Sensory system - Smell
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
what are chemoreceptors
they are receptors taste and smell
they are detect certain chemical through sense of smell are odors
what is a olfactory bulb
The olfactory bulb is a neural structure located in the forebrain
the olfactory receptors cells directly detect chemicals we breathe into the nasal cavity
what are basal cells
Basal cells are stem cells located in the olfactory epithelium that continuously regenerate olfactory receptor neurons throughout a person's life
what are the bi-polar 2 projections
goes down to the epithelium surface where the cilia extends to the mucus layer
goes opposite direction into the plate of the olfcatory
why are odorants volatile & soluble in the mucous layer
Odorants must be volatile to evaporate and enter the nasal cavity, and they must be soluble in the mucous layer to interact with olfactory receptors effectively.
where does olfactory transduction occurs
t the olfactory mucosa located in the nasal cavity
how many olfactory receptors in humans
it has 400
each neurons expresses a single type of odorant receptor
what type of receptor is a odorant
a GPCR(G protein-coupled receptor).
How many odorant does a mice have
approx 1000
what are trace-amine associated receptor (TAARs)
they recognise volatile amines that play a role in detecting odors related to pheromones and environmental cues.
what is a formyl peptide receptor (FPRs)
It is involved in chemo taxis and immune response by recognizing formylated peptides.
what Vomeronasal Receptor (V1R, V2R)
are part of the vomeronasal organ and are responsible for detecting pheromones and other social cues.
what is a sensitive smell
methyl mercaptan ( the smell of gas)
it can be detected at 1 molecule in 50 billion
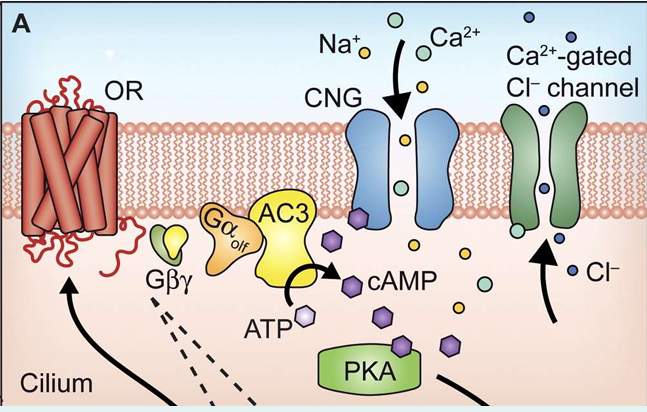
describe the olfactory signal transduction
chemoreceptors are GPCRs
activation of this causes an increase in cAMP through a small G protein - Gαolf which is related to Gαs
the increase in the cAMP causes the activation of a cation channel, a cyclic-nucleotide gated (CNG)
Channel opening allows Na+ & Ca2+ influx causing a depolarisation - the receptor potential
what is higher processing in the olfactory cortex
when signal is passed from the olfactory bulb to the primary olfactory cortex
the axon converge on secondary neurons sending information to the CNS in different combination
what is the term for loss of smell
anosmia
some people cannot smell certain odorants - this is due to genetic variation e.g 1% of people cannot detects the smell of vanilla