S1.2 Nuclear Atom
1/17
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
What are subatomic particles?
The protons, neutrons and electrons that an atom is made up of are called subatomic particles
Protons have a relative mass of 1 and a relative charge of +1
Neutrons have a relative mass of 1 and a relative charge of 0
Electrons have a relative mass of weell and a relative charge of -1
Why are they referred to as relative charge and relative mass?
Subatomic particles are so small that they cannot be measured through normal units and thus, their mass is comparative/in comparison to each other.
It is also referred to as relative charge, because it is in comparison to each other.
Define Mass number
The mass number determines the mass of an atom and is the total number of nucleons in an atom.
Define atomic number
the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom
Why is a typical atom neutral?
In a typical atom, the number of protons, which are positively charged are equal to the number of electrons, which are negatively charged and so, they cancel each other out
Define the Nuclear Notation
It is the way elements are presented
The upper number is the mass number known as A
The lower number is the atomic number known as Z
What are the roles of protons, neutrons and electrons?
Protons :
The number of protons in an atom determines its atomic number, which in turn identifies the element.
Protons contribute to the overall positive charge of the nucleus.
In chemical reactions, the number of protons remains constant
Neutrons:
Neutrons are neutrally charged particles found in the nucleus of an atom.
Neutrons contribute to the mass of the atom without significantly affecting its chemical properties (except in nuclear reactions).
The number of neutrons can vary within atoms of the same element, giving rise to isotopes.
Neutrons help stabilize the nucleus by counteracting the repulsive forces between positively charged protons.
Electrons:
Electrons are negatively charged particles that orbit the nucleus of an atom in specific energy levels or shells.
Electrons determine the chemical behavior of an atom, as they participate in bonding with other atoms to form molecules and compounds.
The number and arrangement of electrons determine the atom's size, shape, and reactivity.
Electrons are involved in various chemical reactions
Electrons are also involved in phenomena such as electricity and magnetism due to their charge and motion.
Describe the structure of an atom
Atoms have a a positively charged, dense nucleus
This is because the nucleus has protons and because most of the mass of an electron is concentrated there
Negative electrons occupy the space outside the nucleus, electron cloud
The electrostatic attraction between the positive nucleus and negatively charged electrons orbiting around it is what holds an atom together
Define Ions
ions are atoms or molecules that have gained or lost one or more electrons, thus acquiring a net electrical charge.
When an atom gains electrons, it becomes negatively charged and is called an anion. When an atom loses electrons, it becomes positively charged and is called a cation.
Define Isotopes
different atoms of the same element that contain the same number of protons and electrons but a different number of neutrons
Define Relative Atomic Mass
the average mass of one atom of an element compared to one twelfth of the mass of an atom of carbon-12'
How do you calculate relative atomic mass using abundance values?
total mass of 100 atoms = (% abundanceA x massA) + (% abundanceB x massB)
What is a mass spectrometer?
an instrument to accurately determine the relative atomic mass
separates atoms or molecules based on their charge
this can be used to identify substances
Describe the layout of a mass spectrometer
There are four key stages
Ionisation where atoms are converted to ions
Acceleration where ions are accelerated
Deflection according to their mass and charge
Detection arrival at detector
→ this must happen in a vaccum so ions do not collide with air molecules which may stop them from reaching the detector
→ must be in gaseous state
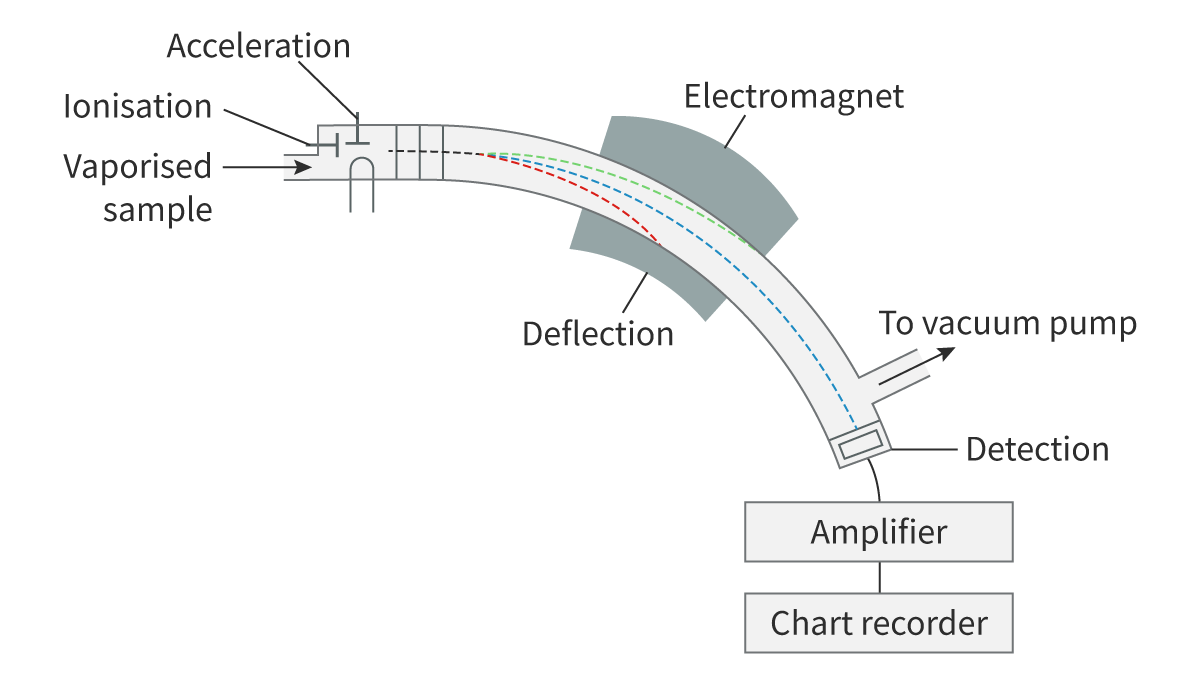
Describe Stage 1
Ionisation
A beam of electrons knock into electrons from atoms or molecules in the sample
Nearly all will lose at least one electron even the noble gasses and non-metals which typically gain electrons
In this case, all ions in a mass spectrometer are positive
Describe Stage 2
Acceleration
The ions are accelerated so they have the same energy
Describe Stage 3
Deflection
Ions deflected by a magnetic field according to the ratio of their mass to charge (m/z)
heavier ions are deflected less than lighter ones
Describe Stage 4
Detection
Magnetic field is gradually increased which increases deflection
allows ions of increasing mass to enter the detector
when striking the detector they accept electrons, lose charge and create a current
current is proportional to abundance of each ions