Microbial Growth
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
What is and isn’t microbial growth
it is NUMBER of cells, NOT size (observed in colonies/pop)
4 requirements for microbial growth (ideal)
temp
pH
osmotic pressure
organic growth factors
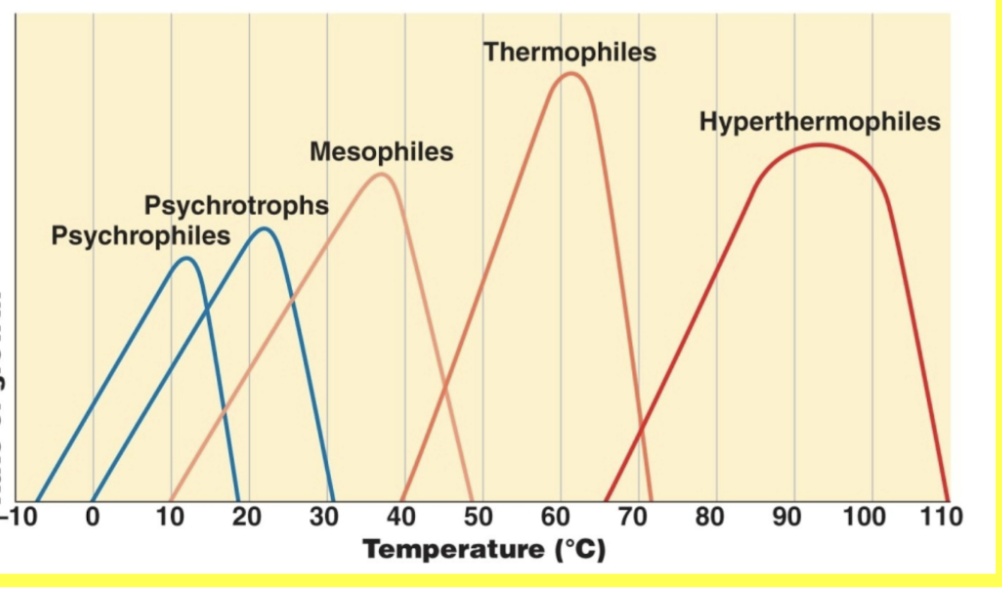
Psychrophiles:
growth range
optimal growth
& what they cause
-10-20 °C
~12 °C
food spoilage 👹🤢

example of Psychrophiles & 2 things they do
Chlamydomonas nivalis 🧊☃🧤❄
grow on Alaskan glaciers &
photosynthetic pigment makes snow red

Psychrotrophs:
growth temp range
optimal growth
0-30 °C
~20s °C

Mesophiles:
growth temp range
optimal growth
10s-50s °C
~30s °C
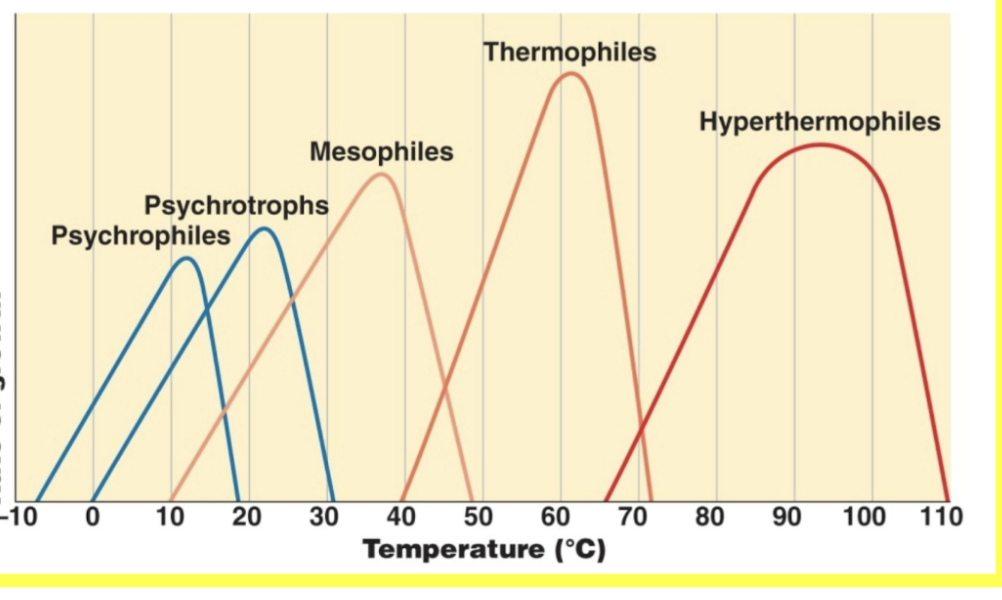
Thermophiles:
growth temp range
optimal growth
40-70s °C
60s °C

Hyperthermophiles
growth temp range
optimal growth
60s-110 °C
90s °C
Optimal pH for most bacteria?
6.5–7.5
Optimal pH for molds and yeasts?
5.0–6.0
Microbes that grow in acidic environments.
Acidophiles
What happens to microbes in hypertonic environments?
↑ salt/sugar🧂 cause plasmolysis.
Difference between:
extreme/obligate halophiles &
facultative halophiles?
require high osmotic pressure
tolerate high osmotic pressure
Barophiles survive under ___, but rupture at ___
extreme pressure,
normal atmospheric pressure
4 examples of organic growth factors
purines 😇
pyrimidines 🛕
amino acids 🧬
vitamins 💊
Why do some microbes live in oxygen free habitats
bc they cant detoxify toxic products
4 examples of toxic products
👱🏻♀️Singlet oxygen (O2)
🦸♂ Superoxide ion (O2-)
👋 Hydroxyl (OH-)
❤🩹 Peroxide (H2O2)

Label these 5 left → right
a) Obligate Aerobes
b) Facultative Anaerobes
c) Obligate Anaerobes
d) Aerotolerant Anaerobes
e) Microaerophiles

Which 2 enzymes neutralize toxic oxygen?
Catalase
Superoxide Dismutase

Biofilms:
mechanism used
form _
share _
communicating microbial communities🗣🌳
form hydrogels/slime💧
share nutrients/shelter 🍔🏕

Hydrogels:
mechanism used
formed by
attracted to
quorum sensing
biofilms
chemicals 🧪

Biosafety Level Labs (BSL) precautions
no special, but
cabinets for airborne pathogens 🌬🗄
sealed,neg pressure rooms w filtered exhausts🔒𖣘
4 ways bacteria reproduce thru
conidiospores (actinomycetes🎭🎬)
filament/fragmentation
binary fission
budding
Phase: Cells not dividing yet
Lag Phase
Phase: Cells dividing rapidly bc metabolically active
Log Phase
Phase: Net growth zero bc death and birth rate equal & limited nutrients
Stationary Phase
Phase: Cells dying exponentially
Death Phase
What are the 3 direct methods of measuring microbial growth?
filtration 🚿
plate count 🍽
direct microscope count 🔬
Direct Plate Count:
counts _
how many _
involves _
colonies after incubation 🍽
25-250 CFUS
serial dilutions 1:10 1:100 1:1000 till all counted
Pour Plate Method:
describe
where colonies grow
dilution mixed with melted agar;
colonies grow inside AND on surface.

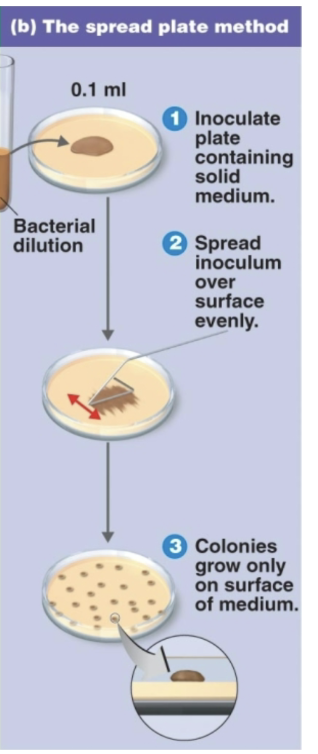
Spread plate
describe
where colonies grow
dilution spread on agar surface;
colonies grow only on surface.
Direct membrane filtration
what kind of bacteria
what used
how counted
bacteria low conc (i.e. water)
100ml water filtered thru mem w holes
those stuck on mem incubated & counted

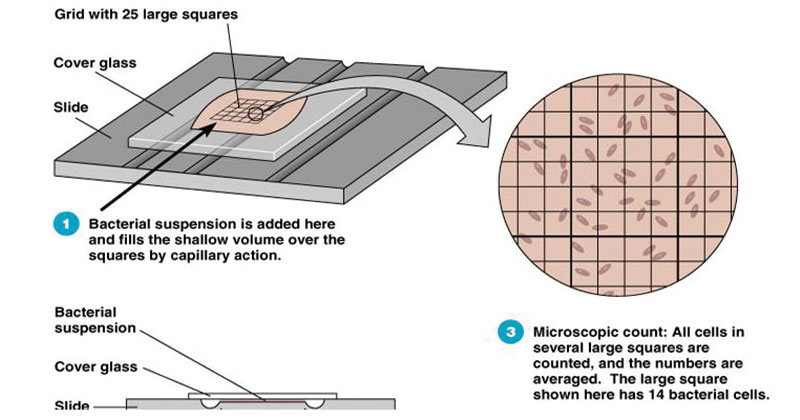
Direct microscopic count:
instrument
counts all _
disadvantage
advantage
hemocytometer grid 🩸🧫📏
counts all cells in fixed volume, →
can't distinguish live/dead cells
fast
Direct Microscopic Count:
Viable Colony Count
Direct Cell COunt
Viable: counts only living cells able to form colonies
Direct: counts all cells (living/dead)
most common indirect method of measuring microbial growth & describe
spectrophotometry 📸
measures turbidity (cloudiness)
more turbidity= ↑ bacterial pop
