Biological bases of behaviours
1/47
Earn XP
Description and Tags
The Neuron
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
What are neurons?
The basic units of the nervous system that coordinate thinking, feeling, & acting
What is the function of neurons
Neurons carry info between cells, muscles, & organs to enable body functions
How many neurons are in the human body?
The human body contains 10-100 billion neurons
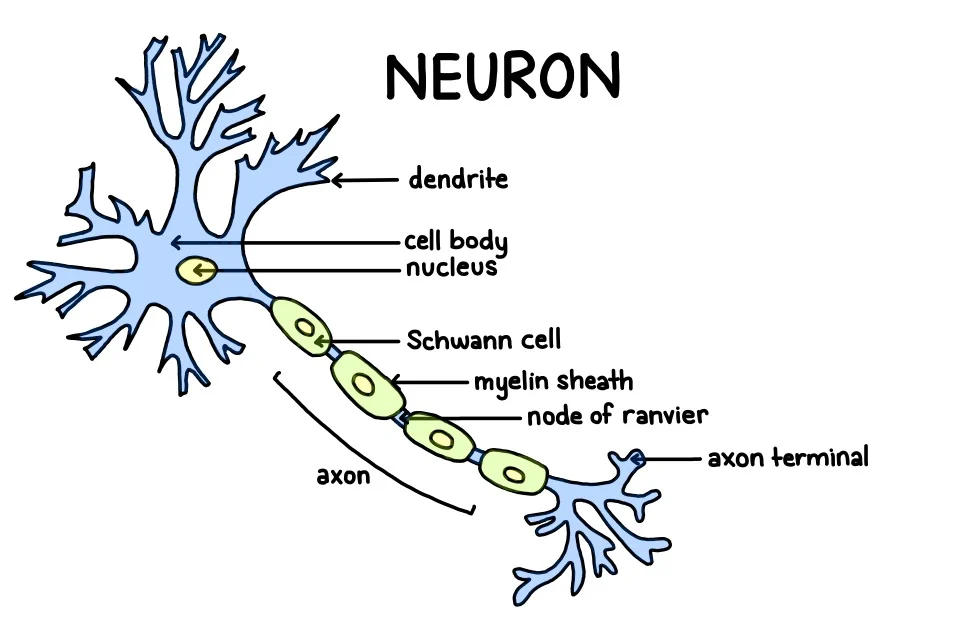
What are neurons
Excitable cells that create & propagate neural impulses to transmit information
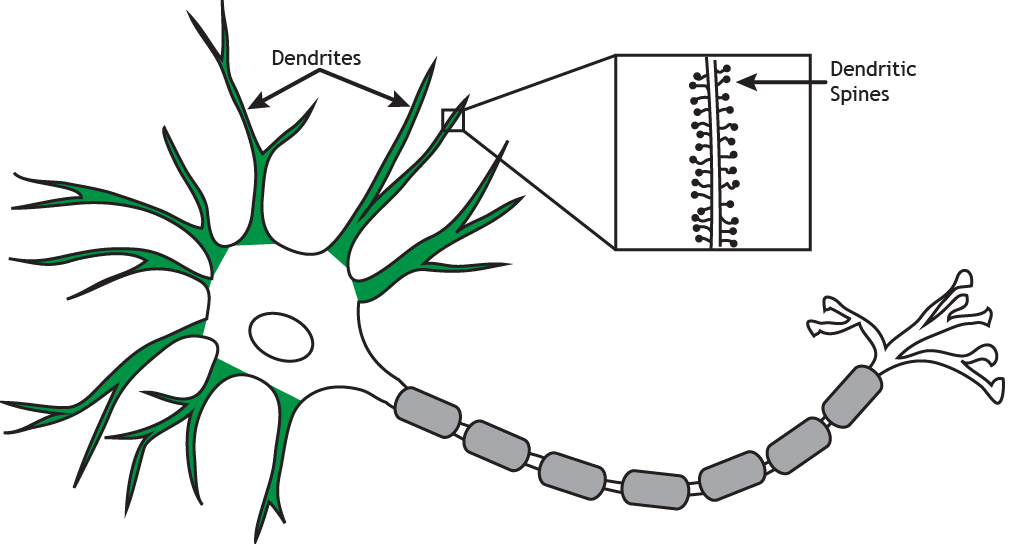
What is the function of dendrites?
Receive info from other neurons & send it to the cell body
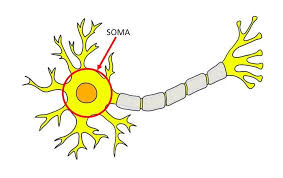
What is the function of the SOMA
The soma (cell body) contains nucleus & processes incoming info
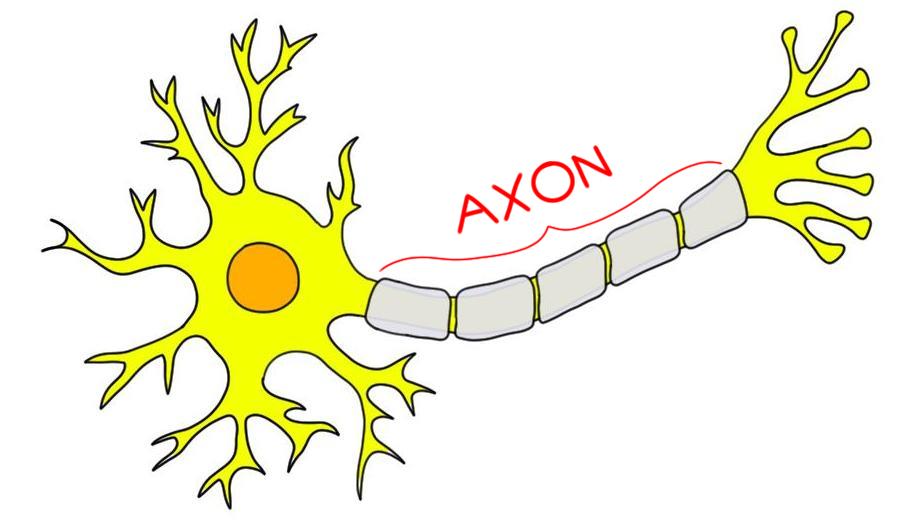
What does the axon do?
Transmits signals away from the soma to other neurons
What is the myelin sheath?
A fatty substance that encases axons, speeding up signal transmissions
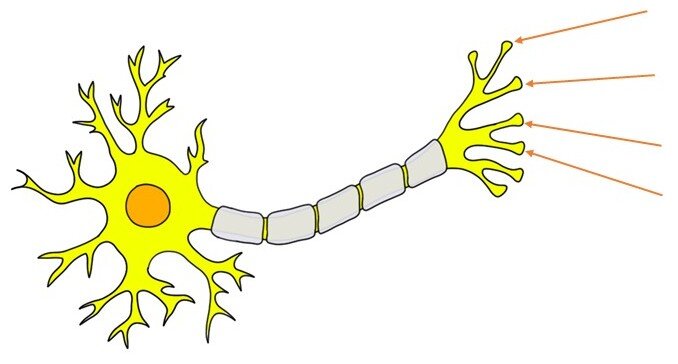
What is the function of terminal buttons
Secrete neurotransmitters, which help transmit signals to other neurons
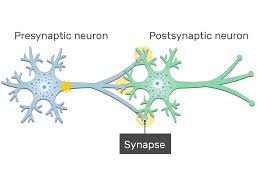
What is a synapse
The gap where info is transmitted between neurons
Sensory (Afferent) Neurons
Carry info from sensory receptors to the brain
Responsible for sensations
Interneurons
Connect neurons together
Found in the brain & spinal cord
Motor (Efferent) Neurons
Send commands from interneurons to muscles
Control voluntary actions (e.g. dancing) & bodily functions (e.g. heartbeat)
Glial Cells (Support Cells)
Make up >50% of brain volume
Support neurons; non-excitable cells
Function of Glial Cells
Supply nourishment to neurons
Remove waste
Form myelin sheaths for insulation
Additional Roles of Glial Cells
Detect neural impulses & send signals to other glial cells
Play a role in memory formation
Glial Cells & Disease
Deterioration may contribute to Alzheimer’s disease
What is a Neural Impulse
An electrochemical reaction
How neurons communicate with one another
Ions involved in Neural Impulse
Positive ions: Sodium (Na⁺) & Potassium (K⁺)
Negative ion: Chloride (Cl⁻)
Ion Movement in Neurons
Ions flow across the membrane at different rates
The inside of the neuron is more negative than the outside
Resting Potential
A stable negative charge inside the neuron when at rest
How does a neural impulse move through a neuron
When activated, positive ions (e.g. sodium) rush into the neuron
The neuron becomes less negative or positive
Direction of Action Potential
Travels along the axon in ONE direction only
Channels then close, & resting potential is restored
Absolute Refractory Period
Minimum time before another action potential can begin
Lasts 1-2 milliseconds
Relative Refractory Period
Higher threshold needed for a new action potential
“All-or-None” Principle
A neural impulse either fires or it doesn’t
No partial firing
Action Potential Size
Always the same size, regardless of stimulus strength
How is Stimulus Strength Conveyed
Stronger stimulus = faster firing rate of action potentials
Example: Pin prick vs. car running over your toe
What is the Synapse
The point where a neural impulse is transmitted from one neuron to another
Synaptic Cleft
A gap that separates 2 neurons
Neurotransmitters jump the gap to send signals
What does the Presynaptic Neuron do
Sends signals
What does the postsynaptic neuron do
Receives signals
Neurotransmitter Release
Action potential triggers the release of neurotransmitters
Where are Neurotransmitters Stored
Stored in the synaptic vesicles inside the presynaptic neuron
How are neurotransmitters released
Vesicles fuse with the membrane & release neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft
Neurotransmitter Binding
Neurotransmitters bind to specific receptor sites on the postsynaptic neuron
What is Postsynaptic Potential (PSP)
A voltage change at the receptor site
Caused when a neurotransmitter binds to a receptor
Effect of PSP on Neural Impulse
PSPs vary in size
Can increase or decrease the chance of a neural impulse in the receiving cell
What is Excitatory PSP
Positive voltage shift (more likely to fire)
What is inhibitory PSP
Negative voltage shift (less likely to fire)
Duration of PSP
Lasts only milliseconds
Neurotransmitters Fate after PSP
Neurotransmitters drift away, are broken down by enzyms, or undergo reuptake
Neural Connections
Each neuron is connected to thousands of other neurons
Neurons integrate signals from multiple sources
Excitatory PSP in Neural Networks
Enough excitatory PSPs → Action potential fires
Inhibitory PSP in Neural Networks
Many inhibitory PSPs → Cancel excitatory effects
Neural Networks & thought
Thoughts depend on interconnected neurons
Neurons are linked by synapses
Synaptic Pruning
Less active synapses are removed over time
What does Synaptic Pruning do
Help improve neural efficiency