QUIZ 3 BIO80
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
Stomata
an opening that can open or close depending on environmental conditions and allows CO2 to enter and O2 to exit
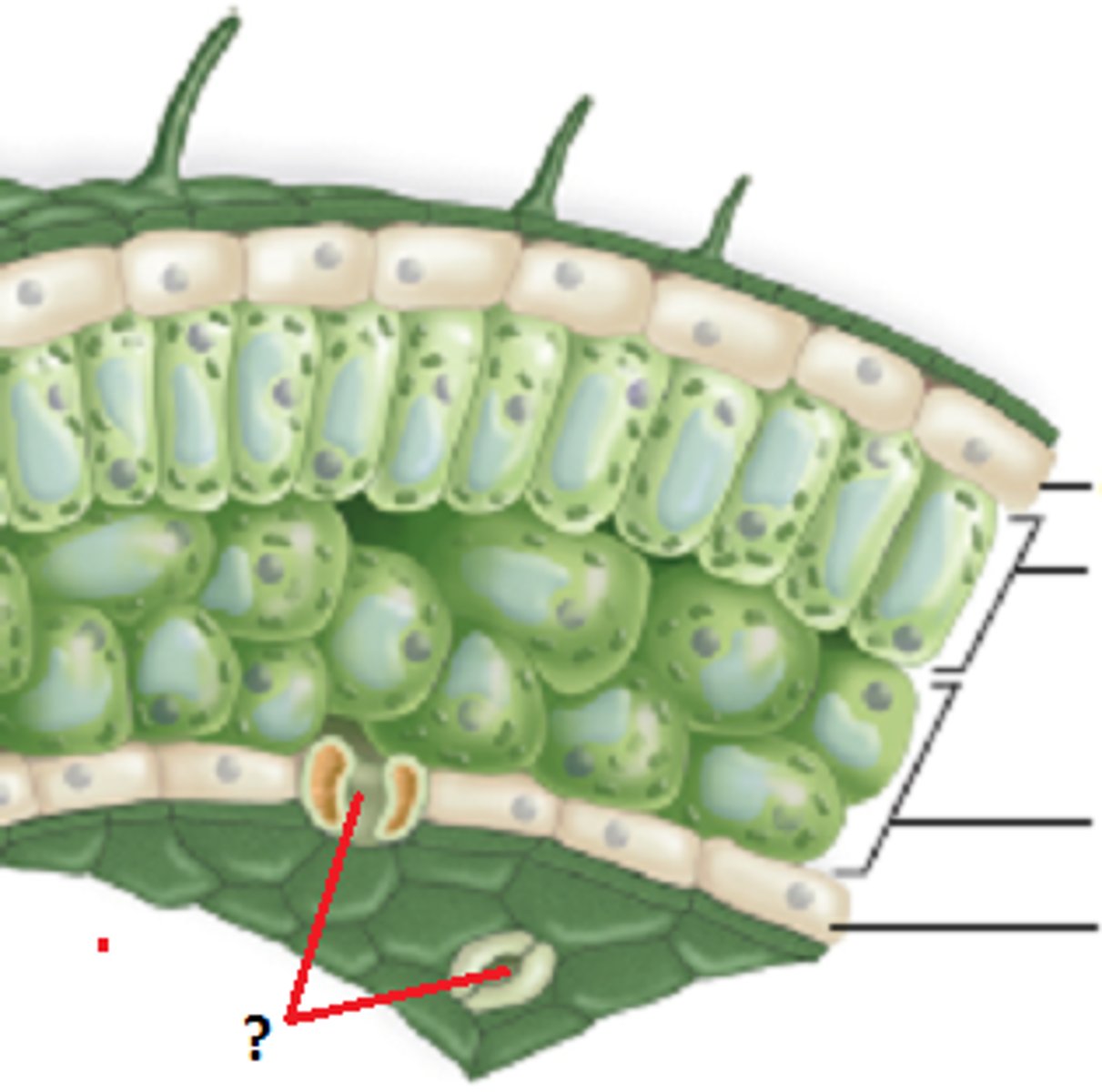
Guard Cells
control the opening and closing of stomata to help the cell not lose too much water
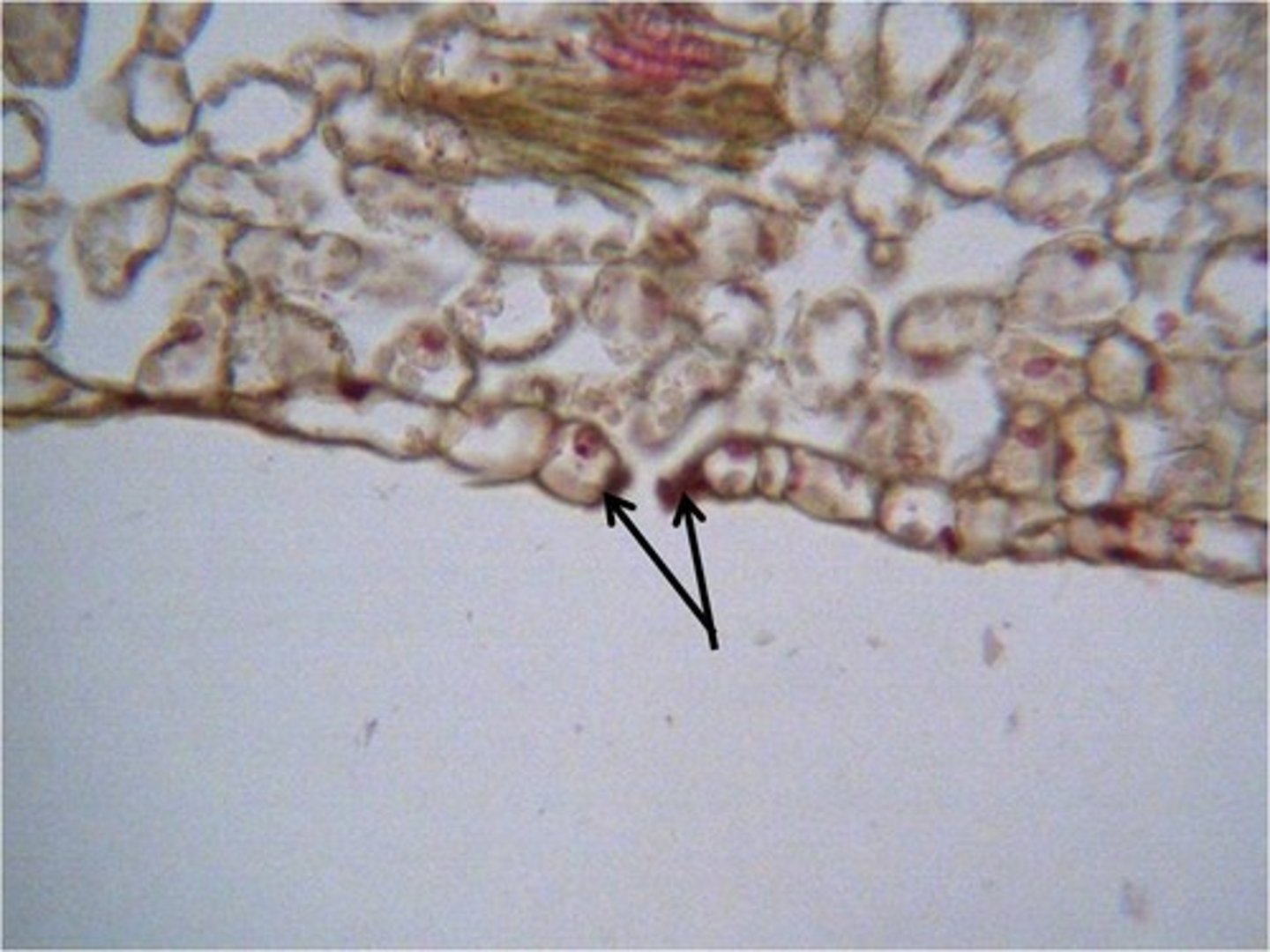
Root Hairs
take in water and minerals
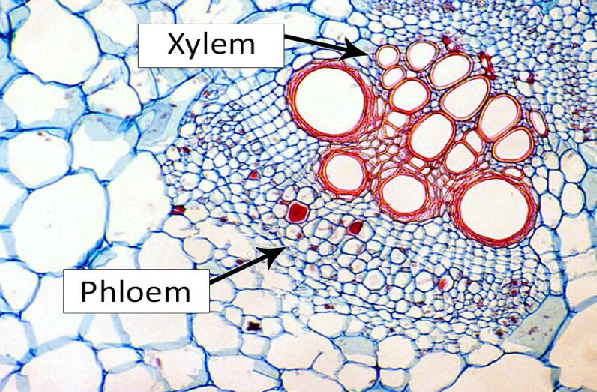
Xylem
transports water, minerals, and hormones from the root to the leaves and is composed of tracheids
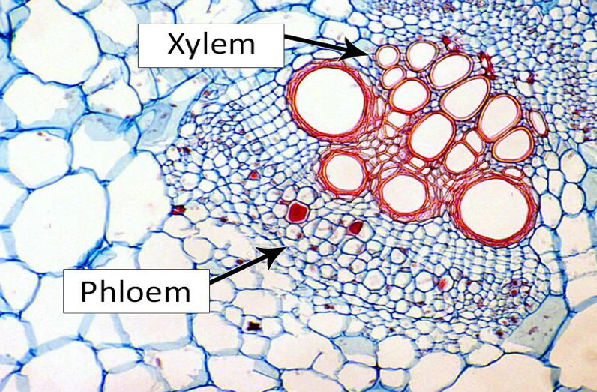
Phloem
transports water, sugar, and other molecules up and down and side to side and is composed of sieve tubes
Bark
protect the tree, insulate, fend off predators
Leaves
to carry out photosynthesis and facilitate the exchange of gasses
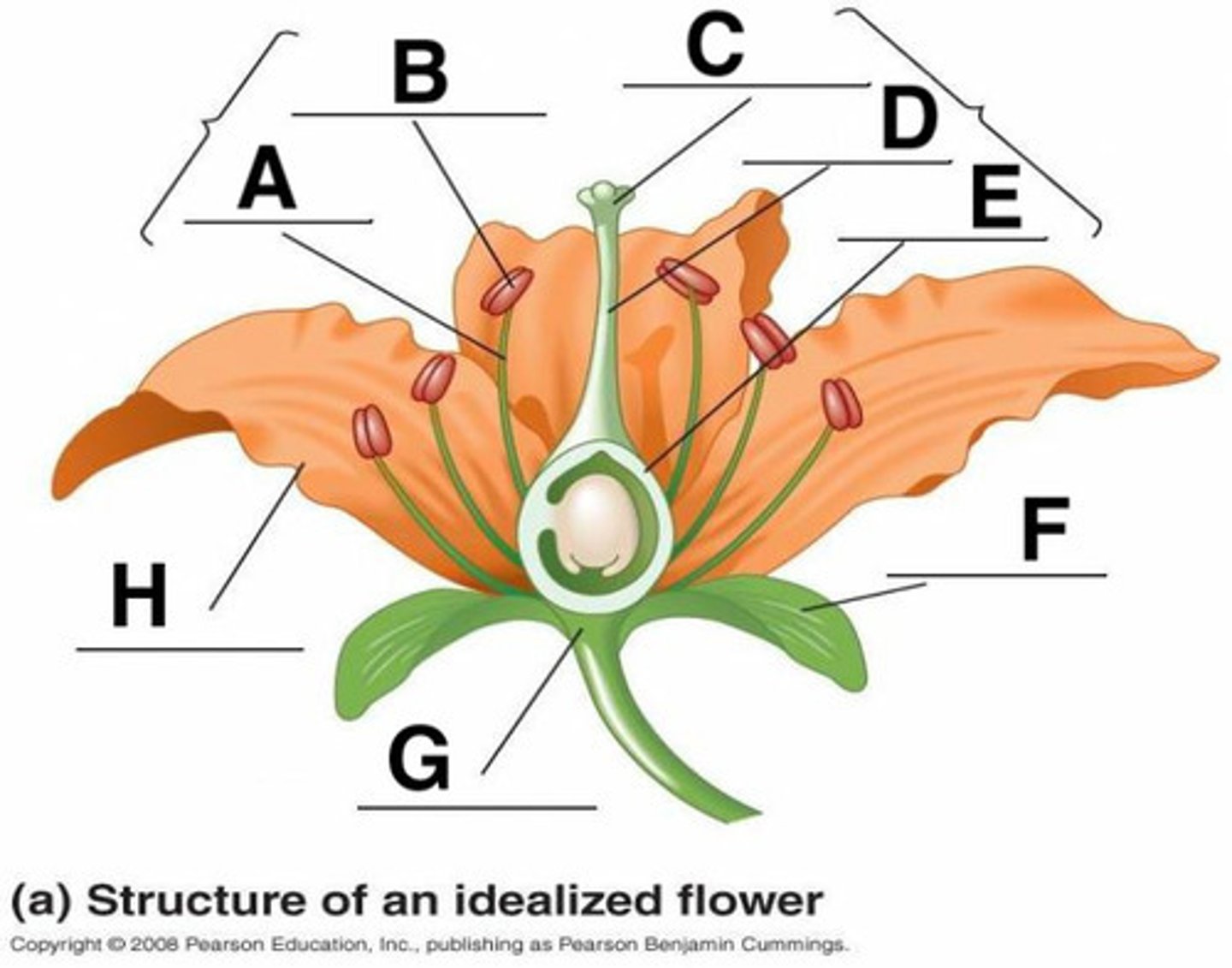
Anther
B
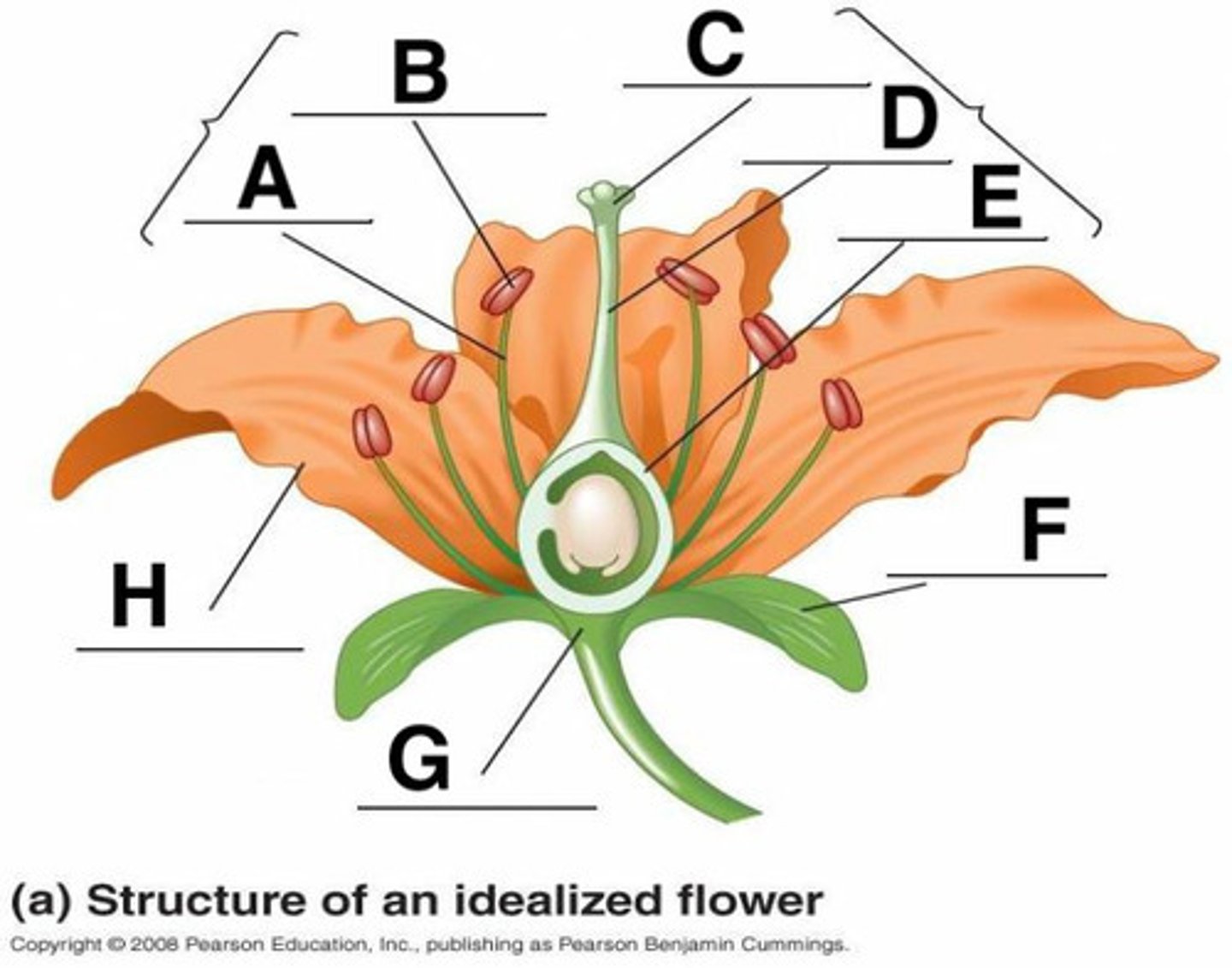
Calyx (sepals combined)
F
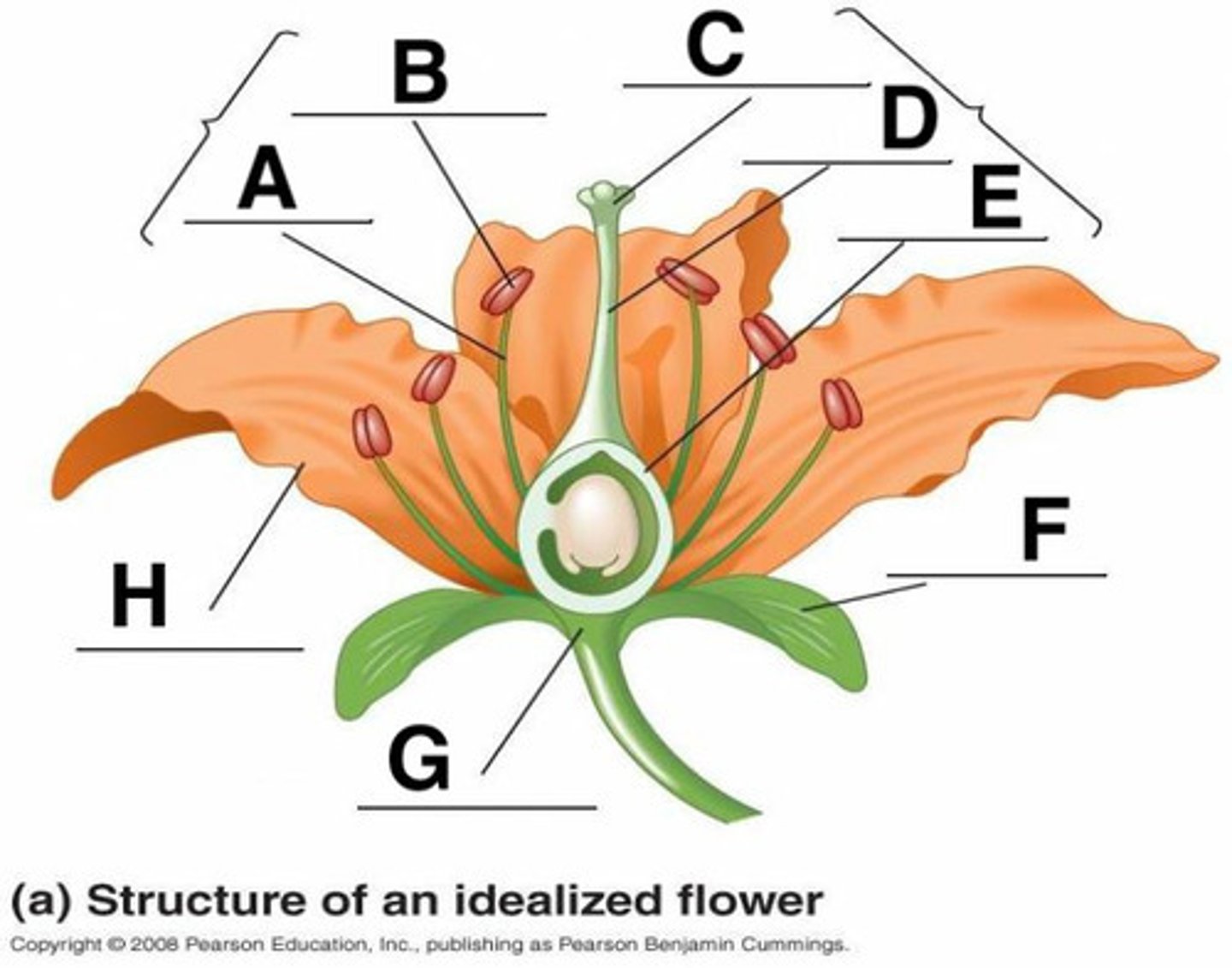
Corolla (petals)
H
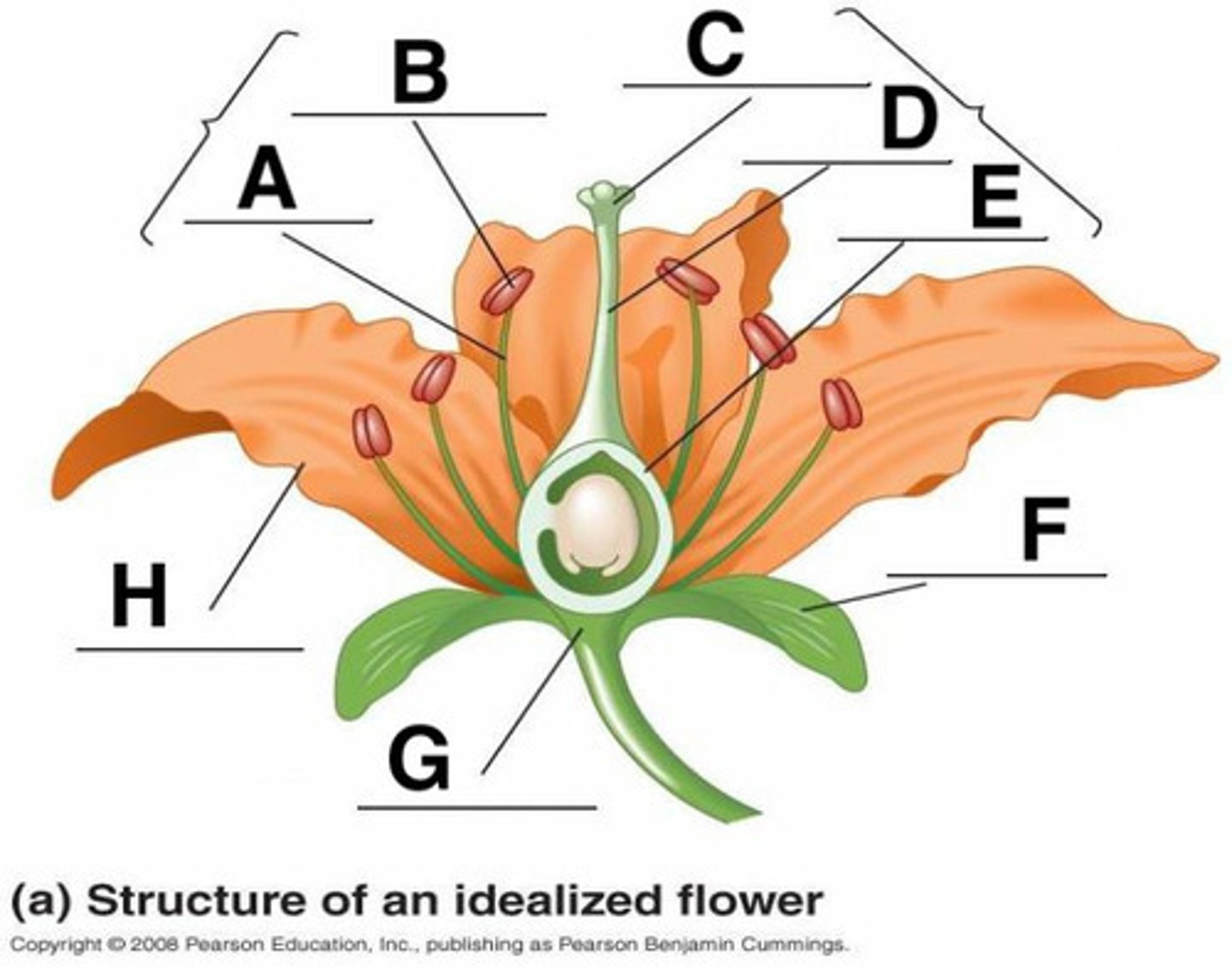
Filament
A
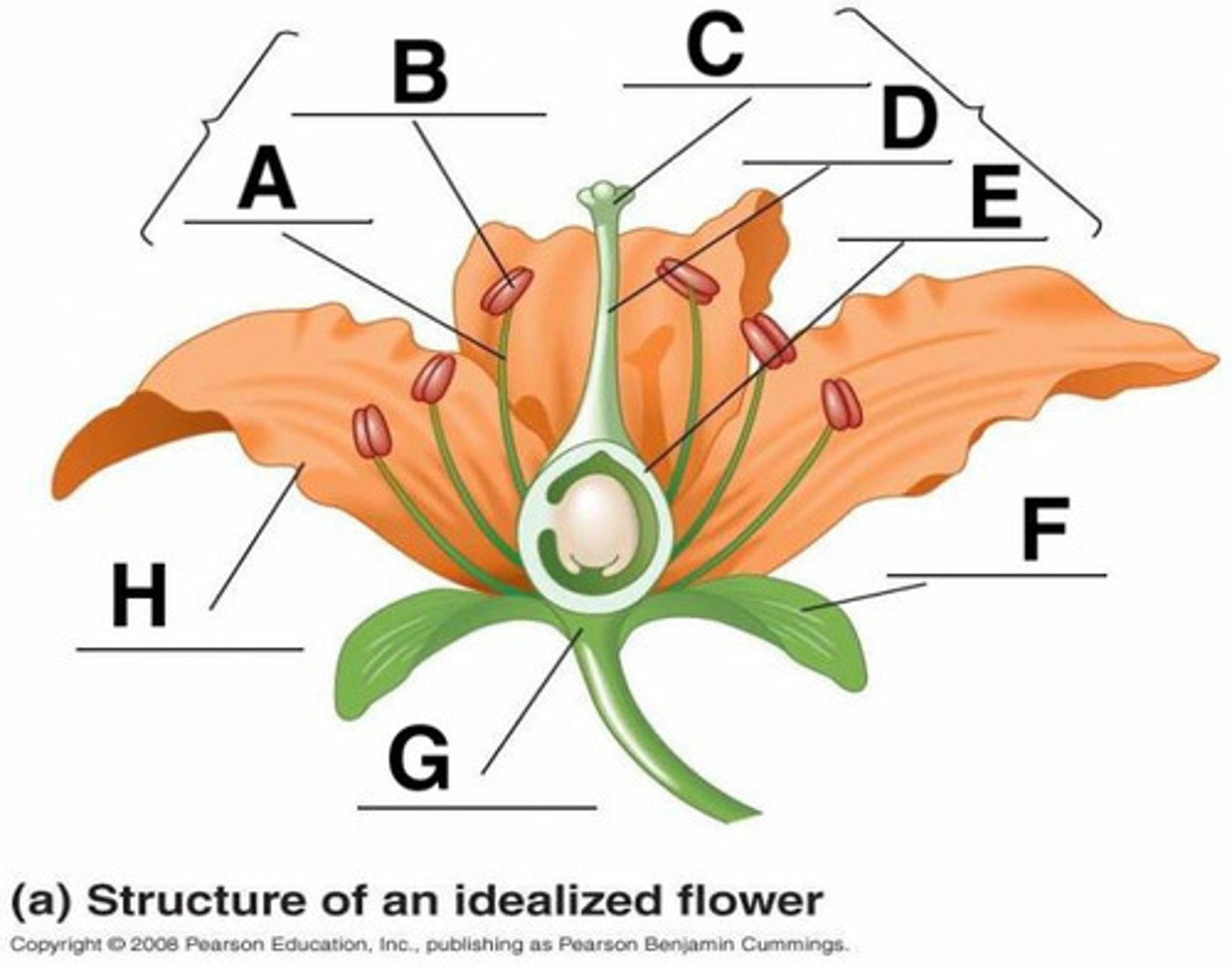
Ovary
3
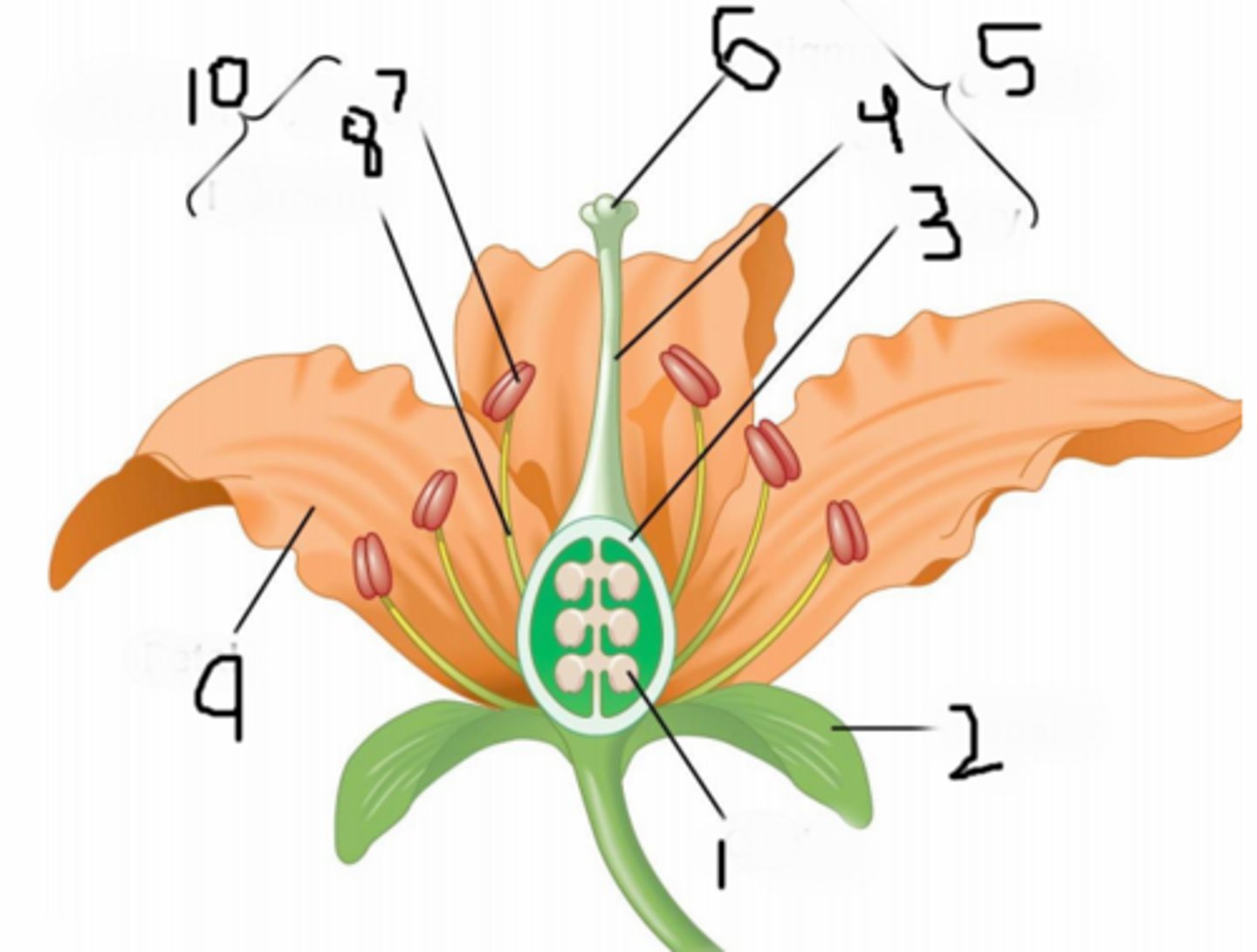
Pedicel
12
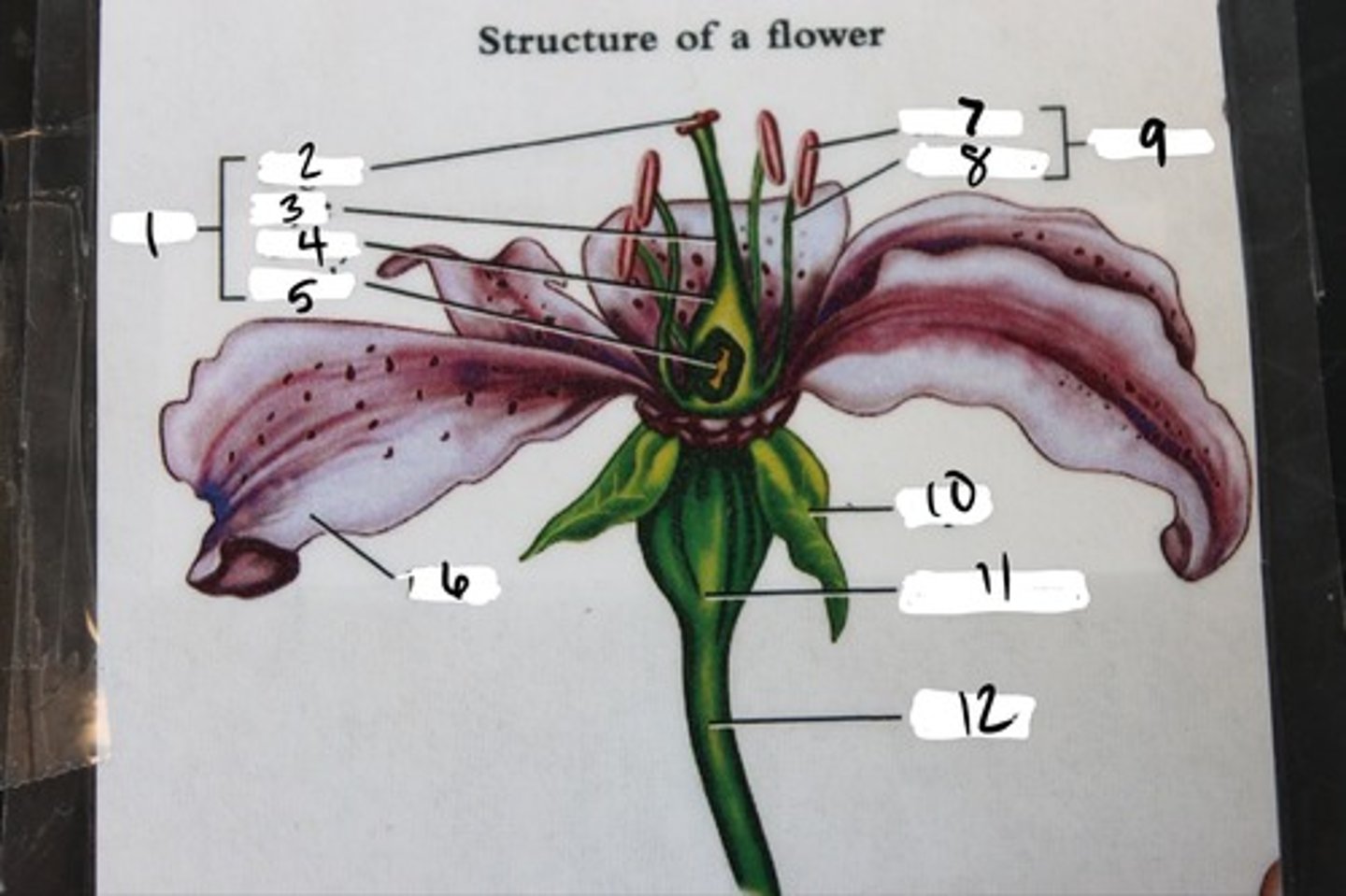
Pistil (carpal)
stigma + style + ovary

Receptacle
G
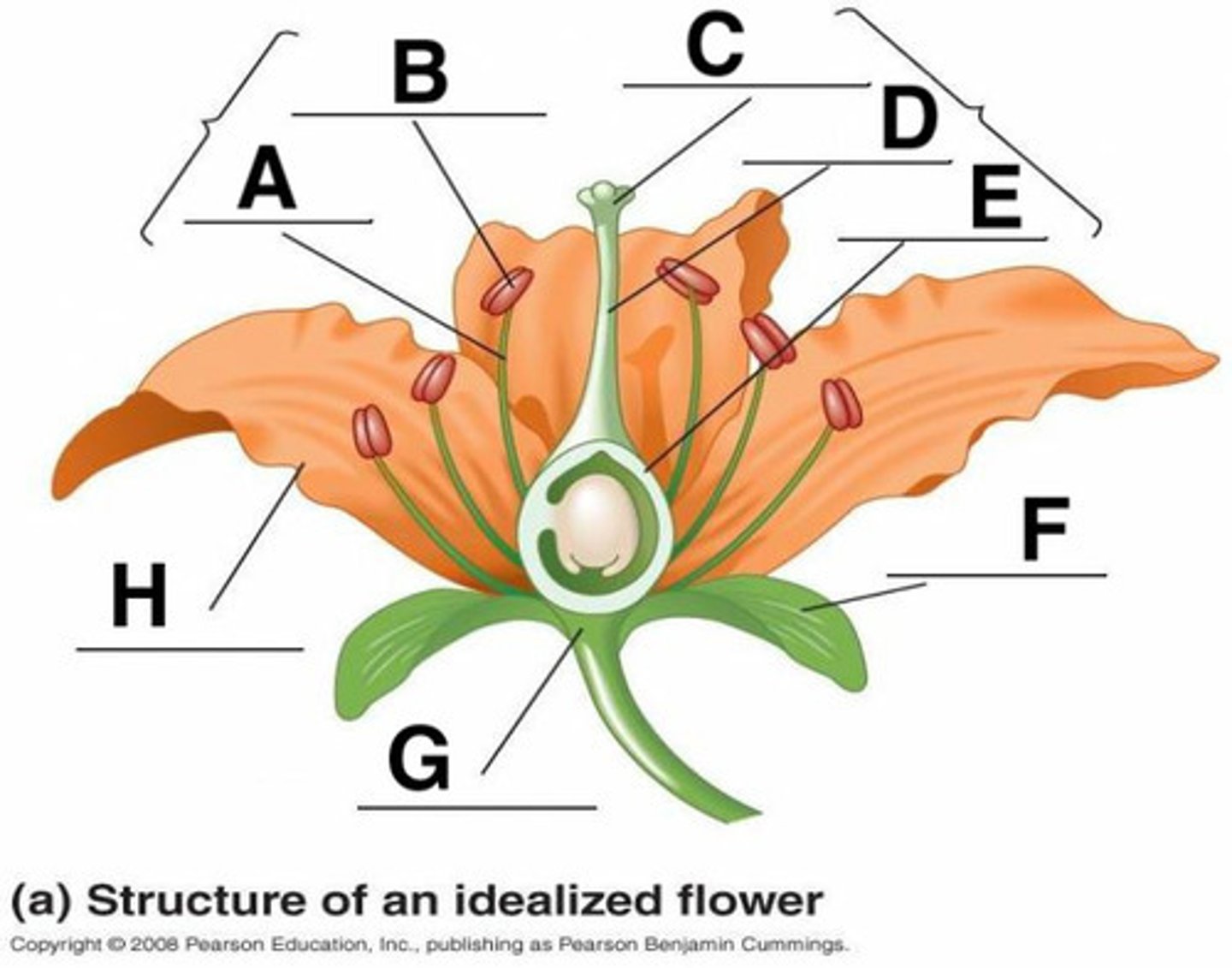
Stigma
C
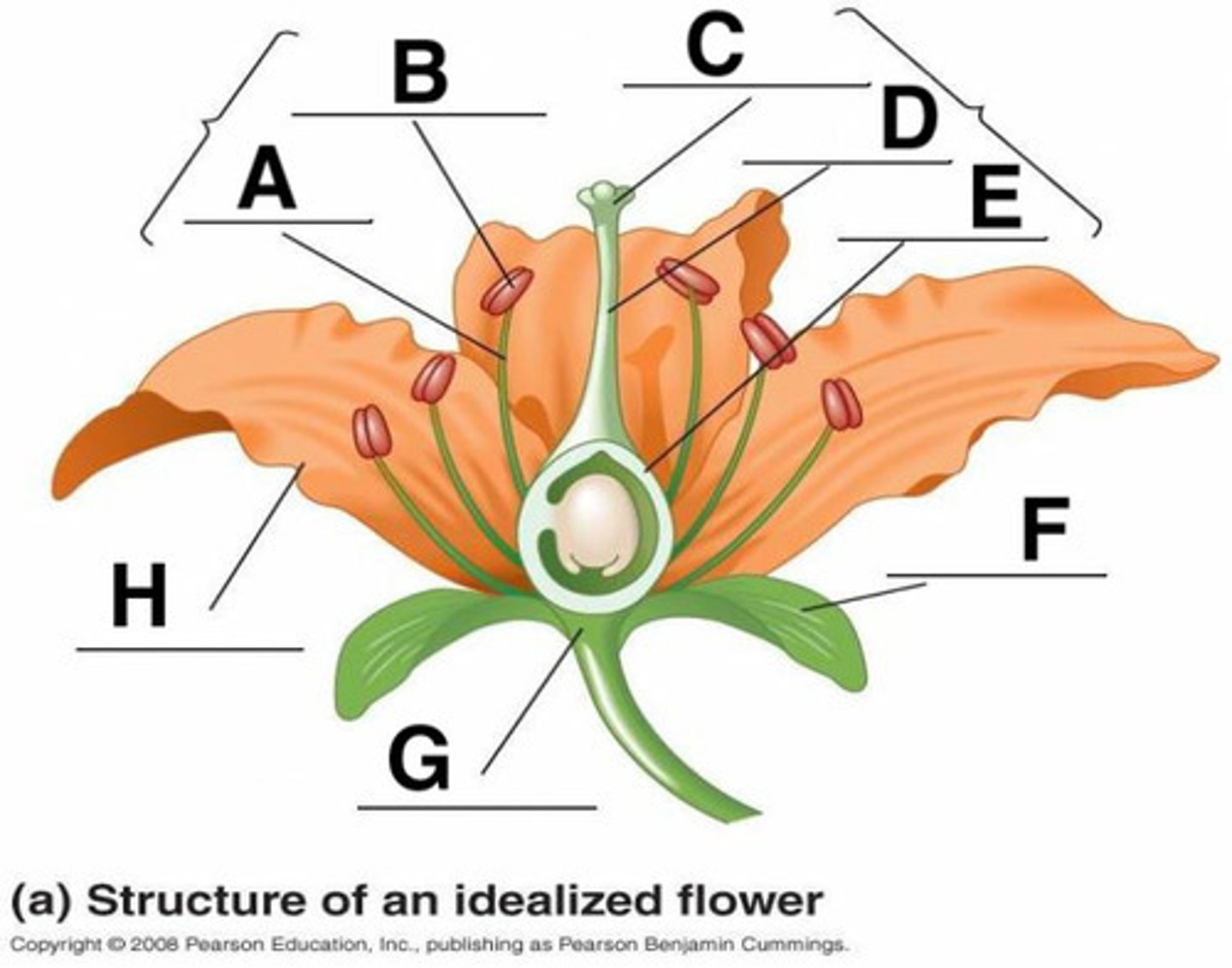
Style
D
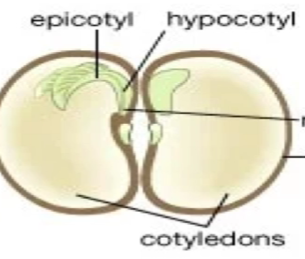
Monocots
One cotyledon, parallel venation, fibrous roots, multiples of 3
Dicots
Two cotyledon, netlike venation, taproot, multiples of 4 or 5
Basidiomycetes (fungi)
have gill-like structures where 4 spores are produced

Ascomycetes (sac fungi)
have cup-like structures that produce 8 spores

Asci
A; sac-shaped cells/sporangium containing ascospores - haploid sexual spores produced by meiosis; terminal hyphae
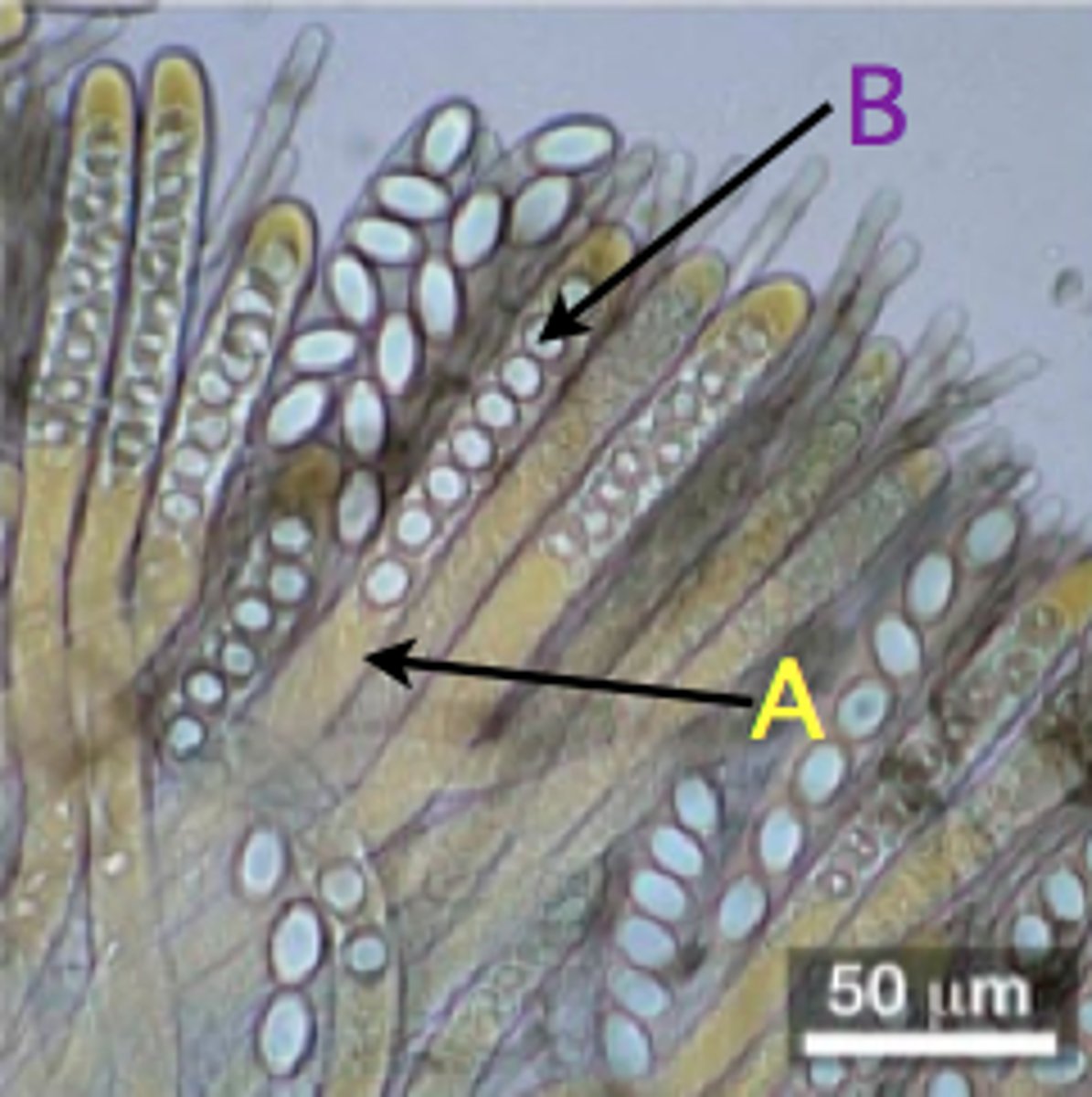
Basidia
club-shaped cells on gills that produce haploid sexual basidiospores in basidiomycetes; found along of gills of basidiocarp
Gills
structure under mushroom caps that contain basidia, where spores are produced
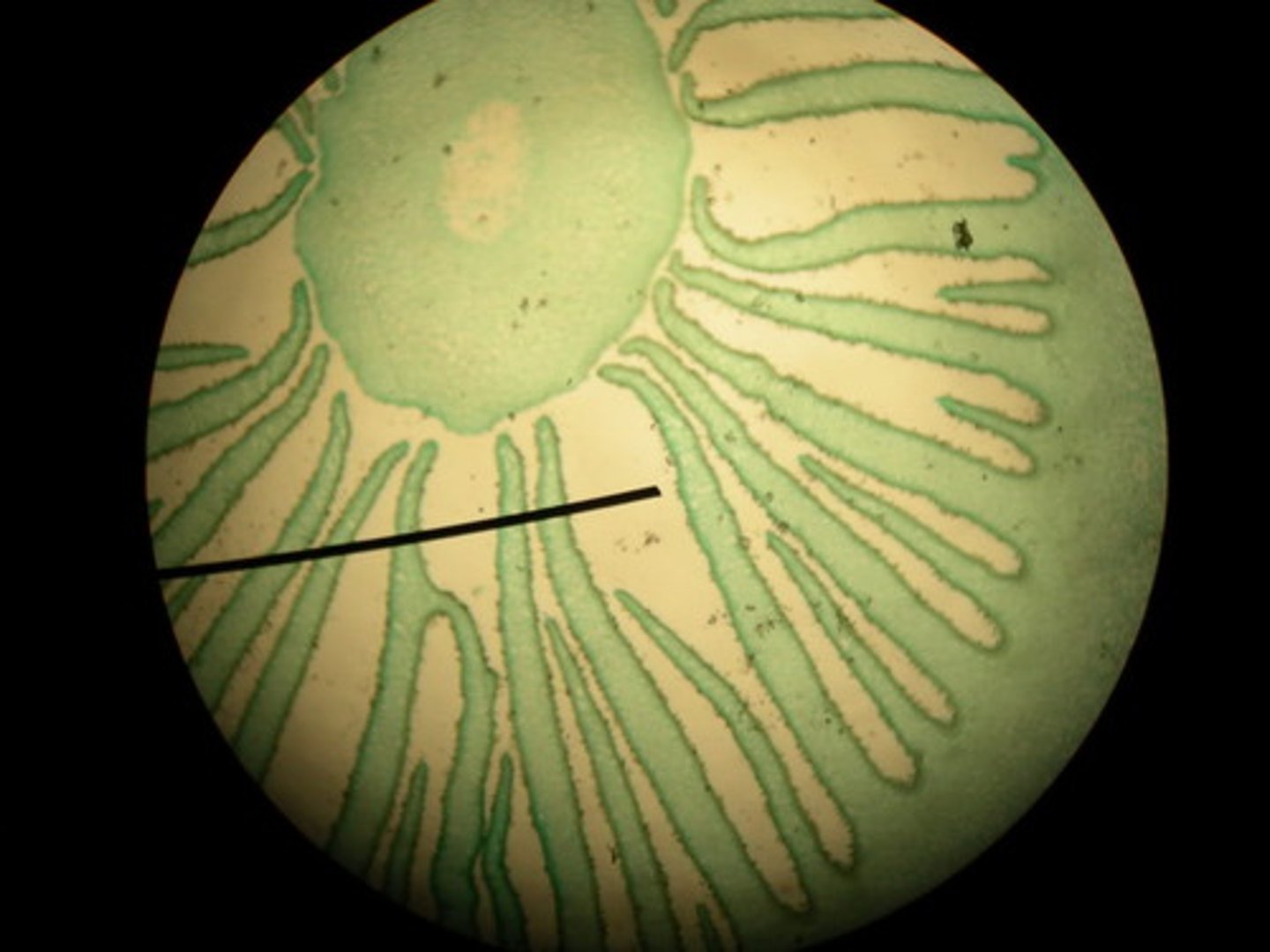
Hyphae
long branches of fungal cells; release enzymes into soil or host organism or remains of organisms to break down organic matter; typically have 2 nuclei per cell, a condition known as being dikaryotic
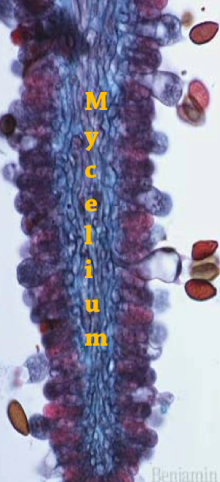
Mycelia
interconnected hyphae and produces myocarp and maximizes surface area
Thallus
body of fungus
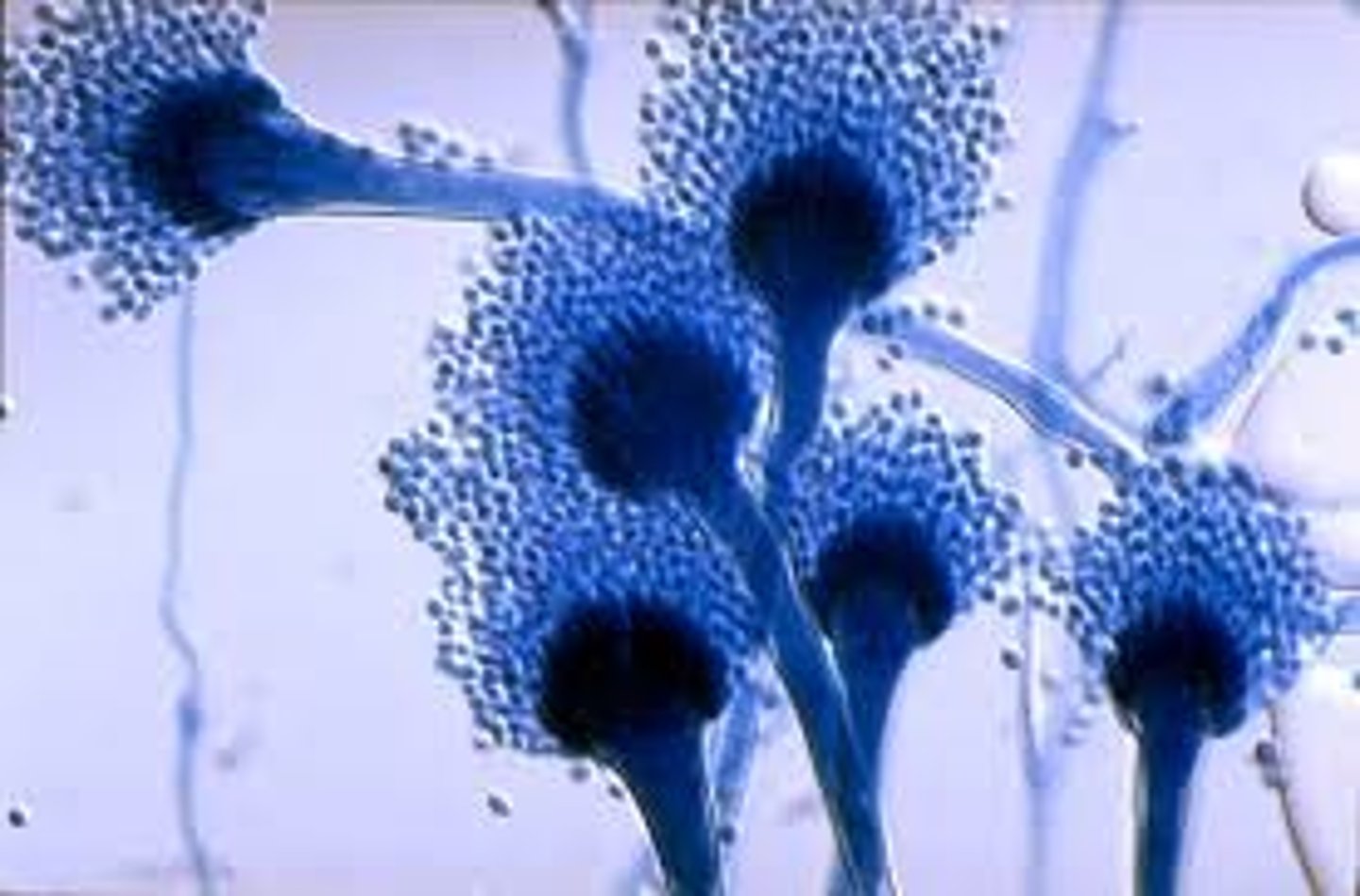
Conidiophores
produces conidia and is specialized hyphae
Asexual Reproduction in Fungi
fragmentation, budding, producing spores
Sexual Reproduction in Fungi
Plasmogamy, karyogamy, meiosis
Mutualism between plants and fungus
mycorrhiza
Mycorrhiza
fungal species that have mutualistic associations with plants
Endomycorrhizal fungi
go directly into the plant cells
Ectomycorrhizal fungi
form mantles around plant roots and sink their cells between extracellar spaces of plant
Crustose

Foliose

Fruticose

Lichen is made up by
cyanobacteria and algae
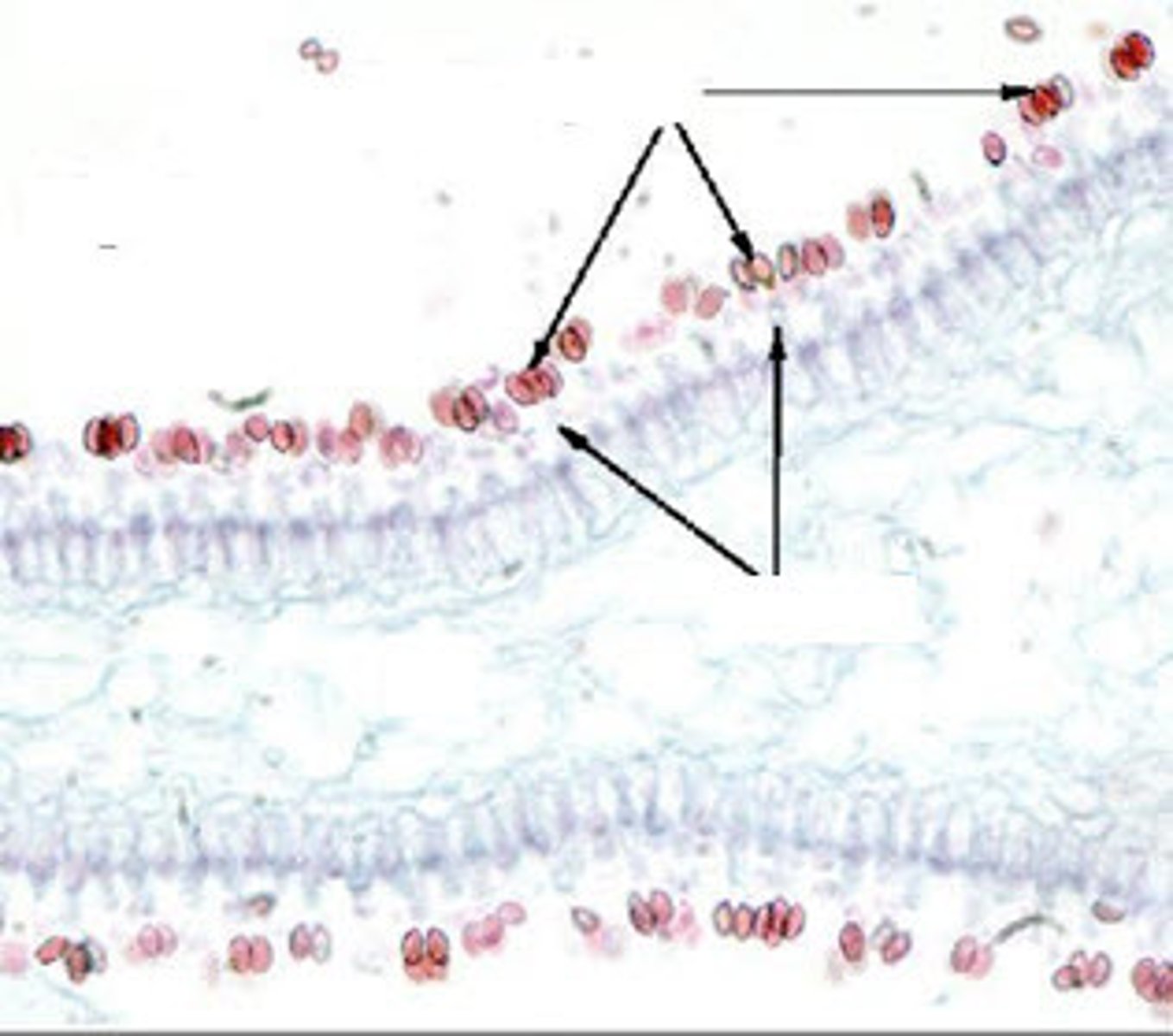
Choanocytes (collar cells)
feeding cells with long flagellum
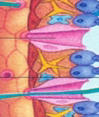
Pinacocytes (porocytes)
cells that line the outside and give shape and form (pink things)
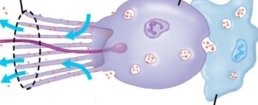
Amoebocytes
transfer nutrients between the other cells, will give rise to eggs (light blue in the picture)
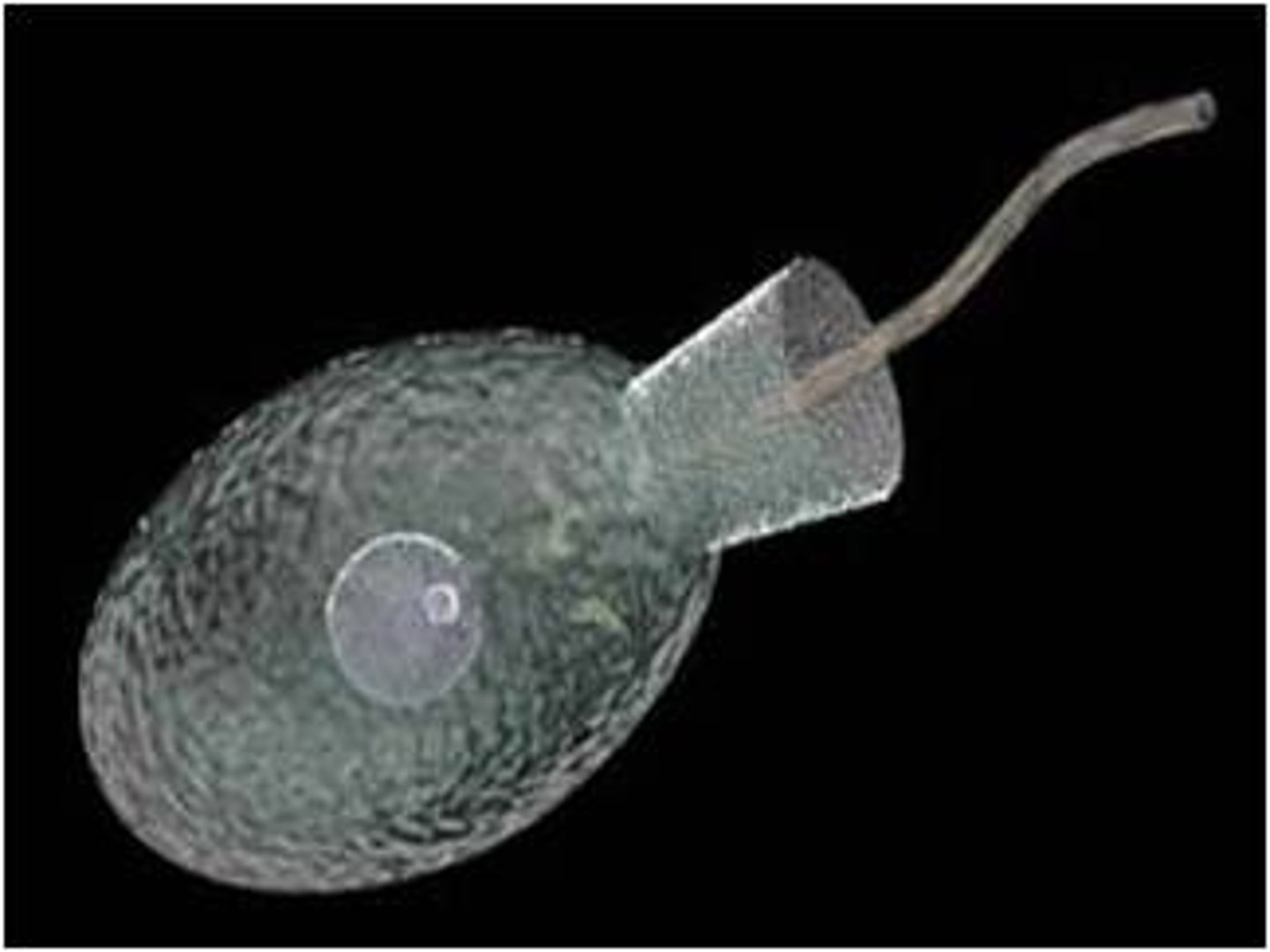
Spongocoel
large central cavity of the sponge
Spicule Composition
Calcium carbonate or silica
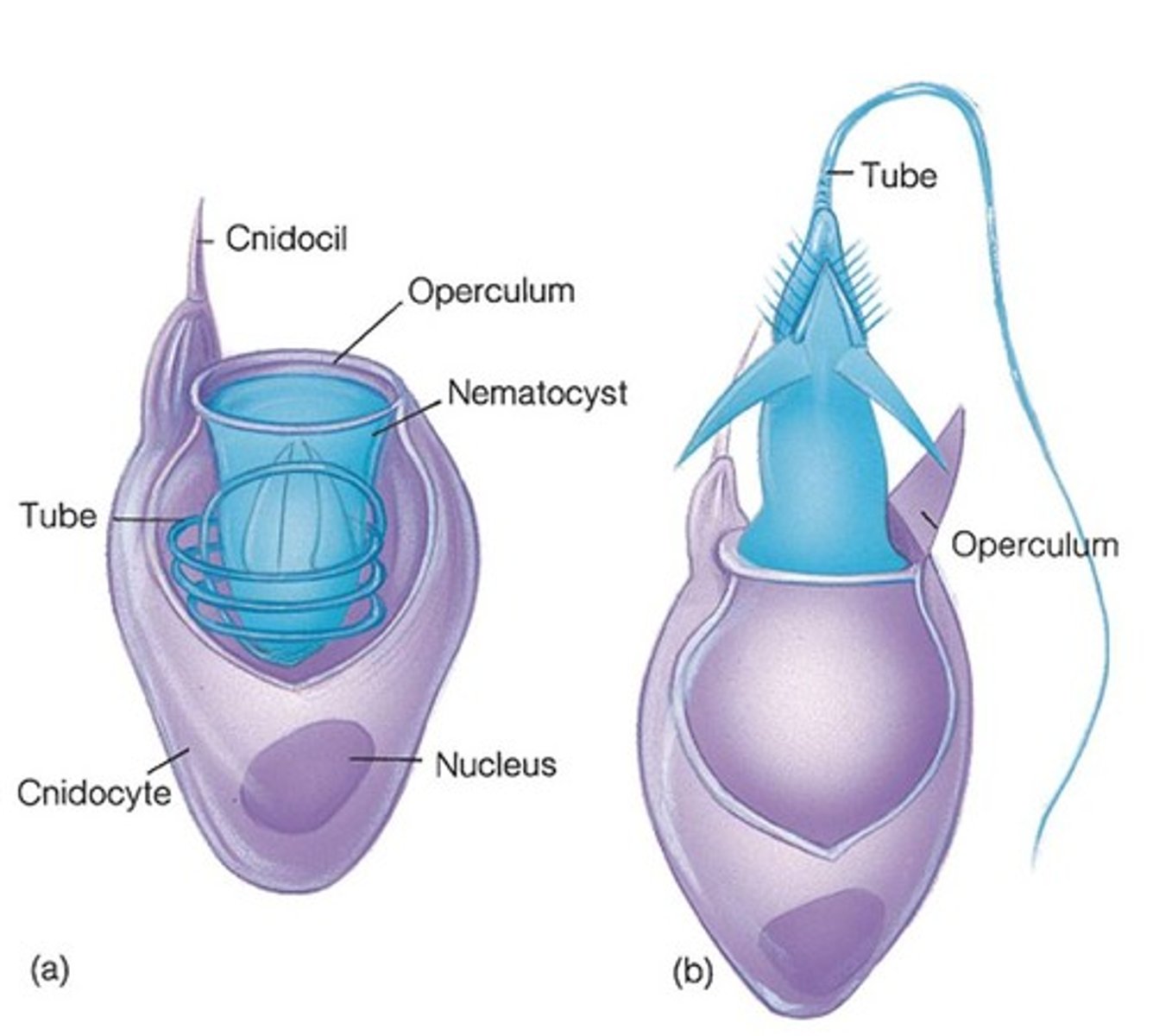
Cnidocyte
stinging cell

Nematocysts
within cnidocytes that eject a stinging thread and wrap around the prey
Tentacles
grab food and put into mouth

Buds
idk
Polyps
Medusae
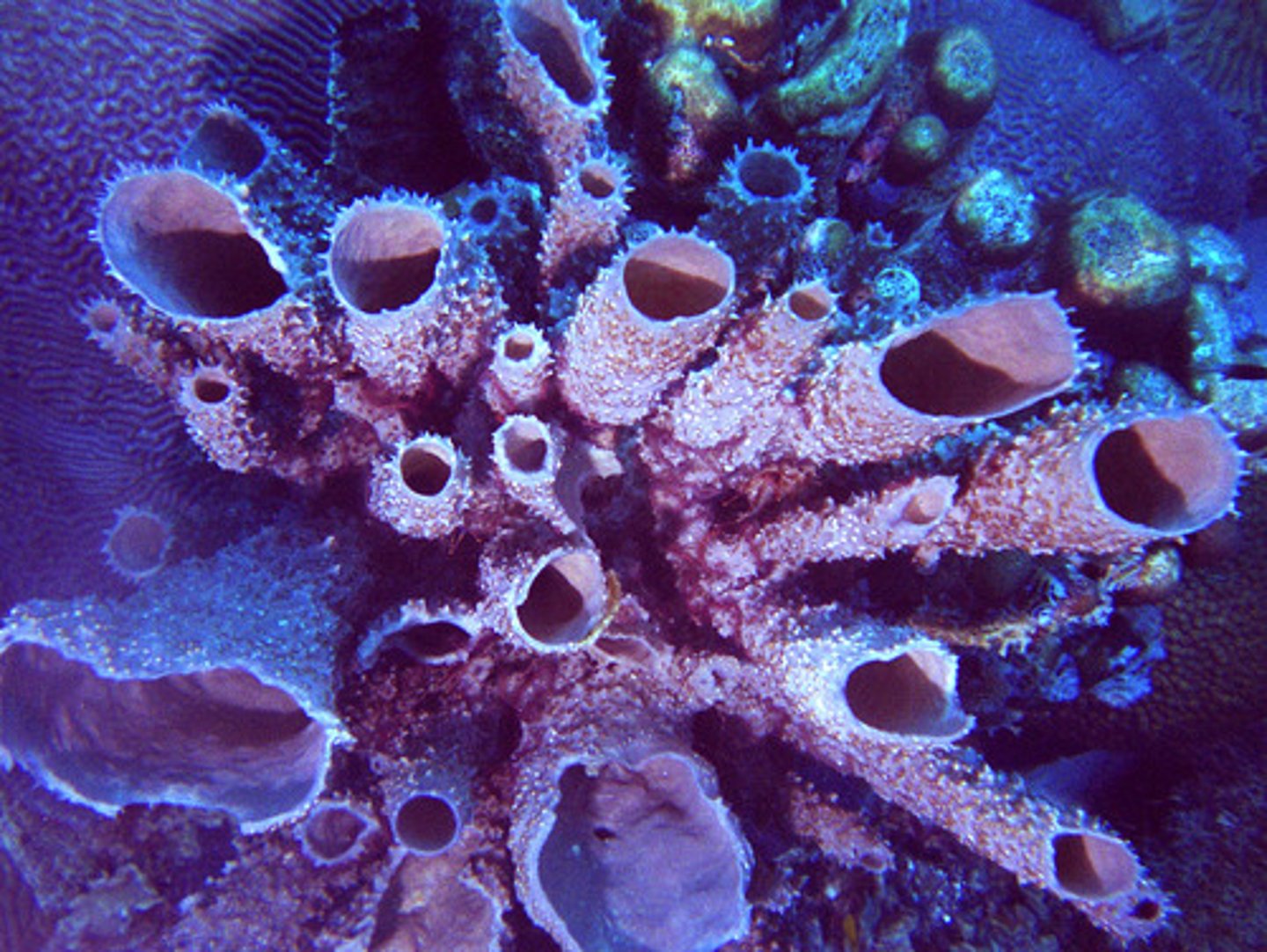
Porifera
sponges

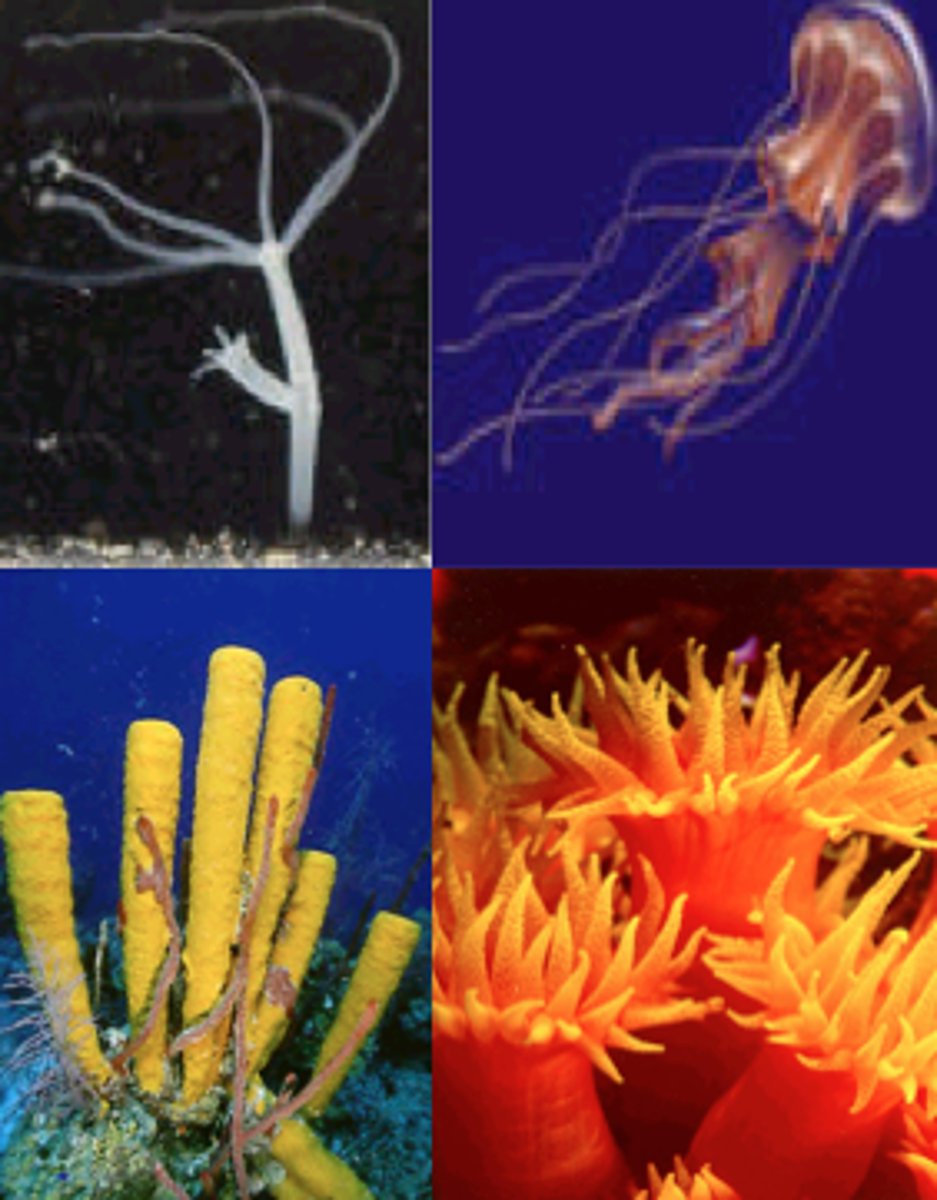
Cnidaria
sea anemone, coral, jellyfish, cube jellies, hydrozoa

Ctenophora
comb jellies
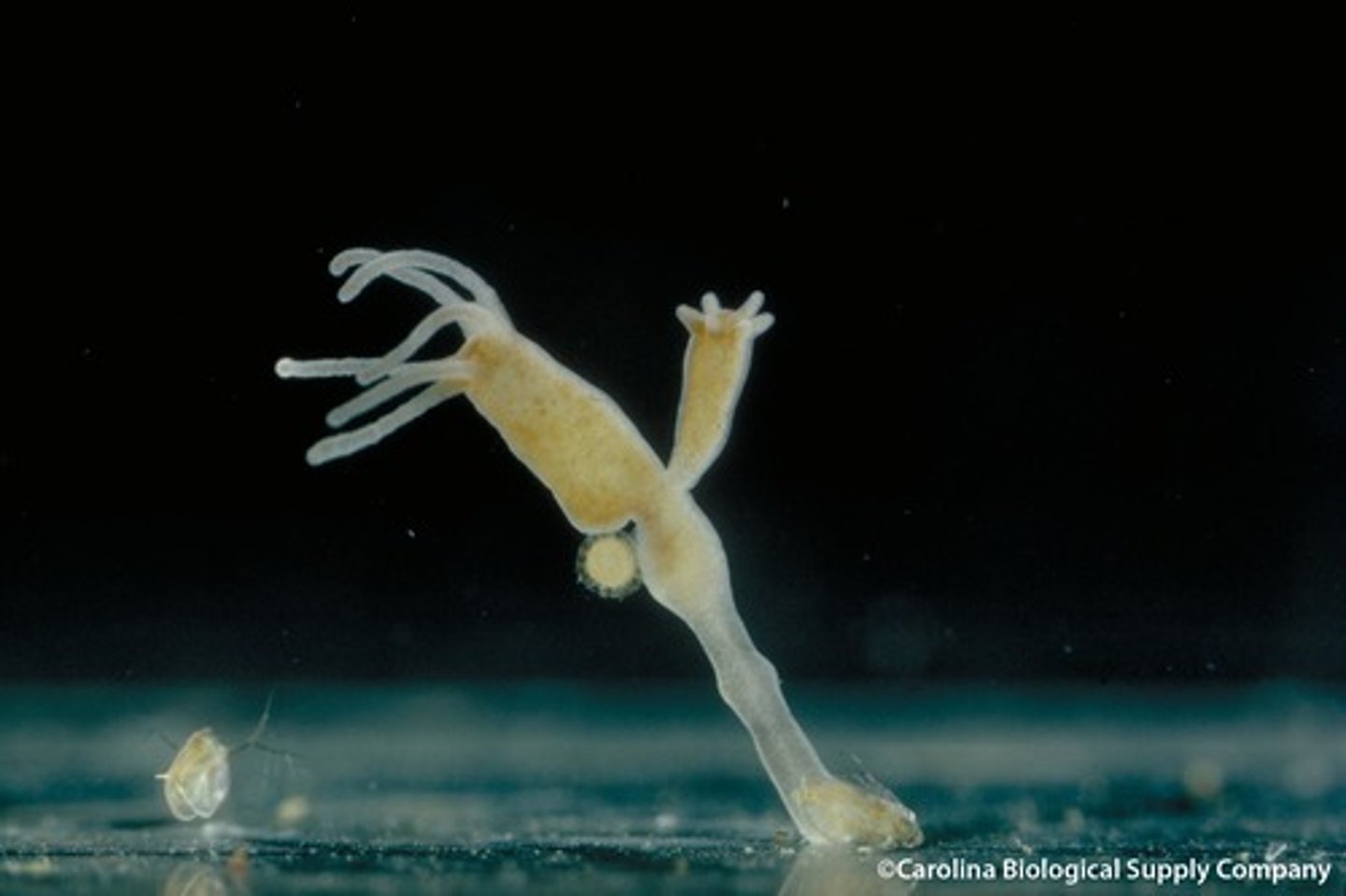
Hydrozoa
polyp or medusae

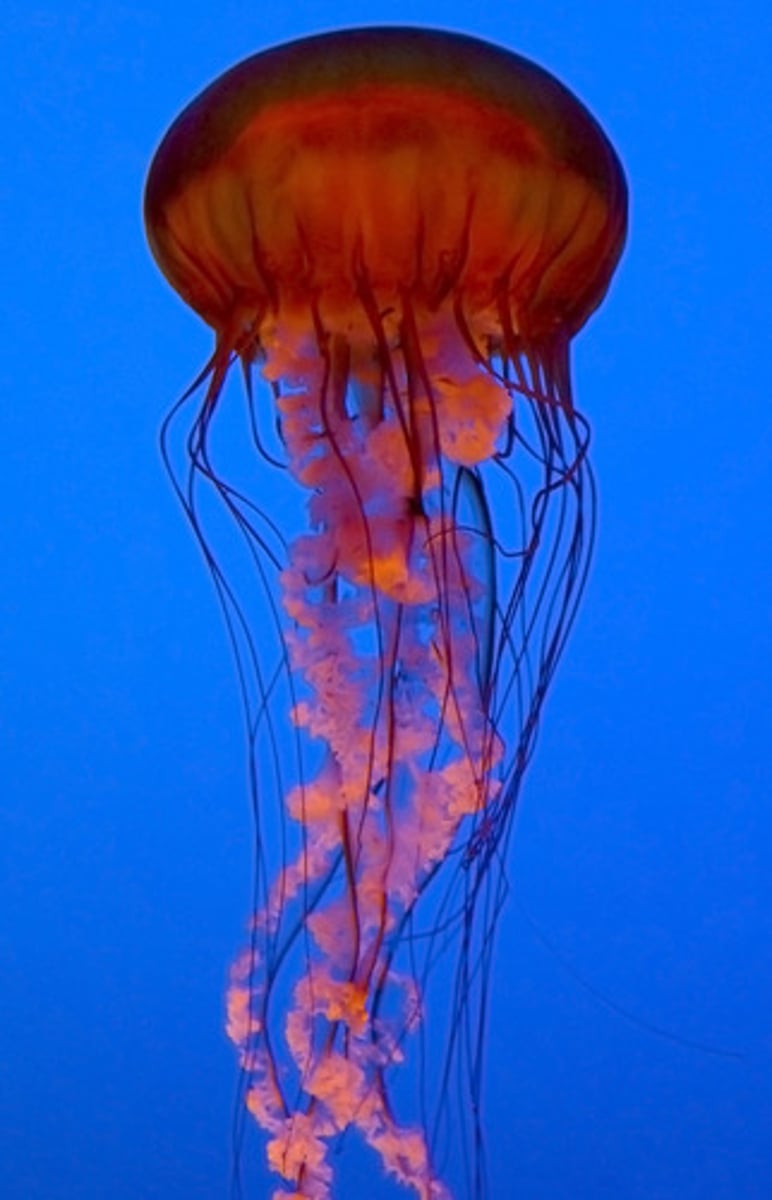
Scyphozoa
jellyfish

Anthozoa
sea anemones and corals
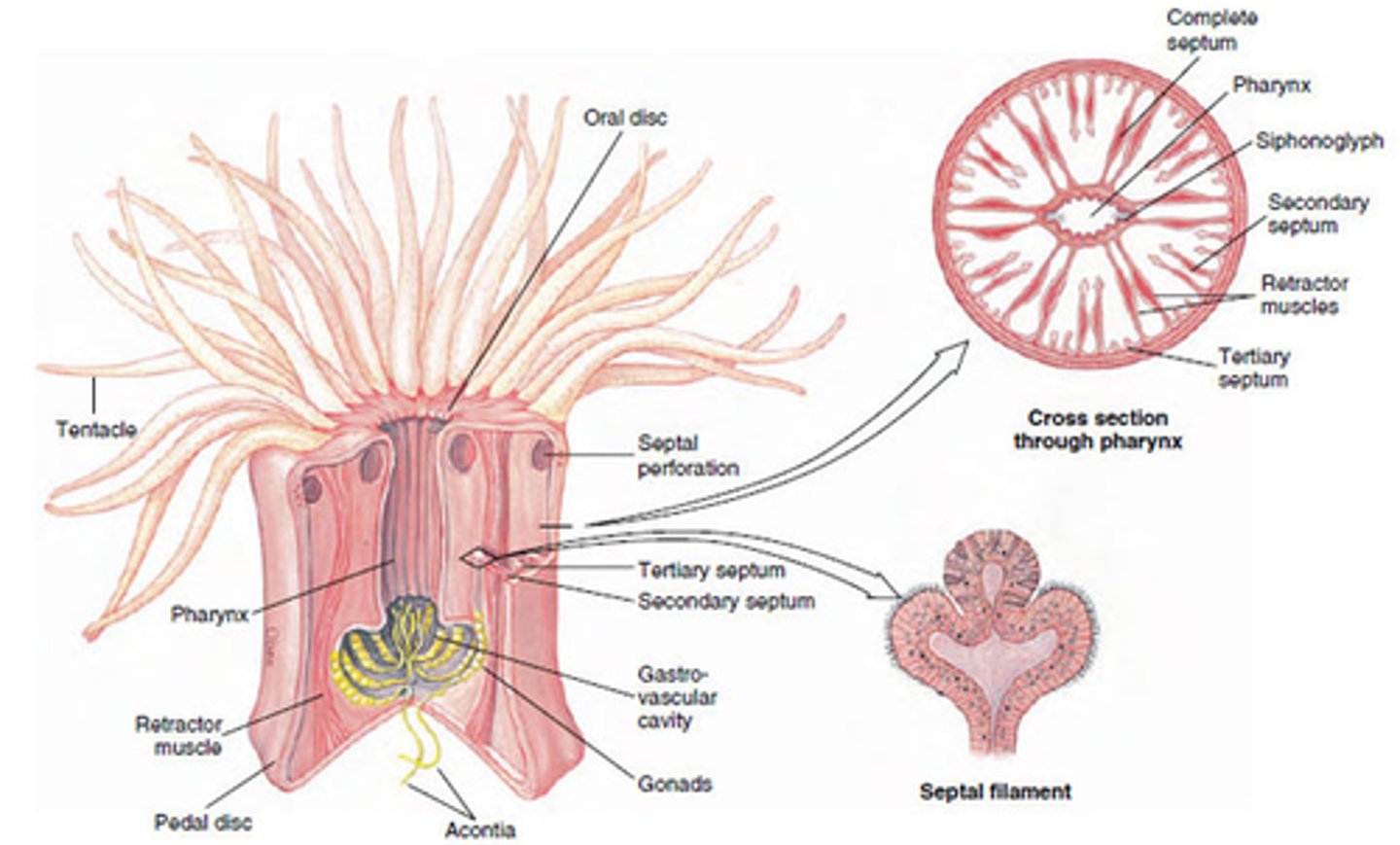
Corals Class & Material
Cnidarians & calcium carbonate
Zygote
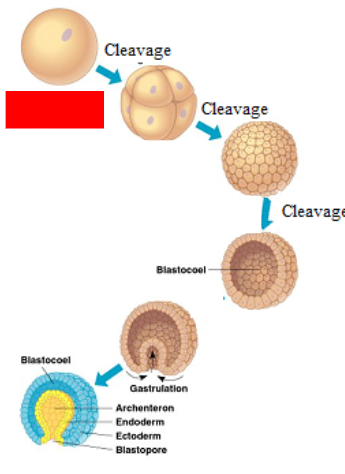
Morula
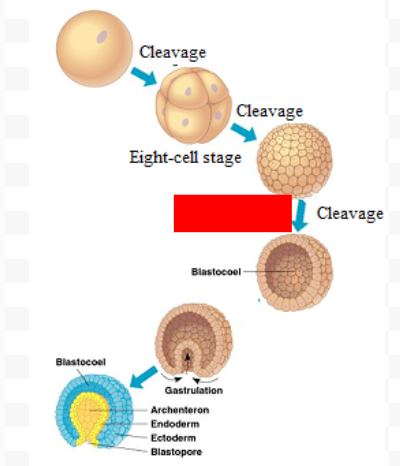
Blastula
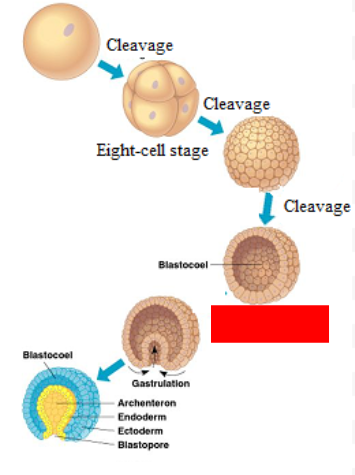
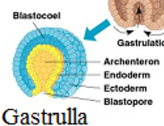
Gastrula
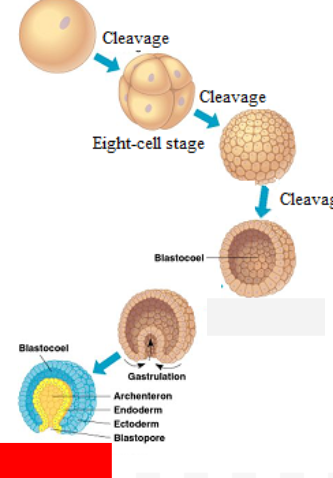
What are the 3 germ layers?
Ectoderm (skin + brain), Endoderm (lungs + intestines), Mesoderm (muscles + heart + kidney + gonads)
Archenteron
Forms the pocket inside and gives rise to the digestive tract/intestinal system
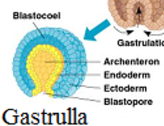
Blastopore
Gives rise to the mouth and BUTTHOLE
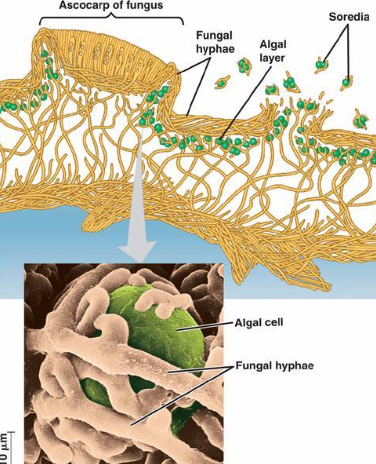
Soredia
thallic fragments of fungal and algal cells for asexual reproduction in lichens
Plasmogamy
fusion of cytoplasm or two different cells
Karyogamy
fusion of 2 nuclei