Unit 2.6 Reversible Reactions, Industrial Processes and Important Chemicals
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
What is a reversible reaction
A reaction which occurs in 2 direction, the product can react to form the original reactants.
A+B⇌C+D
For A+B⇌C+D, which are the products for the forward reaction and which are the product for the backward reaction?
Forward = C+D
Backward = A+B
How can the direction of a reversible reaction be changed
Changing these condition
Pressure
Temperature
Concentration
If the forward reaction is exothermic, will the backward reaction be endothermic or exothermic
Endothermic, the same amounts of energy is transferred
What is the reaction in Haber process
Nitrogen + Hydrogen ⇌ Ammonia
N2 + 3H2 ⇌ 2NH3
What can ammonia be used for
To produce nitrogen-based fertiliser
Where can nitrogen and hydrogen gas be obtained
Nitrogen = air
Hydrogen - natural gas or other sources
What condition required for the Haber Process
High temperature (450 degree)
High pressure (200 atm)
Iron catalyst
What happens during the Haber Process
Purified bases passed over iron catalyst
Some nitrogen and hydrogen reacts to form ammonia
Some ammonia breaks down into nitrogen and hydrogen because the reaction is reversible
Mixture is cooled, ammonia liquefies and is removed
Remaining nitrogen and hydrogen is recycled
What does it mean for the Haber proceed to be in dynamic equilibrium
Forward and backward reaction happen at a constant rate once equilibrium is reached
In which way does the equilibrium shift in the Haber process when pressure is increased? Why?
Equilibrium shift to the right. Because the total number of mole of gas is fewer on the right
The forward reaction of the Haber process is exothermic. How can the conditions be changed to produce more ammonia?
By lowering the temperature, the forward reaction is favoured
What are the disadvantage of using a low temperature and very high pressure
Low temperature = slow rate of reaction
High pressure = requires high energy
What are the two things aimed to be maximised when choosing the condition of the Haber process
Rate of reaction and the yield of ammonia
How can the presence of ammonia gas be tested
Moist red litmus paper will grin blue as ammonia is alkaline
How can the presence of ammonium ions be tested? What is the ionic equation for this reaction
Add solution containing hydroxide ion such as NaOH
Test for ammonia gas
NH4 + OH —> NH3 + H20
What kind of reactions are used to make nitrogenous fertiliser from ammonia
Neutralisation reaction
What are some example of nitrogen Ouse fertiliser
Ammonium sulfate
Ammonium nitrate
How can ammonium sulfate be formed from sulfuric acid
Ammonia + Sulfuric acid —> Ammonium sulfate
Ammonium hydroxide + sulfuric acid —> ammonium sulfate + water
What are the 2 ways used to form ammonium nitrate from nitric acid
Ammonia + nitric acid —> ammonium nitrate
Ammonium hydroxide + nitric acid —> ammonium nitrate + water
What are the advantage of using fertiliser
Increases crop yield and growth
Increase profit for farmer
What are the disadvantage of using fertiliser
Eutrophication when fertiliser are washed off into rivers and lakes
Change pH of soil
Cause cause baby blue syndrome
What does it mean for sulfuric acid to be a strong acid
It completely dissociated H+ ion in aqueous solution
What is the molecular formula and structure of sulfuric acid
H2SO4
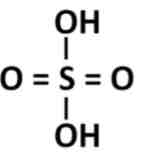
What is the contact process
The manufacture of sulfuric acid
What is the first, second and final step of the contact process
Sulfur is burned in air and reacts with oxygen to form sulfur dioxide
S + O2 —> SO2
Sulfur dioxide reacts further with oxygen to form Sulfur trioxide
2SO2 + O2 ⇌ SO3
Reversible
Temperature = 450
Catalyst = V2O5
Pressure = 2atm
Sulfur trioxide reacts with water to form sulfuric acid
H2O + SO3 —> H2SO4
What are the uses of sulfuric acid
Fertiliser
Processing metals
Petroleum refining
What does a dehydrating agent do
Removes water from other compounds
How does concentrated sulfuric acid acts as a dehydrating agent with sugar
Concentrated sulfuric acid removes 6 water molecule per glucose molecule
Highly exothermic reaction
Water molecules released as steam and a black mass of carbon forms
What change can be observed when concentrated sulfuric acid act as a dehydrating agent on hydrated copper sulfate
Blue crystal (hydrated cooper sulfate) —> white powder (anhydrous copper sulfate)