Week 5: Firewalls
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
What is a firewall?
A computer/network security system sitting between the internal network and the rest of the network
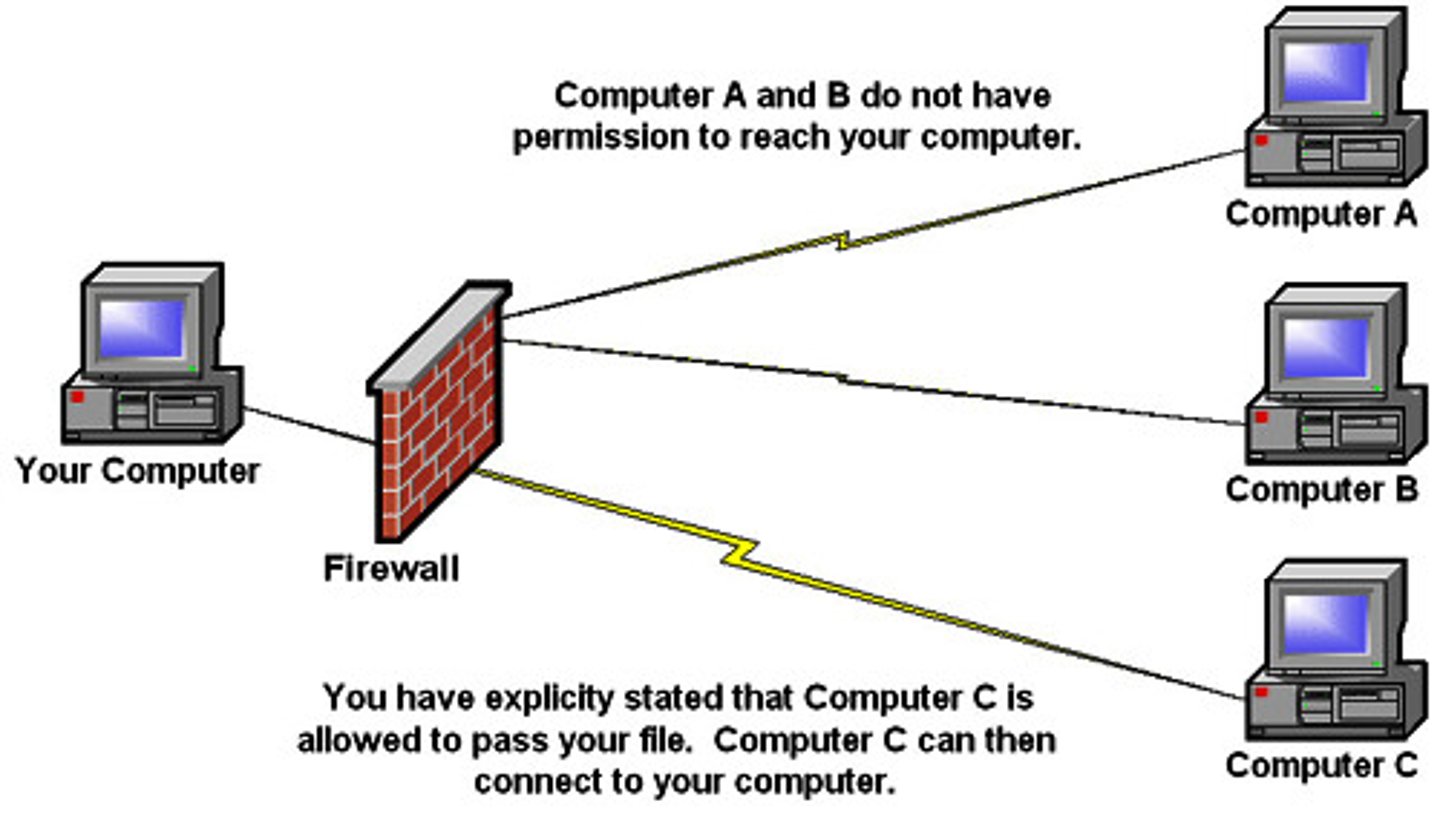
What are the objectives of firewalls?
To provide access control - preventing bad things from happening without preventing good things from happening
What are the general functionalities of a firewall?
Choke point of control and monitoring, filtering at the protocol layers
Imposes restrictions on network services to allow authorised traffic
Provide Network Address Translation and usage monitoring
Implementing VPNs using IPsec
What is a security policy?
A policy to dictate authorised traffic in both directions
What are the techniques for firewalls to control access?
- Service control (What)
- Direction control (Where)
- User control (Who)
- Behaviour control (How)
What is service control?
Determines the types of Internet services accessible (inbound and outbound) via transport layer ports
What is direction control?
Determines the direction of service requests allowed through the firewall
What is user control?
Controls access to services based on the user attempting access
What is behaviour control?
Controls how particular services are used
What are the types of firewall filtering?
Positive and negative filter
What is a positive filter?
Passes only packets that meet specific criteria (default = discard, using a whitelist)
What is a negative filter?
Rejects any packets that meet specific criteria (default = forward, using a blacklist)
What are the limitations of using a firewall?
Firewalls cannot protect against attacks bypassing them, malware imported via infected devices (like through sneakernet), improperly secured WiFi access, or internal threats
What is sneakernet?
transfer of information by physically moving removable media like CDs/USBs or external hard drives from one computer to another
Why might using firewalls not be suitable for WiFi networks?
If the firewall is placed before the WiFi router, then the attacker can just access wireless encryption and bypass the firewall if they are in close proximity
What is a packet filtering firewall?
A firewall that individually examines and filters packets backed on rules
The foundation of firewalls, simplest and fastest type
What are the default policies for packet filtering firewalls?
Default = discard (positive filtering): Everything is blocked initially, and services must be added case-by-case. This is more conservative
Default = forward (negative filtering): Everything is allowed initially, and threats are blocked as they become known. This is less secure
What are the advantages of packet filtering firewalls?
Packet filtering firewalls are very simple, their rules are transparent to users, and they are very fast
What are the disadvantages of packet filtering firewalls?
Cannot examine upper-layer data and cannot detect application-layer attacks
Logging is only done for access control, cannot authenticate
Vulnerable to attacks exploiting the TCP/IP specification, like IP address spoofing
How are packet filtering firewalls vulnerable to attacks exploiting the TCP/IP specification?
Packet filtering firewalls are generally vulnerable to attacks exploiting weaknesses in the TCP/IP specification, such as network layer address spoofing.
This means they might not be able to identify packets with altered IP addresses
How does the limited number of variables in decision-making make packet filtering firewalls vulnerable?
Packet filtering firewalls are vulnerable to misconfigurations due to the limited number of variables used in their decision-making process.
This can easily lead to the unintended allowance of prohibited traffic
What are the countermeasures that firewalls can take against IP spoofing attacks?
Discard the packets with an inside source address if it arrives on an external interface, and add filters on the router to block the packets
What is a source routing attack and how can it exploit a packet filtering firewall?
In a source routing attack, the sender of a packet can include information specifying the route the packet should take.
An attacker can generate traffic claiming to be from inside the firewall (even if sent from outside) and specify a route hoping to bypass security measures that do not analyse the source routing information
What are countermeasures that firewalls can take against source routing attacks?
Block all source routed packets and discard all packets that use the option
What are tiny fragment attacks and how can it exploit a packet filtering firewall?
Tiny fragment attacks involve splitting header information over several tiny packets using IP fragmentation, forcing the TCP header information into a separate packet fragment.
The attacker hopes the filtering firewall examines only the first fragment and passes the remaining fragments through, thus circumventing filtering rules that depend on TCP header information
What are countermeasures that firewalls can take against tiny fragment attacks?
Discard all fragmented packets using the TCP protocol
Reassemble before checking
Enforce a rule that the first fragment of a packet must contain a predefined minimum amount of the transport header
What is the main problem with traditional packet filters?
Makes filtering decision without considering layer context, so they do not match return packets with outgoing flow
What is a stateful firewall?
A firewall that examines each IP packet in context, keeping track of client-server sessions (TCP connections). They check if each packet belongs to an existing session, making them better at detecting out-of-context or bogus packets
What is the range for TCP port numbers of servers?
Less than 1024
What is the range of TCP port numbers for clients?
Between 1024 and 65535, they are dynamically generated
What is the vulnerability of dynamic generation of TCP ports?
Because the client's port number is dynamically generated, the firewall must permit the inbound network traffic on all the high-numbered ports because it doesn't know which port will be assigned
How does stateful packet filtering work?
There is a directory of outbound TCP connections, and an entry represents a currently established connection
The packet filter allows incoming traffic to high-numbered ports only if they fit the profile of the directory entries
What else can a stateful packet filter keep track of?
TCP sequence numbers to prevent TCP session hijacking
Limited amounts of app data for protocols like FTP and SIP to identify and track related connections
What is an application-level gateway/proxy firewall?
A relay of application-level traffic with full access to the protocol, to determine allowed connections.
What are the advantages of proxy firewalls?
More secure than packet filtering firewalls - only scrutinises a few allowable applications
Easy to log and audit incoming traffic at application level
What are the disadvantages of proxy firewalls?
Needs separate proxies for each service
Additional processing overhead per connection - must examine and forward all traffic in both directions of the connection between end users
What is a circuit-level proxy firewall?
They operate at the session layer (between the transport and application layer) to set up and relay TCP connections without examining the contents - they primarily determine which connections will be allowed
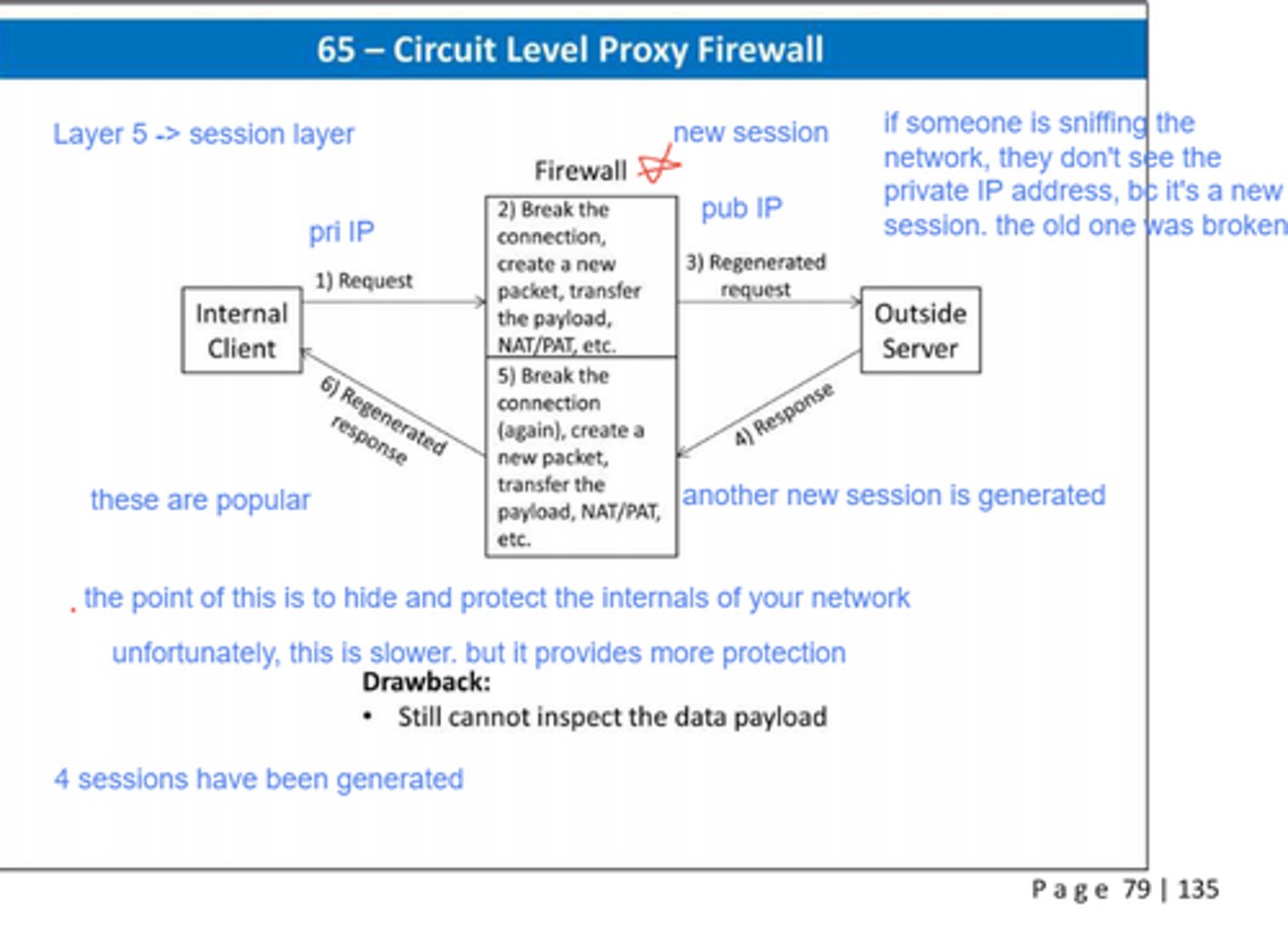
Where are circuit-level proxy firewalls often used?
For outbound connections when internal users are trusted
How many sessions does a circuit-level proxy firewall create?
4 - two for connecting the proxy to the internal network host and the outside host, and two for relaying TCP segments between the connections without examining its contents
Where can firewalls be located?
Firewalls can be located on the premise (personal, host-based, DMZ networks, VPNs, distributed firewalls) or in the cloud (virtual private cloud, public subnet = DMZ, bastion host, DMZ in the cloud)
What is the Demilitarised Zone Network (DMZ)?
A physical or logical subnet that separates an internal LAN from untrusted networks like the Internet, which has an external firewall and an internal firewall
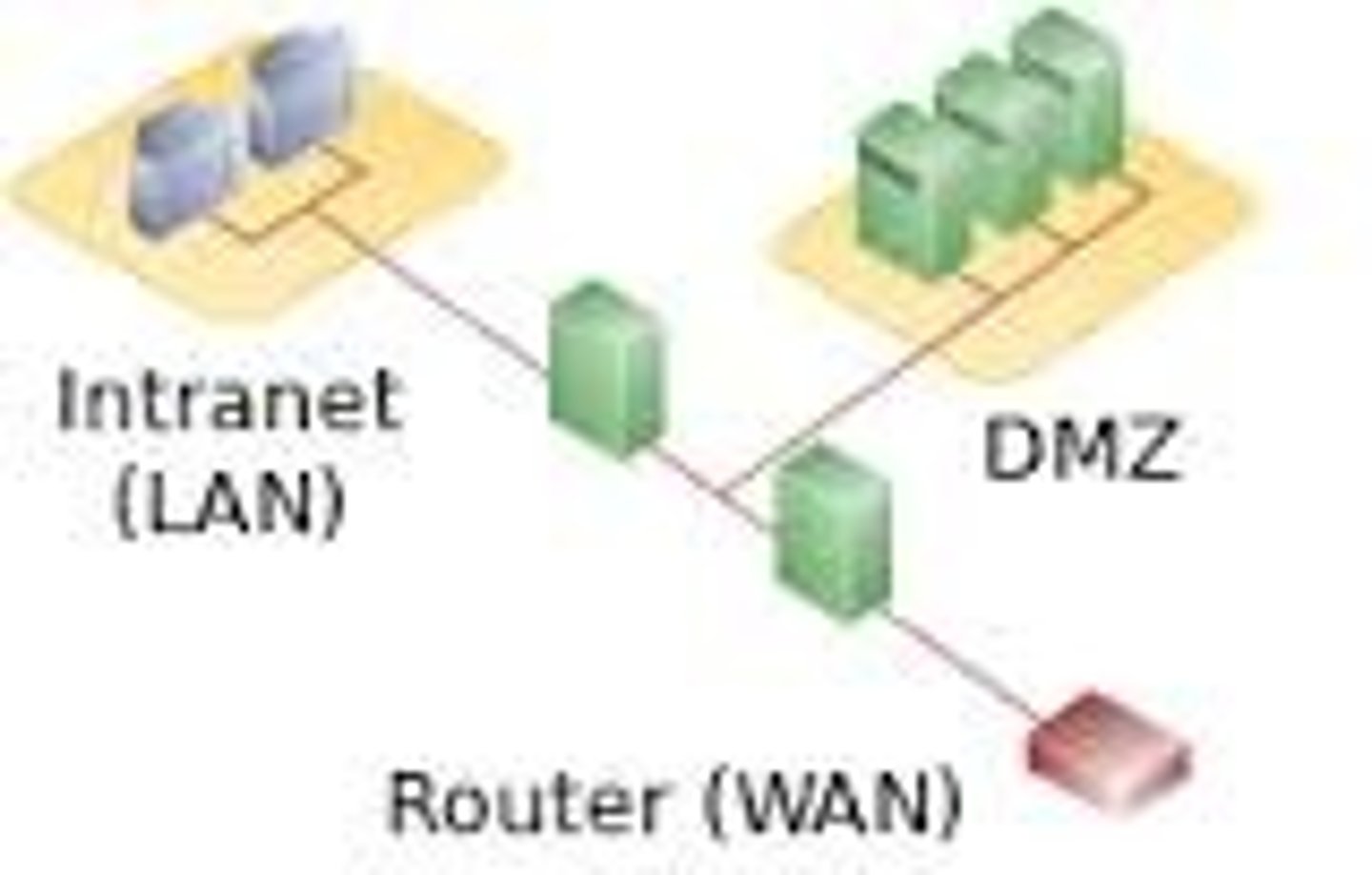
What does the external firewall in a DMZ do?
Provides basic level of protections for the remainder of the network and is a measure of access control for external connectivity
What does the internal firewall in a DMZ do?
Provides protection from external attacks with more stringent filtering to enterprise servers and workstations
Why does the internal firewall provide two-way protection wrt the DMZ?
It protects the remainder of the network from attacks from the DMZ
It protects DMZ systems from attacks in the internal protected network
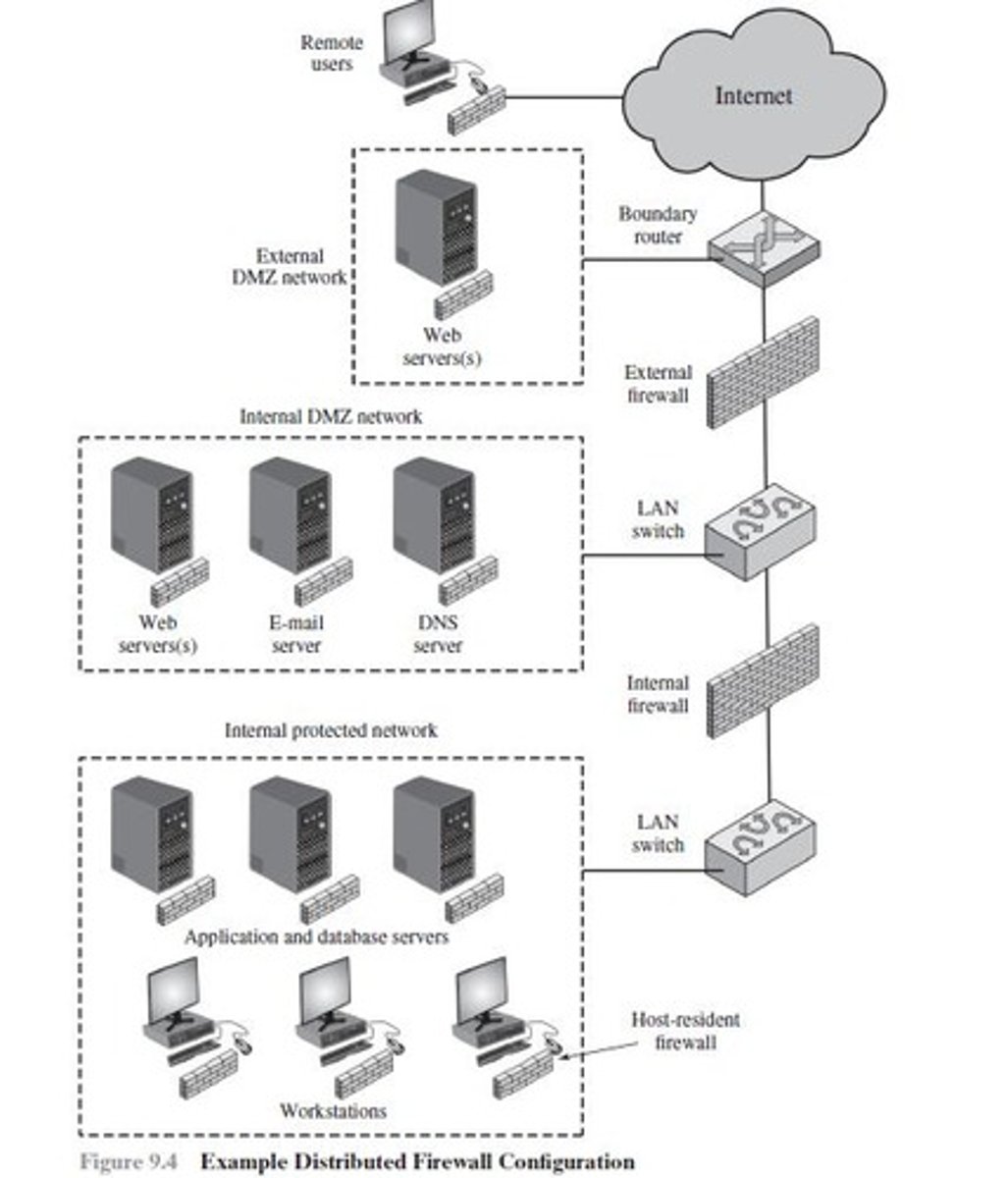
What is a distributed firewall?
A configuration involving both standalone firewall devices and host-based firewalls working together under central administrative control, including both internal and external DMZs
What is a VPN (Virtual Private Network)?
Consists of a set of computers interconnected by an insecure network, using encryption and special protocols (like IPsec5) to provide a secure connection.
How does a VPN perform encryption?
Encryption can be performed by firewall software or a router
What is a VPC (Virtual Private Cloud)?
An on-demand configurable pool of shared resources allocated within a public cloud environment, offering infrastructure as a service
Why is a VPC virtual?
Because the cloud is shared, and a private IP subnet is allocated. Public subnets within a VPC are similar to the DMZ
What is a bastion host?
A system identified by the firewall administrator as a critical strong point in the network's security, serving as a platform for proxy services or externally accessible services
How is a bastion host secured to withstand hostile elements?
Bastion host hardware platform executes a secure version of its operating system, making it a hardened system
Only services that the admin considers essential are installed