cardiovascular system - anatomy
1/39
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
Name 3 formed elements found in whole blood.
Erythrocytes, leukocytes and thrombocytes
Which formed element is used to determine a hematocrit?
Red blood cells or Erythrocyte
Which layer is the buffy coat?
White blood cells or Leukocytes or Platelets (layer 2)
Blood plasma is primarily made of water. What else is found in it?
Proteins and salts, hormones, gases, minerals, nutrients, enzymes, waste
Name 3 ways in which the structure of red blood cells illustrates their function in the body.
BIconcave shape allows greater surface area, Round to get through blood vessels, and No nucleus and few organelles to not use oxygen while transporting.
Why can’t oxygen travel through the blood on its own?
Oxygen is not soluble in blood non polar
How many oxygen molecules can one hemoglobin protein carry?
Up to four
In the centre of each heme group can be found an atom of which element?
Iron atom
What is the function of the cells known as leukocytes? (general description)
To protect the body from foreign cells or substances.
Name 4 ways erythrocytes differ from leukocytes.
RBC’s Out number Leukocytes 1,000 to 1, RBC’s Mature cells don't contain nuclei, RBC’s Live for 100 - 200 days, and concentration in blood is always consistent.
What is diapedesis? What type of blood cells use this process?
The process by which blood cells squeeze through blood vessel walls; WBC (Leukocytes)
Name 2 differences between granulocytes and agrunalocytes.
Granulocytes have lobe - shaped nuclei and visible granules. Agranulocytes have Spherical or Kidney - shaped nuclei and no visible granules.
Name the 5 types of leukocytes from highest concentration to lowest concentration in the blood.
Neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils, & basophils
Blood cells are formed by what process? Where does this occur?
Hematopoiesis and in the red bone marrow
The stem cell that differentiates into all others is known as a ___.
Hemocytoplast
Immature erythrocytes have huge numbers of ribosomes. What protein are they manufacturing?
Hemoglobin
Describe what happens when oxygen levels drop in blood.
Hypoxemia occurs as the body begins to exit homeostasis; oxygen levels drop, kidney and liver produces erythropoietin , red bone marrow produces more RBCs
What does a sphygmo-m anometer mesure?
Blood pressure
Name one of the arteries that can be used to take your pulse and the location of that artery.
Radial artery in wrist, carotid artery in neck, brachial inside elbow
An individual has type A blood. You would expect to find A ____ on the erythrocytes and anti-B ____ in their blood plasma.
Antigens and antibodies.
What is hypertension? Why can it adversely affect a person’s health?
Hypertension (High Blood Pressure) is the state blood enters when it is too high and reaches too far up the artery walls; makes the heart work too hard and can lead to heart disease and or stroke.
Which blood type is known as the universal donor? Which is the universal recipient?
Type O is the universal donor and AB+ is the universal recipient.
Two parents (heterozygous blood type A and blood type O) have children. What blood types are possible for the children? (Show Punnett square.)
The punnet square shows that the children have 75% percent chance to get blood type A and 25% percent chance to receive blood type O
Which 2 heart chambers contain deoxygenated blood? Which 2 heart chambers contain oxygenated blood?
The Left atrium and the Left Ventricle contain oxygenated blood and the right atrium and the right ventricle contain deoxygenated blood.
Briefly explain the 3 steps of hemostasis.
Sensing changes- our body has specialized sensors that constantly monitor different aspects like temperature, blood sugar levels, and pH balance. Processing information- it determines whether any adjustments need to be made to bring things back into balance. Making adjustments- sends signals to various organs and systems in our body to initiate appropriate responses.
Vessels Contract, platelets activated and stick to wound, enzymes form fibrin mesh
What is the difference between an embolus and a thrombus?
An embolus is a particle or mass that flows through the bloodstream.A thrombus i a blood clot (stationary) in a blood vessel
A blood type characterized by erythrocytes that have no A or B antigen on them is?
Type O
An Rh- mother gave birth to an Rh+ infant. Explain the concern for another pregnancy.
might develop antibodies against the rh factor which could affect future pregnancies
Name the three layers of the pericardium and give their functions.
Fibrous Pericardium, Parietal Pericardium, visceral Pericardium
Name the three layers of heart tissue.
epicardium, endocardium, myocardium
What are the 2 cardiovascular circuits and where do they deliver blood?
Pulmonary circuit: heart to lungs back to heart. Systemic: Heart to body tissues to hearttra
Blood just returned through the pulmonary veins. It will enter the ___ (chamber) and then pass through the ___ wave.
Left atrium, bicuspid valve
Where are auricles found?
On the outside of the Atria
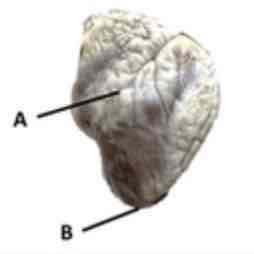
Name these structures.
A- interventricular sulcus B- apex
Describe the path of an impulse leaving the SA node.
SA Node→ AV Node→ AV Bundle → Bundle Branches → Purkinjie fibers
What are the two major portions of the cardiac cycle?
Diastole and systole
What is the formula for calculating cardiac output?
heart rate x stroke volume
Describe 2 differences between veins and arteries.
Veins carry blood towards the heart and have thinner walls, low pressure. Arteries carry away from heart and thicker walls, high pressure
Arteries and veins have 3 tissue layers. Name them starting with the outermost layer.
Tunica intima, tunica media, tunica externa
How can capillaries restrict the flow of blood when it is not needed in a certain tissue?
Capillaries can use sphincters to restrict blood flow from the true capillaries through the shunt