BIOL 2460 Chapter 9: Microbial Growth
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Most common form of bacterial reproduction
Binary fission
4 Basic Steps of Binary Fission
1. Growth of cell size and increase in cell components
2. Replication of DNA/chromosomes
3. Division of cytoplasm (cytokinesis)
4. Septum formation and division of daughter cells
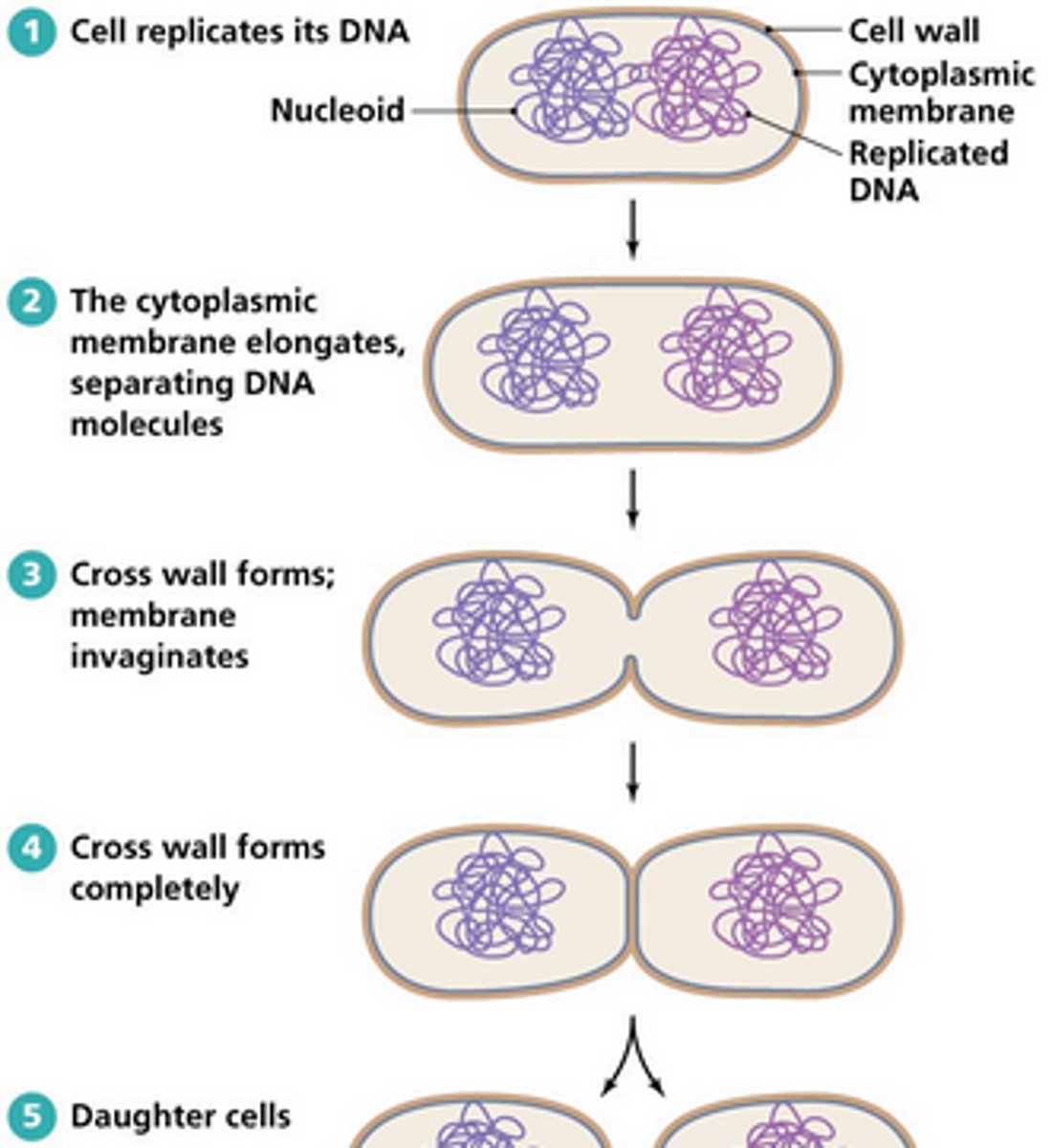
Cytokinesis is directed by the ___________ protein.
FtsZ
Where is the Z ring assembled during binary fission?
On the cytoplasmic membrane
Divisome activates the production of __________________ and ____________.
Peptidoglycan; septum
Generation Time
Also known as doubling time; the time it takes to double the bacterial population (or one round of binary fission).
Generation Time for E. Coli
20 minutes
Generation time for B. subtilis
120 minutes
Generation time for M. tuberculosis
15-20 hours
Generation time for S. aureus
30 minutes
Bacterial population size calculation
𝑁𝑛=𝑁02𝑛
The Z ring is anchored by what?
FtsZ binding proteins; also helps define the division plane between daughter cells.
𝑁𝑛 is what?
The number of cells at generation n.
n is what?
The number of generations.
N0 is what?
The initial number of cells.
Growth curve
Microorganisms grown in closed culture, in which no nutrients are added and waste is not removed, follow a reproducible growth pattern.
Culture Density
The number of cells per unit volume.
Within a closed culture, it can also refer to a measure of the number of cells in the population.
Phases of the Growth Curve
1. Lag phase
2. Log phase
3. Stationary phase
4. Death phase
Lag Phase
Period where inoculum are gearing up for the next phase of growth; the number of cells doesn't change, however, they grow larger and are metabolically active.
If any cells were damaged during the transfer, they will be repaired during this phase.
Inoculum
Microbes that are introduced into a culture medium to initiate growth.
Culture Medium
Nutritional broth that supports microbe growth.
The duration of the lag phase is determined by what factors?
Species and genetic makeup of cells
Media composition
Initial size of inoculum
Log Phase
Sometimes called the exponential growth phase; cells are actively undergoing binary fission and cell replication is greater than cell death; cells are constantly growing and are most susceptible to disinfectants and antibiotics that target proteins, DNA, and cell-wall synthesis at this point.
Intrinsic Growth Rate
Generation time under specific conditions is genetically determined.
Stationary Phase
Waste products accumulate and nutrients get used up, so the growth rate slows; oxygen depletion limits aerobic cell growth and population growth starts to stall; the number of cells dying is equal to the number of cells replicating.
Cells are less susceptible to antibiotics during this phase and certain pathogenic bacteria express virulence factors.
What pathogenic bacteria expresses virulence during the stationary phase of the growth curve?
S. aureus; during the stationary phase, it initiates the production of enzymes that help break down human tissue to enable spread to new tissues, where nutrients are more abundant.
Death Phase
The number of dying cells exceeds the number of cells replicating at this point; cells are lysing and releasing nutrients into the medium, allowing any existing cells to maintain viability and form endospores; persistent cells have slow metabolic rates and do not respond to antibiotic treatments.
During which phase would you see the most endospores?
Death phase.
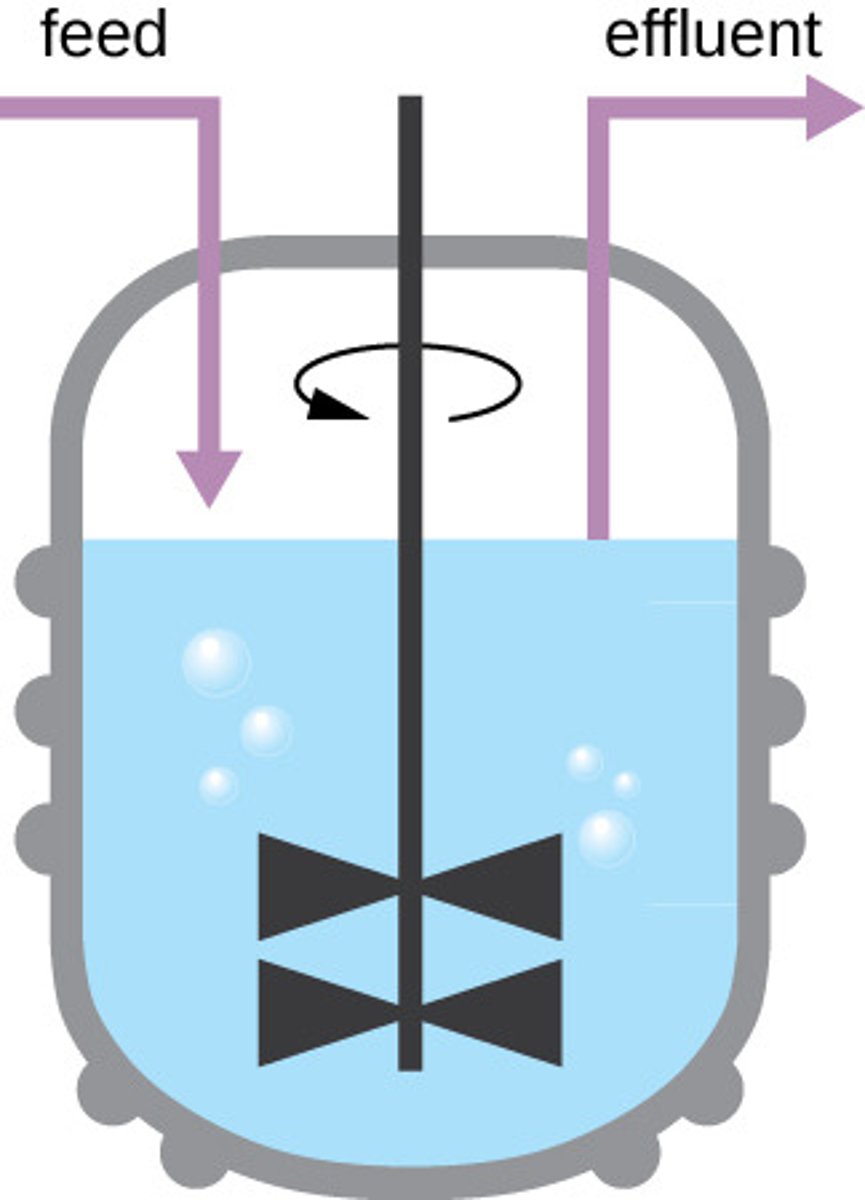
What is a chemostat used for?
To maintain a microbial population in which nutrients and air are supplied at a steady rate and dead cells are waste are simultaneously removed.
The number of bacteria in a clinical sample serves as an indication of what?
The extent of infection.
Bacterial count
Estimating the number of bacterial cells in a sample.
What approaches are used to measure cell numbers?
Direct and indirect methods.
Types of direct measuring methods:
Microscopic cell count
Fluorescent staining (for alive and dead cells)
Coulter count
Viable cell count
Direct Cell Count
Refers to counting the cells in a liquid culture or colonies on a plate.
Direct Microscopic Cell Count
Transferring a known volume of a culture to a calibrated slide and counting the cells under a light microscope.