BEO Final - Chapter 10
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
what is Canada one of the largest producers of?
forest products in the world, with plants in nearly all provinces turning out a vast array of wood, furniture, and paper products.
The fourth industrial revolution
the phase of digitization in the manufacturing sector that involves data, analytics, and improved robotics
Research and Development (R&D)
work directed toward the innovation, introduction, and improvement of products and processes
newer and more advanced technologies/practices helps industries increase their production capability, improve productivity and expand their lines of new goods and services
production
the creation of goods and services using the factors of production: land, labour, capital, entrepreneurship, and knowledge.
historically was associated with manufacturing but has changed significantly
Production Management
has been the term used to describe all of the activities that managers do to help their firms create goods
Operations Management
a specialized area in management that converts or transforms resources (including human resources) into goods and services.
includes inventory management, quality control, production scheduling, follow-up services, and more
in the service industry this is all about creating high value experience for those who use the service.
service industries have increased their use of AI in their operations
Operations management planning
involves many of the same issues in both the service and manufacturing sectors
Facility location
the process of selecting a geographic location for a companies operations
the shift of manufacturing organizations from one city or province to another in Canada, or to other foreign sites is a major issue of the recent past
business move operations to:
reduce time to market
to build factories in foreign countries to get closer to international customers
or they move for the availability of inexpensive labour or the right kind of skilled labour
Outsourcing goods and services
this has become a cost saving practice
for example software development, call-center jobs, and back office jobs have been moving out of North America to developing countries
recently jobs like accounting, financial analysis, medicine, law, architecture and more have been outsourced
Facility layout
the physical arrangement of resources (including people) in the production process
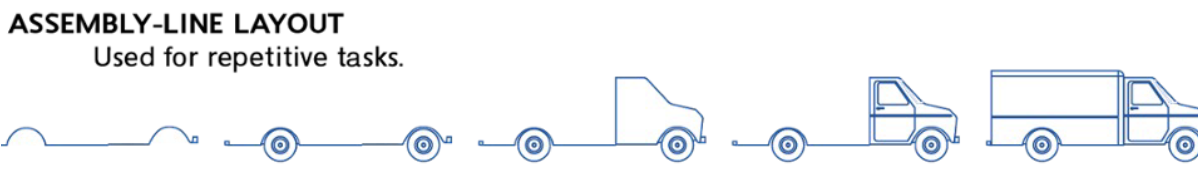
Assembly-line layout
used for repetitive tasks
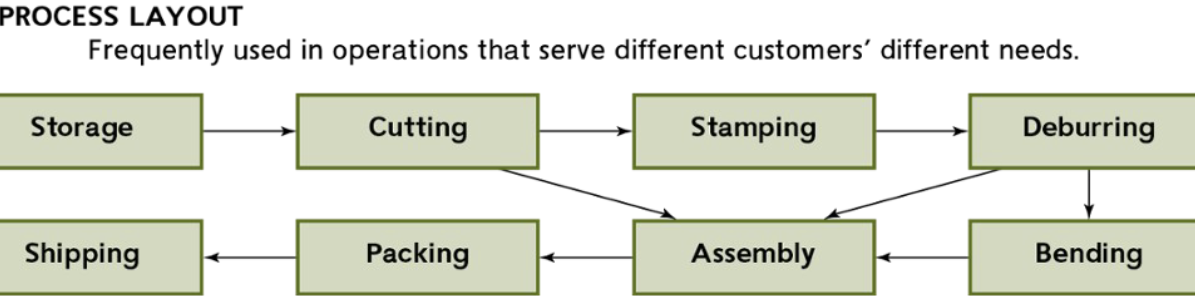
Process layout
frequently used in operations that serve different customers different needs
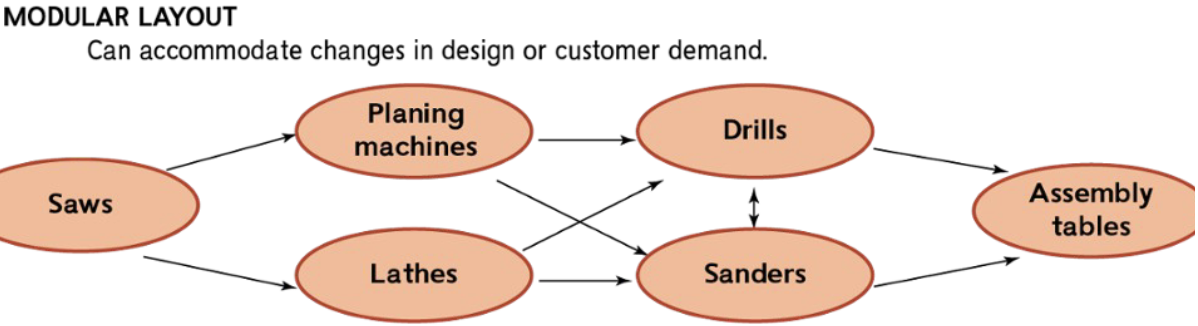
Modular layout
Can acomodate changes in design or customer demand
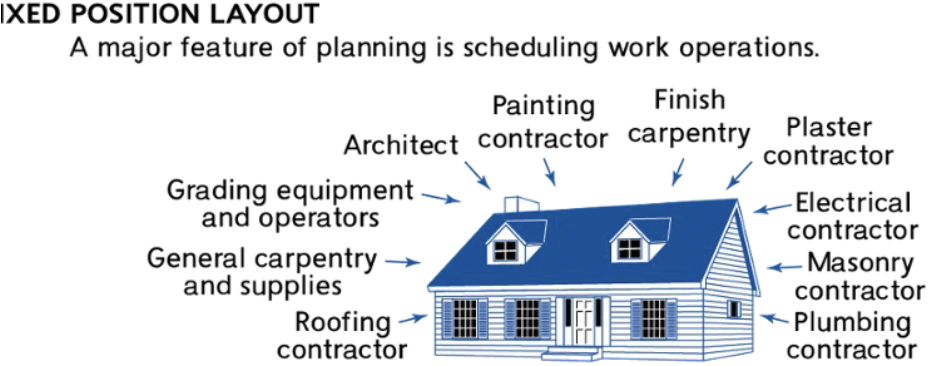
fixed position layout
a major feature of planning is scheduling work operations
Materials Requirement planning (MRP)
a computer-based operations management system that uses sales forecasts to ensure that needed parts and materials are available at the right time and place in a specific company
Enterprise resource planning (ERP)
a computer based application that enables multiple firms to manage all of their operations (finance, requirements planning, human resources, and order fulfilment) on the basis of a single, integrated set of corporate data
the newest version of MRP
Purchasing
the functional area in a firm that searches for quality material resources, finds the best suppliers, and negotiates the best price for quality goods and services
Just-in-time inventory (JIT)
keeps a minimum of inventory on the premises and parts, supplies, and other needs are delivered just in time to go one the assembly line.
to be effective this system requires excellent coordination
will run into problems when suppliers are farther apart
shipments could be delayed for a variety of reasons
Quality Control
maintaining quality means constantly producing what the customer wants while reducing errors before and after delivery to the customer
quality control approaches: Six Sigma Quality
sets a benchmark of just 3.4 defects per million opportunities, detecte potential problems to prevent their occurance
quality control approaches: statistical quality control (SQC)
the process some managers use to continually monitor all phases of he production process and assure quality is built into the product from the beginning
Quality control approaches : statistical process control (SPC)
the process of testing statistical samples of product components at each stage of production and plotting the test results on a graph
quality control approaches: Deming cycle
the process of testing statistical samples of product components at each stage of production and plotting the test results on a graph
Excellence Canada
this is the leading authority in Canada on organizational excellence based on quality systems, innovation, and healthy workplace criteria
The Canada awards for excellence (CAE) are presented annually to private, public, and not-for-profit organizations
ISO series and standards
the international organization for standardization (ISO) is a worldwide federation of national standards bodies from more than 160 countries that set global measures for the quality of individual products
it is a non-governmental organization established to promote the development of world standards to facilitate the international exchange of goods and services
ISO 9001
the common name given to quality management and assurance standards
the standards require that a company must determine what customer needs are, including regulatory and legal requirements
why is ISO 9001 so important
the European Union is demanding that companies that want to do business with the EU be certified by ISO standards
some major Canadian companies are also demanding that suppliers meet these standards
ISO 14001
a collection of the best practices for managing an organizations impact on the environment
certifications in both ISO 9001 and ISO 14001 would show that a fime has world class management system in both quality and environmental standards
Logistics
activities that focus on getting the right amount of the right product or services to the right place at the right time at the lowest possible cost
Supply chain
the sequences of firms that perform activities required to create and deliver a good or service to consumers or industrial users
supply chain management
the integration and organization of information and logistics activities across firms in a supply chain for the purpose of creating and delivering goods and services that provide value to customers
When implementing supply chain management, firms are trying to improve quality, reduce costs, increase flexibility and speed, and improve customer service while reducing the number of suppliers used.
Production Process
consists of taking the factors of production and using the inputs to produce goods, services, and ideas. planning, routing, scheduling, and the other activities are the other activities are the means to accomplish the objective—output
can either be continuous or intermittent
form utility
the value producers add to materials in the creation of finished goods and services (example making silicone unto computer chips as this changes the form)
also exists in services (example: baker turning flour into bread)
process manufacturing
physically or chemically changes materials
assembly process
puts together components
example: eggs, toast, and coffee → breakfast
Ways in which you can improve production techniques
flexible manufacturing
lean manufacturing
mass customization
robotics
computer aided design and manufacturing
3D and additive manufacturing
Flexible Manufacturing
involves designing machines to do multiple tasks so that they can produce a variety of products.
Flexible manufacturing (also known as flex) not only leads to improved productivity, but it may also result in cost savings.
lean manufacturing
the production of goods using less of everything compared to mass production: less human effort, less manufacturing space, less investment in tools, and less
engineering time to develop a new product.A company becomes lean by continuously increasing its capacity to produce high-quality goods while decreasing its need for resources.
Mass customization
tailoring products to meet the needs of a large number of individual customers
Robotics
Mass customization is easy for industrial robotics where machines can work 24 hours a day, seven days a week, with great precision.
Current studies predict that almost a quarter of automated tasks will be performed by robots in the next decade.
CAD, CAM and 3D printing
CAD/CAM, the use of both computer-aided design and computer-aided manufacturing made it possible to custom-design products to meet the
needs of small markets with very little increase in cost.The latest CAM technology includes 3D printers that make a product layer by layer until it appears as a finished good.
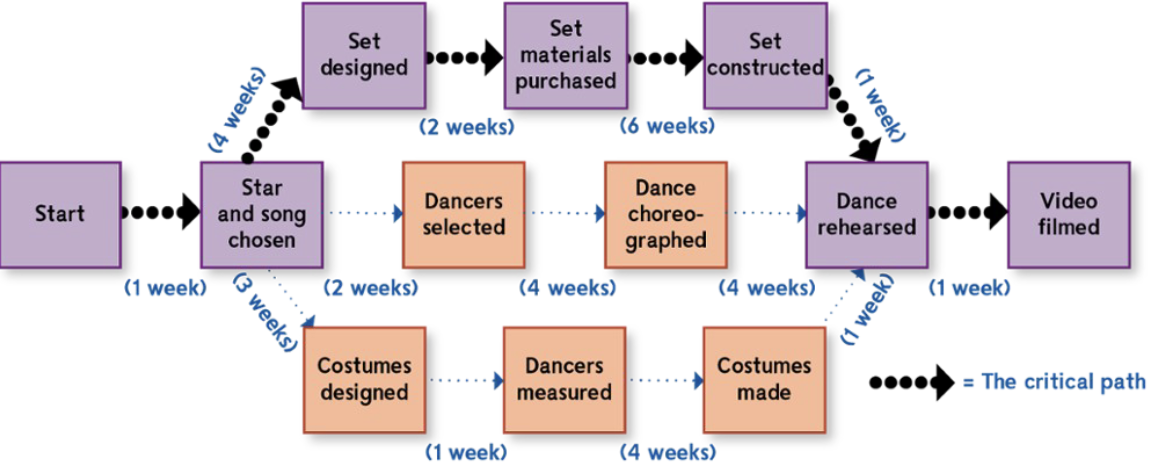
Control Procedurs: PERT
program evaluation and review techniques (PERT) is the technique for monitoring the progress of production
users analyze the tasks to complete a given project, estimate the time needed to complete each task, and compute the minimum time needed to complete the whole project.
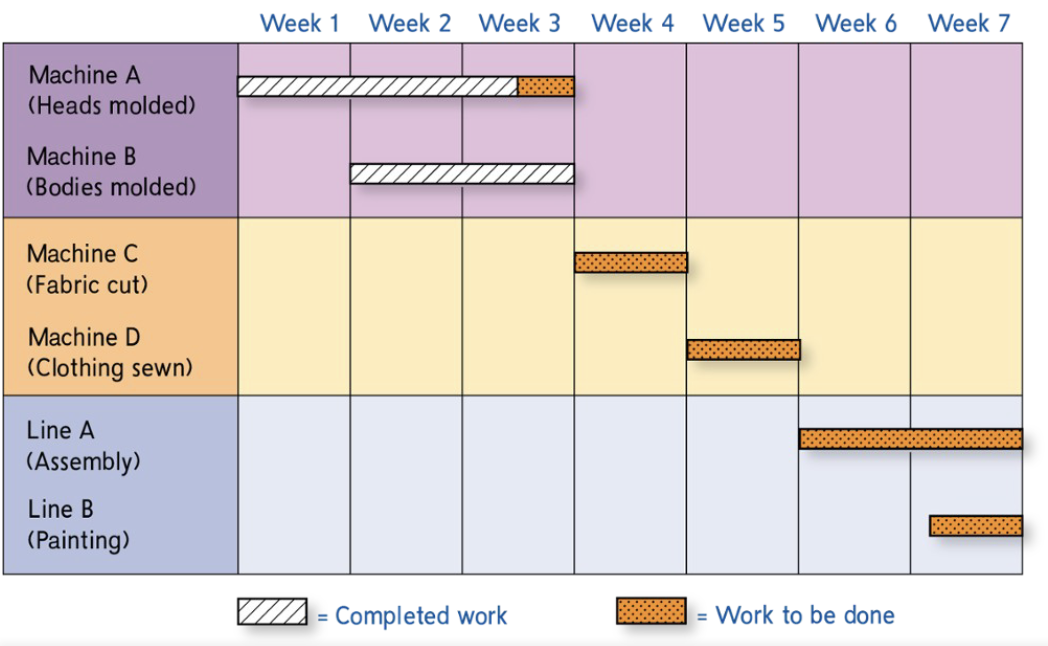
Control procedures: GNATT
A Gnatt chart is a bar graph, now also preperd by computer, that clearly shows what projects are underway and how much of the project has been completed at any given time