Midterm Exam Study Guide
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
What does VISTA stand for?
Variation, Inheritance, Selection, Time, and Adaptation
Gene flow
Consists of the movement of alleles among populations
Can increase or decrease fitness
Alleles can be transferred through the movement of
fertile individuals or gametes (for example, pollen)
Ends to reduce variation among populations over time
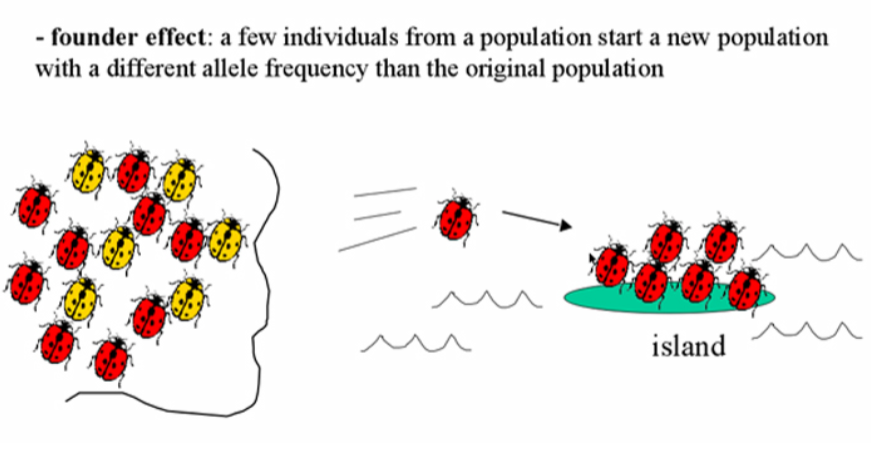
Founder Effect
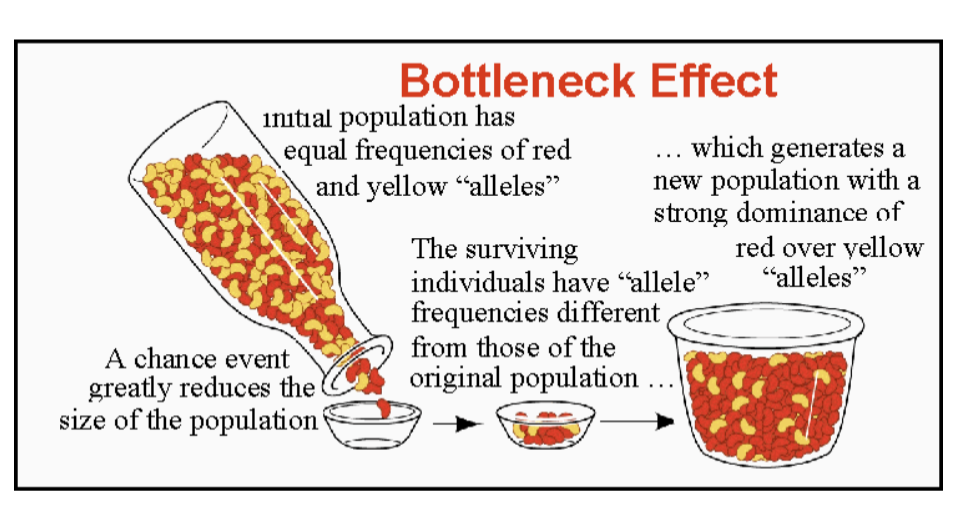
Bottleneck Effect
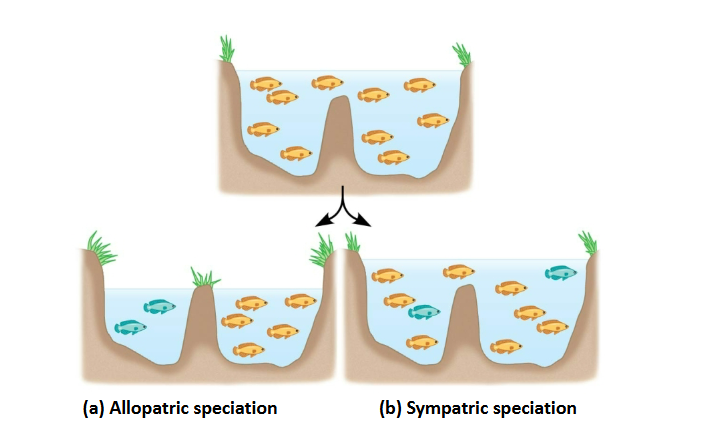
Types Of Speciation
Allopatric
Sympatric
Allopatric speciation
Gene flow is interrupted or reduced when a population is divided into geographically isolated subpopulations
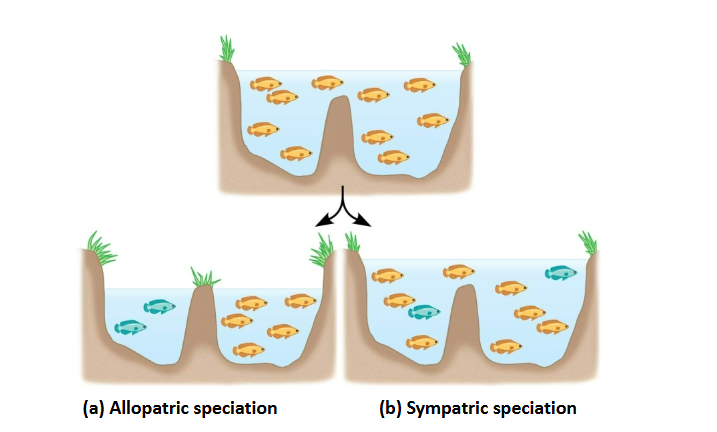
Sympatric speciation
Speciation takes place in geographically overlapping populations
End of the Ordovician
444 mya) – 86% species loss – short, severe ice age
Late Devonian
375 mya) – 75% species loss – land plants (stirred up nutrients?)
End of the Permian
251 mya) – 96% species loss – “The Great Dying” – cataclysmic eruption
End of Triassic
(200 mya) – 80% species loss – Why???????
End of Cretaceous
(66 mya) – 76% species loss -asteroid
Endosymbiont theory
Proposes that mitochondria and plastids (chloroplasts and related organelles) were formerly small prokaryotes living within larger host cells
a cell that lives within a host cell
Basal taxon
diverges early in the history of a group and originates near the common ancestor of the group
Sister taxa
groups that share an immediate common ancestor
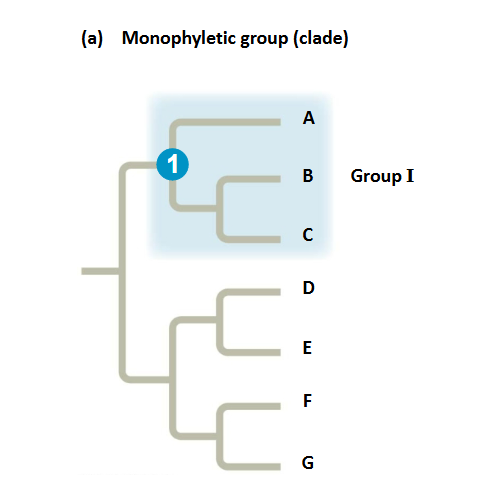
Clade
a group of species that includes an ancestral species and all its descendants
can be nested in larger clades, but not all groupings of organisms qualify as clades
Monophyletic
signifying that it consists of the ancestor species and all its descendants
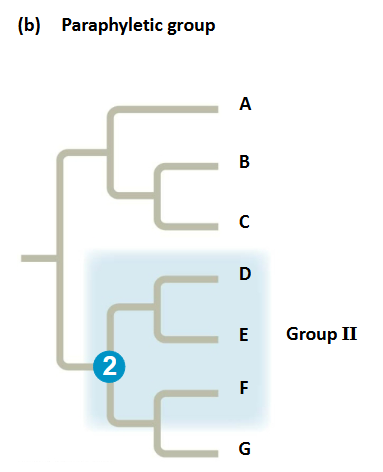
Paraphyletic
grouping consists of an ancestral species and some, but not all, of the descendants
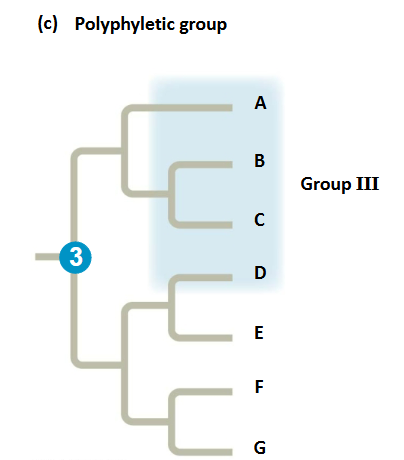
Polyphyletic
grouping includes distantly related species but does not include their most recent common ancestor
Outgroup
is a species or group of species that is closely related to the ingroup, the various species being studied
differentiate between shared derived and shared ancestral characteristics
a group that has diverged before the ingroup
Homology (Homologous)
is similarity due to shared ancestry
Bat and bird wings are homologous as forelimbs
The more elements that are similar in two complex structures, the more likely it is that they are homologous
Analogy (Analogous)
is similarity due to convergent evolution
Bat and bird as functional wings
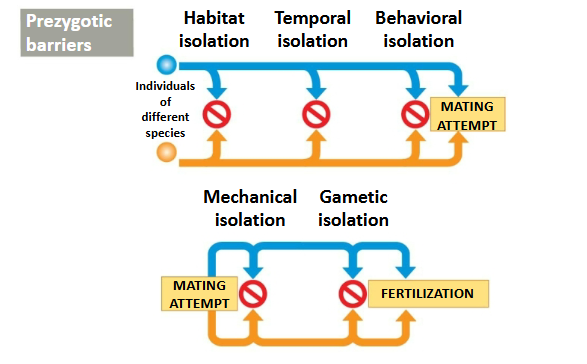
Types of reproductive isolation
Prezygotic barriers (Habitat Isolation, Temporal Isolation, Behavioral Isolation, Mechanical Isolation, and Gametic Isolation)
Postzygotic barriers
Prezygotic barriers
Block fertilization from occurring by:
Impeding different species from attempting to mate
Preventing the successful completion of mating
Hindering fertilization if mating is successful
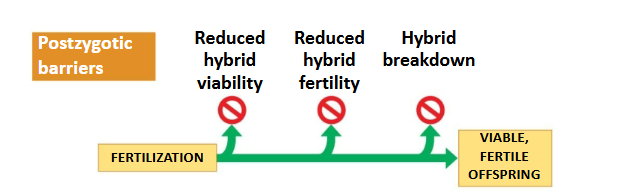
Postzygotic barriers
Prevent the hybrid zygote from developing into a viable, fertile adult
Reduced hybrid viability
Reduced hybrid fertility
Hybrid breakdown
Genetic Drift
is significant in small populations
can cause allele frequencies to change at random
can lead to a loss of genetic variation within populations
can cause harmful alleles to become fixed
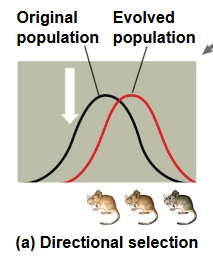
Directional selection
favors individuals at one extreme end of the phenotypic range
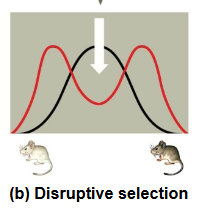
Disruptive selection
favors individuals at both extremes of the phenotypic range
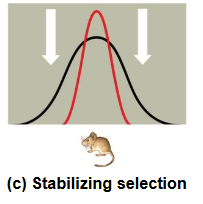
Stabilizing selection
favors intermediate variants and acts against extreme phenotypes
RNA Hypothesis
Natural selection produced self-replicating RNA molecules
The first genetic material was probably RNA, not DNA
The early genetic material might have formed an “RNA world”
RNA molecules that were more stable or replicated more
quickly would have left the most descendant RNA molecules