1.5 Systems software
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
Operating systems
An operating system is software that helps to manage the resources of a computer system and provide the interface between the user and the computer's hardware. There are 5 main functions of an operating system;
Providing a user interface
Memory management and multitasking
Peripheral management and drivers
User management
File management
Providing a user interface
This allows users to interact with the computer system. The way in which a user can navigate a computer system is called human-computer interaction (HCI).
Memory management and multitasking
All programs must be temporarily stored in RAM for the CPU to process them. The OS transfers programs in and out of memory from the hard drive (or virtual memory) when processing is required. Programs are removed from RAM when closed to free up space for other tasks. The OS can only perform one process at a time, but through memory management it can appear that more than one process is being executed, this is called multitasking.
Peripheral management and drivers
A peripheral is an external device connected to a computer system to input or output data. Data is transferred between external devices and the processor, this process needs to be managed by the OS. A device driver is a program that provides an interface for the OS to interact and communicate with an external device. Drivers are hardware dependent and OS-specific. The driver translates the OS' instructions into a format the specific hardware can understand. Because the CPU and the peripheral will process data at different speeds, a buffer is typically used to temporarily store data until it can be processed.
User management
The OS allows users to create, manage and delete individual accounts. User accounts can be granted different access rights such as an administrator or guest. The OS will manage security settings such as allowing passwords to be reset and can also be used to monitor login activity.
File management
The OS creates and maintains a logical management system to organise files and directories (folders). File management allows files to be named, renamed, opened, copied, moved, saved, searched for, sorted allocated to folders, deleted, and restore deleted ones. It also allows users to set access rights for specific files and to view file properties.
What is the most common type of UI
The most common type of UI is a Graphical User Interface (GUI).
Command-Line Interface (CLI)
This type of interface is entirely text-based and requires users to interact with the system by typing commands. This is a complicated process and mistakes could easily accidentally delete data. There are many commands to learn so only experts who have been trained to learn this interface will be able to efficiently make use of it.
This is used with smartphones and tablets. A human interacts with the device by pressing on a touchscreen, making it very intuitive and suitable for most users without training. Touch-sensitive interfaces may not work with dirty or wet fingers and it will take longer to write text compared to using a keyboard.
Touch-Sensitive Interface (TSI)
Menu-Driven Interface (MDI)
This displays data in a series of linked menus. Examples include cash machines (ATMs) and old iPods. This type of interface is generally user friendly and easy to use as commands do not need to be memorised. However it can be annoying to find specific data through a large number of menus without a search feature.
Utility software
Utility software are dedicated programs used for the maintenance and organisation of a computer system, this is known as housekeeping. Utilities are required to run additional tasks not performed by the operating system. Anti-malware (such as anti-virus or anti-spyware) firewalls, and encryption software are examples of utilities.
Defragmentation
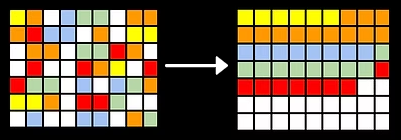
Over time files stored on a hard disk drive may become fragmented, this is when the file is split into parts that are saved in different storage locations. Fragmentation occurs when there is limited contiguous space in which to store a file. This may happen as data is stored and then later deleted on the hard drive. New files are created which may be bigger than the spaces left by the deleted files. The new files are then split up. Fragmentation increases access time, files that are fragmented take longer to load and read because of the distance between the fragments of the file. Defragmentation works by collecting together empty spaces on the hard disk drive and file fragments are moved to be stored together. This means that fewer disc accesses are needed (requiring less physical movement) as file fragments can be read consecutively. A defragmented file takes less time to read and access because the data is stored contiguously. The read/write head of the hard drive does not need to move as far to read the next piece of data because it is in the adjacent memory location, saving time. It also quicker to save new files because there is more free space together so it does not need to split the file and can store the data contiguously.
Data compression
To compress a file means to make its size smaller. Benefits of compression include:
Files take up less storage space (so more files can be stored).
Files can be transferred quicker (because they are smaller).
Files can be read from or written to quicker.
There are two methods that are used to compress files: Lossy and Lossless.
Lossy compression uses an algorithm (set of instructions) to analyse a file and remove data that cannot be heard or seen by humans. For example, a lossy algorithm would analyse the sound waves of an audio file and remove any frequencies which humans cannot hear. This process reduces the size of the file. Further lossy compression will remove data that humans can see/hear. Lossy compression removes the data permanently, so the file can never return to its original form. Lossy compression is often used with images, audio and video to reduce the file size, for example to send over the internet.
Lossless compression reduces the size of a file without permanently removing any data. Because of this, the file is returned to its original form when decompressed, so no quality is lost. A file that is compressed with a lossless algorithm is usually larger than a file compressed with a lossy algorithm because no data has been permanently removed. Lossless compression is used with files that would not work if data was removed, for example executable files (e.g. programs and games) or word documents.
Lossy and Lossless compression do not just refer to images, audio files can also be compressed using these.
Encryption
Encryption utilities are used to encrypt or decrypt files or folders held on a computer, transmitted across a network or when they are transferred to external devices such as a USB key.