Class 6- Carbs, Sugars, starches, and fibres
1/47
Earn XP
Description and Tags
sandy Phillips, she. 4
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
carbohydrates name meaning
carbo (C) + hydrate (h20)= CH2O
why are plants important in relation to carbs?
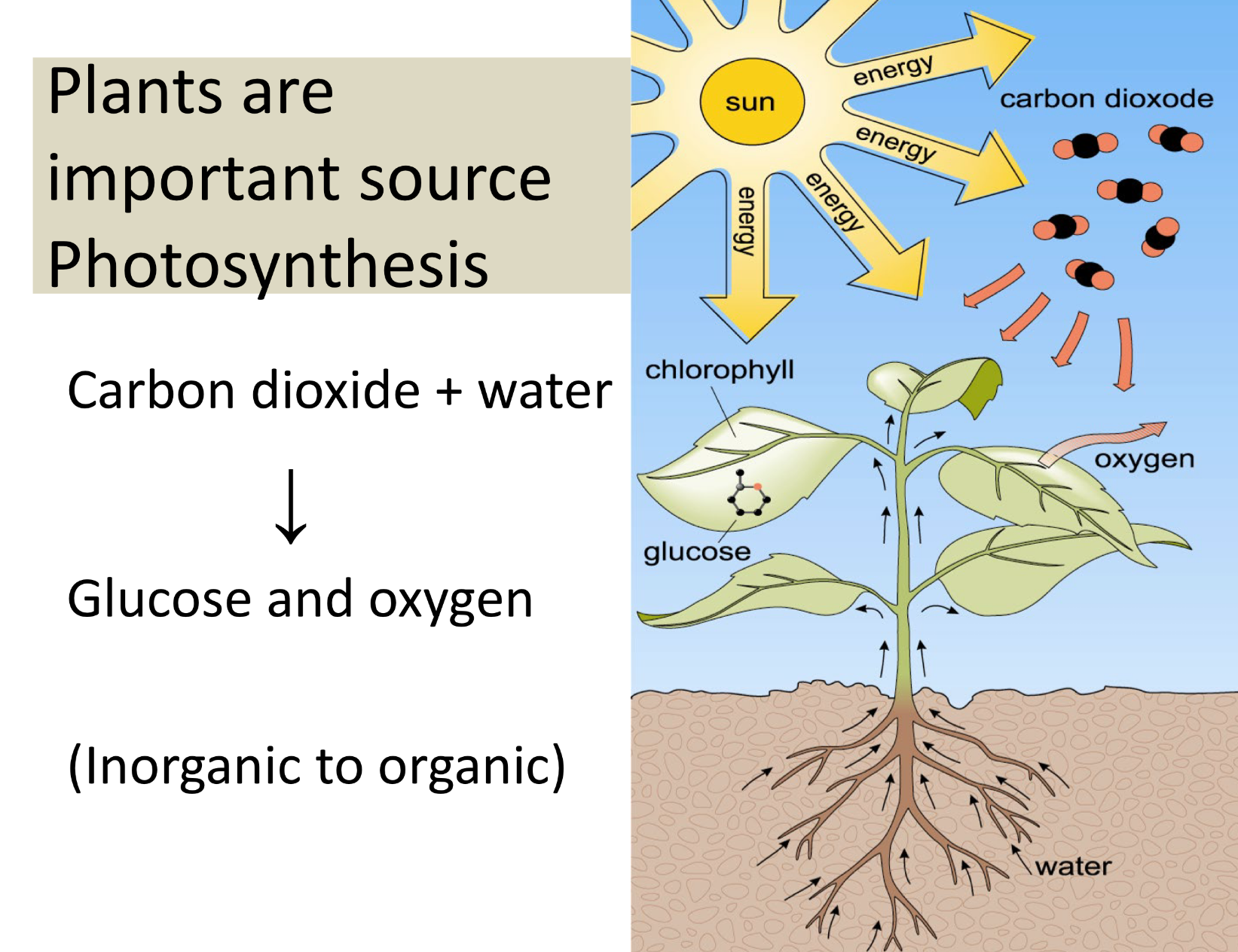
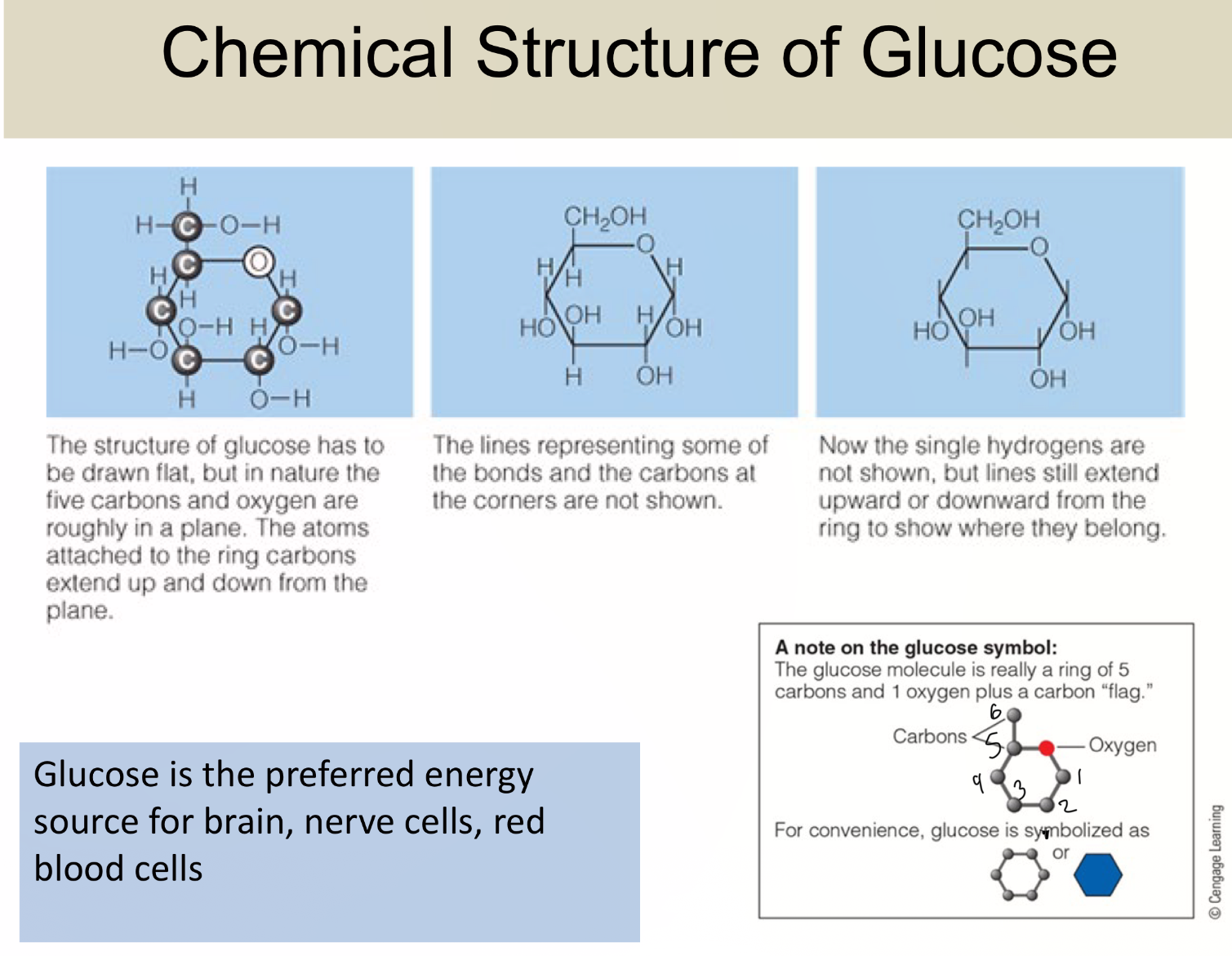
glucose is..
PREFERRED energy for brain, nerve cells, RBC,
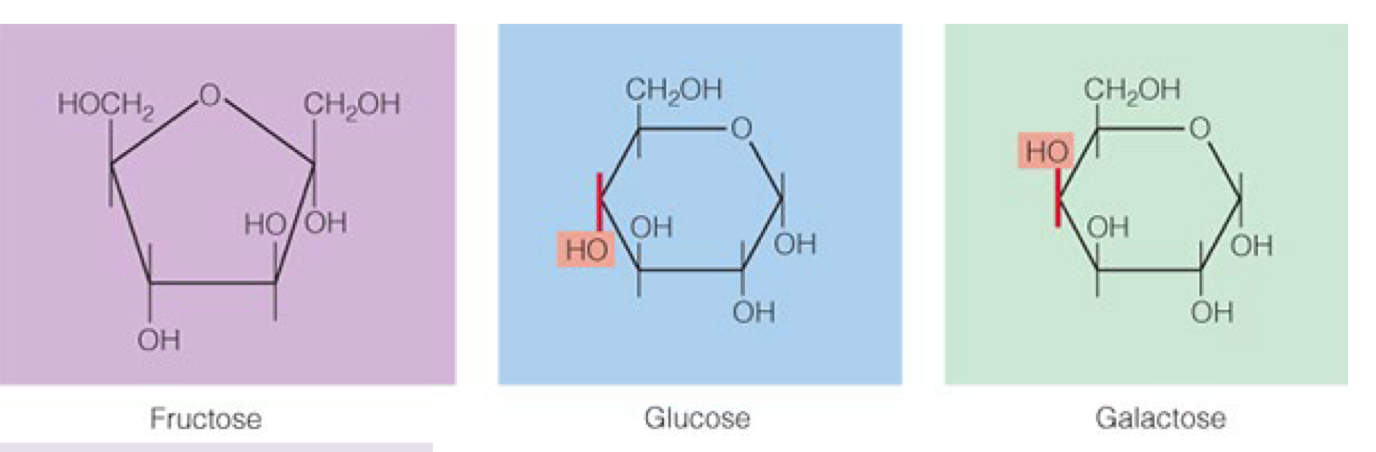
classic monosaccharides (3):
ALL C6H12O6
Fructose= pentagon, founding fruits and honey, the SWEETEST of all sugars
glucose=blood sugar, part of every disaccaride
galactose= naturally in dairy
**Glucose and galactose differ in orientation of OH position**
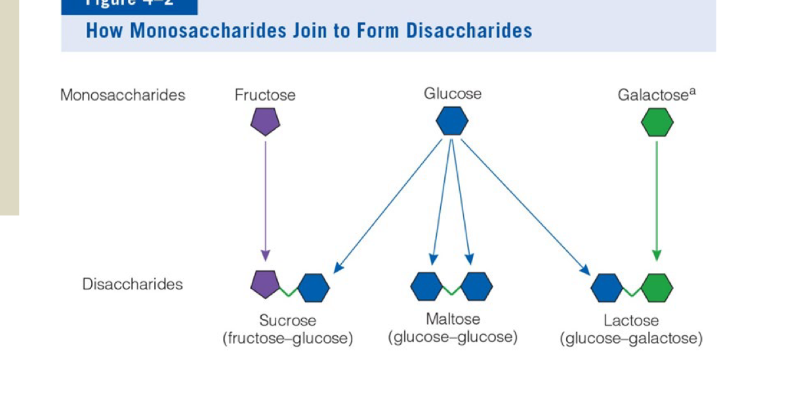
classic disaccharides (3), how are they formed VS broken
all formed via condensation rain, water molecule is released
all broken via hydrolysis, usually occurs during digestion
maltose= glucose+glucose, eg barley
sucrose= glucose+fructose, eg table sugar
Lactose=glucose+galactose, eg milk
why is fructose special
metabolized in liver, can make fat in liver itself
if high intake of added sugar (which is ½ fructose), liver responds by making extra fat —→ results in fatty liver OR can be transported into raise blood lipids and inc fat stores
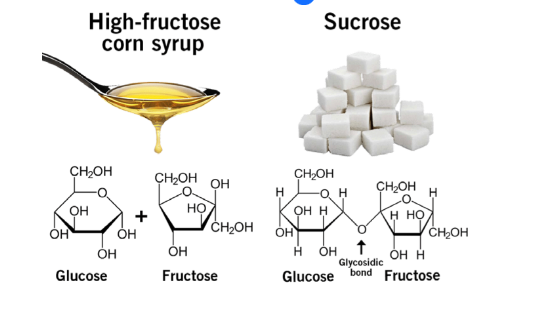
difference between high fructose corn syrup VS sucrose
Both are frequently approx. 50:50 fructose
and glucose. (Some HFCS has higher level of fructose)
• Sucrose (table sugar) bound like disaccharide
• HFCS separate glucose and fructose molecules
in liquid format
• HFCS intake declining in North America
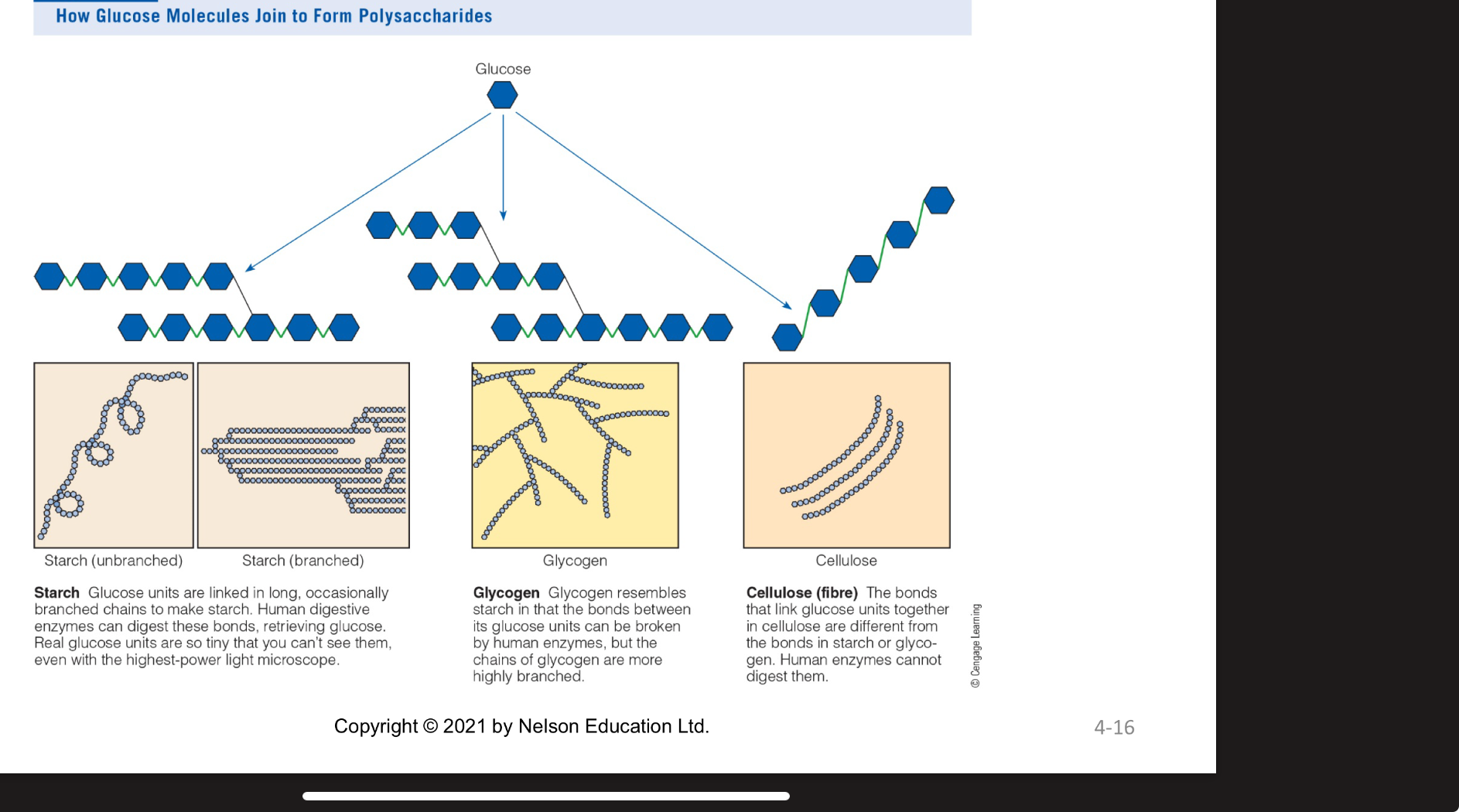
3 classes of polysaccharides
Glycogen=stored in liver and muscles, highly branched, reserve for energy
starch= storage form of ;glucose for plants’ long branched AND unbranched chains
Fibre= structural part of plants,
What is glycogen?
Liver makes some glucose into glycogen which is stored
in the liver.
• Muscles can also make and store glycogen from glucose.
• Glycogen can be broken down to release glucose when needed
• Liver is “generous” with its glycogen bc glycogen from liver is broken down to glucose, delivered via blood to organ that needs it. Glycogen can sustain needs when a long time
between meals.
• Muscle cells are “greedy”. They use glucose to make and store glycogen for their own use as energy source for the muscle itself. —> they use glycogen they store themselves
how is glycogen stored throughout body?, how long doe sit last
liver= about 1/3 of glycogen stores, readily available for brains, nerves, blood cells
muscles= 2/3 of glycogen stores (300-400g) in body
GLYCOGEN STORES LAST ~1 day
summary of carbohydrates uses in body

How much carbs does DRI and RDA reccomend?
-minimum of 130g
-RDA reflects need of brain, nerves and
blood cells for glucose, and does not meet
most individuals energy needs
-no UL!
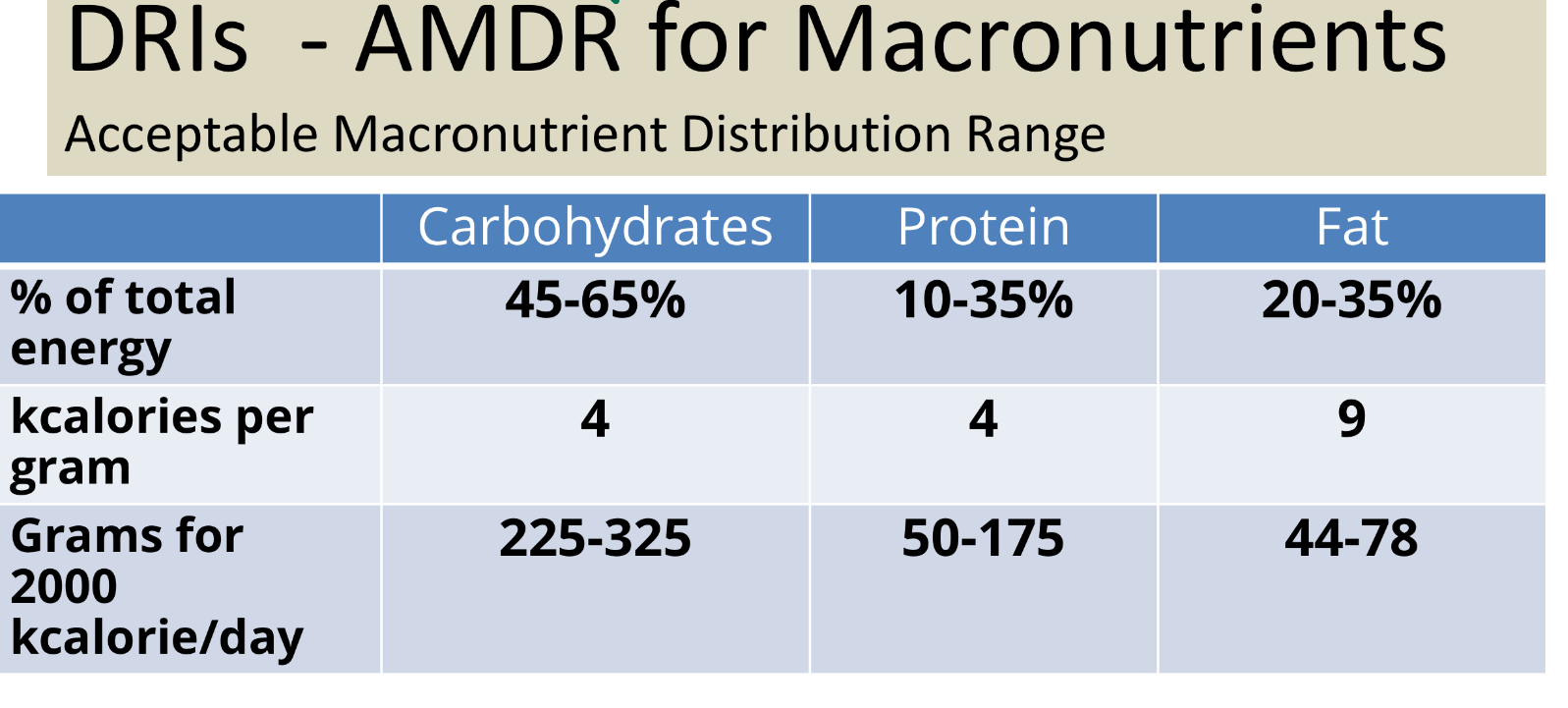
what is DRI AMDR for carbs?
45-65% of total cals
what enzymes begins carb digestion?
amylase, makes smaller polysaccharides, maltose
what inactivates salivary enzymes?
stomach acids
what produces amylase (after salivary glands), where is it released?
The pancreas produces an
amylase that is released through
the pancreatic duct into the small
intestine
Then xxx xxxx on
the surface of the small intestinal
cells hydrolyze the disaccharides
into monosaccharides
Then disaccharidase enzymes on
the surface of the small intestinal
cells hydrolyze the disaccharides
into monosaccharides
general steps of monosaccharide absorption
monosaccharides enter capillaries of intestinal villi (of small intestine)
monosaccharides travel to liver via portal vein
in liver, galactose and fructose are converted to glucose
which disaccharides enter xxxx using active vs passive transport?
entering intestinal cells
ACTIVE transport—> glucose & galactose
PASSIVE transport—> facilitated diffusion
once in the liver, fructose and galactose can be converted into glucose
As blood glucose levels rise/drops, what responds first ?
pancreas
if blood glucose drops, xxx releases yyy
pancreas releases hormone glucagon
if blood glucose rises xxx releases yyy
pancreas releases insulin
does brain store any ‘energy"‘?
yes, brain store some glucose
acts as Emergency reserve to fuel the brain in severe glucose deprivation
glycogenolysis
breakdown to release glucose
very simple way that insulin works is..
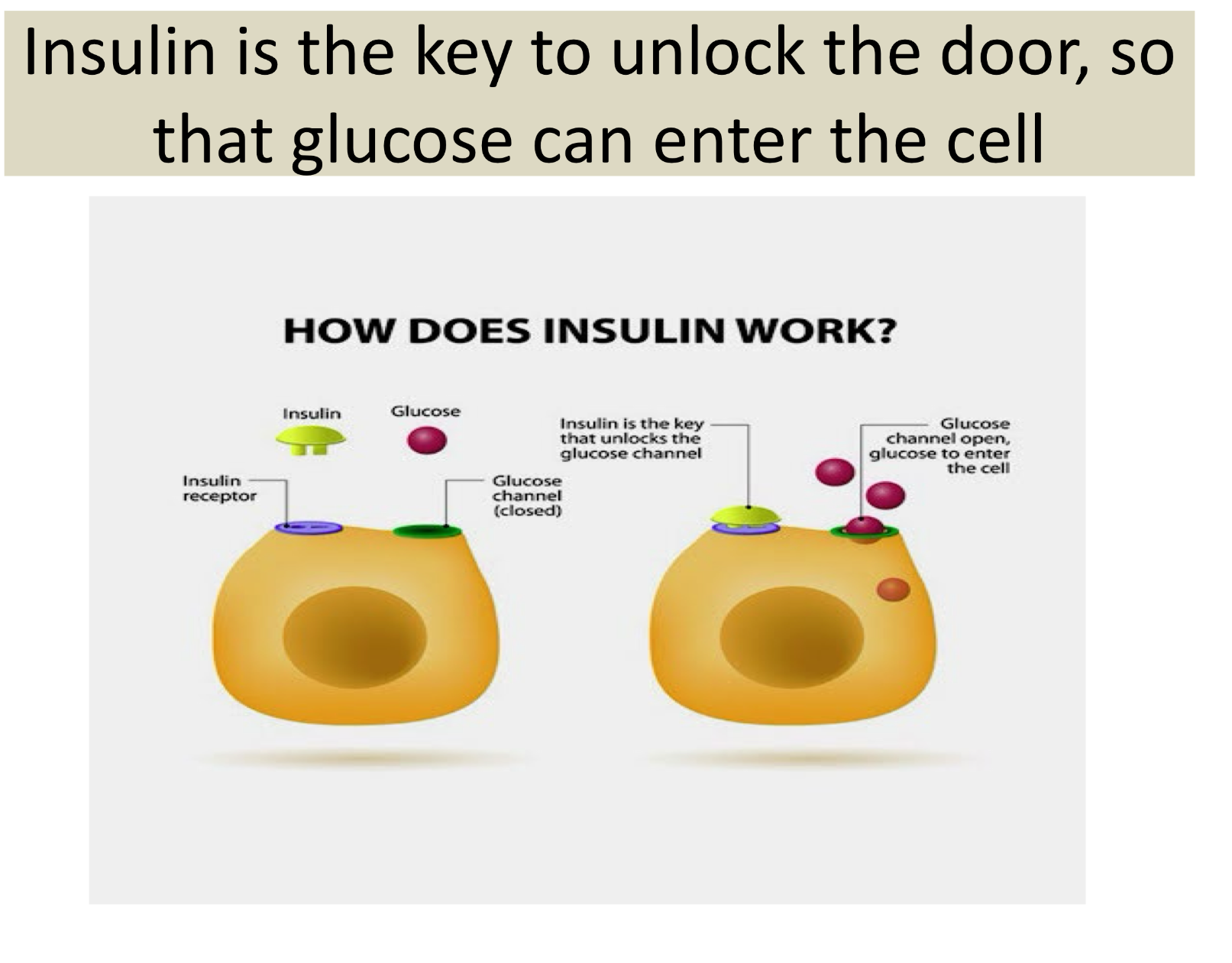
how does body handle excess glucose?
Once the liver and muscles have supplied tissues with needed glucose and stored glycogen to max capacity, then the body burns excess glucose for energy OR converts to fat and stores as fat
pathway of fibre digestion
mouth crushes and tears fibre in food and mixes it w saliva to moisten for swallowing
stomach, not digested there and DELAYS gastric emptying
large intestine, most fibre remain in tact and bacterial enzymes digest fibre
About 1–4 hours after a meal, all the —- and
— have been digested/absorbed. Only the xxx remains
About 1–4 hours after a meal, all the sugars and
starches have been digested/absorbed.
Only the fibres remain. In the colon fibres attract
water, which softens the stool.
bacteria ferment fibre causing gases (3 types) and xxx:
methane, co2, h2, and short-chain fatty acids (acetate, propionate, butyrate)
how are short chain fatty acids used (SCFA)s
can be used by colonic cells for energy
generally, fibre contributes xx cal/gram
1.5-2.5 cal/gram
2 types of fibre, which is more fermented and what are common sources?
– Soluble, viscous, fermentable fibres are often
gummy or add thickness to foods
ex: pectin, gums, legumes, additives like xanthum gum , guar gum
– Insoluble, nonviscous, less fermentable fibres
are often tough, stringy, or gritty in foods
ex: cellulose inver wheat bran,
action of fibre in stomach
delays gastric emptying
fullness sensation, satiety
action of fibre in small intestine (soluble vs insoluble)
• not digested by our enzymes
• slows absorption
– better glycemic control
• Soluble - binds bile acids
– ↓ enterohepatic circulation
– ↓ fat, cholesterol and fat sol vitamin
absorption
– ↓ cholesterol levels
• Insoluble - binds cations
– ↓ Fe, Ca, Zn absorption
low vs high fibre diet in relation to cholesterol

what are DRI recommendations of fibre?
AI for fibre is based on caloric energy intake (25g per 2000cal)
– 38 g/day for men
– 25 g/day for women
• No UL (though greatly exceeding the AI or
increasing too quickly could have some
negative consequences)
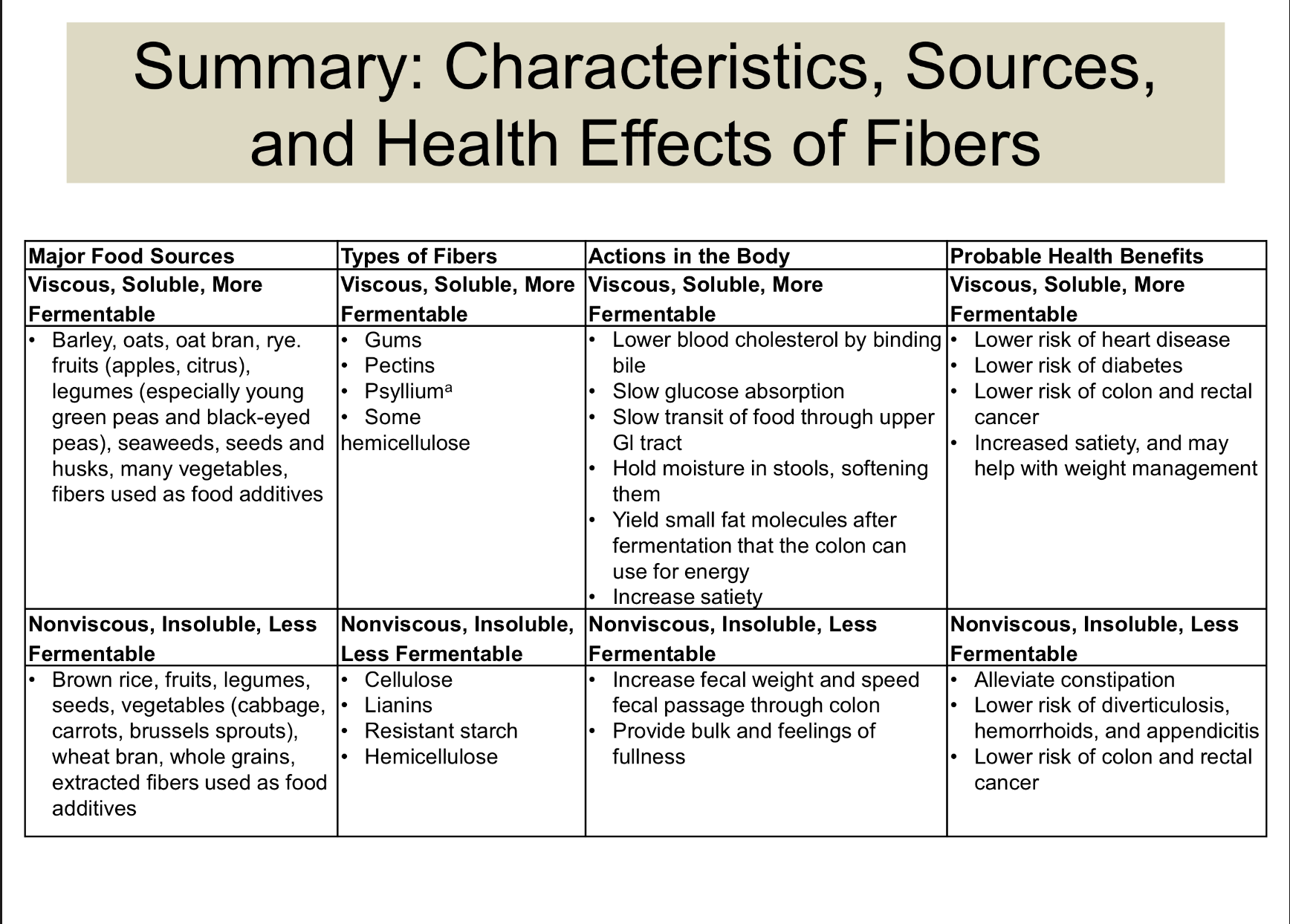
summary of characteristic , sources, and health effects of fibre
glycemic response definition
extent to which a food raises
blood glucose
glycemic index (GI) definition
scale that ranks a arbohydrate-containing food or drink by how much it raises blood sugar levels after it is consumed
glycemic load (GL) definition
takes into account both the GI and the amount of available carbohydrates in that serving.
how long does juice, simple/refined carbs, vs mixed meals take to consume/digest/absorb
Juice: 10 – 20 min
Refined (simple) carbohydrates by itself, ex: plain cooked white rice, pasta or bread: 30 - 60min
• Mixed meals with Carb + Protein/Fat: Protein and fat stay longer in stomach. 2 - 4 hours
what type of factors can affect glycemic index
varies between individual people:
Time of day, body size and weight, blood volume, and metabolic rate
Amount consumed
Depends on how the food is prepared (raw, cooked, cooled, al dente vs well-cooked…)
Food combinations in a meal
why is sourdough lower GI?
high resistant starch, low glycemic index
“Sourdough fermentation is the oldest method of dough fermentation and occurs with the help of yeast and lactic acid bacteria. Acetic acid appears to be associated with a delay in gastric emptying. Acid induces interactions between starch and gluten during dough baking and reduces starch availability.”
why is resistant starch beneficial ?
Instead of being fully digested and absorbed by
the time passes through the small intestine, the
resistant starch may arrive in the colon (similar to
fiber in that sense) and ferment there.
• Lower glycemic index.
Examples:
– Raw potato versus cooked.
– Green-tipped or green bananas versus ripe bananas.
– Starch inside seeds.
– Cooked starchy food that is then cooled
why are resistant starches harder to digest?
resistance starch has highly ordered starch structure —> difficult for humans to digest.
• ex: Cooking potatoes weakens the structure,
making it easier for break down and
digestion.
how to calculate starch in food
