Basic Ultrasound Imaging: Techniques, Terminology & Tips
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
US322
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
curved array transducer
provides a large field of view, but in some patients this transducer may be too large to fit in between the ribs to provide adequate contact for accurate reflection of the sound wave
When scanning a patient always use the __________ frequency possible.
highest
smaller footprint transducer
allows the sonographer to scan between intercostal spaces with the patient in a supine, coronal, decubitus, or upright position, but limits the near field of view
It is recommended that the patient fast for _____ hours prior to ultrasound examination of the abdomen.
eight
Fasting helps to reduce the interference that may be caused from ___ overlying the midline abdominal structures
gas
before you scan
patient positions, transducer selection, transducer positions, initial survey of the abdomen
Typical examination is performed primarily in the _______ position.
supine
The beam is ideally reflected when the transducer is ___________ to the surface.
perpendicular
perpendicular
the transducer is straight up and down
subcostal
the transducer is angled superiorly just beneath the inferior costal margin
intercostal
the transducer is between the ribs. it can be perpendicular, subcostal, or angled
angled
the transducer is angled superiorly, inferiorly, or right and left laterally at varying degrees
rotated
the transducer is rotated varying degrees to oblique the scanning plane
The ______ movement of the probe is used with the sweep and slide motion in which the probe is moved greater than one centimeter.
macro
The _____ movement of the probe is used with the sweep and slide motion in which the probe is moved less than one centimeter.
micro
In a survey of the abdomen, the sonographer will initially use the “_____” motion.
sweep
The “_____” motion is used when the transducer is physically moved along the abdomen, such as a longitudinal movement to follow the course of the abdominal aorta into the bifurcation of the iliac arteries.
slide
Once an area of interest is located, the sonographer may pause over the
structure and slowly “____” or pivot the transducer back and forth or up
and down to image the area completely or to follow the anatomical
structure.
rock
A smaller version of the sweep motion is the “___” motion, which is
used when the transducer is minutely swept, pivoting on a point of
interest.
fan
The “______” motion is useful to navigate between the ribs or to
change from transverse to longitudinal planes, where the transducer
is held in one area and rotated 90 degrees to the opposite plane.
rotate
For each study a sonographer should enter
the patient’s name andid#, select the transducer, adjust the TGC, focal zones and image size
Annotation on/off switch
allows comments to be entered on the screen
trackball
allows you to control the position of the measurement cursors
TGC and Gain controls
will brighten or darken areas or whole portions of the image.
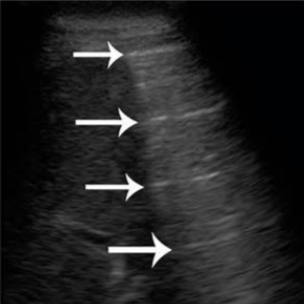
What artifact is this?
reverberation
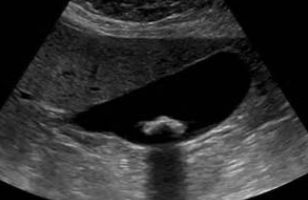
What artifact is shown?
shadowing