Chapter 4: Carbon and the Molecular Diversity of Life
1/25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Organic chemistry
The study of compounds that contain carbon, regardless of origin
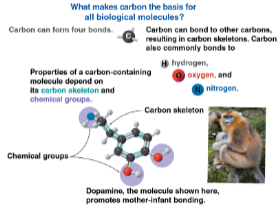
Properties of carbon
Can form four bonds, allowing it to make a wide variety of moleucles
This makes it responsible for the planet’s variety of organisms
Major elements of life
The elements:
Carbon (C)
Hydrogen (H)
Oxygen (O)
Nitrogen (N)
Sulfur (S)
Phosphorus (P)
Distributions are quite uniform from one organism to the other
Organic compounds
Compounds that contain carbon; these can range from small to colossal molecules
Electron configuration
How an atom’s electrons are arranged; the key to atomic bond types and numbers as part of their characteristics
Carbon
An atom with four valence electrons that can form four covalent bonds
Molecules with multiple of these have a tetrahedral shape when joined to four other atoms
Two of these together in a double bond allow other atoms to stay in the same plane
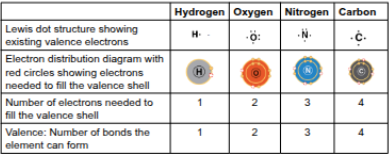
Valence
The number of unpaired electrons in the valence shell of an atom, determining the number of covalent bonds it can form
Carbon bonding partners
Most frequent are:
Hydrogen
Oxygen
Nitrogen
Carbon molecule examples
Carbon dioxide: CO2
Urea: CO(NH2)2
Estradiol and Testosterone
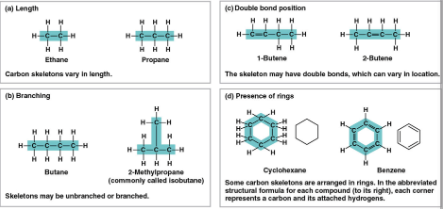
Carbon chains
The skeletons of most organic molecules that vary in length, shape, double bond position, branches, and ring presence
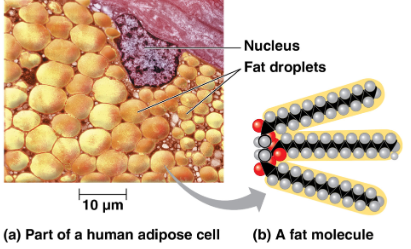
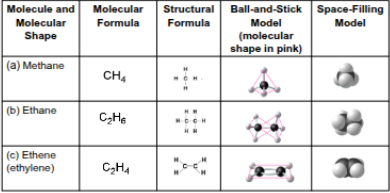
Hydrocarbons
Organic molecules consisting of only carbon and hydrogen
Many organic molecules, such as fats, have these as they can release a large amount of energy in some reactions
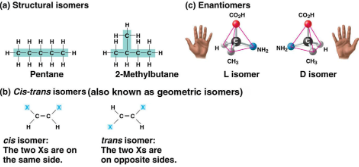
Isomers
Compounds with the same molecular formula (ratio) but different structures (arrangements) and properties, includes:
Structural: Different covalent bonds and arrangements
Cis-trans: Differing spatial arrangements, same covalent bonds
Enantiomers: Mirror images
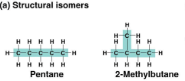
Structural isomers
Isomers with different covalent bonds and arrangements
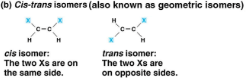
Cis-trans isomers
Isomers with the same covalent bonds but differing spatial arragnements
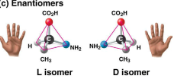
Enantiomers
Isomers that are mirror images of each other
Important in the pharmaceutical industry, as each pair may have different effects or not be effective at all, demonstrating molecular sensitivity
Ibuprofen’s and albuterol’s versions are ineffective
Organic molecule properties
Depends on the carbon skeleton and chemical groups attached to it, giving it unique properties
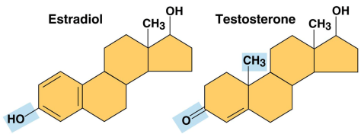
Estradiol and testosterone
Steroids with a common carbon skeleton in the form of four fused rings, differing only in the chemical groups attached to the skeleton’s rings
Functional groups
The components of organic molecules most commonly involved in chemical reactions and molecular properties
Includes groups of:
Hydroxyl
Carbonyl
Carboxyl
Amino
Sulfhydryl
Phosphate
Methyl

Hydroxyl
Functional group with the formula (—OH) or (HO—), also known as alcohol and included in ethanol

Carbonyl
Functional group with the formula (>C=O), also known as ketone or aldehyde and included in acetone or propanal

Carboxyl
Functional group with the formula (—COOH), also known as carboxylic acid or organic acid and included in acetic acid as well as its ionized form

Amino
Functional group with the formula (—NH2), also known as amine and included in glycine as well as its ionized form

Sulfhydryl
Functional group with the formula (—SH) or (HS—), also known as thiol and included in cysteine

Phosphate
Funcational group with the formula (—OPO32-), also known as organic phosphate and included in glycerol phosphate

Methyl
Functional group with the formula (—CH3), also known as methylated compound and included in 5-Methylcytosine
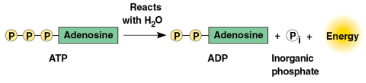
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
An important organic phosphate, consisting of an organic molecule called adenosine attached to a string of three phosphate groups
Reacts with water easily to release energy for cell utilization