AP Microeconomics Unit 1 & 2
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
normal goods
goods sensitive to purchasing power; direct relationship with income; as income increases, the demand for these goods increases; as income decreases, the demand for these goods decreases
inferior goods
goods sensitive to purchasing power; indirect relationship with income; as income increases, the demand for these goods decreases; as income decreases, the demand for these goods increases
demand
different quantities of goods that consumers are willing and able to buy at different prices
law of demand
there is an indirect relationship between price and quantity demanded
substitution effect
if the price goes up for a product, consumers will buy less of that product and more of another substitute product
substitutes
goods that are used in place of one another; direct relationship
complements
two goods that are bought and used together; inverse relationship
income effect
if the price goes down for a product, the purchasing power increases for consumers -- allowing them to purchase more
law of diminishing marginal utility
as you consume anything, the additional satisfaction you receive from each additional unit will eventually decrease
law of diminishing marginal utility and law of demand
the law of diminishing marginal utility causes the inverse relationship as consumers are willing to pay more for a unit that offers them the most benefit, while the amount they demand and are willing to pay for decreases as it does not offer as much utility
market demand
the demand of the entire population (add the market - adding the individual demands)
5 shifters of demand
1. Tastes and Preferences
2. Number of Consumers
3. Price of Related Goods
4. Income
5. Future Expectations (how will what happens in the future, impact demand right now)
law of supply
there is a direct relationship between price and quantity supplied
supply
the different quantities of a good that sellers are willing and able to sell (produce) at different prices
5 shifters of supply
1. Prices/Availability of Inputs (Resources)
2. Number of Sellers
3. Technology
4. Government Actions (Taxes, Subsidies)
5. Expectations of Future Profit
why doesn't price shift the curve
changes in price only cause movement along the curve because demand and supply addresses the quantities demanded or supplied at different price points
equilibrium
where supply and demand intersect, producing the optimum price and quantity
shortage
when quantity demanded is greater than quantity supplied, resulting in higher prices
surplus
when quantity supplied is greater than quantity demanded, resulting in lower prices
double shift rule
if two curves shift at the same time, either price or quantity will be intermediate
price above equilibrium
surplus occurs; price floor forms
price below equilibirum
shortage occurs, price ceiling forms
consumer surplus
the difference between what a consumer is willing to pay and what they actually pay
producer surplus
the difference between what a producer receives and what they were willing to sell for
elasticity of demand
describes how sensitive quantity is to a change in price
elasticity of supply
describes how sensitive quantity supplied is to a change in price
total revenue test
uses elasticity to show how changes in price will affect total revenue
inelastic demand
quantity is insensitive to a change in price; people will continue to buy the good even as price changes
inelastic goods
few substitutes, small portion of income, necessities
elastic demand
quantity is sensitive to a change in price; people will buy more or less amounts of the good as the price changes
elastic goods
many substitues, luxury items, large portions of income
perfect inelastic
coefficient = 0; you need a product and will pay anything for it, ex. insulin
relatively inelastic
coefficient = <1; steep curve; direct relationship witht total revenue
unit elastic
coefficient = 1; no changes in total revenue in response to changes in price
relatively elastic
coefficient = >1; indirect relationship with total revenue
perfectly elastic
coefficient = ∞
cross price elasticity of demand
shows how sensitive a product is to a change in a price of another good; shows if two goods are substitutes or complements
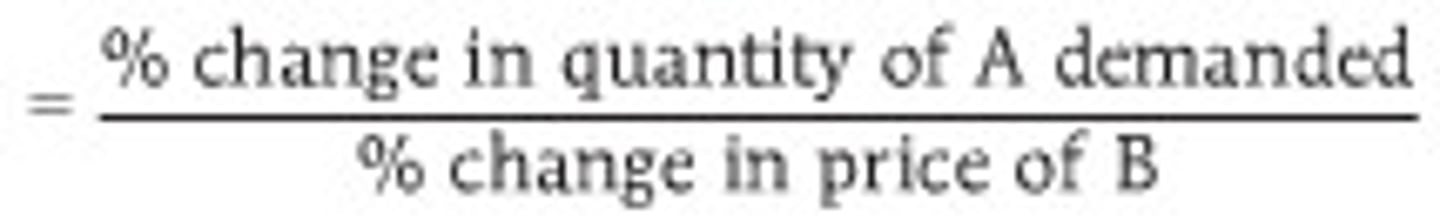
income elasticity of demand
shows how sensitive a product is to a change in income; shows if goods are normal or inferior
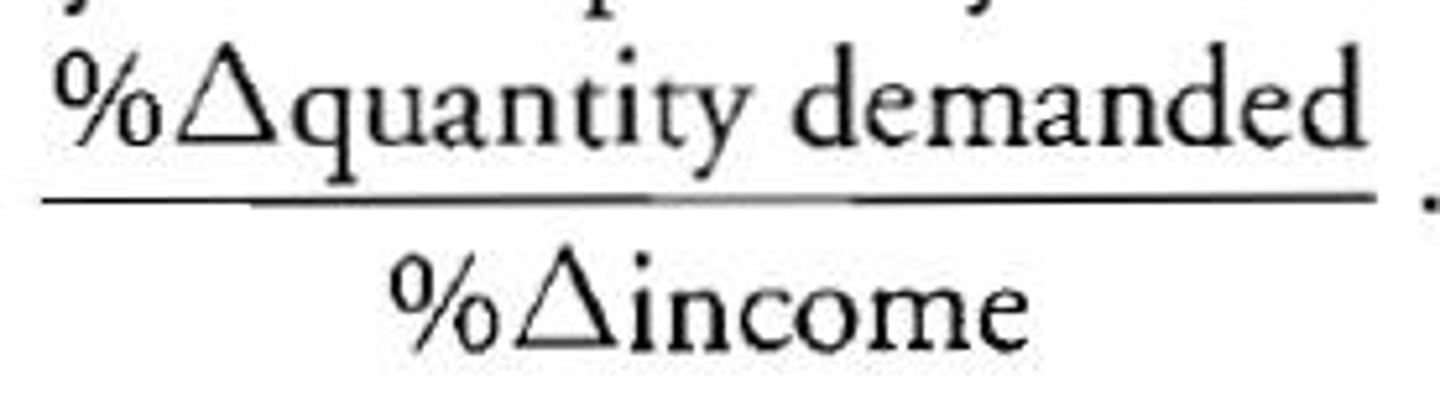
price elasticity of supply
shows how sensitive producers are to a change in price; alternative to total revenue test
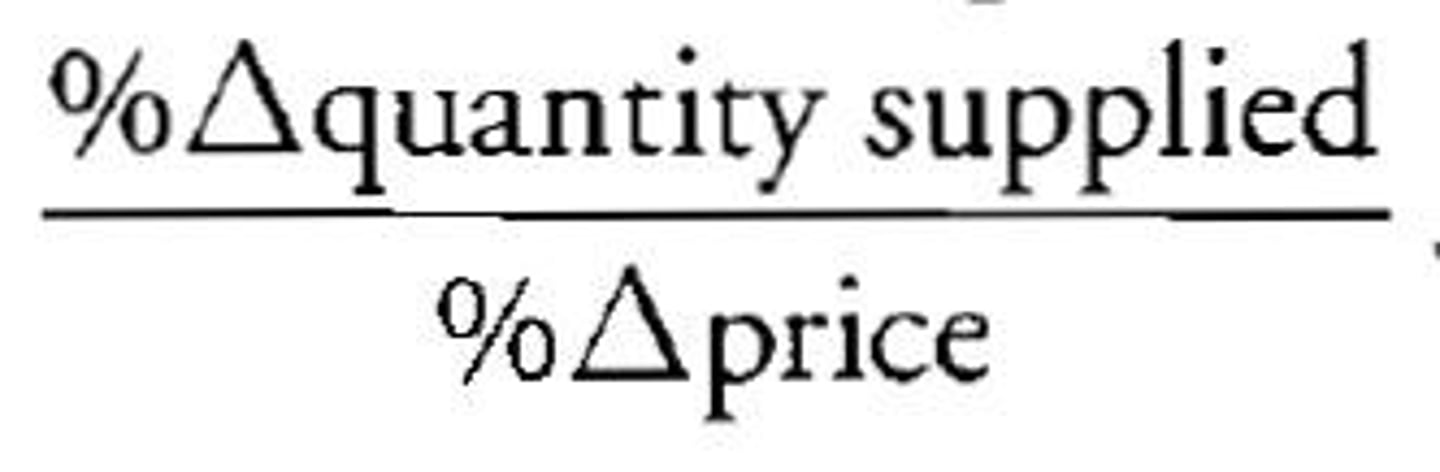
price ceiling
the maximum legal price a seller can charge for a product; must be below equilibrium to be effective; result in black markets, caused by shortage
price floor
the minimum legal price a seller can sell a product; must be above equilibrium to be effective; result in surplus
deadweight loss
the lost consumer surplus and producer surplus caused by inefficiency
world price
countries can buy products at their own domestic price or they can buy the products at a cheaper world price
tariff
a tax on imports that increase the world price
quota
a limit on the number of imports
purpose of tarriffs and quotas
to protect domestic producers from a cheaper world price and to prevent domestic unemployment; if you have a shortage you will import goods
excise tax
a per unit tax on producers that encourages them not to produce goods the government deems "bad"; shift supply upwards
tax incidence - perfectly inelastic
tax completely on consumers
tax incidence - relatively inelastic
tax mostly on consumers
tax incidence - unit elastic
tax shared by producers and consumers
tax incidence - relatively elastic
tax mostly on producers
tax incidence - perfectly elastic
tax completely on producers
Economics
the science of scarcity/choices
Microeconomics
study of small economic units such as firms, individuals, and industries
Macroeconomics
study of large economy as a whole or economic aggregates
Theoretical Economics
Economics use the scientific method to make generalizations and abstractions to develop theories
Positive Economics
this type of economics is based on facts; avoids value judgments (what is)
Normative Economics
this type of economics includes value judgments (what ought to be)
Marginal Analysis
making decisions based on additional benefit vs. additional cost; more commonly used than, "all or nothing method."
Utility
Satisfaction
Marginal
Additional
Allocate
Distribute
Shortages
occur when producers will not or cannot offer goods or services at current prices (temporary)
Price
Amount buyer/consumer pays
Cost
Amount seller pays to produce a good
Investment
money spent by BUSINESSES to improve their production
Goods
physical objects that satisfy needs and wants
Consumer Goods
created for direct consumption
Capital Goods
created for indirect consumption
Services
actions/activities that one person performs for another
Accountants
look at only EXPLICIT costs (out of pocket costs)
Economists
look at EXPLICIT and IMPLICIT costs
Implicit Costs
opportunity costs such as forgone time and forgone outcome
Physical Capital
tools, tractors, machinery, buildings
Human Capital
college degrees, vocational training (skills and knowledge gained)
Prediction Possibilities Graph
A model that shows alternative ways that an economy can use its scarce resources; graphically demonstrates scarcity, trade-offs, opportunity costs, and efficiency
Constant Opportunity Cost
Resources are easily adaptable for producing either good
Law of Increasing Opportunity Cost
As you produce more of any good, the opportunity cost will increase
True
True or False: Resources are NOT easily adaptable to producing both goods.
Productive Efficiency
products are being produced in least costly way; any point on production possibilities curve
Allocative Efficiency
products being produced are ones most desired by society; optimal point on PPC depends on desires of society
Absolute Advantage
producer that co-produces most output OR requires least amount of inputs (resources)
Comparative Advantage
producer with lowest opportunity cost
Makes product cheater and Increases quality of product
What does specialization do for a product?