Exercise physiology 3
1/121
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
122 Terms
Physical activity
Bodily movement that is produced by the contraction of skeletal muscle and that substantially increases energy expenditure.
Exercise
Planned, structured,, and repetitive bodily movement done to improve or maintain one or more components of fitness.
physical fitness
a set of attributes that people have or achieve, which relates to the ability to perform physical activity.
Health related physical activity Components
cardiorespiratory endurance, body composition, muscular strength, muscular endurance, flexibility
cardiorespiratory endurance
maximal ability to use oxygen (tested by vo2 max)
muscular endurance
the ability of muscle to perform continuously without fatigue (ex. push ups to fatigue)
muscular stregnth
The most force produced one time. (one rep with a heavy set)
body composition
The percentage that is fat tissue to lean tissue.
flexibility
range of motion about a joint.
Skill related physical fitness components
Agility, coordination, balance, power, reaction time, speed
agility
ability to change the position of the body in space with speed and accuracy
coordination
ability to use the senses, such as sight and hearing together with body parts in performing tasks
balance
maintenance of equilibrium
power
ability or rate at which one can perform work
reaction time
the time elapsed between stimulation and the beginning of the reaction to it
speed
ability to perform a movement within a short period of time
EPOC
Excess Post exercise O2 Consumption
Who was the founder of Oxygen deficit and EPOC
A.V. Hill
example of O2 defecit and EPOC on a graph draw the one in ur notes
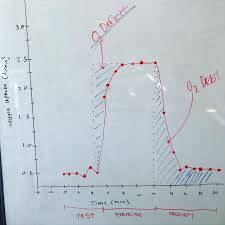
A.V. Hill thought that the size of the O2 debt was equal to the O2 deficit size, but what do we know now?
The O2 debt (EPOC) is larger than the O2 deficit
O2 debt (epoc) ATP-PC. glycolysis→ lactic acid→ O2 consumption
↑ body temp, ↑ HR, ↑ VE (ventilation muscles, ↑ NE/EPI
Ventilation (l/min)
Volume of gas inspired & expired.
ventilation at rest
Inspired (Vi) is greater than expired (Ve). Vi > Ve
Ventilation during intense exercise
expired is greater than inspiration. V i< Ve
Q=
HR x SV
Ve is measured in
ml/min which we then divide by 1000 to get L/min
F means
frequency of breathing. measured in b/min
tv means
Tital volume of gas in each breath. measured in ml/b
Ve=
f X tv
Ve/f=
tv
example of Ve = f x tv
Ve= 12 × 50= 6000 ml/min= 6 L/min
Ambient air is made up of what 3 gasses
Nitrogen (N2), Oxygen (O2), Carbon Dioxide (CO2)
what percentage of nitrogen do we breathe?
79.04%
what percentage of oxygen do we breathe?
20.93%
what percentage of carbon dioxide do we breathe?
0.03%
What is the partial pressure of Nitrogen
600 mmHg
What is the partial pressure of oxygen
159 mmHg
What is the partial pressure of carbon dioxide
.2 mmHg
What is the Alveoli partial pressure of Nitrogen
571 mmHg
What is the Alveoli partial pressure of oxygen
103 mmHg
What is the Alveoli partial pressure of carbon dioxide
39 mmHg
what is the mitochondrial partial pressure of oxygen
3-5 mmHg
Barometric percentage
pressure exerted by the gasses in the air
What is a normal barometric pressure at sea level
760 mmHg
to calculate the partial pressure of any of the elements we
take the barometric pressure and multiply it by the percentage that we breathe.
Example of calculating the nitrogen partial pressure
760 x .7904=600
Like with blood,gasses flow from
high pressure to low pressure
How is O2 transported in blood?
Hemoglobin
In Hemoglobin Fe how many oxygens?
4
In myoglobin Fe carries how many oxygens
1
oxyhemoglobin saturation curve
the points are at (20,25), (30,50), (40,75), (100,100)
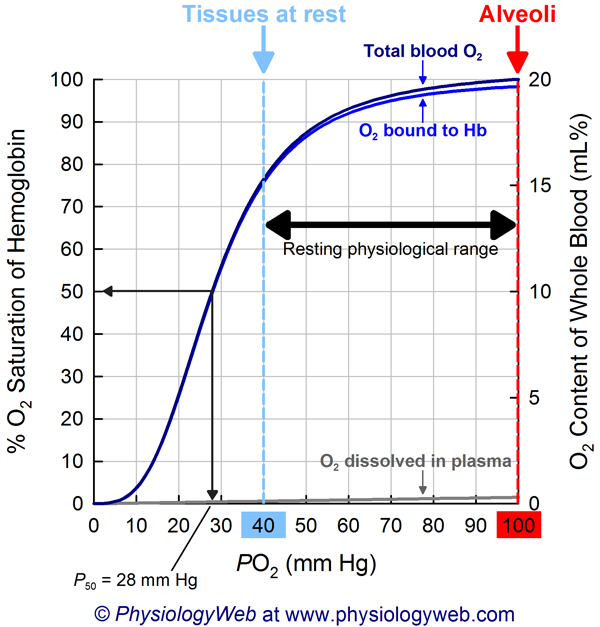
for the oxyhemoglobin saturation curve at the top (100,100)
this is where we are in systemic arterial blood
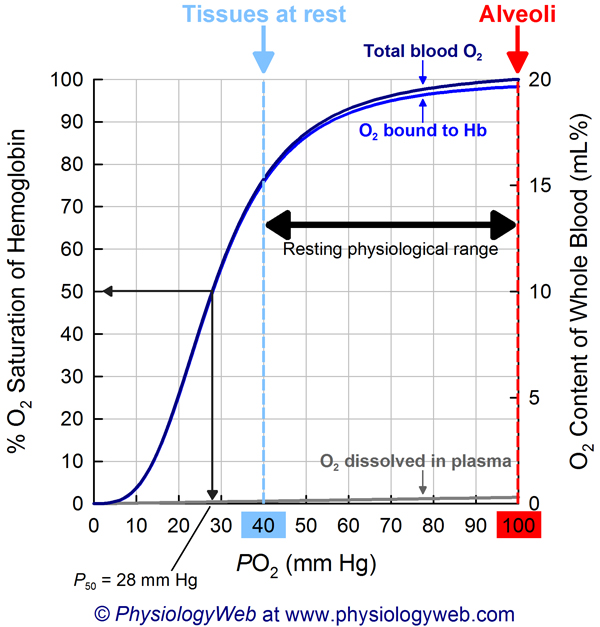
for the oxyhemoglobin saturation curve at point (40,60)
this is where systemic venous blood is at rest
looking at the systemic artery, the blood will be
20 ml o2/ 100 ml bl
As long as we are breathing normal air and not in high elevation,
we will be at 100% saturation
Why do we need to use the saturation quickly?
becuase our muscles need it to do more work
acid makes pH
go down
looking at the oxyhemoglobin saturation curve during exercise, the curve shifts
to the right
during exercise, pH decreases and
causes more oxygen to move into the tissues.
The red line in the graph is the
baseline
When the blood gets hot (increases in temp) during exercise the curve shiftss
to the rightt
In total, the affect of exercise will cause the graph to shift to the left
False (the right)
which people have the lowest cardiorespiratory fitness
ppl who have had heart attacks, which is damage to the heart muscles
what is lean?
anything that is not fat ( tendons, bones, cartilage, organs, liquid etc.)
diseases of too much fat
Some cancers, diabetes, heart disease, high cholesterol, hypertension, obesity, osteoporosis
3 different types of exercise prescriptions
Aerobic, resistance, flexibility.
aerobic exercise prescription
this is to maintain or improve cardiorespiratory
resistance exercise prescription
This is to maintain or improve muscular strength and endurance
Flexibility exercise prescription
This is to maintain or improve the range of motion about a joint
All three of these prescriptions make up what?
they make up the maintaining and improving of the body composition
F.I.T.T
Frequency, Intensity, Time, Type
Frequency
how often (ex. 3 days a week)
Intensity
How hard. (ex. Moderate or Intensity)
Time
How long (ex. 30-60 min a day)
Type
what type (aerobic/resistance)
Aerobic FITT
I will start all the aerobic ones with an AE
AE frequency
3-5 days a week
AE intensity
moderate (40-59% HRR or VO2) and Vigorous (60-89% HRR or VO2)
AE type
Continuous or intermittent involving major muscle groups
Resistance FITT
I will start all the resistance ones with an RE
RE frequency
Novice-major muscle groups at least 2 days a week.
Experienced- frequency is secondary to training volume
RE Intensity
novice- 60-70% of the 1 rep max, 8-12 reps (to improve muscular fitness)
experienced- wide range of intensities, reps, and sets that are effective.
RE Type
multi joint- target agonist and antagonist muscles first
single joint- do theses second
RE Time
there is no time for it
To estimate maximal HR we use
220 - age
As we age
maximal HR decreases
After calculating the HR max, to get the HHR we
take the HR max and subtract it from the resting HR
after collecting the HHR we should
multiply it by the desired intensity to get a value hr
after getting the value we should
Add the resting HR back in
after adding in the HR what does this give u
It gives u what the Target HR should be at for the intensity u want to workout.
Example of THR for a 20 year old with a resting HR of 60, wanting to work out at an intensity of 50
220 - 20= 200
200 - 60= 140
140 x .50= 70
70 + 60= 130
Example of THR w/o values
220 - age= HR max
HR max - HR rest= HR Reserve
HRR x Desired intensity= Value
Value + HR rest= THR
To get THR using VO2 we are going to use the same person
20 year old with a vo2 max of 3.2 l/min and a resting vo2 of .3 l/min
We should first take the VO2 max and
minus it from the VO2 rest
after subtracting the vo2 max from the Vo2 rest we get
VO2 Reserve
Take the VO2 R and
multiply it by the desired intensity to get a value
take that value and
Add back in the VO2 rest to get the target VO2
Example of Target VO2: 20 year old with a vo2 max of 3.2 l/min and a resting vo2 of .3 l/min
3.2 - .30= 2.90
2.90 x .70= 2.03
2.03 + .30=2.33 l/min
Example of getting Target VO2 w/o values
vo2 max - vo2 rest= vo2 reserve
vo2 reserve x desired intensity = value
value + vo2 rest= Target Vo2
If you are at 70% of the HRR then you are also at
70% of the VO2 reserve. Same with any value