Science Report
Strengthening Forensic Science in the United States: A Path Forward
Scientific validation
Standardized practice
Quality control and oversight
Accreditation and certification
Education and training
Bias and subjectivity
coronal suture

sagittal suture

lambdoidal suture

supraorbital margin
supraorbital foramen or notch

frontal eminence or boss
temporal lines
:watermark(/images/watermark_only_413.png,0,0,0):watermark(/logos/logo_url_sm.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/learnable/superior-temporal-line/oZAnHhsdco9QFxJzkIdirQ_Superior_temporal_line.png)
glabella
:watermark(/images/watermark_only_413.png,0,0,0):watermark(/logos/logo_url_sm.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/learnable/glabella/TNAbds9X0N88aRM7bqCVg_Glabella_-_Frontal_bone_01.png)
zygomatic

zygomatic arch
:watermark(/images/watermark_only_413.png,0,0,0):watermark(/logos/logo_url_sm.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/learnable/temporal-process-of-zygomatic-bone/c6OQYtf0SXCAIbxZG3oxQ_Zygomatic_process.png)
nasal part and notch
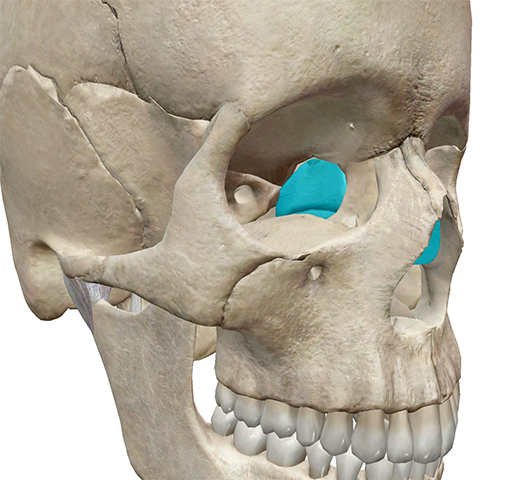
ethmoid
squamous suture

external acoustic meatus (eam)
:watermark(/images/watermark_only_413.png,0,0,0):watermark(/logos/logo_url_sm.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/learnable/meatus-acusticus-externus/fuIS9985iIRldd7imuNcTg_External_acoustic_meatus_01.png)
mastoid process
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/mastoid-process/ClIMCrIgcC9TIahlAyVdQA_i69qkAHvcUSvEuXXQsZVTQ_Mastoid_process_01.png)
nuchal crest
:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/logos/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/learnable/linea-nuchalis-suprema/uanIgjMmfxs9p7JdPEMfnA_Highest_nuchal_line_01.png)
external occipital protuberance
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/external-occipital-protuberance/kzbcXmIZUJ6UrwTnMdMA_LUw6Z4Y4Kui0RDN57lTgw_External_occipital_protuberance_01.jpg)
nasal aperture
:watermark(/images/watermark_only_413.png,0,0,0):watermark(/logos/logo_url_sm.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/learnable/anterior-nasal-aperture/DVLnsESy3GbydJbjaMyw_Apertura_piriformis_02.png)
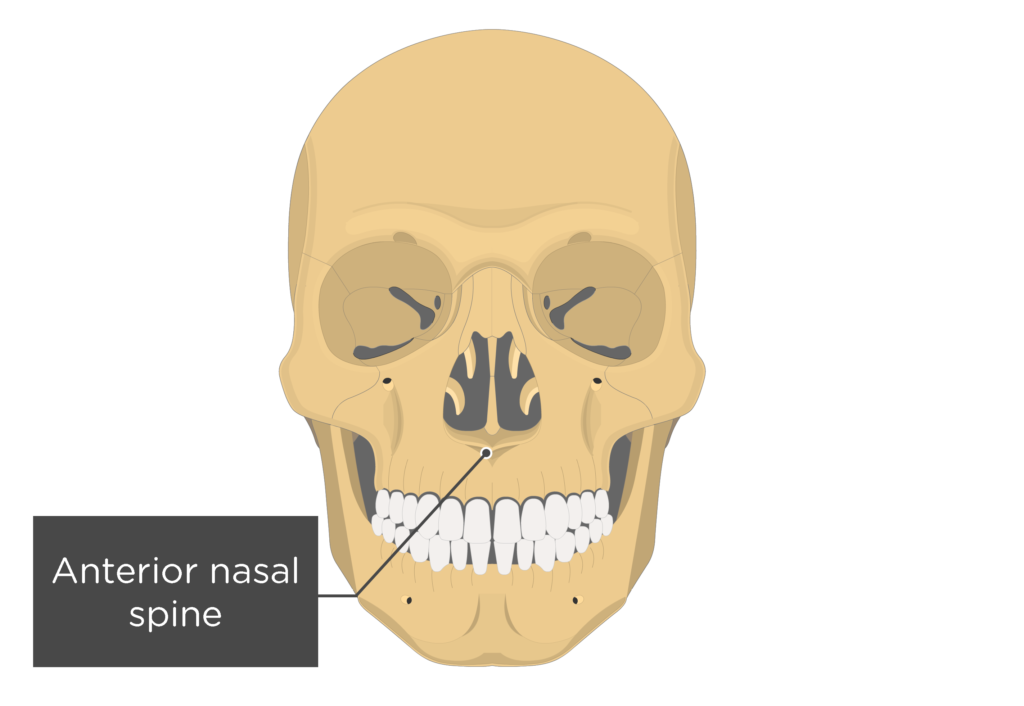
anterior nasal spine