Biology: Cell Theory, Microscope Functions, and Human Chromosomes
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
86 Terms
What is biology?
The study of life
Name three careers that require an understanding of biology.
1. Biologist
2. Medical Doctor
3. Environmental Scientist
Complete the three parts of the cell theory.
1. All cells come from pre-existing cells.
2. All living things are made up of one or more cells.
3. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in all organisms.
Put the following levels of biological organization in order from the most simple to most complex.
1. Cell
2. Tissue
3. Organ
4. Organ System
5. Organism
What is the total magnification if the ocular lens is 5x and the objective lens is 10x?
Total magnification = Ocular magnification x Objective magnification = 5x x 10x = 50x.
What is the function of the eyepiece in a microscope?
The eyepiece magnifies the object, usually by 10x.
What is the function of the revolving nosepiece in a microscope?
The revolving nosepiece holds the objective lenses and allows the user to switch between different magnifications.
What is the function of the objective lenses in a microscope?
Objective lenses magnify the object, typically at powers of 4x, 10x, 40x, and 100x.
What is the function of the stage in a microscope?
The stage supports the microscope slide and holds it in place.
What is the function of the diaphragm in a microscope?
The diaphragm controls the amount of light reaching the object being viewed.
What is the function of the coarse focus knob in a microscope?
The coarse focus knob moves the tube or stage up and down to bring the object into focus, used with low power objective lenses.
What is the function of the fine focus knob in a microscope?
The fine focus knob moves the tube or stage up and down to bring the object into sharper focus, used with medium and high-power objective lenses.
What is the difference between active and passive transport?
Active transport requires energy to move substances against their concentration gradient, while passive transport does not require energy and moves substances along their concentration gradient.
What is the function of vacuoles in a cell?
Vacuoles store materials within the cell, such as food, enzymes, and waste products.
What is the function of the Golgi apparatus?
The Golgi apparatus is responsible for closely stacked, flattened sacs that package proteins for transport out of the cell.
What is the function of ribosomes?
Ribosomes are the site of protein synthesis in the cell.
What is the function of the endoplasmic reticulum?
The endoplasmic reticulum transports materials within the cell.
What is the cytoplasm?
The cytoplasm is the region inside the cell, except for the nucleus, that holds organelles in place.
What is the function of the nucleus?
The nucleus manages or controls the cell functions in a eukaryotic cell.
What is the function of chloroplasts?
Chloroplasts contain chlorophyll, which traps energy from sunlight and gives plants their green color.
What is the function of lysosomes?
Lysosomes digest excess or worn-out cell parts, food particles, and invading viruses or bacteria.
What is the function of the cell wall?
The cell wall is a firm, protective structure that gives the cell its shape in plants
What is the function of mitochondria?
Mitochondria produce a usable form of energy for the cell, often referred to as the 'powerhouse' of the cell.
What is the function of the nucleolus?
The nucleolus is the site where ribosomes are made.
What is the structure surrounding the cell?
The structure surrounding the cell is the cell membrane, composed of a phospholipid bilayer.
diffusion
movement of a substance from high concentration to low concentration
osmosis
movement of water from high concentration to low concentration
facilitated diffusion
movement of a substance from high to low concentration with the use of protein channel or carrier protein
What are chromosomes?
Chromosomes are strands of DNA in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells.
How many chromosomes are present in a human body cell?
There are 46 chromosomes in a human body cell.
How many chromosomes are present in a human sperm cell?
There are 23 chromosomes in a human sperm cell.
How many chromosomes are present in a human egg cell?
There are 23 chromosomes in a human egg cell.
In which stage of the cell cycle does a cell spend most of its time?
A cell spends most of its time in interphase.
What are the key events that occur during interphase?
1. Cell growth and increase in size.
2. DNA replication.
3. Preparation for mitosis.
Identify the phases of mitosis.
1. Prophase
2. Metaphase
3. Anaphase
4. Telophase.
What are the phases of mitosis?
The phases of mitosis are prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. In prophase, chromosomes condense and the nuclear envelope breaks down. In metaphase, chromosomes align at the cell's equator. In anaphase, sister chromatids are pulled apart to opposite poles. In telophase, nuclear envelopes reform around the separated chromosomes.
List three reasons why cells divide.
- Surface area to volume ratio
- cells get old and worn out
- reproduction/growth
How does cytokinesis differ in plant and animal cells?
In animal cells, cytokinesis occurs through the formation of a cleavage furrow that pinches the cell into two. In plant cells, a cell plate forms along the center of the cell, developing into a new cell wall.
What are cell cycle checkpoints?
Cell cycle checkpoints are regulatory points in the cell cycle that ensure the proper progression of cell division.
List the major checkpoints in the cell cycle.
1. G1 checkpoint (restriction point) 2. G2 checkpoint 3. M checkpoint (spindle checkpoint)
What is cancer?
Cancer is a disease characterized by uncontrolled cell division, leading to the formation of tumors and the potential spread of cancerous cells to other parts of the body.
List three different causes of cancer.
- viruses
- chemicals
- smoking
Define a tumor.
abnormal lump of cells
What is a benign tumor?
tumor that remains in one place in the body
What is a malignant tumor?
tumor that can spread throughout the body
What is DNA screening?
DNA screening is a process used to analyze an individual's genetic material to identify genetic disorders or predispositions to certain diseases.
Define cloning.
Cloning is the process of creating a genetically identical copy of an organism or cell.
What are some benefits of cloning?
Benefits include the potential for medical advancements, preservation of endangered species, and agricultural improvements.
What are some drawbacks of cloning?
Drawbacks include ethical concerns, reduced genetic diversity, and potential health issues in cloned organisms.
What are the four types of tissues found in animals?
1. Epithelial tissue - covers body surfaces and lines cavities. 2. Connective tissue - supports and binds other tissues. 3. Muscle tissue - responsible for movement. 4. Nervous tissue - transmits signals and processes information.
What is the primary function of the digestive system?
takes in food and breaks it down; absorbs nutrients and eliminates solid waste from the body
What is the primary function of the respiratory system?
controls breathing; exchanges gases in lungs
What is the primary function of the circulatory system?
transports blood, nutrients, gases and wastes
What are the parts of the digestive tract from mouth to anus?
Mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, anus.
What are the accessory organs used in the digestive process?
liver, pancreas, gallbladder, and salivary glands.
What are the parts of the respiratory system from atmosphere to our lungs?
mouth, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, alveoli
external respiration
exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide gas between the alveoli and capillaries which rest on the surface of the alveoli
circulation
the movement of dissolved oxygen and carbon dioxide being carried by the blood to and from the body cells.
Internal respiration
exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the blood and the body cells
cellular respiration
the process of taking oxygen and glucose into the cell to make energy (ATP) for the organism.
Oxygen + Glucose -> Carbon Dioxide + Water + Energy (ATP)
how are the digestive system and respiratory system are related.
the pharynx is the primary shared structure, acting as a passage way for both air and food/liquid
What are the three parts of the circulatory system?
1. Heart 2. Blood vessels 3. Blood
blood cell types, alternate name, percent of blood, function
red blood cell - erthrocytes - 15% - carry oxygen
white blood cell - leukocytes - 15% - fight infection
platelet - thrombocytes - 15% - clot/form a scab
plasma - 55% - carries formed elements
4 chambers of the heart
right atrium, right ventricle, left atrium, left ventricle
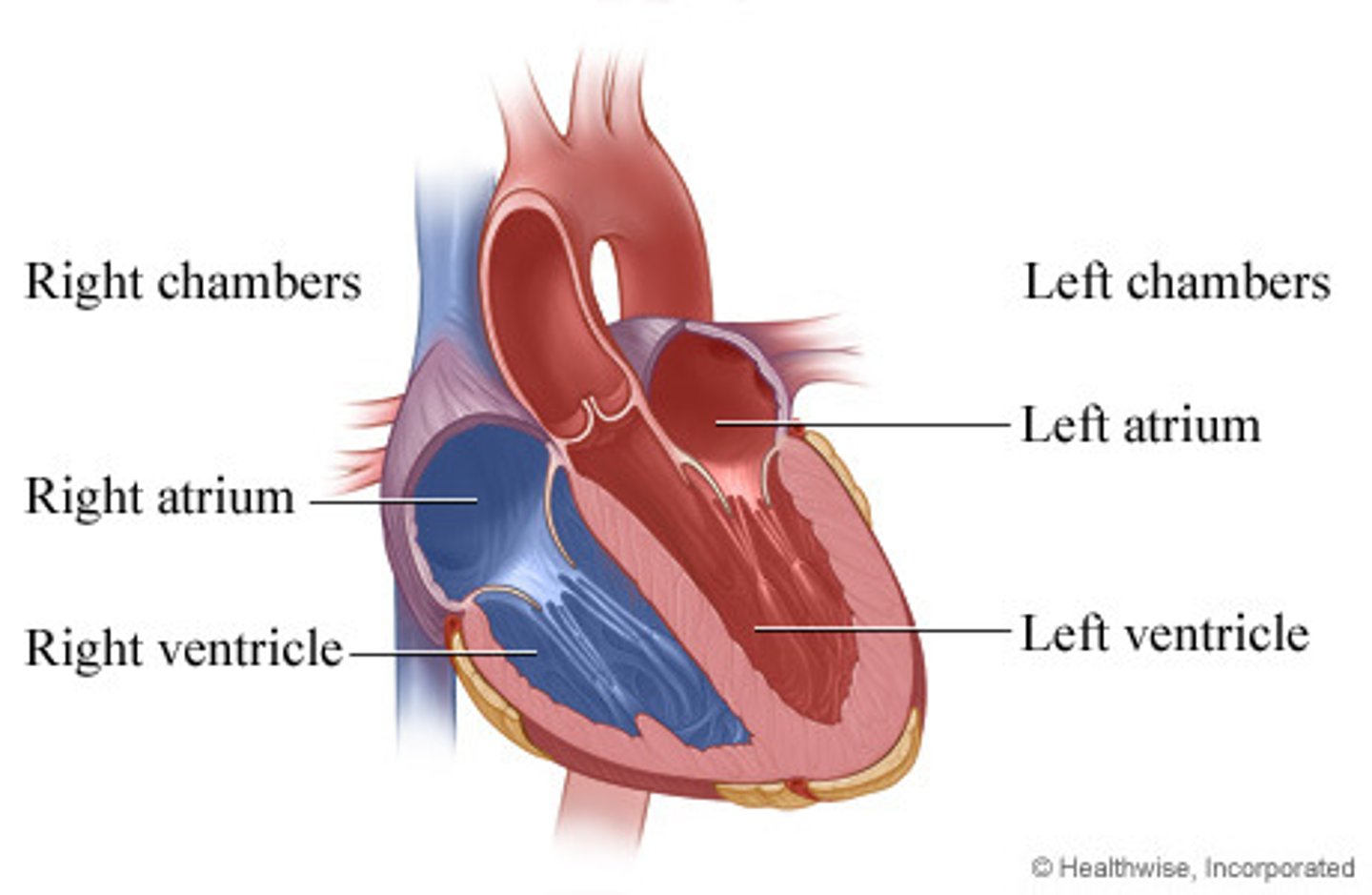
how are the respiratory system and circulatory system are connected
work together to deliver oxygen and remove CO2
dermal tissue
protects the delicate inner issue tissue from damage and controls the exchange of water and gases between the plant and its environment
ground tissue
made of cells that perform photosynthesis/provide support for the plants body.
vascular tissue
provide physical support for the plants body. transports sap throughout the plant.
Xylem
transports water and minerals in plants
Phloem
transports in sugars in plants
bud
a swelling on a plant stem
terminal bud
most active plant growth
lateral bud
inactive, but can produce branches and leaves
What is transpiration?
the evaporation of water from leaves
Cuticle
The waxy, waterproof layer that covers the leaves and stems of most plants.
epidermis
Outer layer of skin
guard cells
control the opening and closing of stomata
palisade layer (mesophyll)
the layer of cells in a leaf where most photosynthesis occurs
spongy layer
Moist, loosely packed layer of cells containing chloroplasts.
Veins
centre of leaf, contains xylem and phloem tissue
What is the role of chloroplasts within plant cells?
Chloroplasts are organelles that conduct photosynthesis, converting light energy into chemical energy stored in glucose.
What are the functions of roots, stems, and leaves in plants?
Roots anchor the plant and absorb water and nutrients, stems support the plant and transport materials, and leaves are the primary site of photosynthesis.
What is medical imaging technology?
Medical imaging technology refers to techniques used to visualize the interior of the body for clinical analysis and medical intervention.
vaccination
used to treat or prevent disease by stimulating the body to fight the organism
List four common technologies currently used in diagnosis.
1. X-ray imaging 2. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) 3. Computed tomography (CT) scans 4. Ultrasound imaging.
List two public health strategies designed to reduce the incidence of smoking-related diseases.
1. Implementing smoking bans in public places. 2. Providing education and resources for smoking cessation programs.