hsc biology - mod 8 non-infectious disease
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
negative feedback loops
a system which maintains homeostasis through counteractive measuers
stimulus
receptor
control centre
effector
response
receptors
sensory cells which detect a stimulus
effectors
muscles, organs, glands which respond to the control centre which receives the stimulus from the receptor
control centre
the CNS which receives signals from receptors detecting stimuli
positive feedback loop
a system which responds to a stimuli by providing a response which amplifies the stimuli
e.g. birth
osmoregulation
homeostasis of the water content of blood to ensure optimal blood pressure.
osmoreceptors
receptors which detect water concentration
anti-diuretic hormone
chemical messenger released by the pituitary gland which communicates with the kidney to control water released into urine. the hypothalamus will detect the water concentration first
homeostasis
maintenance of an internal environment at a constant state despite external environments
•enzymes have specific conditions under which they can operate at an optimal level.
•outside these conditions enzyme activity decreases or can become denatured.
epidemiological studies
a scientific process of answering a question by using data from a population
pinna
outer ear: funnels in sound
external auditory canal
outer ear: funnels in sound toward the tympanic membrane
tympanic membrane
middle ear: also known as ear drum. a thin translucent membrane which vibrates according to the sound waves
malleus
middle ear: ossicle which beats like a hammer on the incus. serves to amplify sound waves
incus
middle ear: ossicle shaped like an anvil which beats on the stapes and amplifies sound. still kinetic energy
stapes
middle ear: ossicle shaped like a loop connected to the oval window. still kinetic energy
oval window
membrane that separates the
middle ear from the fluid-filled inner ear
round window
Vibration pass from the oval window into the upper canal of the cochlea and then through the lower canal to the ___. acts as a valve, relieving built-up pressure from the wave set up in the perilymph of the cochlea.
cochlea
inner ear: fluid filled structure composed of 3 canals. also a spiral structure containing hair cells which convert kinetic to electrical energy.
vestibule
contains vestibular nerve which carries impulses form the organ of balance to the brain
semicircular canals
detect movemnets of the head…
conjunctiva
epithelial cells on the eye for protection
cornea
first bending of light in the eye occurs here. protects eye. dome shaped and transparent. focuses light for clear vision.
aqueous humor
water + salt filled chamber in the front of the eye
iris
pigmented muscle which contracts and expands to control the size of the pupil.
lens
a biconvex clear hard flexible structure which bends light a second time to focus an image on the retina
suspensory ligaments
the string like ligaments which hold the lens
ciliary muscles
the muscles connected to the suspensory ligaments which control the elongation of the lens
vitreous humor
water filled chamber which holds the turgidity of the eye
sclera
the white tough part which encapsulates the eye
retina
part on the back of the eye composed of photoreceptors. this is where an image is received and flipped
macula
small, highly sensitive, central area of the retina at the back of the eye, responsible for sharp, detailed central vision, including reading, driving, and recognizing faces, as well as most color vision
fovea
part of the macula responsible for colour perception
myopia
short sightedness caused by an elongated eyeball. focused image falls before the retina
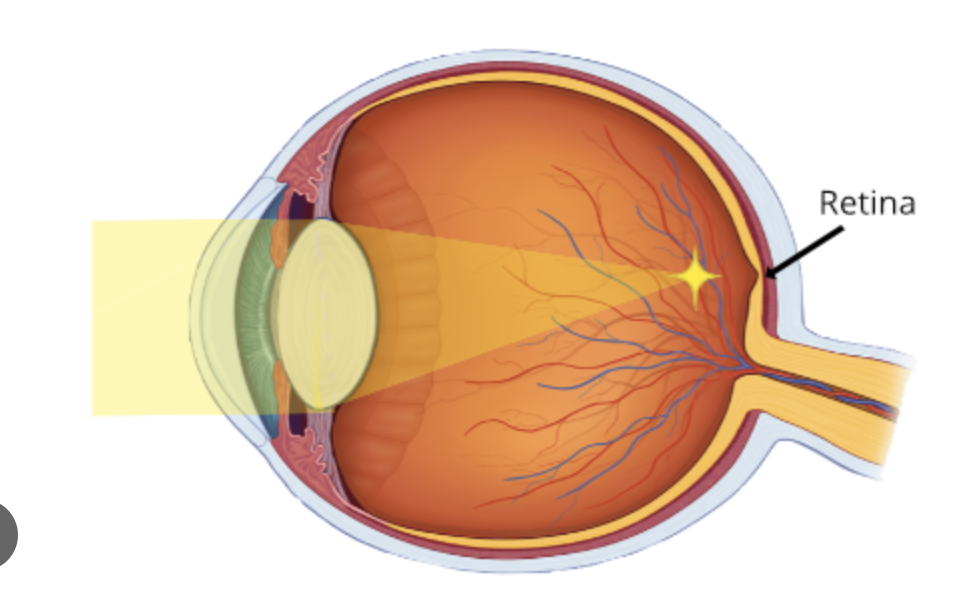
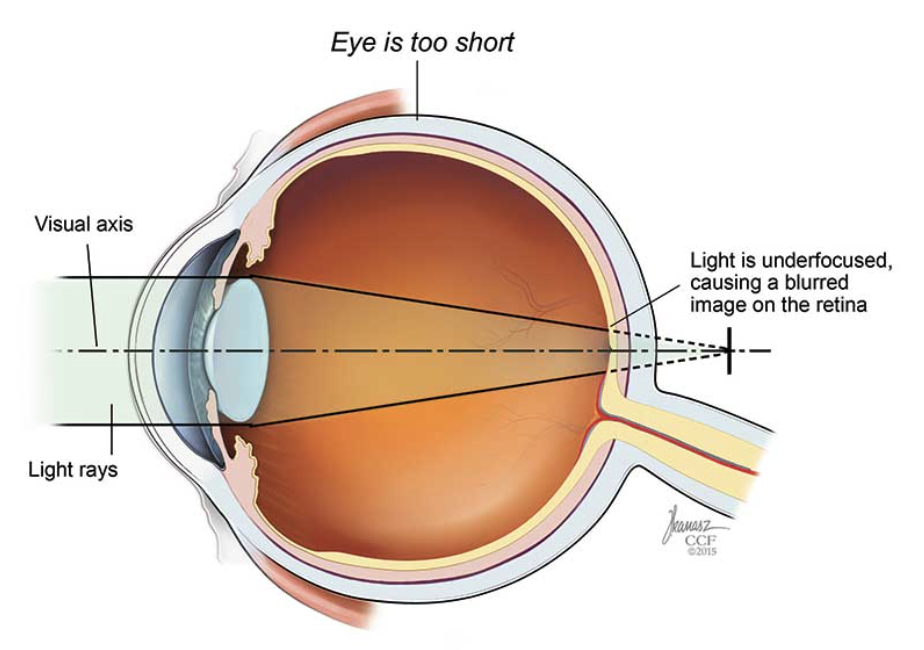
hyperopia
long sightedness caused by a short eyeball. focused image falls after the retina
photoreceptor cells
rod and cone cells located in the retina responsible for receiving focused light energy to convert into electrochemical impulses
rod cells
long cells which receive focused light distributed over most of the retina. absent in the fovea. contains visual pigment rhodopsin which is extremely sensitive to light
125 million
cone cells
pointed cells which receive focused light most densely found in the fovea in the macula. responsible for interpreting colour. contains iodopsins responsible for different wavelengths of light
cataracts
the clouding of a lens. causes blurred vision by reducing transmission of light. increased sensitivity to glare
macular degeneration
the degeneration of cells beneath the retina called retinal pigment epithelium. prevents light from being focused successfully. affects the ability to recognise faces + read
leading cause of legal blindness. 50% of blindness in Aus is caused by this
caused by lifestyle smoking, diet, uv exposure
spectacles
a physical lens used to bend light rays to fix hyperopia and myopia
convex lens
a lens shaped like an open mouth which bends light inwards to fix the focus point of hyperopia
concave lens
bends light outwards to diverge rays which would fall before the retina (myopia)
contact lenses
same principal as spectacles but adjusted to the curvature of the eye
cataract surgery
replacing the cloudy lens in an eye with an artificial one
LASIK surgery
reshaping a cornea with lasers to fix myopia or hyperopia
filtration
removing nitrogenous wastes and other water soluble wastes from the blood in the nephron
reabsorption
returning essential components to the blood. amino acids + vitamins + sodium ions etc
secretion
the removal of waste from the body. disposal of waste in the collecting duct through the urinary tract. urine formation
glomerulus
a network of capillaries in the nephron key in the first part of filtration. blood cells and proteins are retained in the blood while water and dissolved substances like amino acids diffuse through
bowman’s capsule
capsule which collects filtered plasma to begin making urine
afferent arteriole
the junction connecting the artery to the glomerulus
proximal convoluted tubule
part of the nephron where reabsorption of essential amino acids, water and ions occurs via active transport
distal convoluted tubule
part of the nephron where reabsorption occurs, connected to the collecting duct
loop of henle
where reabsorption occurs. descending = passive transport + osmosis
collecting duct
part of the nephron where urine begins to form (secretion). connected to the ureter
haemodialysis
when kidney function goes below 10% toxins build up requiring this technological process. requires dialysis machine and dialysate
blood flows through catheter through fistula
blood travels through fine fibres (semi-permeable membrane)
dialysate solution passes in the opposite direction
waste products diffuse down the concentration gradient
filtered blood returns to the arm