Class 4 - Autism Spectrum Disorders
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
What is ASD?
a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by difficulties with social communication and social interaction and restricted and repetitive patterns in behaviours, interests and activities
What is the prevalence of ASD in Canada as of 2022?
1 in 50 children are diagnosed with ASD
Is ASD more common in males or females? What is the prevalence?
males (1 in 42 males, 1 in 165 females)
ASD is often comorbid with:
ADHD, language disorder, intellectual disability, gastrointestinal and sleep disorders
What is early communication like in ASD?
- reduced eye contact
- reduced social interest and social imitation
- reduced response to their name
- fewer bids of joint attention
- reduced use of gestures
- difficulties regulating emotion
- language delays (or regression)
- lack of babbling
- excessive manipulation/visual exploration of objects
- repetitive action with toys
- under reactive or overreactive to sounds or sensory stimulation
Why do parents think vaccines cause ASD?
sometimes kids with ASD have regression of some skills and its normally around when they get vaccines and this is why they make the correlation, even though it is false
What are 3 cognitive theories of ASD
Theory of Mind
Executive Dysfunction
Weak Central Coherence
What is theory of mind (ToM)?
- ability to infer mental states and intentions of others
- this is key for interaction
How do kids with ASD perform on false belief tasks (ToM task)?
tend to show difficulties
Are ToM deficits universal in ASD?
no, some kids may have deficits in ToM but not all kids with ASD do
What is Weak Central Coherence?
- a detailed-focused processing style
2 principles:
1. tend to focus on the local properties of information
2. difficulties integrating local properties of information into meaningful representations
aka only seeing a small portion and not understand the bigger picture

How does executive dysfunction present in individuals with ASD?
individuals with ASD show difficulties with inhibition, planning and cognitive flexibility
e.g., try to open a door, and get frustrated if it does not work, but they dont try alternatives
What one cognitive theory explains ASD?
none, it is unlikely that only one theory can explain the range of strengths and deficits observed in ASD
What is cognitive development like in ASD? (IQ scores)
data from 7 US sites:
- 38% of children with ASD had intellectual disability (IQ < or equal to 70)
- 24% borderline range (IQ = 71-85)
- 38% average or above average intelligence (IQ > 85)
Do genetics contribute to ASD?
yes, there is a large genetic contribution and heritability ranges from 40-90% with over 100 genes being associated with ASD
What are some risk factors for ASD?
- genetic and environmental factors
- increased parental age
- being premature (< 33 weeks gestation)
- low birth weight ( <2500g)
- exposure to insecticides during pregnancy
- viral or bacterial infections during pregnancy
- maternal mental health conditions
Approximately 10% of children with AS also have _____ or _____
down syndrome or fragile X syndrome
What else may be co-morbid with ASD?
ADHD
Anxiety
Depression
Epilepsy
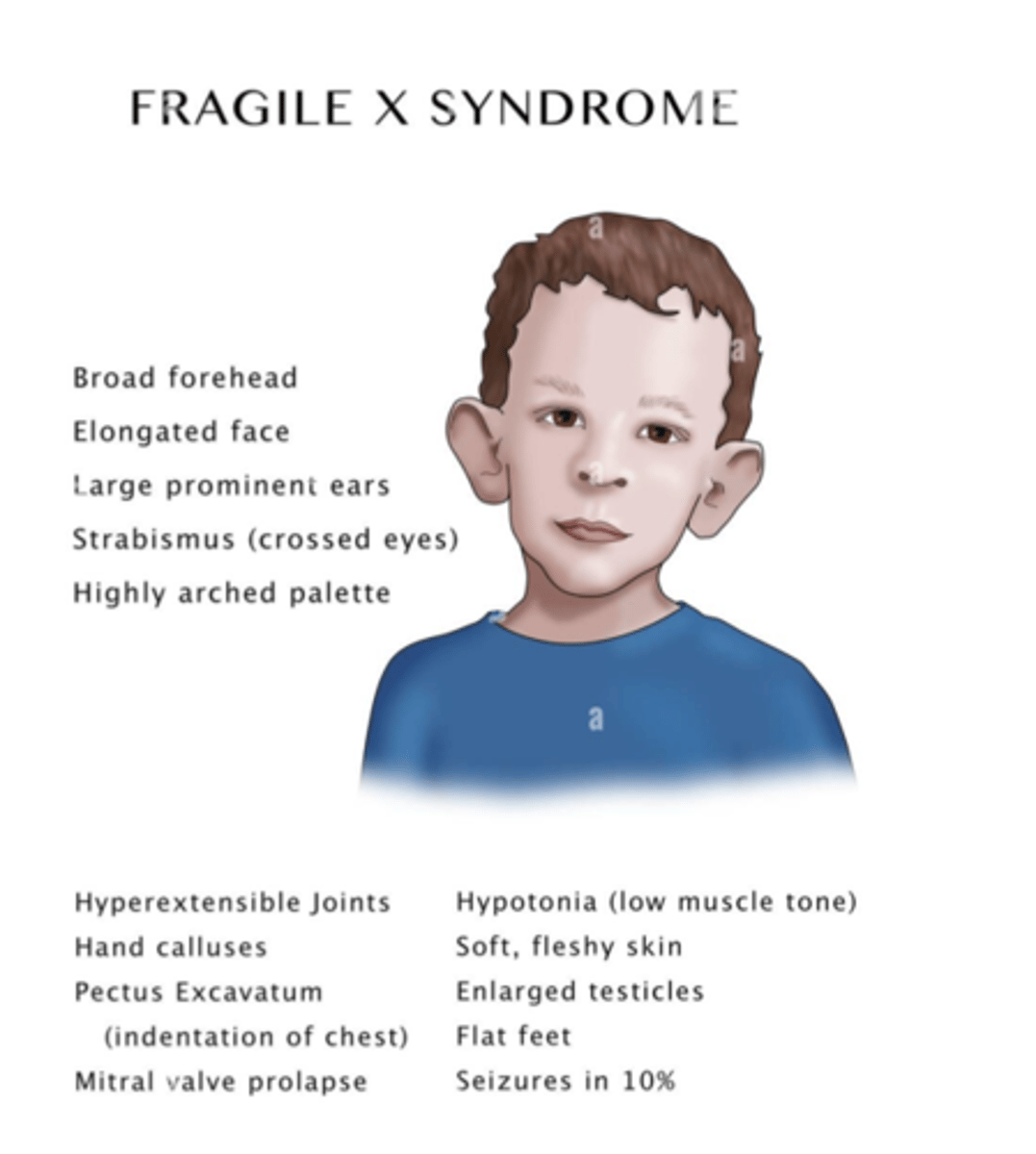
What is Fragile X Syndrome?
- a single gene disorder caused by a significant amount of repetition (200 repetitions compared to 5-44 with TD individuals)
- most common inherited cause of intellectual disability
What disorders/issues co-occur with ASD in preschool?
- language delay
- difficulties with sleep and eating
- highl levels of activity
- epilepsy
- motor problems
What disorders/issues co-occur with ASD in school-aged children?
- ADHD
- Anxiety
- Intellectual disability
- Academic chellenges
- Irritability
- Disruptive behaviours
Who is the first professional that tends too see a child with suspected ASD?
SLPs!
What is the average age of diagnosis for ASD?
~4-5 years old
At what age do parents first concerns about their children typically happen?
Around age 2
What language domain is specifically impaired in ASD?
Pragmatics
Are language profiles the same across all individuals with ASD?
No, there is a high variability in language profiles
What percentage of kids with ASD are minimally verbal?
Approx. 25%
What age do children with ASD produce first words?
around 38 months --> this is a significant language delay
What are 2 common language features observed in ASD?
neologisms (invented novel words)
echolalia --> immediate or delayed imitation of language previously heard
What is immediate echolalia?
occurring within 2 conversational turns
What is delayed echolalia?
repeated utterance occuring after two conversational turns (delay can be hours, days, weeks, etc)
What do recent views of echolalia tell us?
- it is functional --> allows children to participate in social routines, gain time to process language and soothe themselves (self-regulation)
Are pragmatic difficulties universal in ASD?
yes
What difficulties with pragmatics do kids with ASD experience?
- repairing communication breakdowns
- producing adequate answers to questions and comments
- understanding and using humour and inferences
- identifying causes of internal states of characters in a story (related to ToM)
- deficits in narrative tasks (poor referencing in the narrative)
- poor understanding of figurative language
What difficulties with conversational skills do kids with ASD experience?
- poor topic maintenance
- socially inappropriate utterances
- too many or too few initiations
What difficulties with discourse do kids with ASD experience?
- difficulties creating stories that have a clear link across events
- difficulties describing causal structure of a narrative
- less likely to discuss the goals of the characters in a story
- likely to misinterpret what is happening in a story
Is syntax typically impaired in ASD?
no, it is usually preserved
Is morphology typically impaired in ASD?
some difficulties are experienced, specifically for those with ASD and language impairment (LI)
- have shorter and less grammatically complex sentences
- ASD + LI = poor performance on sentence repetition tasks
- some children have difficulties with pronouns, conjunctions and prepositions
Is semantics impaired with ASD?
Mixed results!
- comprehension and production of semantic info is not impaired
- vocabulary is preserved
- difficulties understanding meaning of verbs related to internal mental states (e.g. think, know, remember)
Is phonology impaired in kids with ASD?
- articulation of speech sounds is preserved
- mixed performance on more complex tasks: some kids perform poorly on nonword repetition tasks, also see atypical patterns processing and using prosody
What are some issues in language assessment with ASD?
- children with ASD tend to focus on irrelevant aspects of testing context
- some kids respond better on computer-administered tasks
- spontaneous samples and standard tests may yield different results