IB Chem Unit 3: Acids and Bases
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
What are some properties of acids?
aqueous solutions of acids conduct electricity, tastes sour, causes litmus to turn red and phenolphthalein to turn colorless, neutralize bases to form salt and water
What are the products of a reaction between an acid and an active metal?
hydrogen gas and a salt
What are the products of a reaction between carbonates or hydrocarbonates and acids?
salt, carbon dioxide, and water
What is hydrochloric acid?
HCl
What is hydrofluoric acid?
HF
What is hydrobromic acid?
HBr
What is hydroiodoic acid?
HI
What is nitric acid?
HNO3
What is acetic//ethanoic acid?
HC2H3O2
What is sulfuric acid?
H2SO4
What is sulfurous acid?
H2SO3
What is phosphoric acid?
H3PO4
What are arrenhius acids?
substances that when dissolved in water increase the concentration of H+ ions
What are the strong acids?
HCl, HI, HBr, HNO3, H2SO4, HClO3, HClO4
What are the general properties of bases?
aqueous solutions of bases conduct electricity, taste bitter, feel slippery, cause litmus to turn blue and phenophtalein to turn pink, neutralize acids to form salt and water
What is an arrenhius base?
substance that when dissolved in water increases the concentration of OH- ions
What are strong bases?
substances that dissociate fully in water and thus their solutions are excellent conductors of electricity
What are the strong bases?
LiOH, NaOH, KOH, RbOH, CsOH, Ca(OH)2, Sr(OH)2, Ba(OH)2
What is a Bronsted-Lowry acid?
a substance that can donate a proton to another substance
What is a Bronsted Lowry base?
a substance that can accept a proton from another substance
What are conjugate acid-base pairs?
according to the Bronsted-Lowry definition, an acid and base must both be present, the reaction between an acid and a base always yields their conjugate bases and acids
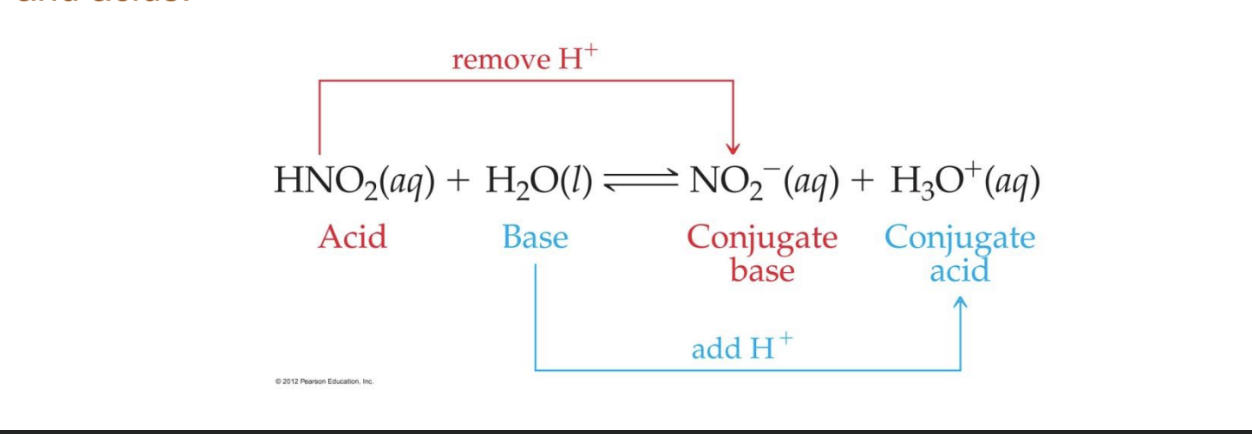
What is the conjugate of a strong acid?
a weak base
What is the conjugate of a weak acid?
a strong base
What is amphoterism?
the property of a substance to act either as an acid or a base depending on the reaction conditions
What are some examples of amphoteric substances?
H2O, HCO3-, HSO4-
In a neutral solution (such as pure water), the concentrations of the hydrogen ion and hydroxide ion are equal. Thus,
Kw = [1.0 x 10-7] [1.0 x 10-7] = 1.0 x 10-14
What is the concentration of OHin a 0.1 mol dm-3 HCl solution?
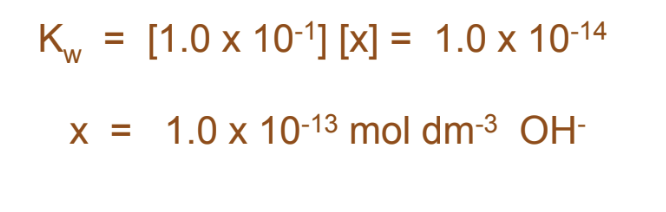
What is the concentration of OHin a solution with a [H+] =2.0 x 10-6 mol dm-3 ?

How can you calculate pH?
pH is the -log(H+ concentration)
How can you calculate pOH?
-log(OH concentration) or 14 + log (H+ concentration)
How do you calculate the pH of a weak acid?
you need to find the hydrogen ion concentration at equilibrium, this requires an equilibrium expression which you use to solve for the H+ concentration and then use that to do the -log equation
The greater the Ka, the _____ the acid
the greater the Ka, the stronger the acid
What is another way to express acid strength?
pKA which is -logKa
What is the relationship between acidity, pKa, pH, and Ka?
as acidity increases, pH and pKa decrease but Ka increases
What are polyprotic acids?
have more than one acidic proton, if the difference between Ka for first dissociation and subsequent Ka values is 10³ or more, the pH generally depends only on the first dissociation
What is the relationship between pKa and pKb?
pKa+pKb = 14 at 25 celsius
How can we calculate Ka from pH?
write the equilibrium reaction, use the pH to determine H+ concentration, set up equilibrium table, plug in equilibrium concentrations into the Ka expression
What is a lewis acid?
an electron pair acceptor
What is a lewis base?
an electron pair donor
Why is rain naturally acidic and what is the equation to represent this?
because of carbon dioxide that dissolves into the rain water and reacts to form carbonic acid
CO2 (g) + H2O (l) ←→ HsCO3 (aq) and then H2CO3 (aq) ←→ HCO3- (aq) + H+(aq)
What does the pH of rain need to be for it to be considered acid rain?
less than 5
What are the two main chemicals that cause acid rain fro our atmosphere?
NOx and Sox