Integumentary system
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
macule
is a flat area of color change and a non-palpable skin lesion
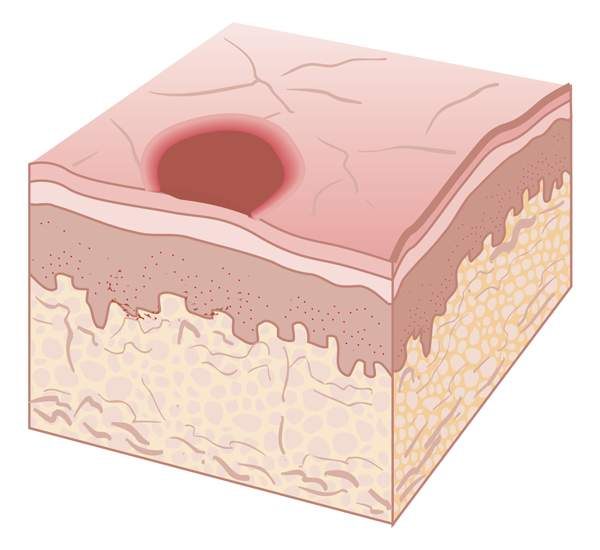
papule
solide elevation < 0.5cm in diameter and has distinct borders
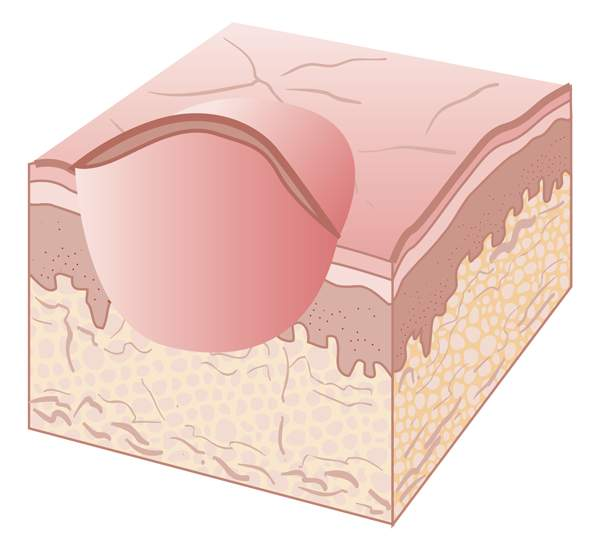
nodule
firm and movable solid elevation 0.5–1 cm in diameter and extends deeper into the dermis than a papule
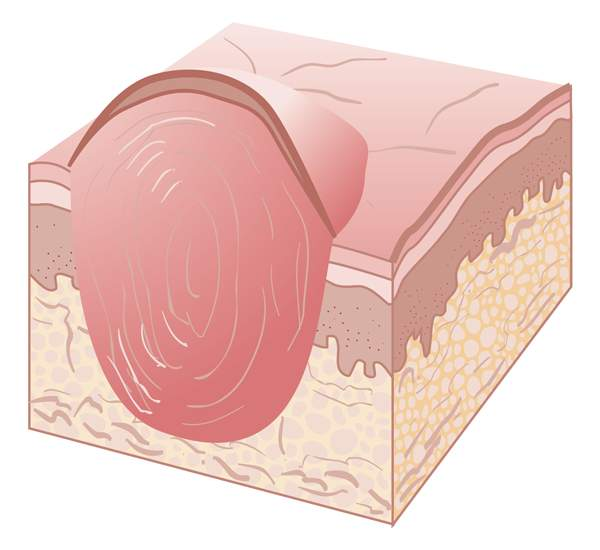
vesicle
is a small, raised blister that contains clear fluid inside or under the epidermis
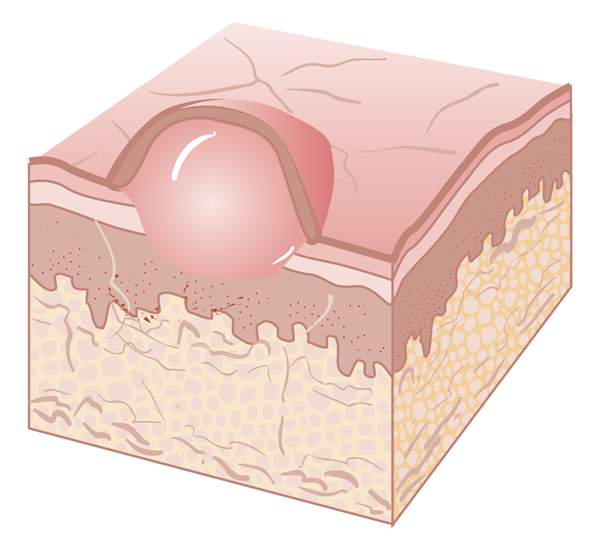
bulla
large vesicle greater than 0.5 cm
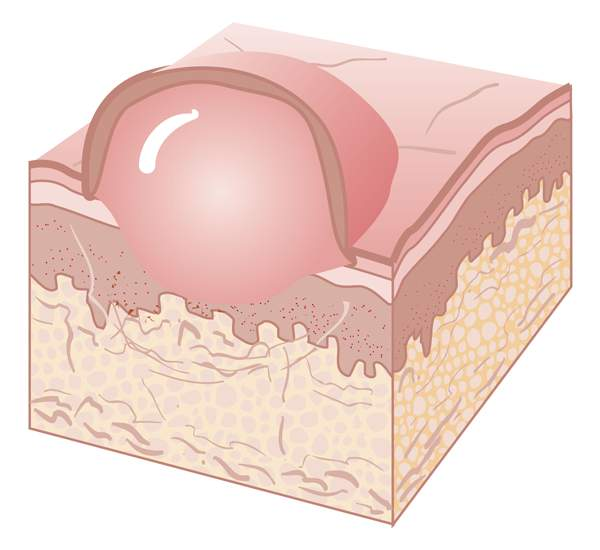
pustule
vesicle with white cellular debris, may be infected or sterile
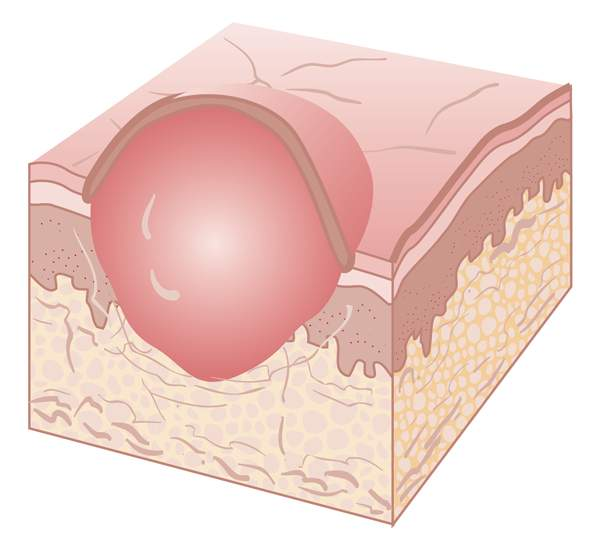
tumor
solid mass larger than 1.0cm
large nodule and may be firm or soft
ex. squamous cell carcinoma
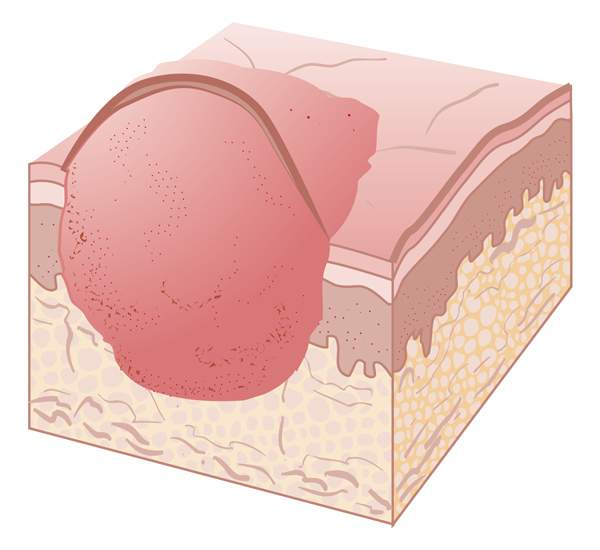
plaque
solid, elevated, flat-top lesion with indistinct borders
It is found on the skin or mucous membrane
Thrush is an example of plaque
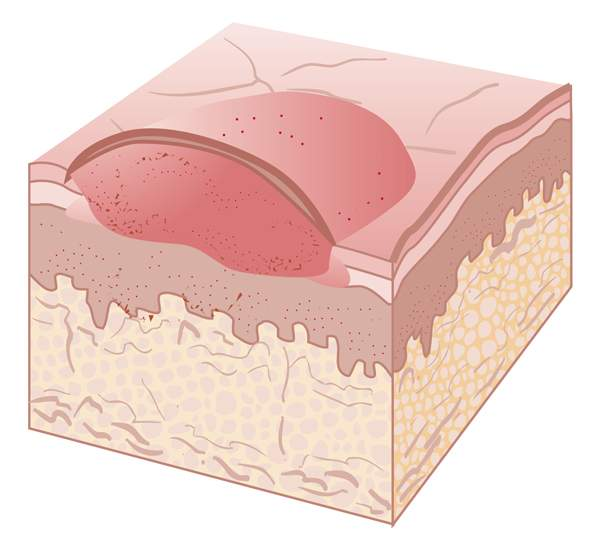
wheal
type of plaque
palpable, red, circumscribed swelling in upper epidermis
intradermal skin tests produce wheals
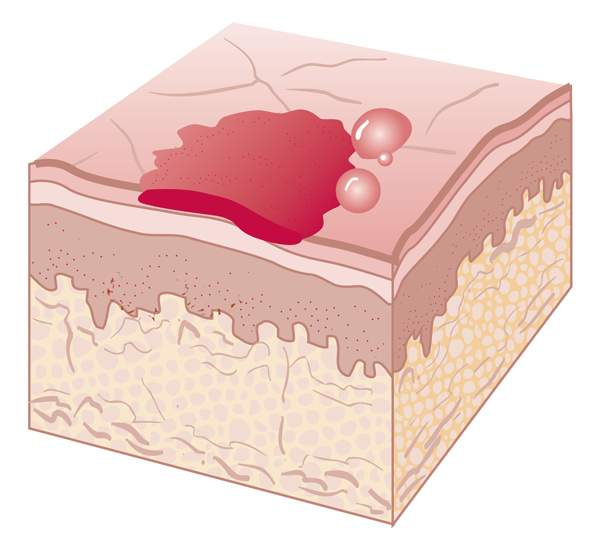
secondary lesions
evolve from primary lesions because of constant irritation or infection
scales
flaking layers of epidermis
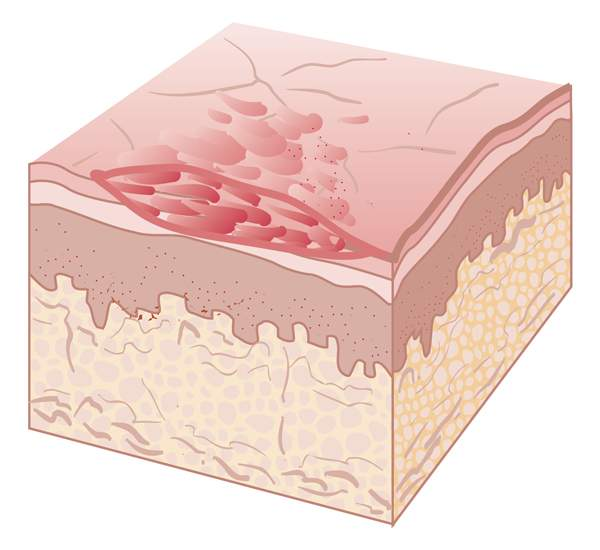
crusts
crust is dried exudate (leaked fluid from blood vessels) on the skin
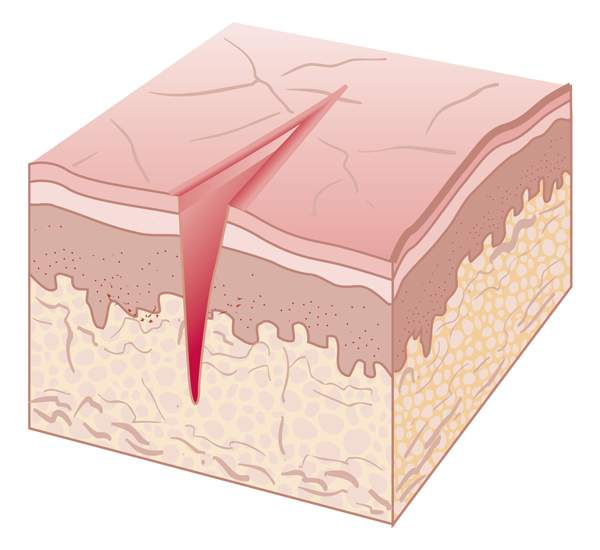
fissures
linear, wedge-shaped crack extending into the dermis
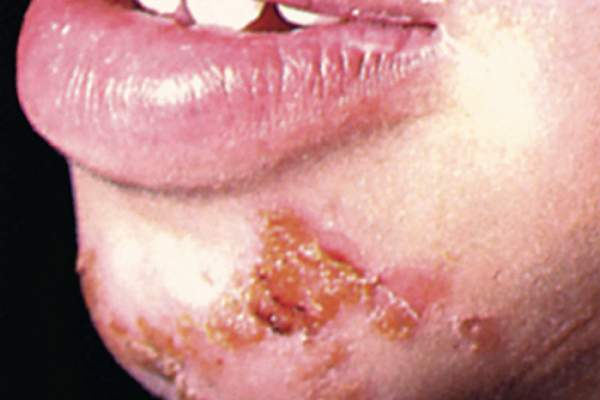
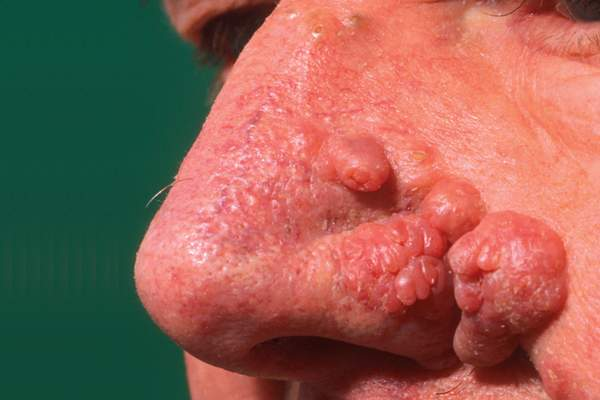
impetigo
caused by streptococcus or staphylococcus aureus. A common characteristic of impetigo is the formation of crusty lesions and small vesicles around the nose and mouth (may often be across the entire face).
Honey-colored exudate is excreted from areas of impetigo.
The treatment includes oral antibiotics and possibly topical antibiotic cream
acne
caused by hair follicles blocked by oil or dead skin
common during puberty
Its causes include an inherited predisposition, hormonal fluctuations, exposure to heat and humidity, and the use of oily creams
The treatment includes using benzoyl peroxide-based face wash twice daily and topical applications. In more severe cases of acne, an oral antibiotic may be prescribed for several weeks or months
rosacea
Rosacea is characterized by inflammation, pustule formation, and small, red, edematous (swollen, puffy appearance) lines on the skin
Treatment includes topical antibiotics and, in severe conditions, oral antibiotics
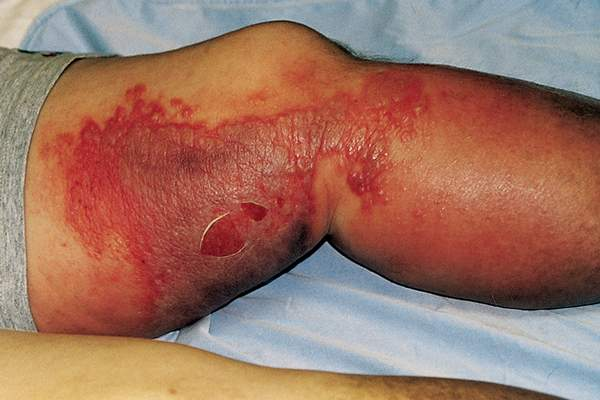
cellulitis
Cellulitis is an acute bacterial infection that involves the subcutaneous tissue and manifests as redness, tenderness, swelling, and warmth at the site
Treatment includes oral antibiotics. In some cases, patients are hospitalized and may receive IV antibiotics
fungal infections
pruritic (itchy) lesions with distinct border
treatment: topical antifungal agents such as clotrimazole (Lotrimin), ketoconazole (Nizoral), econazole, or nystatin (Mycostatin).
commonly caused by pathogens subsisting (surviving) on dead tissue in the epidermis
viral infections
virus invades body
include warts, cold sores/herpes simplex, shingles/herpes zoster,
treatment: analgesic and antipruitic medications
parasitic infections
include scabies and prediculosis
severe rashes and itching over body
scabies
caused by Sarcoptes scabiei and is characterized by intense itching, a body rash, and a sensation of something crawling on the skin.
treated only through prescribed medication.
pediculosis
caused by lice
treatment with lice-medicated shampoo and steps to prevent reinfestation
ulcerations
destruction of epidermis in a area
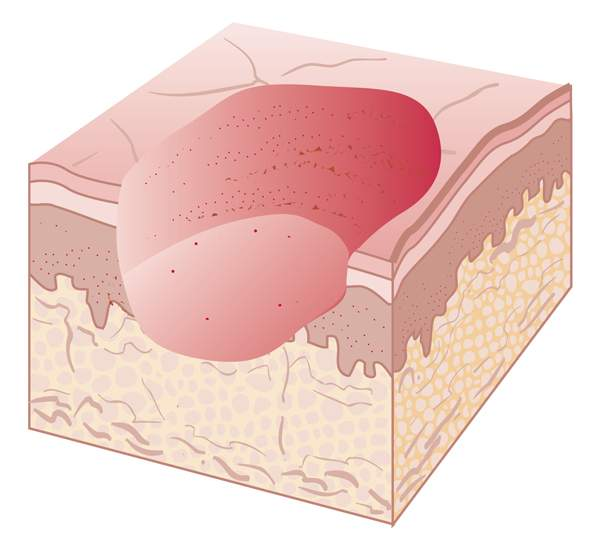
scars
form due to excess collagen production after injury
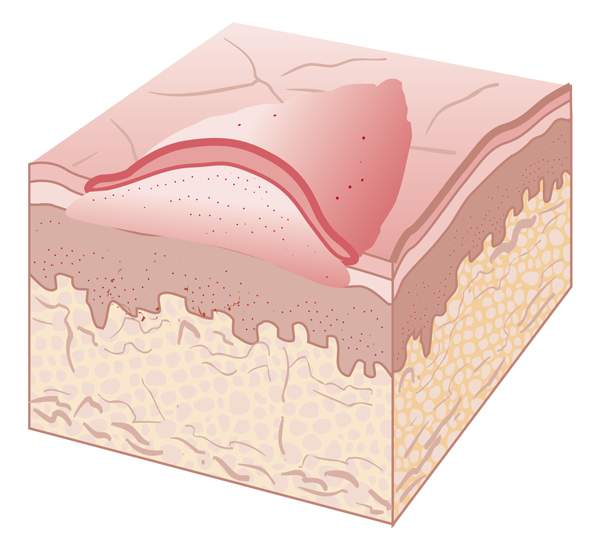
atrophy
loss of a portion of the skin
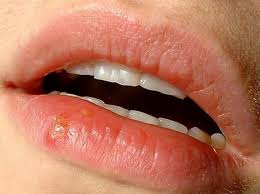
herpes simplex
virus infection
cold sores
caused by herpes simplex virus 1 and manifest as painful ulcers along gumline or mouth or lip
herpes zoster
viral
shingles
acute inflammatory disorder (short-term inflammatory response) caused by herpes zoster virus
painful rashes on body and occasionally face
treatment: vaccines
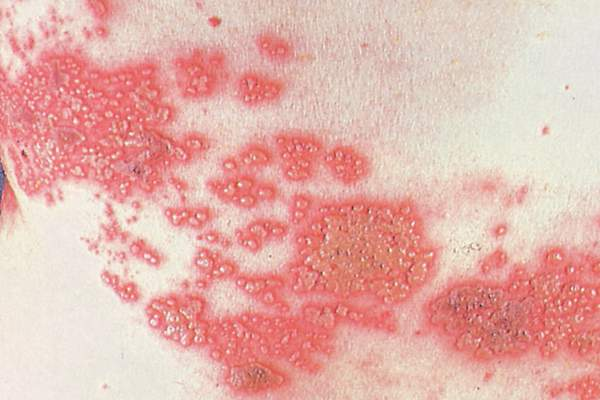
warts
viral
bumps on skin caused by human papilloma virus
tinea pedis
fungal infection
althetes foot
tinea cruris
fungal
jock itch
tinea corporis
fungal
ringworm