Metabolism
1/8
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
Metabolism
All chemical reactions occurring in the cell, including breaking down (digesting) and building.
Catabolic reactions
Hydrolysis; a spontaneous reactions that break down molecules.
high entropy, low potential energy
Anabolic reactions
Dehydration Synthesis; a non-spontaneous reactions that builds molecules up
low entropy, high potential energy
What is true about Metabolic Reactions?
metabolic reactions are always coupled; anabolic reactions cannot happen without the energy input of catabolic reactions.
What is G when measuring enzyme activity?
The measure of free energy, which is the potential energy available to be use
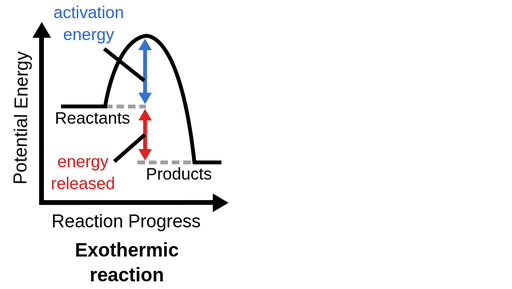
What is an exergonic reaction categorized as?
Catabolic (spontaneous, hydrolysis, increase entropy, decrease potential energy)
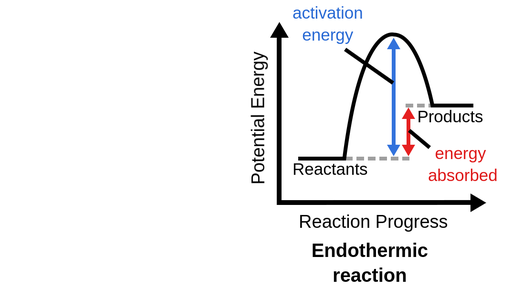
What is an endothermic reaction categorized as?
Anabolic (non-spontaneous, dehydration synthesis, decreased entropy, increased potential energy)
Activation Energy
The input of energy needed to initiate a reaction in catabolic reactions in order for change to happen. Enzymes (catalysts) decrease activation energy to increase the rate of reaction
What is true about enzymes?
Enzymes are always specific to a particular substrate due to its active site, as it is compatible to its shape, polarity, and charge.