MCB3020 Week 1: History & Microscopy
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
Main themes
Understanding basic life processes and the application of that understanding to benefit humans
All cells
Metabolism, growth, evolution
Some cells
Differentiation, genetic exchange, communication, and/or motility
Microorganism interactions
Enzymes, control/influence of ecosystems by changing the physical and chemical properties of their habitats such as removing nutrients from the environment and excretion of waste product
Early earth
Anoxic, cyanobacteria were the first oxygenic lifeform on earth
Microbial mass
Nutrients; carbon, phosphorous, nitrogen
1900 leading causes of death
infectious diseases; flu, pneumonia, tuberculosis
Modern day leading causes of death
nonmicrobial diseases; heart disease, cancer, stroke
Gut high to low microbe count
Large intestine, small intestine, stomach with lower microbe count being more acidic (stomach) with the higher microbe count being neutral (large intestine)
Microbial impact on humans
Disease, food, agriculture, energy/environment, biotechnology
Pasteur
Discovered fermentation is a biological process not chemical, proved all cells come from preexisting cells, developed vaccines for anthrax and rabies
Pasteur’s experiment
Swan neck flask, microorganisms get trapped inside of the bend and there’s no contamination. When spilled, microorganisms enter and the liquid is contaminated.
Koch
Developed techniques for obtaining pure cultures (one microbe)
Koch’s first postulate
The suspected pathogen must be present in all cases of the disease and absent from healthy animals
Koch’s second postulate
The suspected pathogen must be grown in pure culture
Koch’s third postulate
Cells from a pure culture of the suspected pathogen must cause disease in a healthy animal
Koch’s fourth postulate
The suspected pathogen must be reisolated and shown to be the same as the original
Cons of Koch’s postulates
Developed before the knowledge of viruses, animal models aren’t always available to test or can’t cultivate outside host body (pure culture) including cholera or rickettsia’s.
Beijerinck
Developed enrichment culture technique by manipulating nutrient and incubation conditions
Winogradsky
Developed the concept of chemolithotrophy
Chemolithotroph
Obtains energy from the oxidation of inorganic compounds such as sulfur or nitrogen
Chemoorganotroph
Obtains energy from the oxidation of organic compounds
Chemoautotroph
Obtains energy using inorganic energy sources such as hydrogen sulfide, sulfur, ferrous iron, and ammonia with most of these being extremophiles
Oxidation
In this chemical process, oxygen is gained
Reduction
In this chemical process, oxygen is taken away
Fixation
In microbiology this is done to preserve biological tissues or cells for examination
Applied microbiology
Medical microbiology and immunology with roots in Koch’s work. Agricultural and industrial microbiology with roots in Beijerinck and Winogradsky’s work
Basic microbiology
Aquatic and marine microbiology from soil microbiology, and microbial ecology
Distribution of microorganisms
From highest to lowest; marine subsurface, terrestrial subsurface, surface soil, oceans, all other habitats
Hooke
First to use a microscope and describe microbes
Van Leeuwenhoek
First to describe bacteria, described as wee animacules
Cohn
Founded the field of bacteriology and discovered bacterial endospores
Light microscope
This type of microscope is used to look at intact cells under low magnification and are composed of an ocular, objective, stage, condenser, focusing knobs, and a light source
Resolution
Determined by the wavelength of light used
Phase-contrast
Improves contrast of a sample without the use of a stain, results with dark cells on a light background, allows visualization of live samples
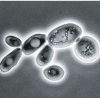
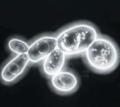
Dark-field
Similar to phase-contrast, results with light cells on a dark background, excellent for observing motility
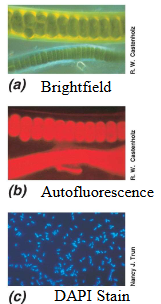
Fluorescence
Used to visualize specimens that fluoresce, fluorescent dye can be used like DAPI and widely used in microbial ecology
Contrast
This can be improved by using a different type of microscopy, such as phase-contrast or dark-field
Total magnification
Product of the magnification of the two sets of lenses; 100x, 400x, 1000x
Gram stain
To perform this, spread culture in thin film over slide, dry in air, pass slide thru flame to heat fix, thinly flood slide with stain, air dry, then place drop of oil on slide to view with 100 objective lens
In more detail, flood the heat-fixed smear with crystal violet for a minute then add iodine solution for a minute. Decolorize with alcohol for 20 seconds; true gram-positive cells will remain purple while the gram-negative ones are colorless. Counterstain with safranin for 1-2 minutes, gram-negatives will appear red/pink.
Gram stain
In this type of staining, different kinds of cells are different colors due to the differences in cell wall thickness
Gram-positive
In gram-staining, the cells turn purple
Gram-negative
In gram-staining, the cells turn red/pink
DIC
Gives structures such as endospores, vacuoles, and granules a 3D appearance
AFM
A stylus is placed close to a specimen and measures weak repulsive forces between it and the specimen. A computer generates an image based on said repulsion.
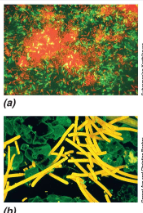
CSLM
Uses a computerized microscope with a laser to generate a 3D image, laser focuses on single layers of the specimen and are then compiled to make a 3D image.