Bio 462 Week 1
1/111
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
112 Terms
Dreams
What does not fit the input-output model for the brain?
Action
Brain is there to predict to lead to
Movement
Appearance of neurons coincided with appearance of
Nervous system
Builds a model of the world (internalizes the physical world)
Future
Nervous system builds a virtual model of the
Neuronal Ensembles
Groups of neurons get activated together to build internal symbolic structures
Thoughts
Symbols, representations, ideas, perceptions, memories, emotions, movement plans
exist internally without outside stimulus
build an “internal brain state”
Hierarchy
The neuronal ensembles are organized in hierarchies (different levels)
Wiring
links different modules (specific diagrams that must be precise)
Precise connections
“labeled lines” design (neurons connect only with particular ones) ex: taste pathways
Distributed connectivity
Indiscriminate, many connections pruned and tweaked through learning
Ensembles
independent units that can construct more complex structures
Learning
shapes the distributed connectivity by pruning connections not needed
Some connections get stronger, some get weaker
The brain draws information from the outside world and stores it
a key component of the prediction-action model
Associative learning
two neurons responding to two separate stimuli
Two stimuli happening over and over at same time: connections strengthen,
neurons form a unit, stimuli get associated, new concept learned
Maps
The wiring diagrams are organized in maps which provide representations
ex: position of object in space correlates to specific position in retina
Control
Compares output with the prediction
if there is an error signal/wrong outcome then fine-tuning of output=feedback control
Optimization
Work must be performed effectively at minimal cost
ex) retina can react to a single photon
1/3 and 2/3
gene expressed uniquely in the nervous system; total genes expressed in the nervous system
Ion currents
Neurons send signals to each other via electricity provided by _____
Axon
Output of the signal, extends for long distance signaling
Dendrites
Receives the signal, axons usually connect to ____ of another neuron
Convergent connection
One neuron connects to another neuron
Divergent connection
One neuron connects to multiple neurons
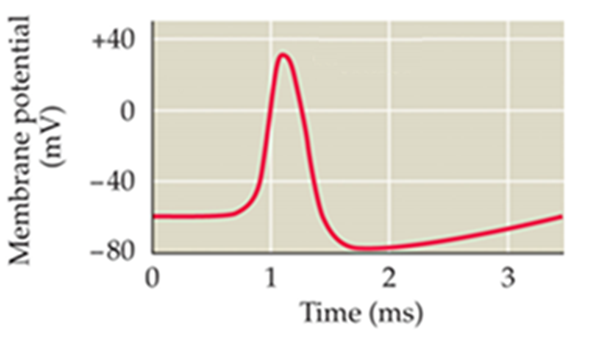
Action potential
All or none. generated by neurons when they want to signal
results from integration of several inputs if the threshold of depolarization is reached
Its amplitude is constant
transient increased permeability to Na followed by slower and prolonged permeability to K+ to restore the resting potential
Synapses
Neurons connect to other neurons through
Chemical synapse
secretion of neurotransmitter between a pre-synaptic and a post-synaptic terminals
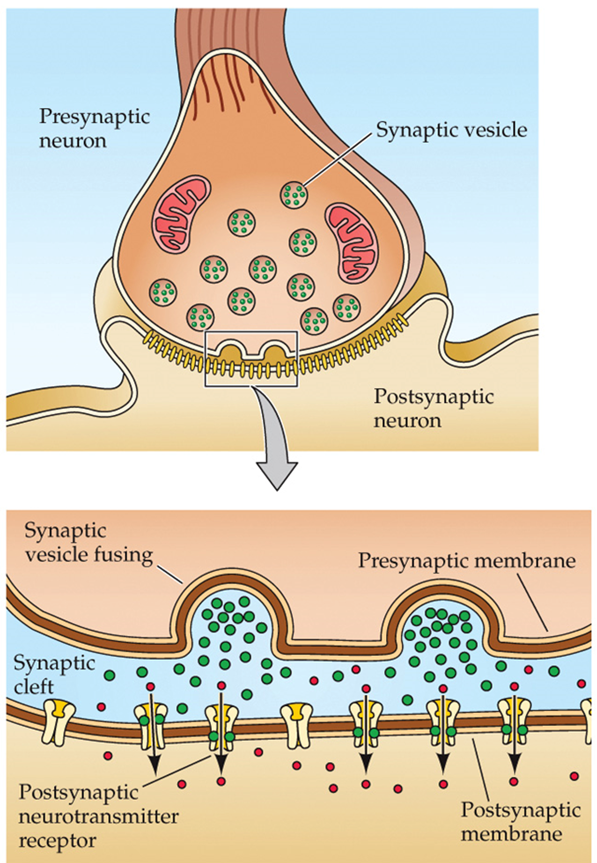
Post-synaptic cell
expresses the receptor of the neurotransmitter (chemical synapse)
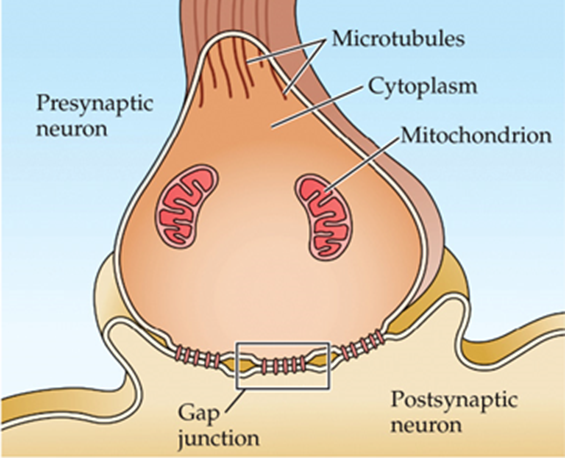
Electrical synapse
direct link between neighboring cytoplasms
Local potential
slow and graded: their amplitude depends on the intensity of the input
ex: Synapses, sensory neurons (sensory receptors)
Ionotropic
-ion channels opening with ligand
Fast acting
Metabotropic
-coupled to second messengers
- Slow acting
Post-synaptic potentials
The movement of ions induces
ESPS
excitatory post-synaptic potential
ISPS
inhibitory post-synaptic potential
Spines
The axons of excitatory terminals contact dendritic
helps signaling become more efficient
Soma
Inhibitory neurons can contact ____, not spines
Central Nervous System
Brain and spinal cord
Cell bodies in brain and spinal cord
Peripheral Nervous System
Cell bodies outside of brin and spinal cord
Sensory systems
Receive and process information from environment (input)
Motor systems
Generate movement (control muscles) (output)
Associational systems
Complex brain functions
Astrocytes
Maintain a balanced environment around neurons, star shaped (“astra”)
Glial cells
Astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, and Schwann cells
Oligodendrocytes
CNS, form myelin around axons
can contact multiple axons at once
Schwann Cells
PNS, form myelin around axons
establish a 1:1 relationship with axons
Microglia
“Immune” cells of the CNS, mediate inflammation, same origin as macrophages, participate in the pruning of synapses
Resting potential
All cells have unequal distribution of ions on both sides of the membrane: creating a
Electroneutral
Inside and outside of the cell
cytosol, extracellular fluid
-40 to -90 mV
Neurons’ resting membrane potential
Impermeable
Plasma membrane is ____ to ions
Electrodes
allow measurements of membrane potentials
There is always a reference __ (outside of the cell)
Electrical potential
amount of work necessary to move charged particles (reflects the difference of charge between two sides)
Expressed as voltage
Greater
A ____ difference of potential will move more charges (more current will flow)
Equilibrium potential
Two compartments separated by impermeable membrane
Only K+ allowed to go through
Same concentrations on both sides = same amounts of ions = no difference of potential
Outside
Which has a higher concentration? outside or inside
Down
K+ ions diffuse ____ their gradient of concentration
Negative
Inside compartment: loses ions = becomes more
Positive
Outside compartment: gains ions = become more
Electric field
Newly established difference of potential creates an _____
Diffusion force
will push the K+ ions from inside to outside
Electric force
will push K+ ions from outside to inside
net flow of ions null + equilibrium potential
When electric force = diffusion force
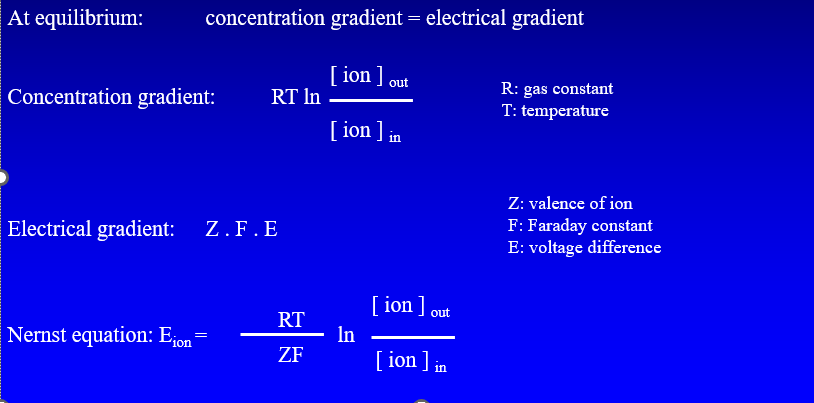
Nernst equation
predicts the equilibrium potential for a given ion across a membrane
Giant squid nerve cells
Insert electrodes into ____
large axon conducts electrical signal fast, allowing rapid excitation and contraction of muscles to escape predators more easily
Current
What is the direction of cation movement called?
Inward
Positive current
depolarization
Outward
Negative current (pos charges leaving the cell)
hyperpolarization (inside is more negative)
ionic concentrations, membrane potential
Small changes in ______ can cause large changes in
Uneven
____ charges align close to the membrane
Capacitance
The membrane “stores”charges
Active transporters
move ions against their concentration gradient
happens when Outside and inside concentrations of ions are different
Lipidic membranes
selectively permeable: ions need to pass through specific channels to diffuse
Equilibrium
balance between chemical and electrical forces
Ion gradient can determine the electrical potential
OR
Electrical potential can determine the ion fluxes
Goldman equation
takes into account the relative permeabilities to ions
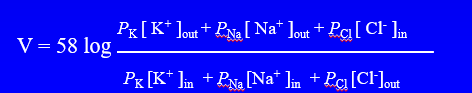
-58 mV
Membrane permeable to K+ only
+58 mV
Membrane permeable to Na+ only
Ion transporters
Maintain different concentration of ions on both sides of the membrane
Rest
Permeability to K+ greater
More K inside than out = negative membrane potential
Depolarization
Na flows in (permeability increases)
positive membrane potential and generation of action potential
Increases resting potential
Increasing the concentration of K+ outside of the neurons causes
Smaller amplitude
Decreasing the external concentration of Na+ induces an action potential with a
True
The resting potential is not affected by the external Na+ concentration
Opening of ion-gated channels that will let in Na+ or K+. Ion permeability is sensitive to the membrane potential which needs to be above a certain threshold to generate an action potential.
What causes these changes in membrane permeabilities ?
Voltage Clamp
to study ion permeability at any level of membrane potential
enables control of the membrane voltage of the cell
Amount of injected current = direct measurement of the sum of all ionic currents across the membrane.
Examines how the membrane potential affects ion flows (currents) across the membrane.
No current flows except for brief ones
What happens after hyperpolarization?
Inward current
Positive charges from outside to inside
voltage changes
What does a Capacitive current compensate for?
Time-dependent
For axons, __________ stimulus will generate an additional capacitive current.
rapid inward current then slow delayed outward current
What happens at depolarization?
voltage-dependent
the membrane permeability of the axons is
Early vs late current
two types of current
Early current: has a U shape, increases with increased membrane potential but starts to decrease with membrane potentials above 0 mv
Late current: increases with increasing membrane potentials
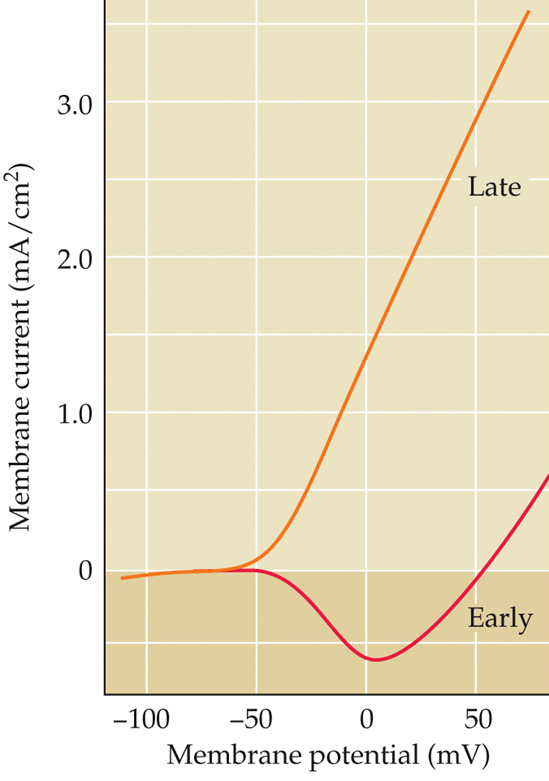
Early current
reverses from inward to outward at around +55 mV = equilibrium potential of Na+
Extracellular concentration of Na is high=early current is inward
extracellular concentration of Na is low= early current is outward (Na leaves the cell)
Late current
Efflux/outward current of K+ affects
External Na+ does not affect this
Early influx of Na+ and delayed efflux of K+ when increasing the membrane potential
Current is affected by
Tetrodotoxin (Na) tetraethylammonium (K)
Toxins that block either Na+ or K+ currents
Membrane Conductance
reciprocal of resistance, related to permeability

Na+: rapid increase, rapid decrease (activation then inactivation after K+ is activated)
K+: slower delayed increase
Both conductances are activated time-dependently
How do the conductances of Na+ and K+ change over time?
Small
Second action potentials are ___ due to 4.5 ms interval between two stimuli
Refractory period
axon is not as excitable
Na+ conductance increasing/depolarization creating a feedback loop
Voltage increase leads to