Biochemistry Ch. 7-9
1/113
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
114 Terms
The linear structure for solid glucose represents an example of a(n)
aldohexose
The structures of D-Mannose and L-Mannose are mirror images that are non-superimposable. D-Mannose and L-Mannose are therefore examples of _______________________ .
enantiomers
If pure alpha-D-glucose is dissolved in water, within a few minutes the solution will contain a mixture of 38% alpha-D-glucose and 62% beta-D-glucose. This process is an example of ____________________________ .
mutarotation
For beta-D-glucose, the position 6 methylene-hydroxyl group and the position 1 hydroxyl group are oriented ________________ relative to the pyranose ring plane.
cis
Maltose is an intermediate product of starch hydrolysis and does not appear to exist freely in nature. If pure amylose was used to make maltose, the two glucose units in maltose would be linked ______________________ .
alpha-1,4
Cellulose is a polymer of glucose that can be digested by ruminants but not by humans and other non-ruminants. The glucose units in cellulose are linked _______________________ .
beta-1,4
The term carbohydrate means ____________________________ .
hydrate of carbon
Amylopectin is the name given to the branched form of starch. In this form, the main polymer strands are linked alpha-1,4 but the branch points are linked _________________________.
alpha-1,6
D-glucose and D-mannose have almost identical structures. These compounds only differ by having the opposite configuration at carbon number 2. These two compounds are said to be _____________________________ of each other.
C-2 epimers
Starch represents a compact way of storing _______________________ molecules.
glucose
Hexokinase is the first enzyme in glycolysis that converts glucose and ATP into___________________ and ADP.
glucose 6-phosphate
phosphoglucose isomerase is the second enzyme in glycolysis that converts glucose 6-phosphate into ____________________.
fructose 6-phosphate
Phosphofructokinase-1 is the main regulatory enzyme in glycolysis that converts fructose 6-phosphate into _____________________.
fructose 1,6-bisphosphate
Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate is converted into dihydroxy acetone phosphate and glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate by an enzyme called _________________ .
aldolase
Triosephosphate Isomerase converts dihydroxy acetone phosphate into ______________.
glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate is converted into 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate by an enzyme called ________________.
glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase
Phosphoglycerate kinase is the enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate into ___________________.
3-phosphoglycerate
The enzyme that converts 3-phosphoglycerate into 2-phosphoglycerate is called ___________________________.
phosphoglycerate mutase
The enzyme enolase converts 2-phosphoglycerate into _____________________.
phosphoenol pyruvate
Pyruvate kinase is an enzyme that converts phosphoenolpyruvate into _______________.
pyruvate
Glucose is metabolized anaerobically by the glycolysis pathway. In what part of a Eukaryotic cell does glycolysis occur ?
cytosol
Glucose is converted to pyruvate by glycolysis with the production of some ATP. The citric acid cycle is able to harvest the remaining chemical bond energy in pyruvate. What must happen before this energy can be harvested ?
pyruvate must be transported into the mitochondrion
The pyruvate dehydrogenase complex transfers an acetyl group from pyruvate to Coenzyme A to produce CO2(g) and acetyl-CoA. What else happens in this reaction ?
NAD+ is converted to NADH
Citrate is converted to isocitrate by an enzyme called ___________ ?
aconitase
Succinate is converted to fumarate by an enzyme called __________.
succinate dehydrogenase
Fumarate is converted to L-malate by an enzyme called ___________.
fumarase
If NADH is processed by the electron transport chain in oxidative phosphorylation (in the mitochondrion), how many ATP equivalents can be produced ?
2.5 ATP equivalents
The structure of acetyl-coenzyme A is shown below. The arrow is pointing to what portion of this molecule ?
= o
acetyl group
The structure of flavine adenine dinucleotide (FAD) is shown below. The arrow is pointing to which part of this molecule ?
riboflavin-5'-monophosphate or adenine
nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (oxidized form)
NAD+
How are carbohydrates formed?
Plants go through photosynthesis and produce them
What is the basic structure of carbohydrates?
[CH2O]n → [C1H2O1]n
What are the various classifications of carbohydrates?
monosaccharide, disaccharide, oligosaccharide, polysaccharide
What is a monosacchiride?
one simple sugar
What is a disaccharide?
two simple sugars
What is an oligosaccharide?
3-10 simple sugars
What is a polysaccharide?
more than 10 simple sugars
What are glycoconjugate?
carbohydrates bonded to other compounds like protein, lipids, etc
What are examples of glycoconjugates?
glycolipids or glycoproteins
What is the most abundant type of monosaccharide found in living cells?
Hexose
Vant Hoffs Rule
2n = # of sterioisomers
Define enantiomers
chiral, non super imposable, mirror image isomers
_____ need minimum of 3 carbons
aldoses
Define diasterioisomers
chiral not required, not mirror image isomers
Define epimers
diasterioisomers that differ at a single asymmetric carbon atom
Define anomers
cyclic epimers, differ C1 or C2
Differ at C1
aldose
Differ at C2
ketose
These compounds tend to be water soluble or at least hydrophillic
Carbohydrates
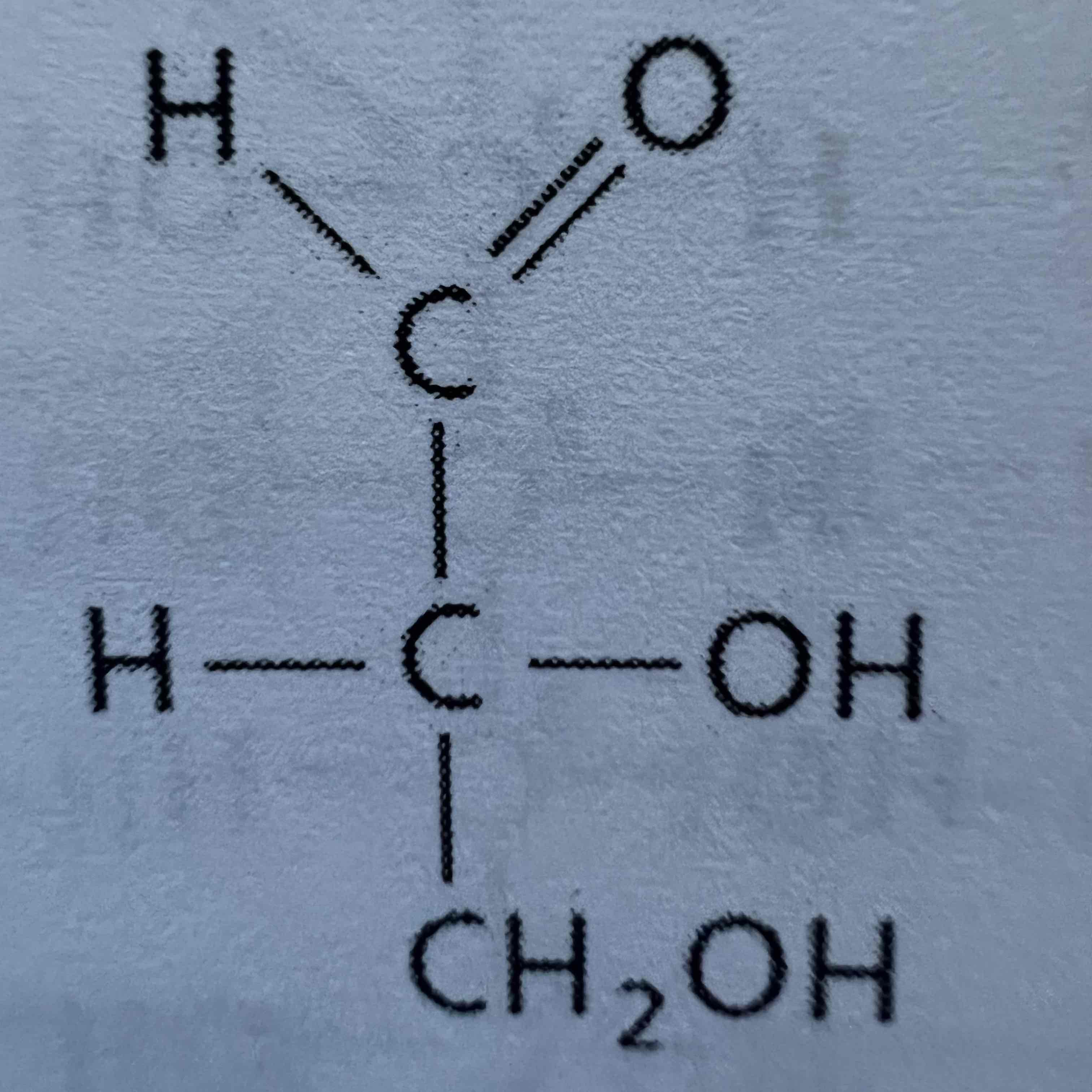
L-Glyceraldehyde
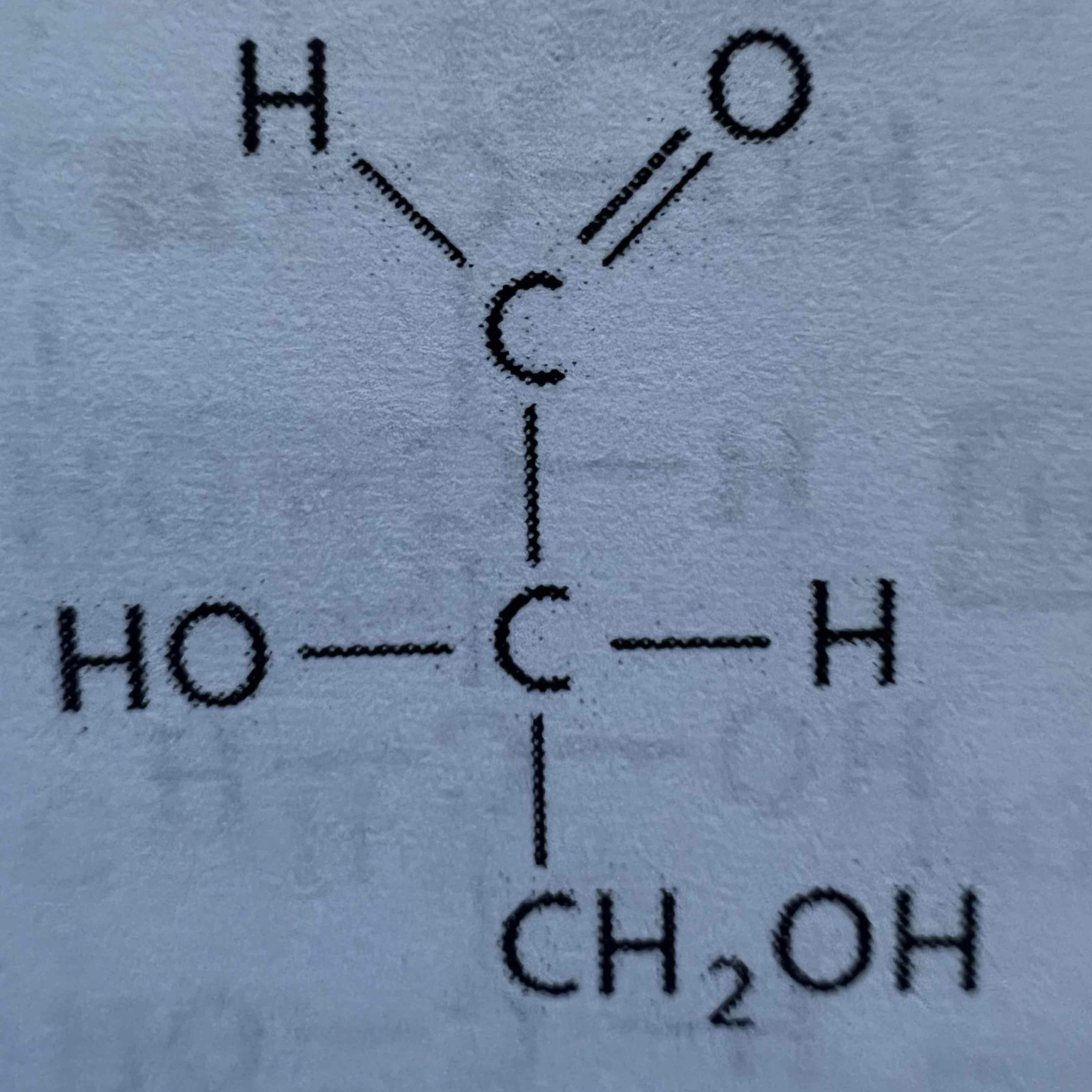
D-Glyceraldehyde
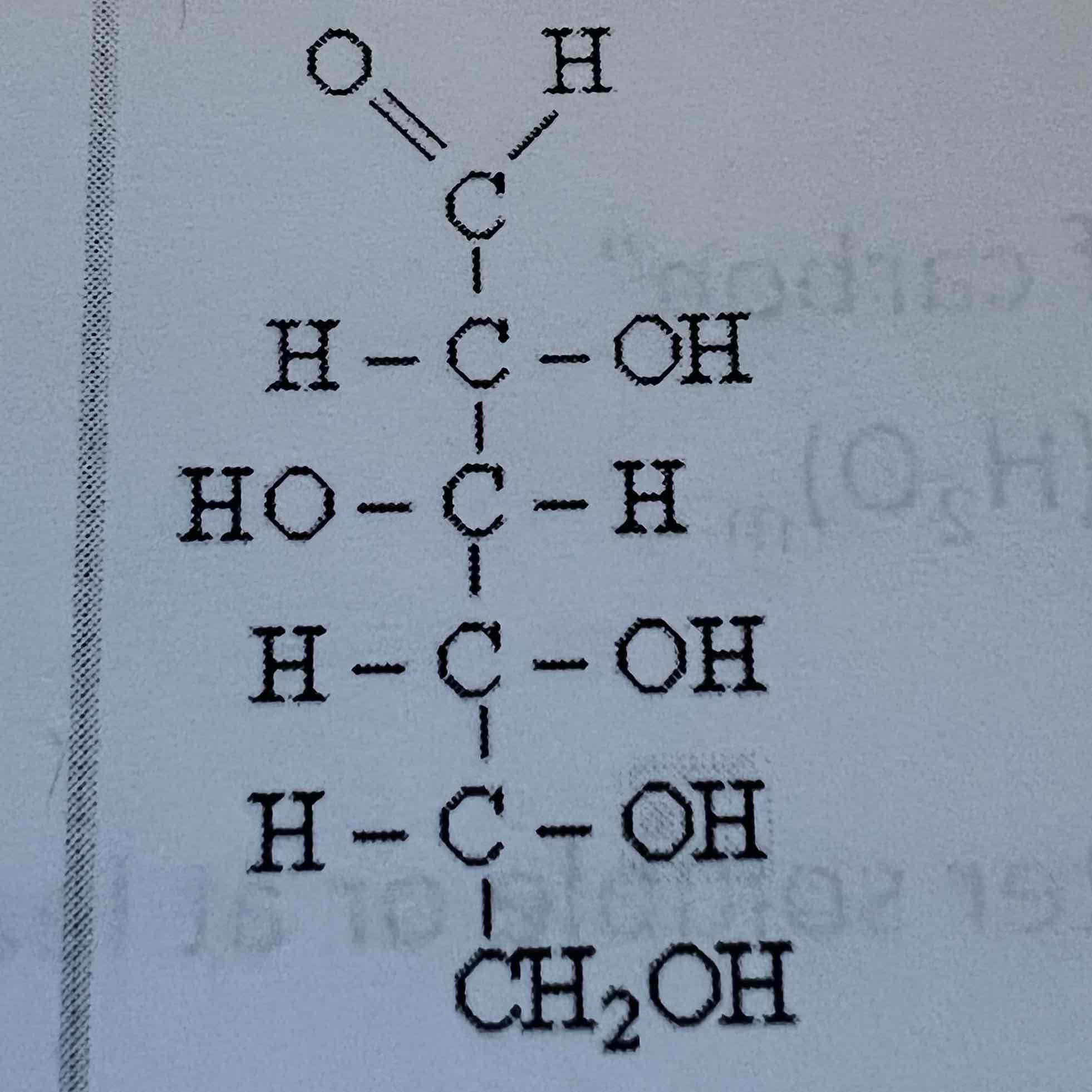
D-Glucose
cyclic epimers, differ C1 or C2
Differ at C1
Differ at C2
ketose
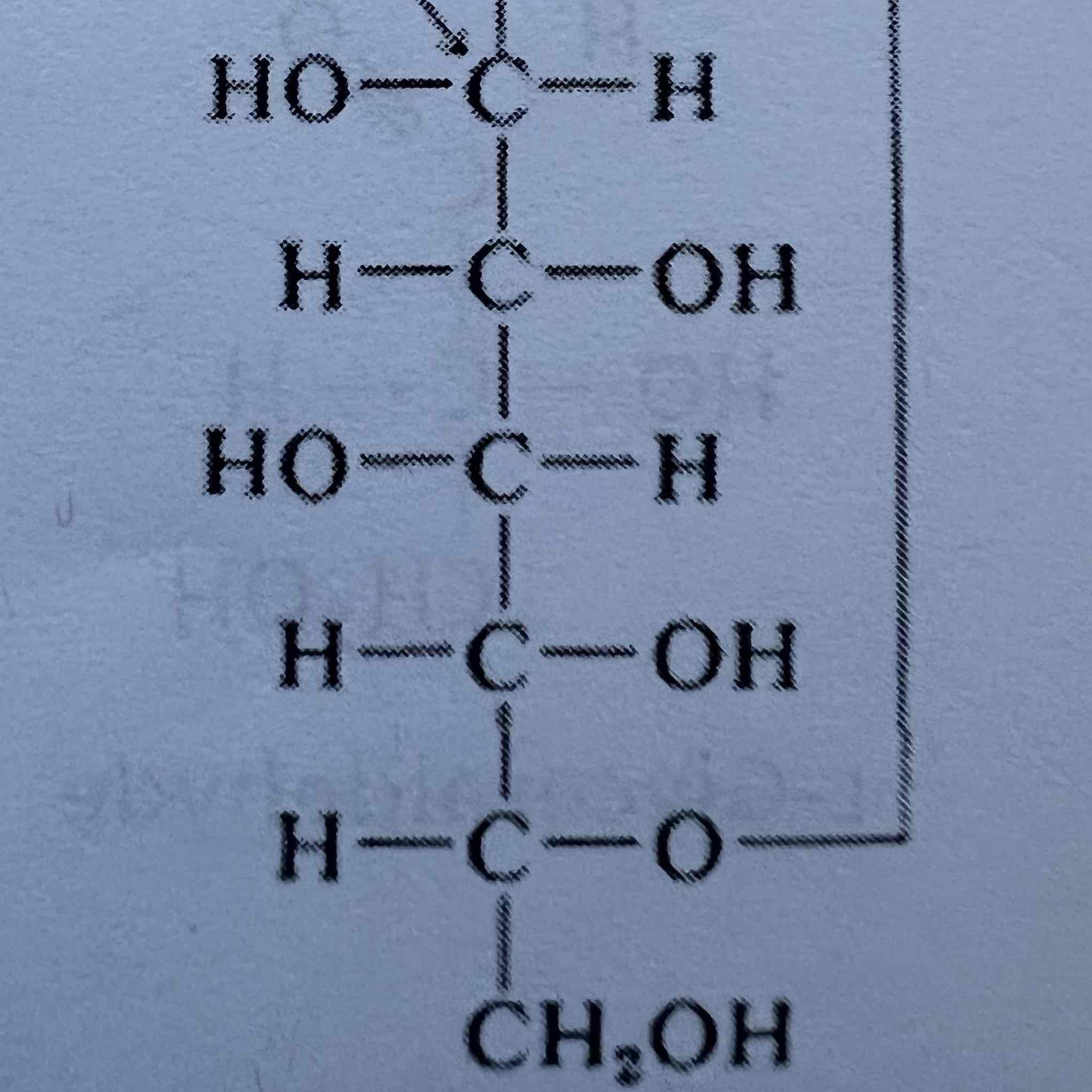
Cyclic a-D-Glucose
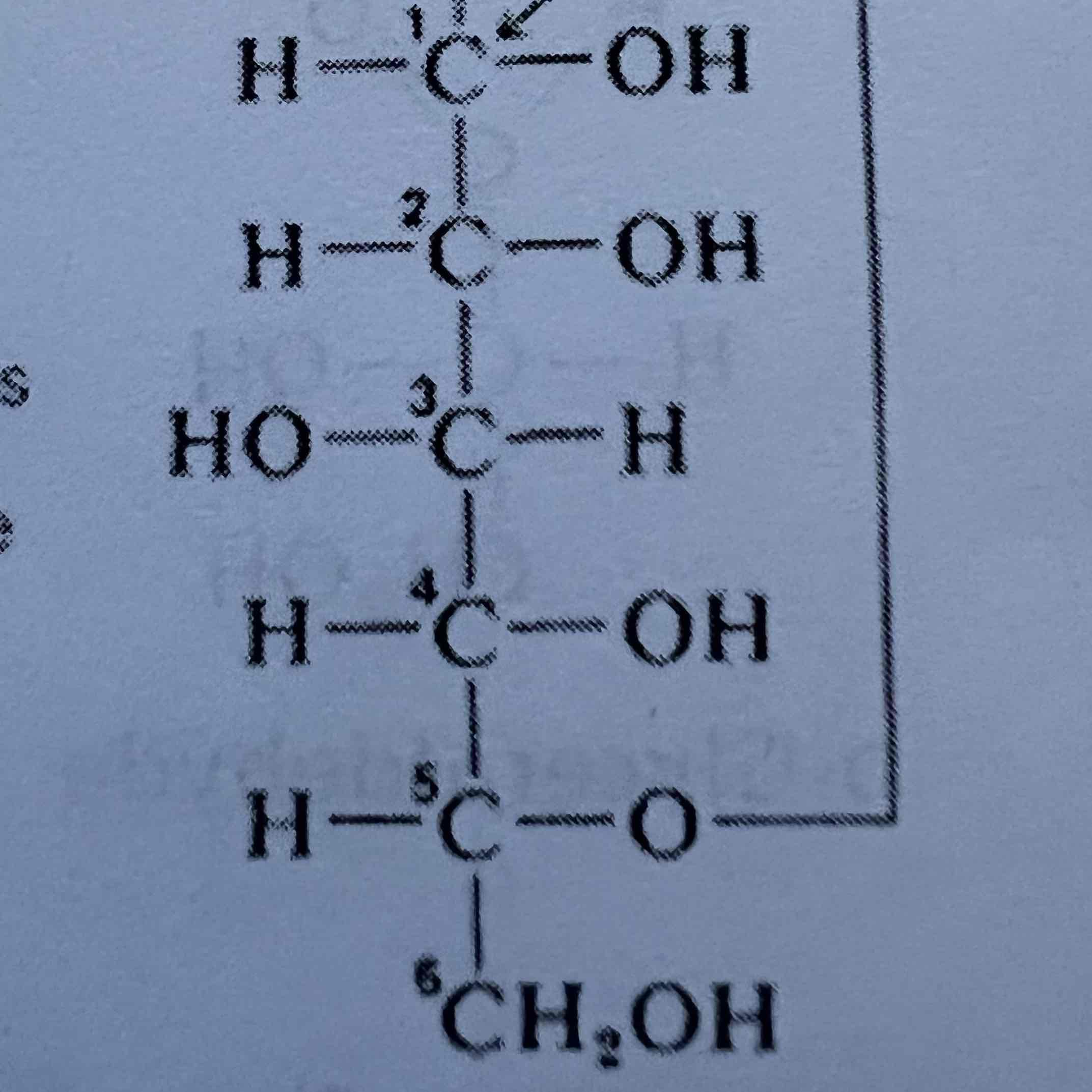
Cyclic B-D-Glucose
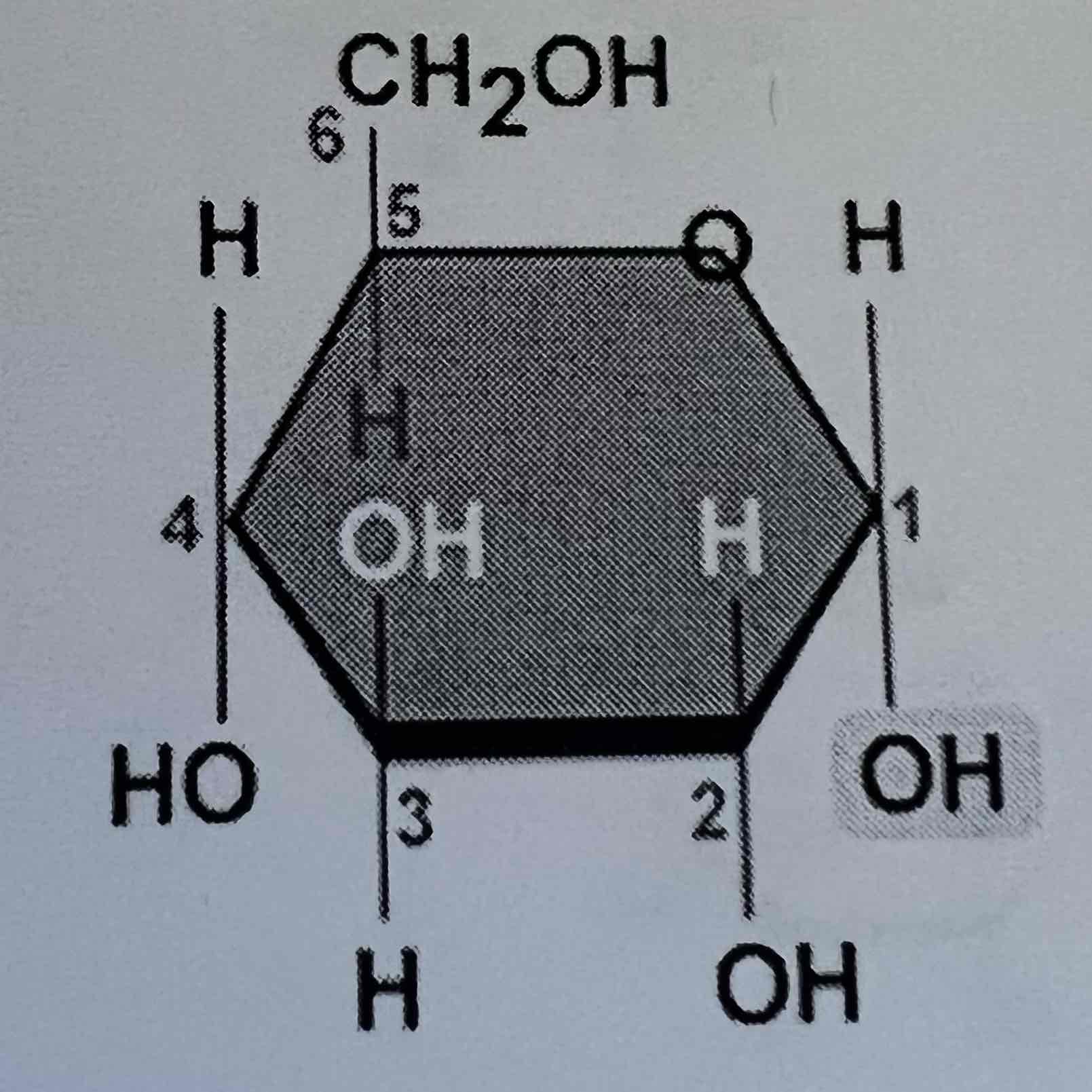
Haworth a-D-Glucose
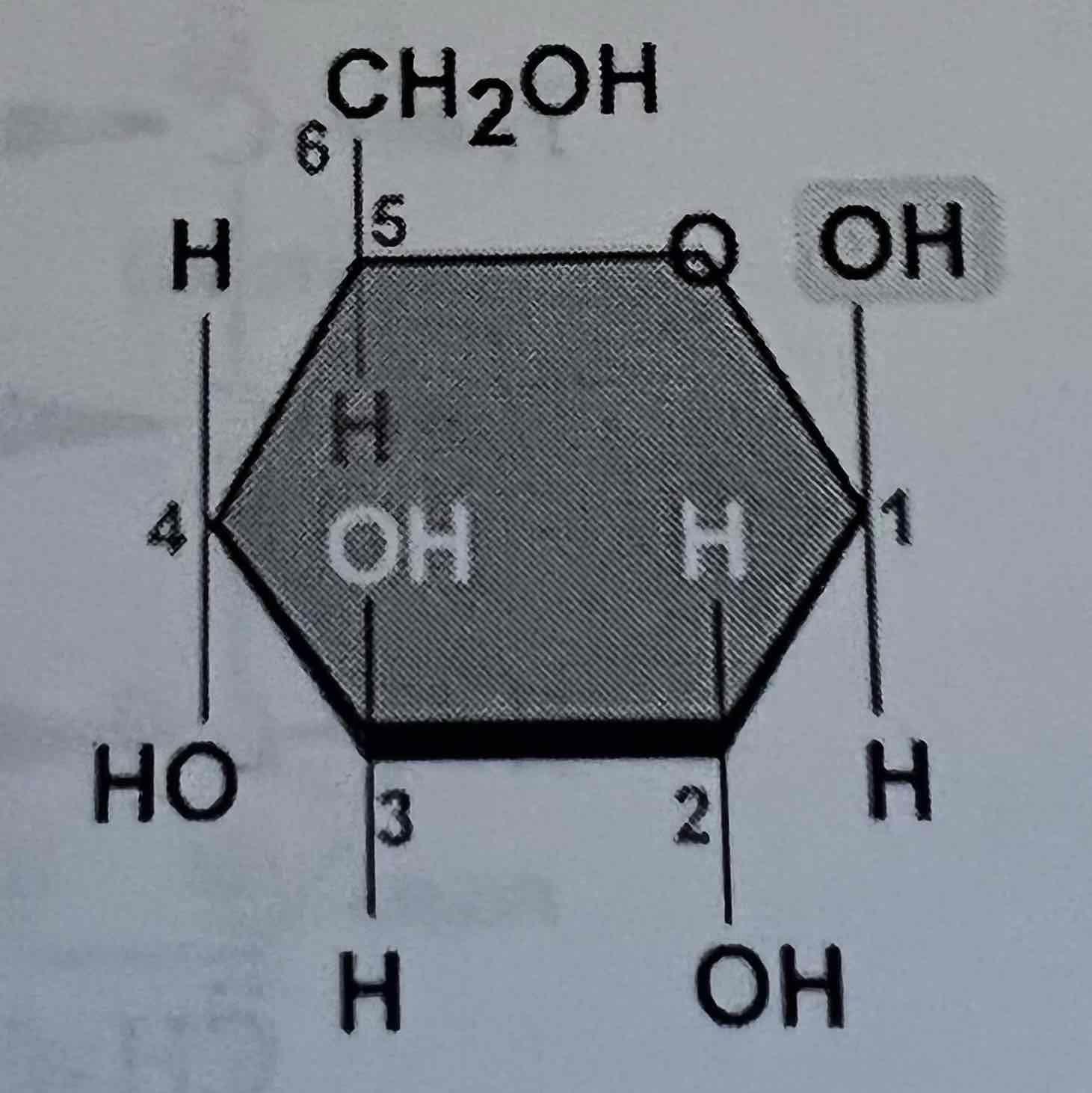
Haworth B-D-Glucose
Difference between D-Glucose and D-mannose
C2 epimer
Difference between D-Glucose and D-galactose
C4 epimer
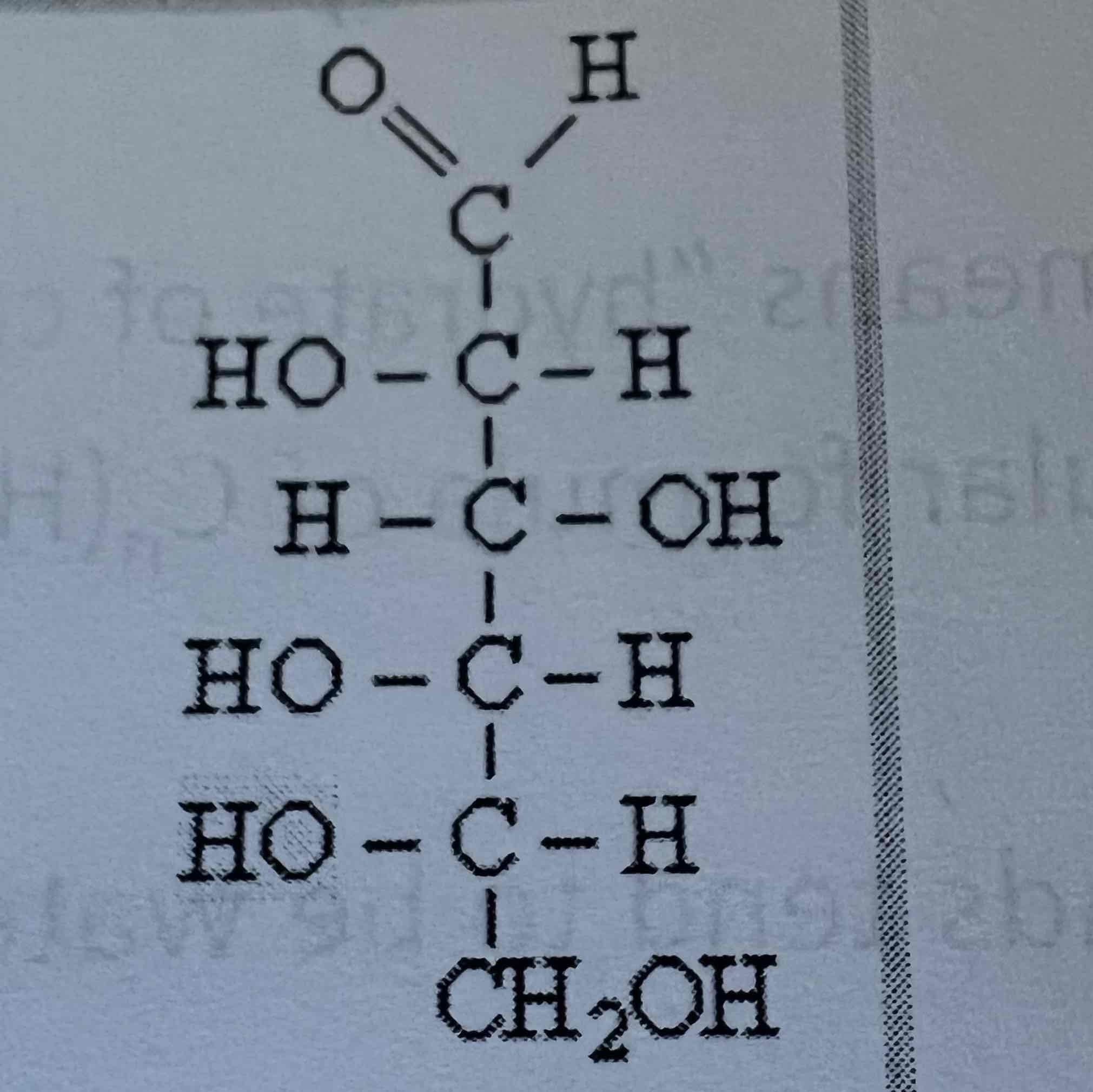
Fisher projection of ribose
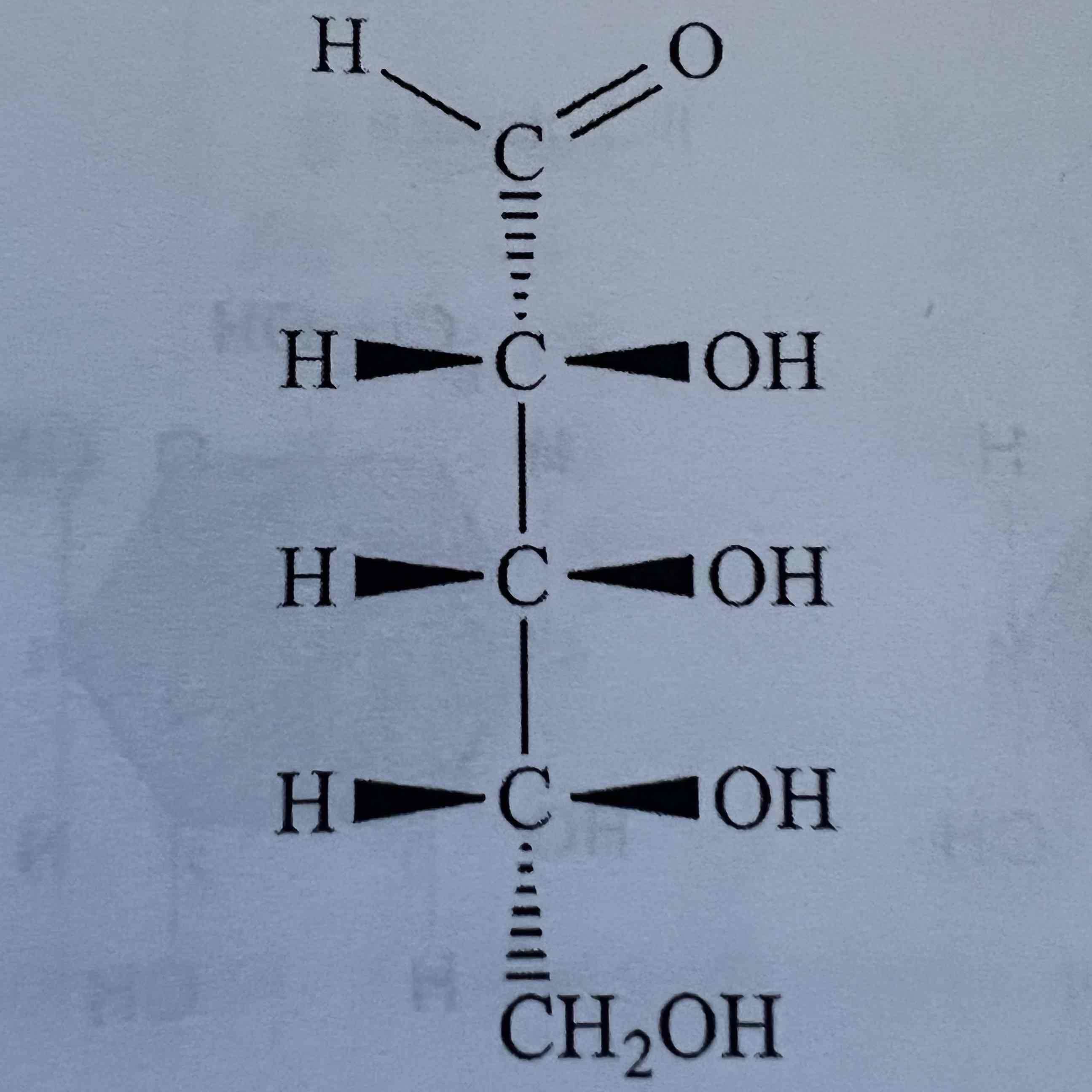
Glucose is a(n) ________
aldose
Fructose is a(n) ________
ketose
a-Glucose and B-Fructose are monosaccharide components of the disaccharide ______
sucrose
How do glucose and fructose connect to form sucrose?
via anomeric carbon via glycosidic linkage
Absence of enzyme required to metabolise galactose causes _______
galactosemia
What is galactosemia?
accumulation of galactose and its derivative that causes liver damage
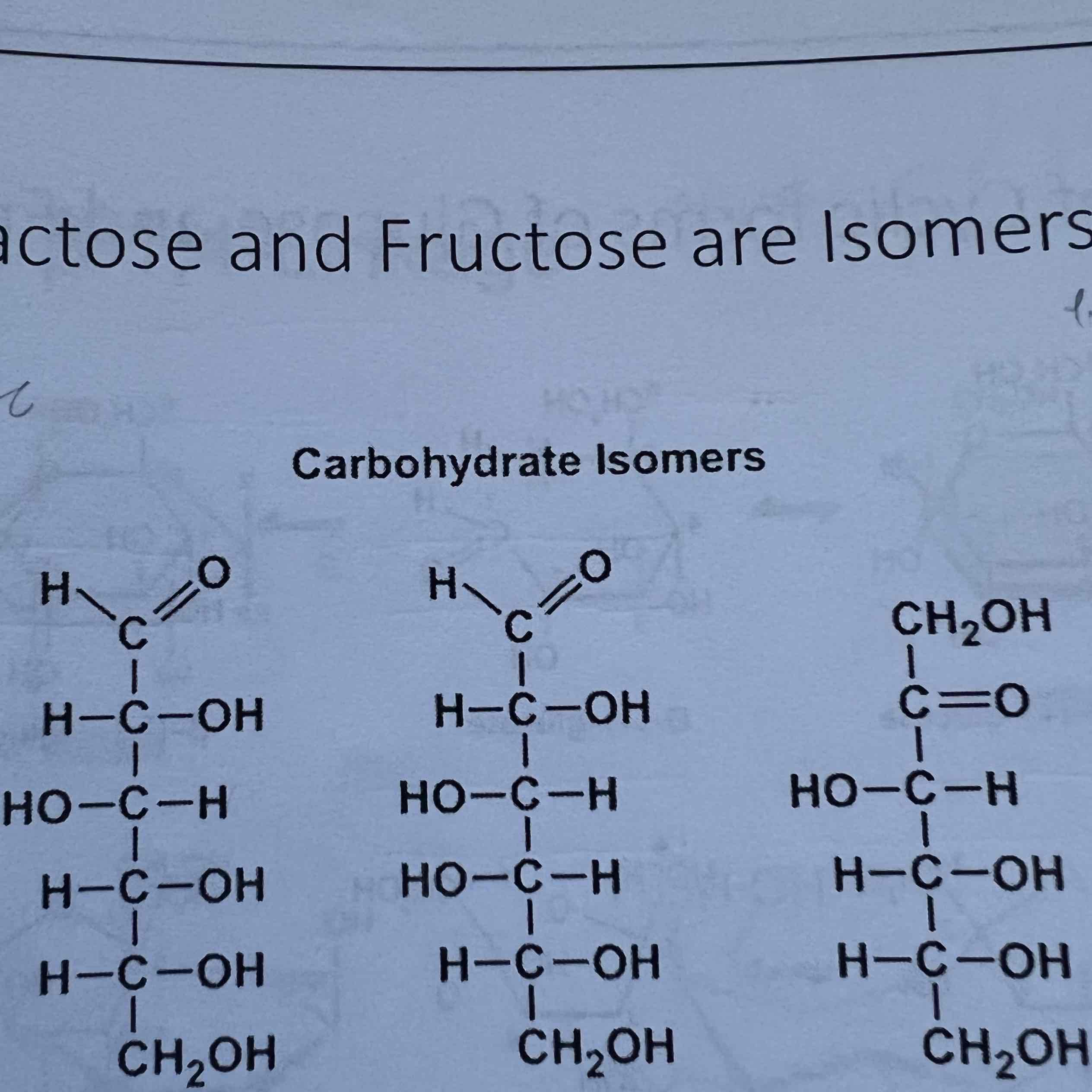
Which of these is galactose?
B
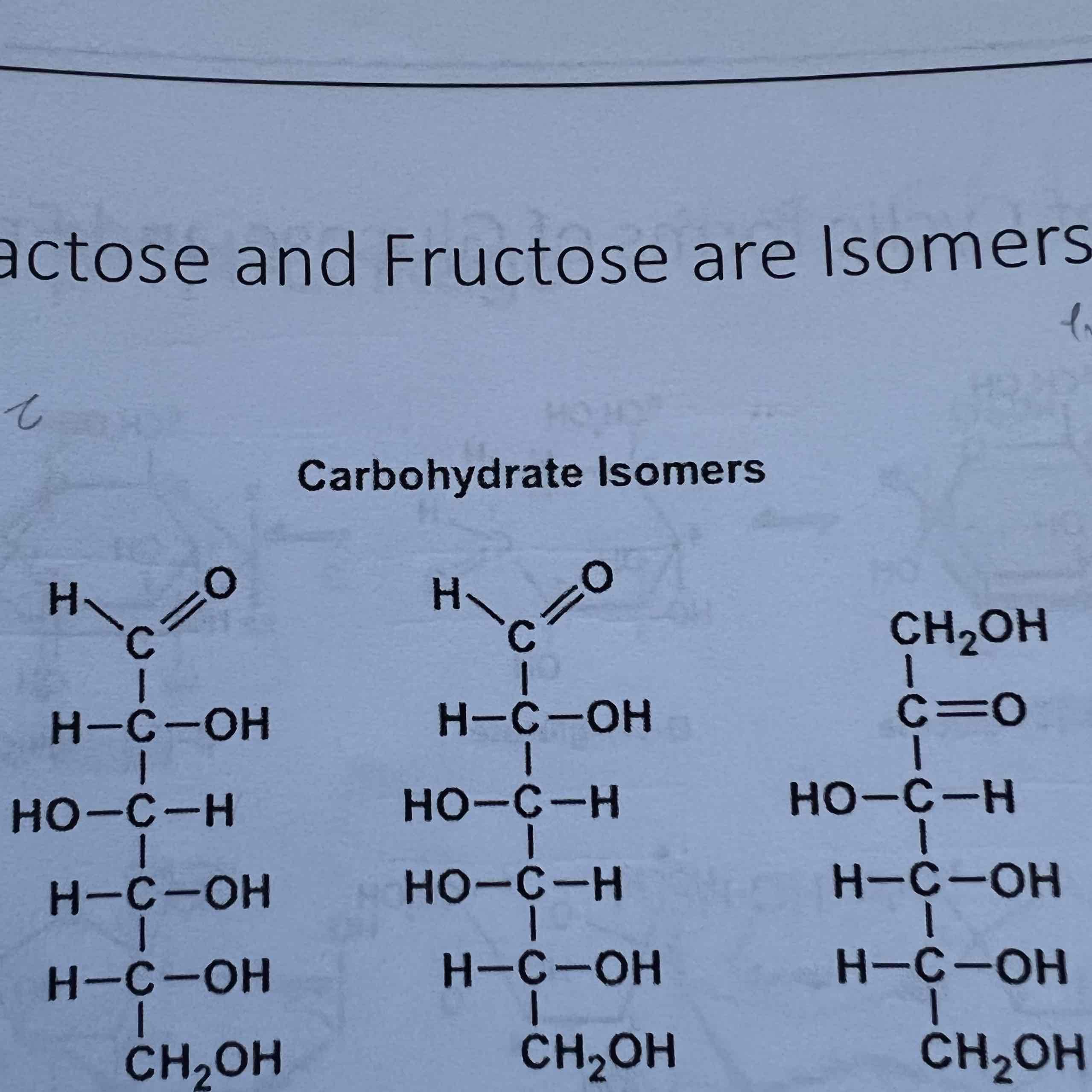
Which of these is glucose?
A
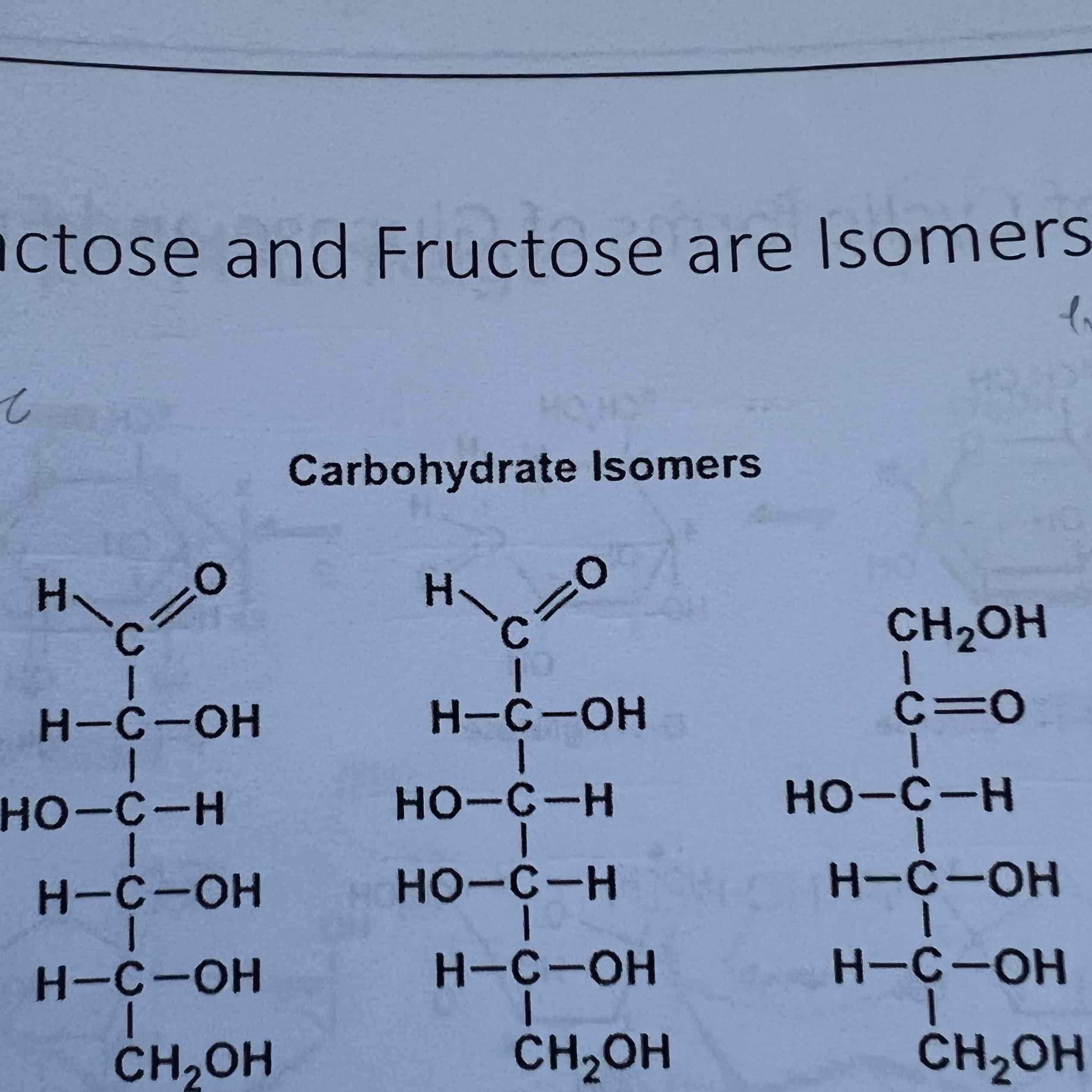
Which of these is fructose?
C
What results in maltose?
breakdown of starch
What is lactose?
a milk sugar
Lactose
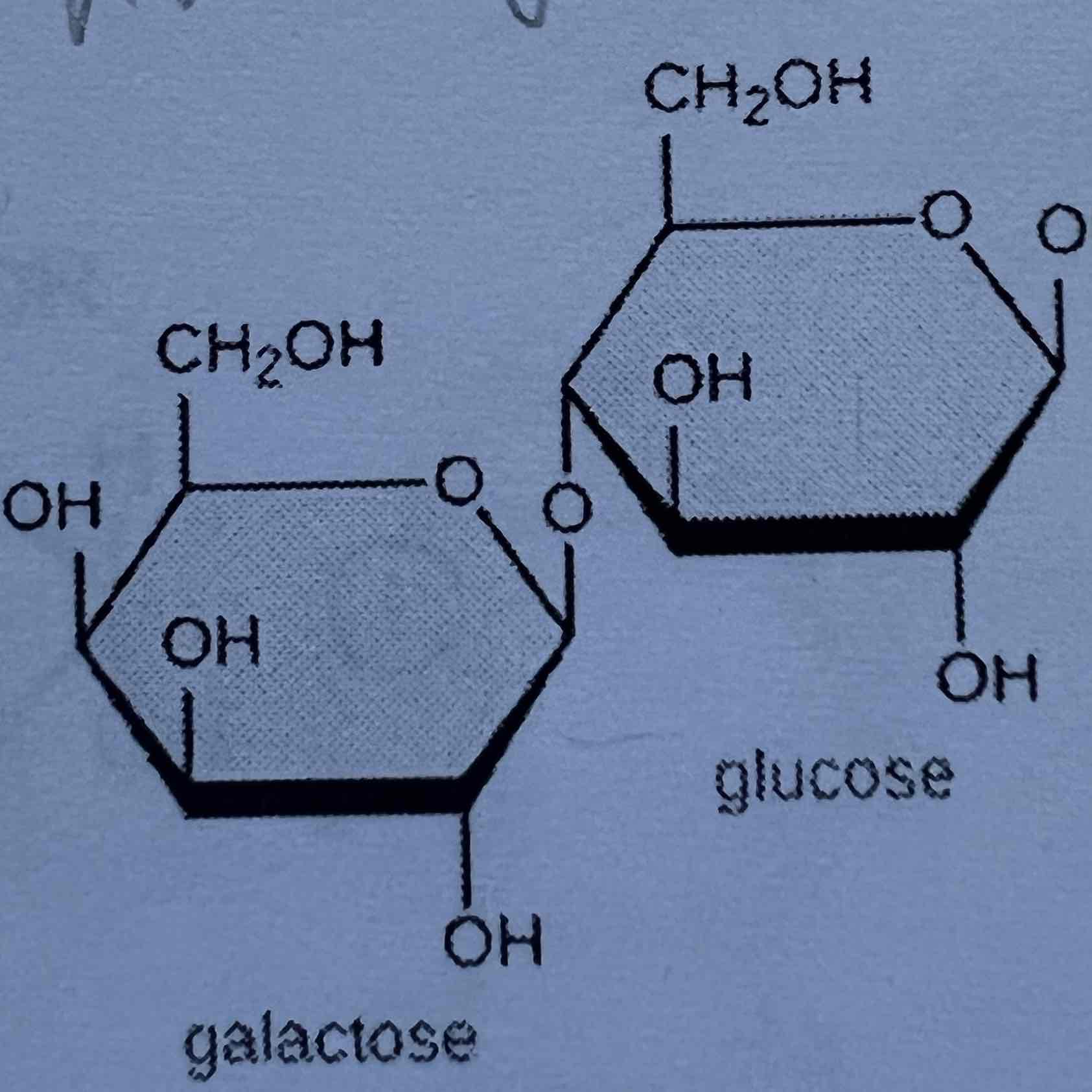
What forms lactose?
Galactose and Glucose
_____ does not naturally exist in nature
Cellobiose
Cellobiose
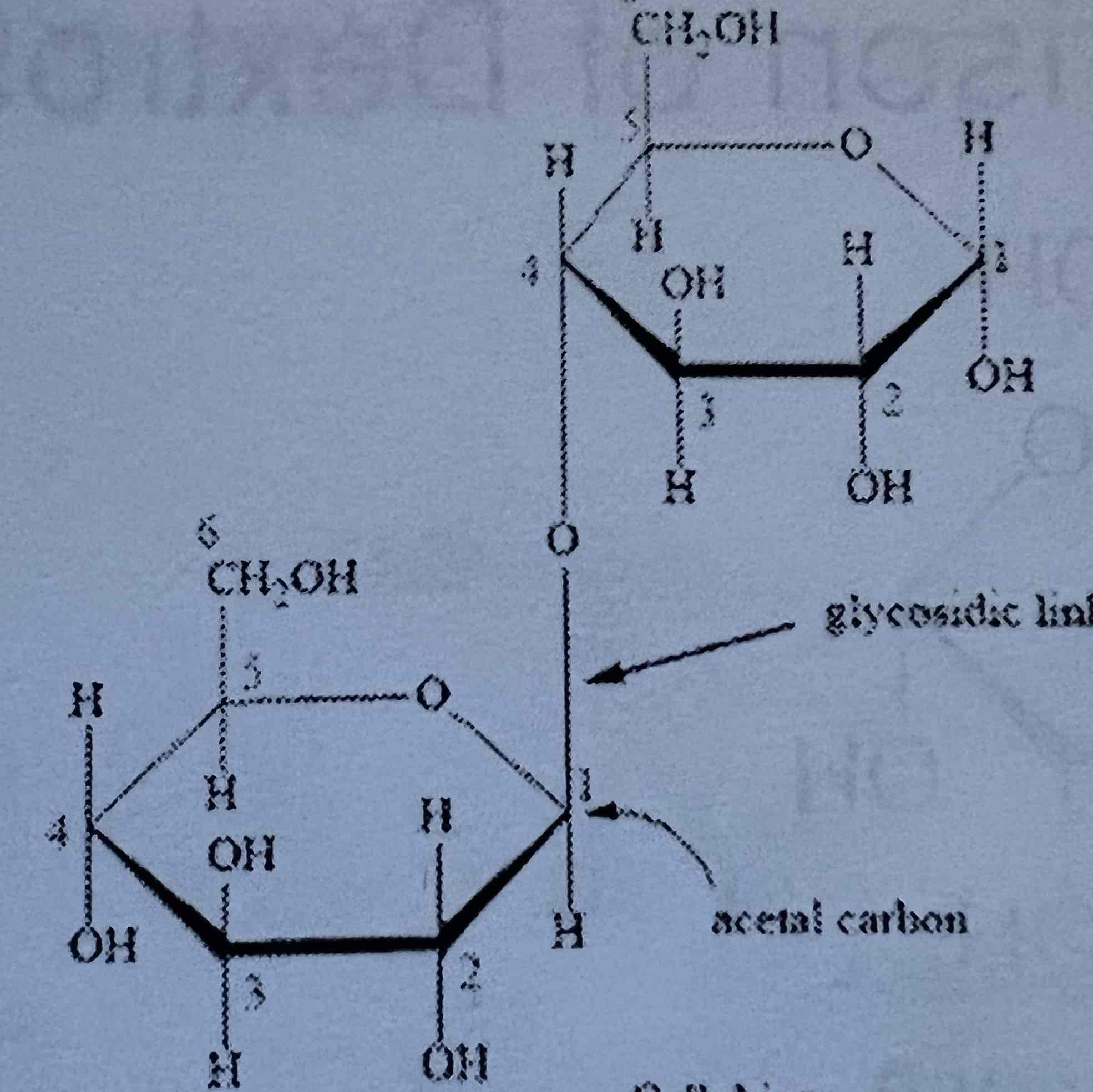
What is the difference between maltose and cellobiose?
maltose has an a linkage
Amylose is a form of _____
starch
Describe Amylose
linear, a-1-4 linkage, a-D-glucose
Describe Amylopectin
branched, a-1-4 linkage, a-1-6 linkage
Amylose
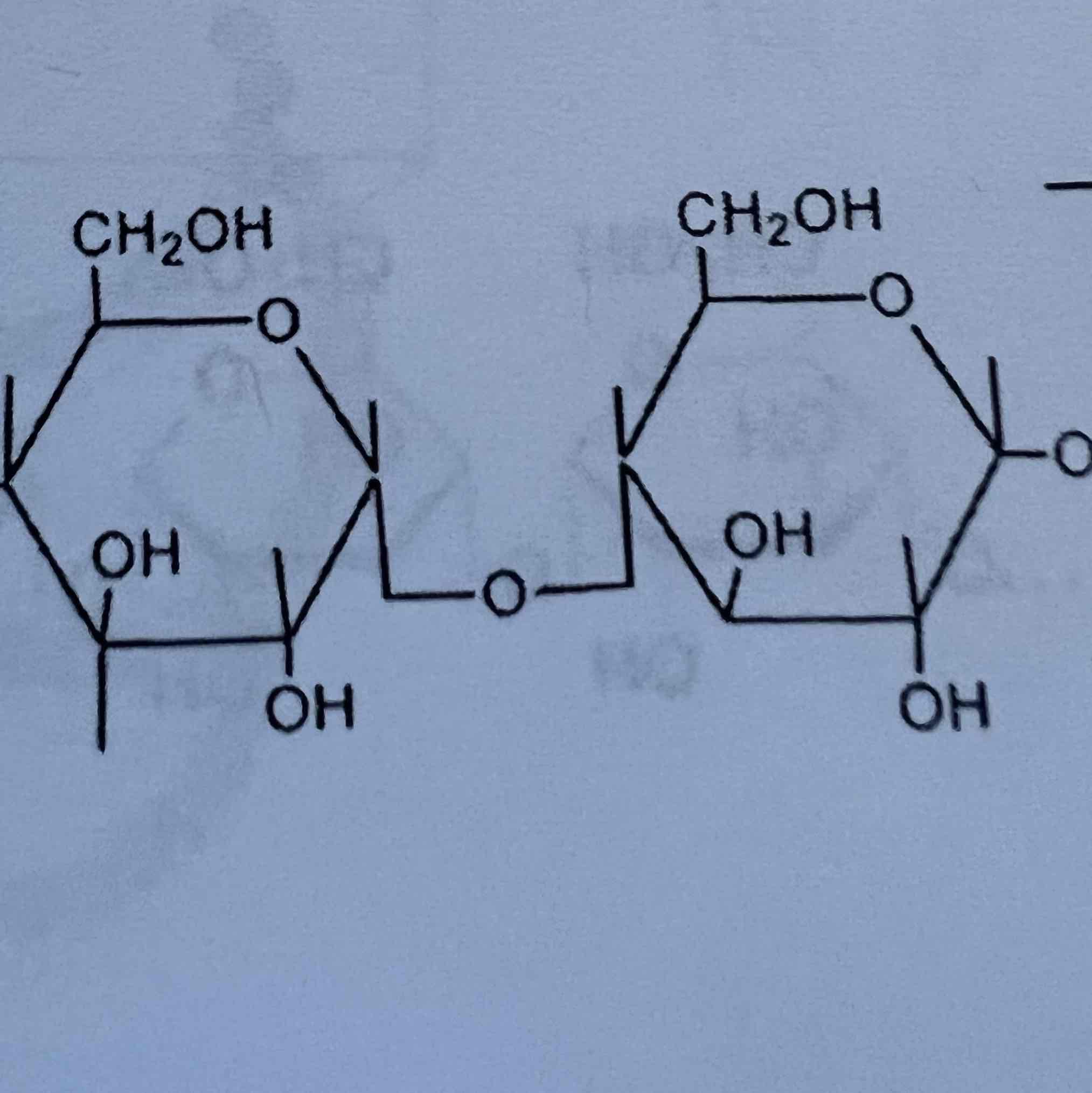
What are some examples of polysaccharides?
starch, glucose, glycogen
What is a polymer of glucose with B-1-4 linkage
cellulose
cellulose
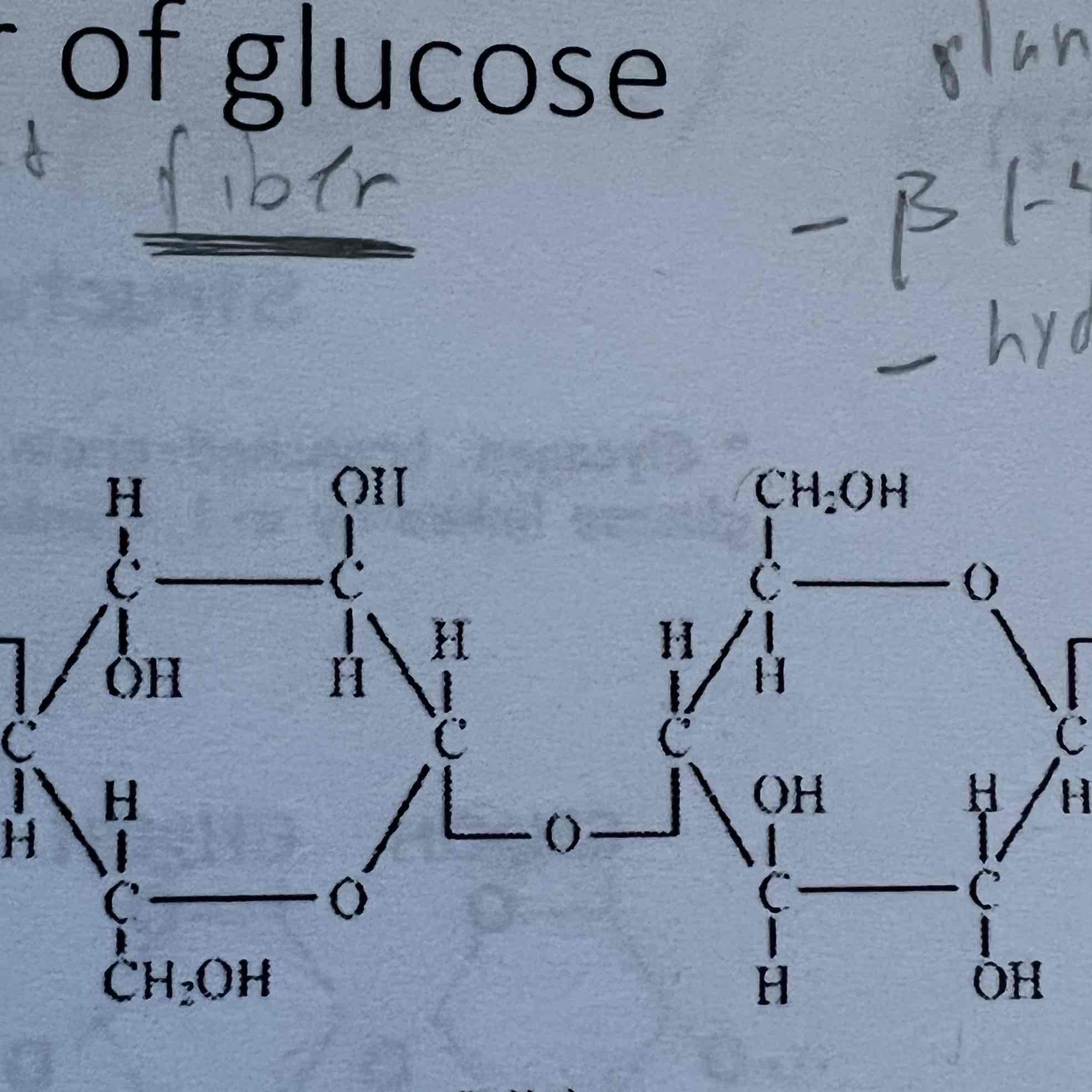
What is cellulose?
structural part of a plant
What are the two classes of polysaccharides?
homopoly and heteropoly
What is a major source of fiber?
cellulose
_____ is a branched starch
glycogen
glycogen
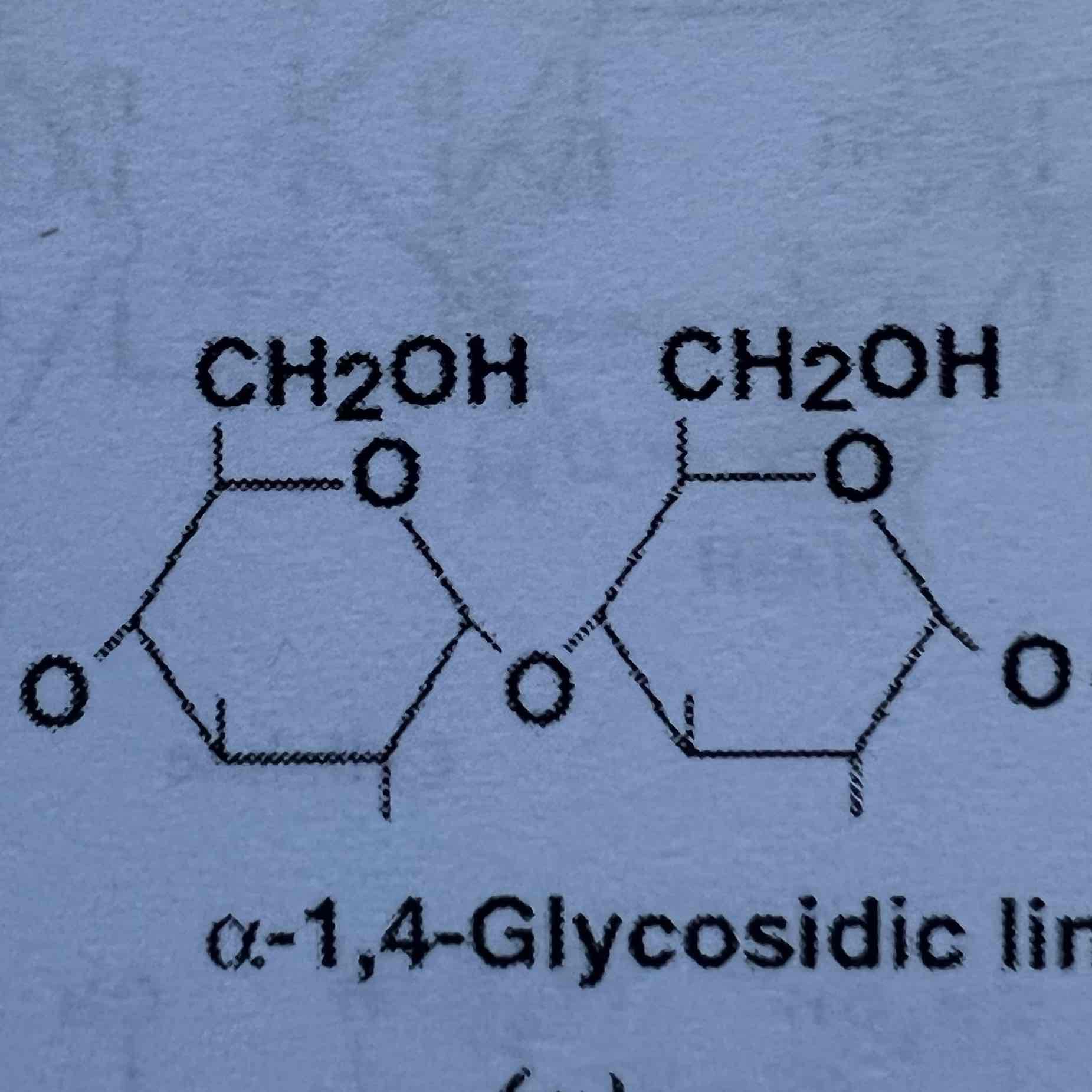
in _____ after every 8-10 glucose residues there is a branch containing a-1-6 linkage
glycogen
What is this describing: main strands linked a-1-4 with branch strands connected a-1-6
glycogen
Examples of heteropolysaccharides
glycoproteins and glycoaminoglycans
What are glycoproteins?
proteins covalently linked to carbs by nitrogen or oxygen
What are glycoaminoglycans?
linear polymers with disaccharide repeated units
What is glycolysis?
biochemical pathway involving 10 enzyme catalyzed reactions that occur in the cytoplasm
Is glycolysis aerobic or anaerobic?
anaerobic
What is the product of glycolysis?
2 pyruvate molecules, 2 ATP molecules, and 2 NADH molecules
Where does glycolysis occur?
cytoplasm
What is stage one of glycolysis?
Prep phase, requires energy
What is stage two of glycolysis?
Pay off phase