Anatomy Chapter 13
1/212
Earn XP
Description and Tags
the nervous system
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
213 Terms
nervous system characteristics
controls and adjusts the activity of the body
provides swift but brief responses
two anatomical divisions of the nervous system
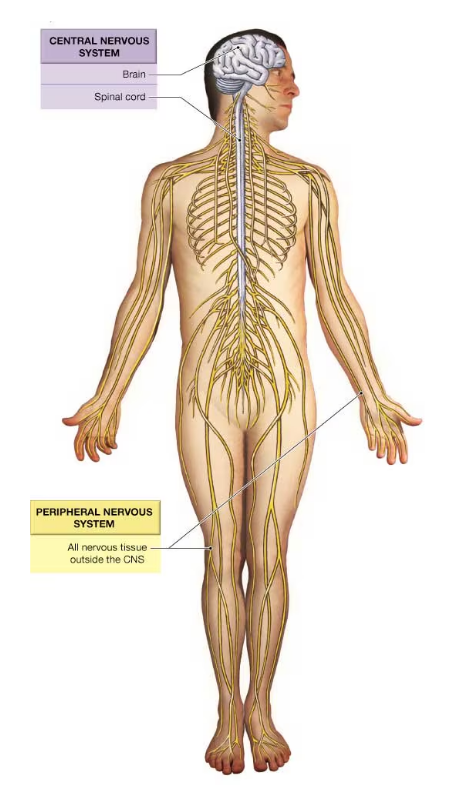
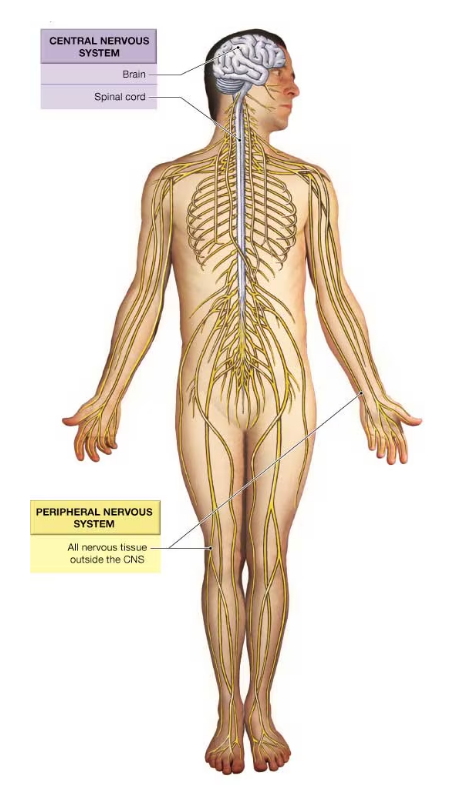
central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nervous system (PNS)
the nervous system consists of _____________________
all the nervous tissue in the body
components of the CNS
the brain and spinal cord
central nervous system (CNS) functions
1) integrating, processing, and coordinating sensory input and motor output
2) acting as the seat of intelligence, memory, learning, and emotion
CNS receives information from the _______ division and commands with the _______ division
afferent, efferent
cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
clear, watery fluid that fills the central canal and ventricles, surrounding the CNS
components of the peripheral nervous system (PNS)
all of the peripheral nerves and nervous tissue outside the CNS
PNS function
provides sensory information to the CNS and carries motor commands away from the CNS

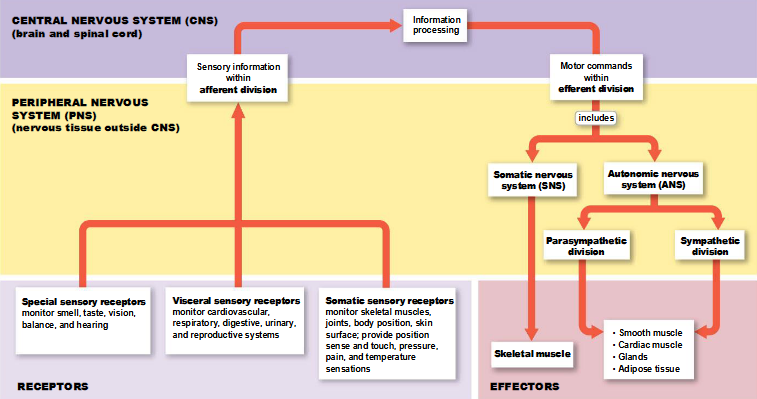
divisions of the PNS
afferent division and efferent division
afferent division of the PNS
carries sensory information to the CNS; begins at receptors that monitor specific characteristics of the environment
the __________ of a receptor carries information to the CNS
stimulation

receptor examples
sensory process, specialized cells or clusters of cells, or complex sense organs
example of a complex sense organ that acts as a receptor
the eye
efferent division of the PNS
carries motor commands from the CNS to muscles and glands; begins inside the CNS and ends at the effector
effector
a peripheral gland or muscle cell innervated by a motor neuron
examples of effectors
muscle cells, gland cells, other cells specialized to perform specific functions
subdivisions of the afferent division of the PNS
somatic and visceral sensory receptors
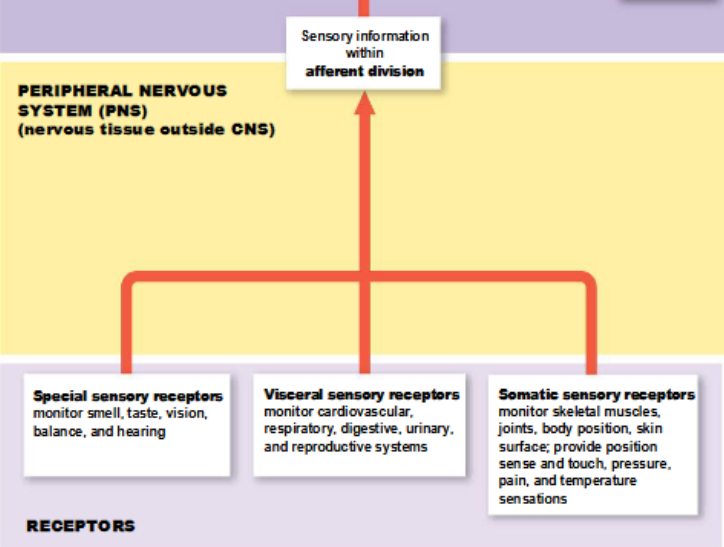
somatic sensory receptors of the afferent division
monitor skeletal muscles, joints, skin, and from the visceral sensory receptors

visceral sensory receptors of the afferent division
monitor other internal structures, such as smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, glands, and respiratory and digestive organs

special sensory receptors of the afferent division
monitor smell, taste, vision, balance, and hearing
subdivisions of the efferent division of the PNS
somatic and autonomic nervous systems
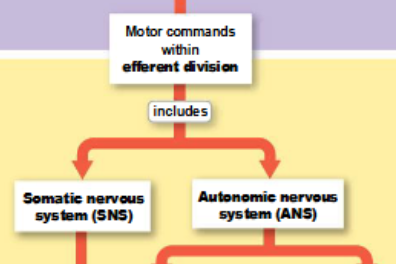
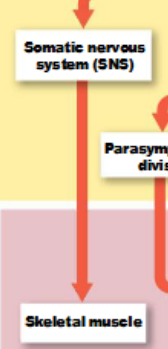
somatic nervous system (SNS)
controls skeletal muscle contraction
autonomic nervous system (ANS)
regulates smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glandular activity
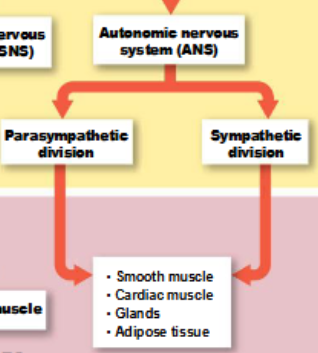
divisions of the ANS
parasympathetic and sympathetic divisions
activities of the somatic nervous system may be under ____________________ control
voluntary or involuntary
example of voluntary control of the SNS
voluntary contractions of the skeletal muscles
example of involuntary control of the SNS
immediately withdrawing your hand from a hot stove even before noticing the pain
examples of involuntary control of the ANS
heartbeat, digestive processes, and instinctive responses to threatening situations
concept check 13.1: what are the two subdivisions of the nervous system?
the central and peripheral nervous systems
two types of cells contained in the nervous system
neurons and neuroglia
neurons
nerve cells that are responsible for the transfer and processing of information in the nervous system
neuroglia
cells that support and protect neurons
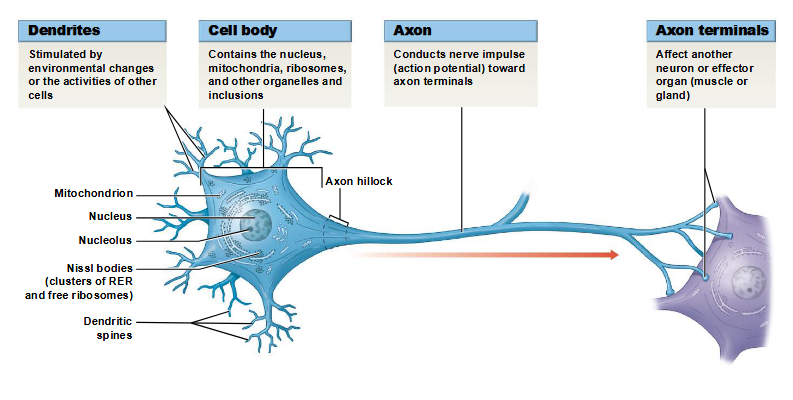
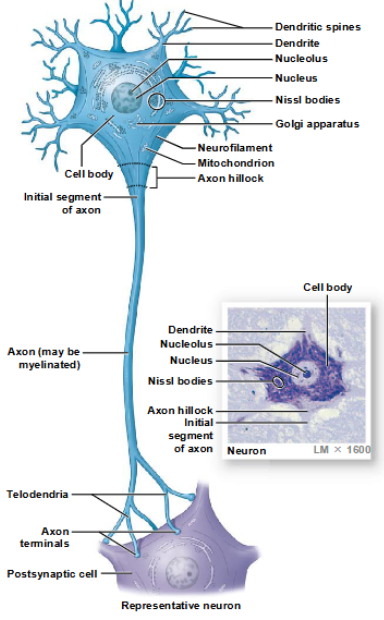
components of neurons
cell body, axon, dendrites, perikaryon, dendritic spines, axon terminals
perikaryon
cytoplasm that surrounds the nucleus in the cell body of a neuron
dendrites
sensory processes of a neuron
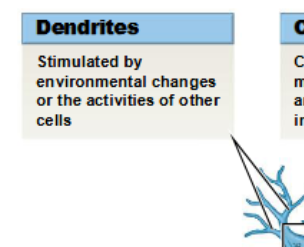
dendritic spines
fine processes of dendrites that receive information from other neurons
percent of dendritic spines making up the total surface area of the neuron
80-90%
axon
elongated extension of a neuron that conducts an action potential away from the cell body and toward the synaptic terminals
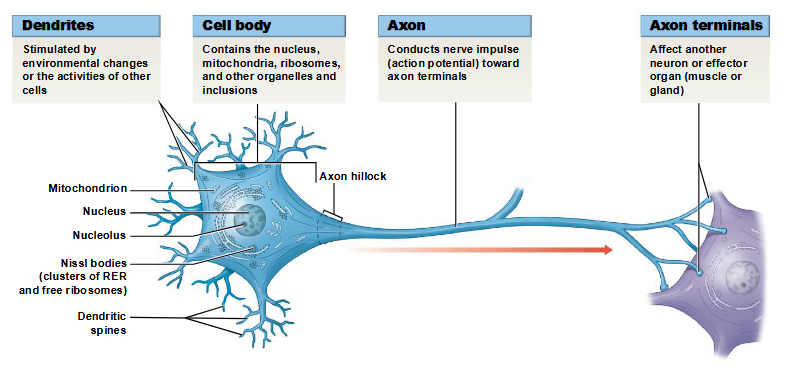
axon terminals
site of neuron communication with another cell
approximate ratio of neuroglia to neurons
5:1
are neuroglia smaller or larger than neurons?
smaller
can neuroglia divide?
yes, neuroglia can divide
concept check 13.2: what are the two distinct cell types found within nervous tissue?
neurons and neuroglia
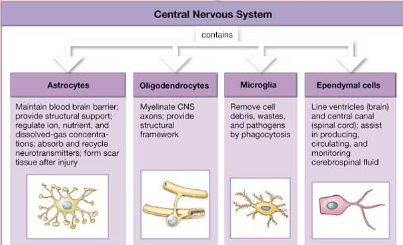
four types of neuroglia in the CNS
astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, microglia, and ependymal cells
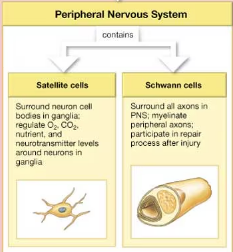
two types of neuroglia in the PNS
satellite cells and Schwann cells
function of neuroglia in the CNS
surround CNS neurons and hold them in place, isolate neurons from each other, supply oxygen ad nutrients to neurons, destroy pathogens, and remove dead or damaged neurons
factors that distinguish neuroglia cells from each other
size, intracellular organization, the presence of specific cytoplasmic processes, and staining properties
astrocytes
star-shaped cells with projections that anchor to capillaries
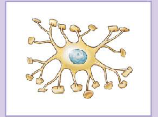
largest and most numerous neuroglia of the CNS
astrocytes
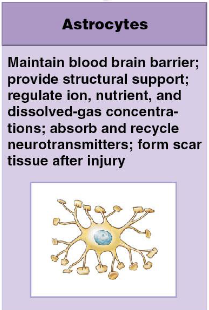
astrocyte functions
1) maintain the blood brain barrier
2) provide structural support
3) regulate ion, nutrient, and dissolved-gas concentrations
4) absorb and recycle neurotransmitters
5) form scar tissue after injury
astrocyte function in the embryonic brain
involved in directing the growth and interconnection of developing neurons through the secretion of neurotropic factors
astrocyte pedicels
cytoplasmic processes that increase surface area for the uptake of ions, neurotransmitters, or metabolic by-products accumulating around the neurons, enabling them to control the chemical content of the interstitial space; contact the surfaces of adjacent neurons to enclose them and isolate them from changes in the chemical composition of the interstitial space
blood brain barrier (BBB)
physical and biochemical isolation of the CNS from general circulation
why is the blood brain barrier necessary?
because hormones or other chemicals in the blood could disrupt neuron function
endothelial cells lining capillaries in the CNS
quite impermeable and therefore control the chemical exchange between blood and interstitial fluid
oligodendrocyte
type of neuroglia in the CNS that forms myelin sheaths, internodes, and myelin sheath gaps
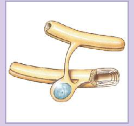
oligodendrocyte functions
1) myelinates CNS axons
2) provide structural framework
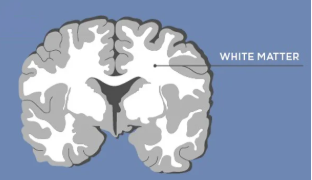
white matter
areas with mostly myelinated axons
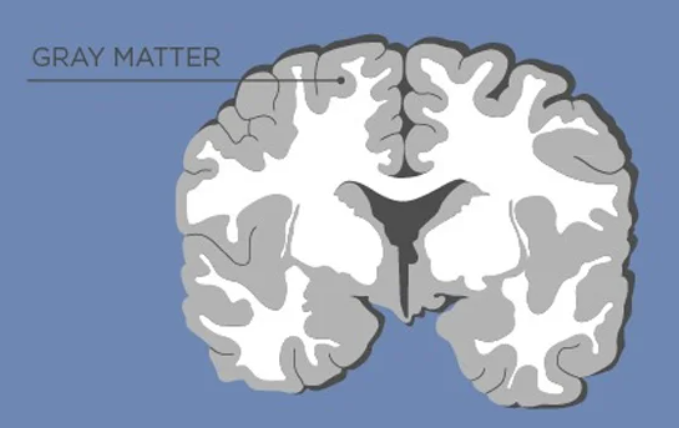
gray matter
areas devoid of myelinated axons and composed of cell bodies and dendrites
internodes
sections of myelinated nerve fibers between two successive nodes
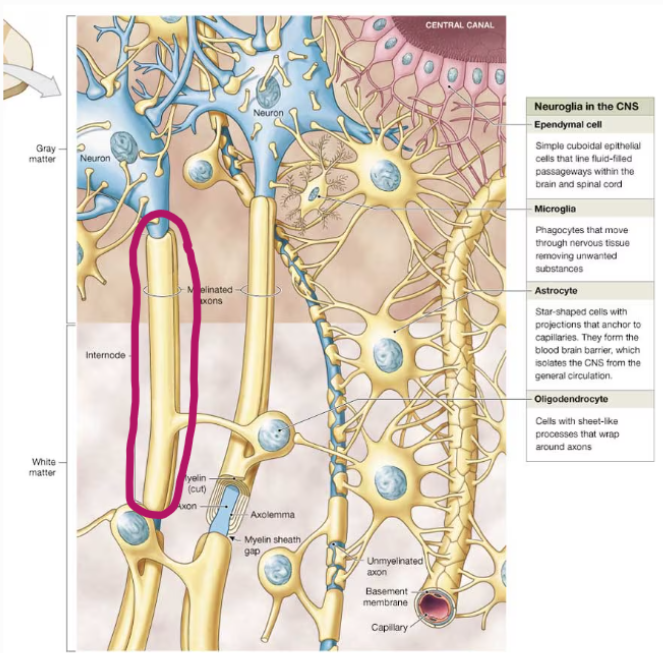
myelin sheath gaps (nodes of Ranvier)
small gaps between the myelin sheaths, produced by adjacent oligodendrocytes
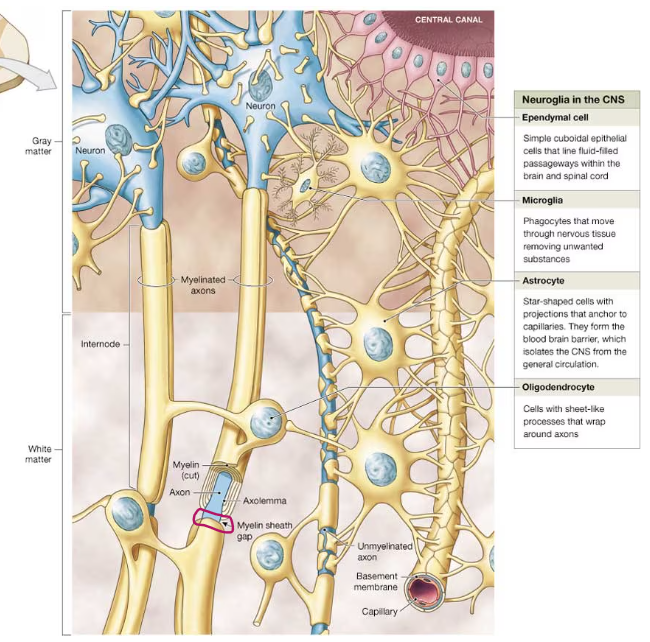
microglia
phagocytic neuroglia in the CNS that are derived from monocytes
stem cells that produce microglia
originate in the bone marrow and are related to stem cells that produce tissue macrophages and monocytes of the blood
microglia function
remove cell debris, wastes, and pathogens by phagocytosis

the smallest neuroglia, possessing slender cytoplasmic processes with many fine branches
microglia
percentage of microglia in the CNS
5%, but increases upon infection or injury
ependymal cells
simple cuboidal epithelial cells that make up the ependyma; type of CNS neuroglia
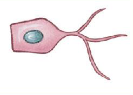
ependyma
layer of cells lining the ventricles and central canal of the CNS
ependymal cells function
1) line the ventricles of the brain and the central canal of the spinal cord
2) assist in producing, circulating, and monitoring cerebrospinal fluid
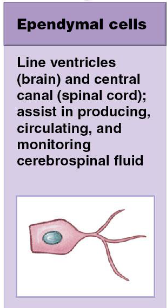
how ependymal cells differ from typical epithelial cells
ependymal cells have slender processes that branch extensively and make direct contact with neuroglia in the surrounding nervous tissue
cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
fluid bathing the internal and external surfaces of the CNS, providing a protective cushion and transportation of dissolved gases, nutrients, wastes, and other materials
choroid plexus
secretes cerebrospinal fluid
cilia in ependymal cells
in adults, cilia and microvilli are found on the apical surface of the ependymal cells lining the spinal cord and the lateral and fourth ventricles of the brain, but those lining the third ventricle lack cilia
what is the role of cilia in ependymal cells? microvilli?
cilia help the CSF circulate and microvilli are involved in the absorption of CSF
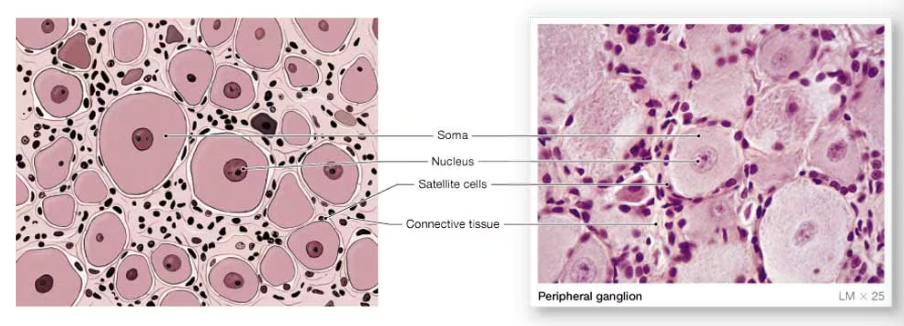
ganglia
collection of neuron cell bodies in the PNS
peripheral nerves
type of nerves in the PNS in which axons are bundled together and wrapped in connective tissue
satellite cells of the PNS
surround neuron cell bodies in peripheral ganglia, regulating the exchange of nutrients and waste products between the neuronal cell body and extracellular fluid; isolate the neuron from stimuli not intended to pass from neuron to neuron sa
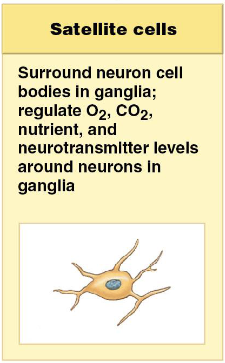
satellite cells surround neuron cell bodies in peripheral ganglia
functions of Schwann cells (neurolemmocytes)
1) surround all axons in the PNS
2) myelinate peripheral axons
3) participate in the repair process after injury
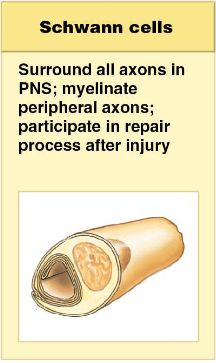
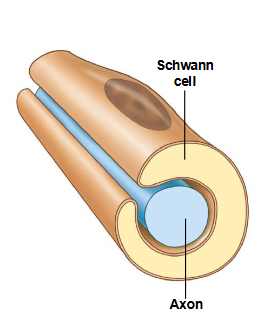
Schwann cells
neuroglia responsible for the neurilemma that surrounds axons in the PNS
axolemma
plasma membrane of an axon
neurolemma
cytoplasmic covering provided by Schwann cells
satellite cell (PNS) analogue in the CNS
astrocytes
Schwann cell (PNS) analogue in the CNS
oligodendroglia
myelin improves the conduction speed of an ____________ (or nerve impulse) along the axon
action potential
axon myelination in the PNS
1) Schwann cell encloses a segment of the axon within a groove of its cytoplasm
2) Schwann cell rotates around the axon
3) as it rotates, the inner membranous layers are compressed and the cytoplasm is forced into more superficial layers
4) when completed, the myelin sheath consists only of the phospholipid bilayers of the plasma membrane, with the Schwann cell nucleus and cytoplasm at the surface
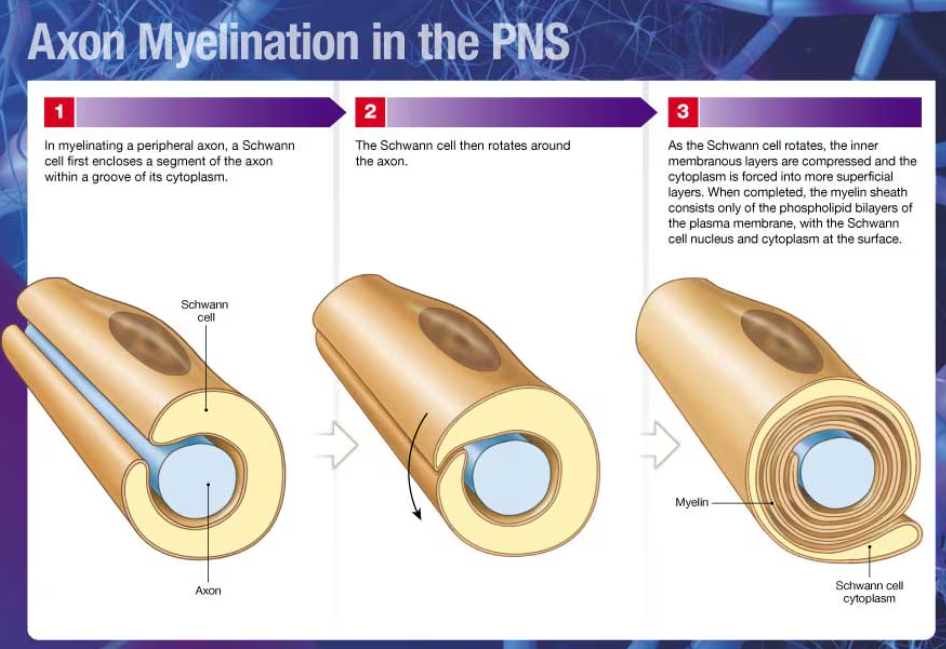
involvement of Schwann cells in a myelinated axon in the PNS
it takes many Schwann cells to myelinate an entire axon
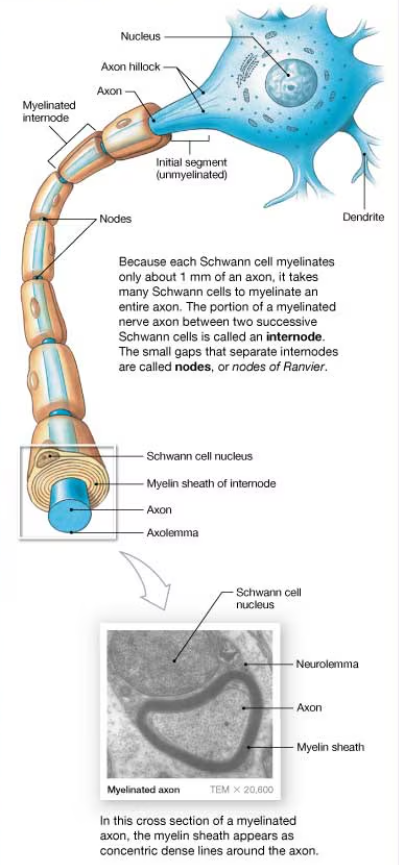
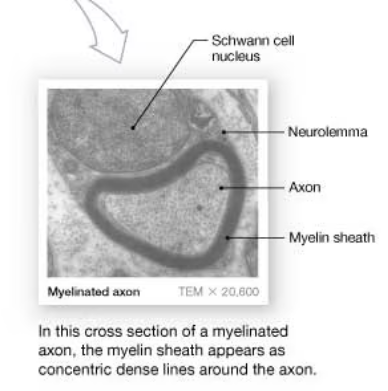
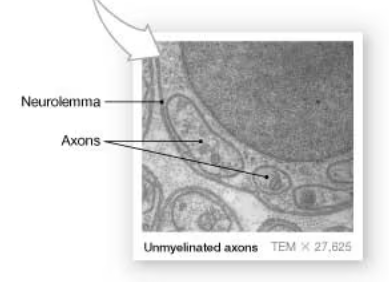
cross section of a myelinated axon
myelin sheath appears as concentric dense lines around the axon
involvement of Schwann cells in an unmyelinated axon of the PNS
a single Schwann cell shields multiple unmyelinated axons within superficial grooves, but a chain of Schwann cells is still needed to enclose an entire axon
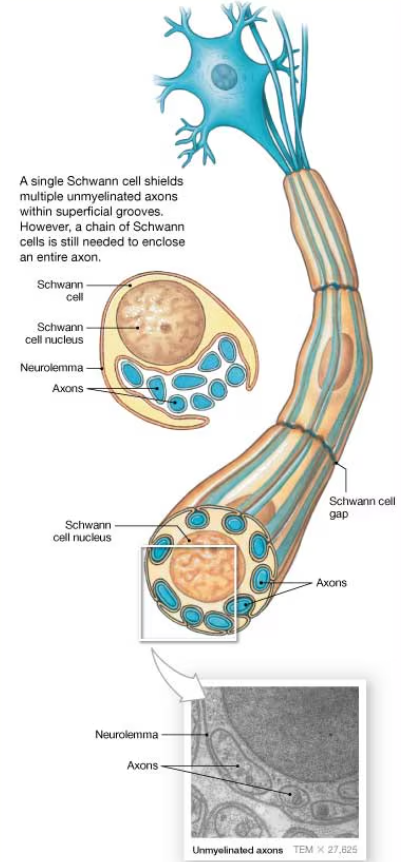
cross section of unmyelinated axons
show axons in a Schwann cell in the neurolemma
concept check 13.3: specifically, what cells help maintain the blood brain barrier (BBB)?
astrocytes of the CNS
components of neurons
perikaryon, neurofilaments/neurotubules, neurofibrils, nissl bodies, axon hillocks, axoplasm, collaterals, telodendria, axon terminals, axoplasmic transport
neurons
transmit information from one part of the nervous system to another via electrical impulses
components of the cell body of a neuron
a large, round nucleus with a prominent nucleolus
perikaryon
cytoplasm of a neuron, containing organelles that provide energy and synthesize organic materials
appearance of the perikaryon
coarse and grainy due to its mitochondria, free and fixed ribosomes, and the membranes of the rough ER
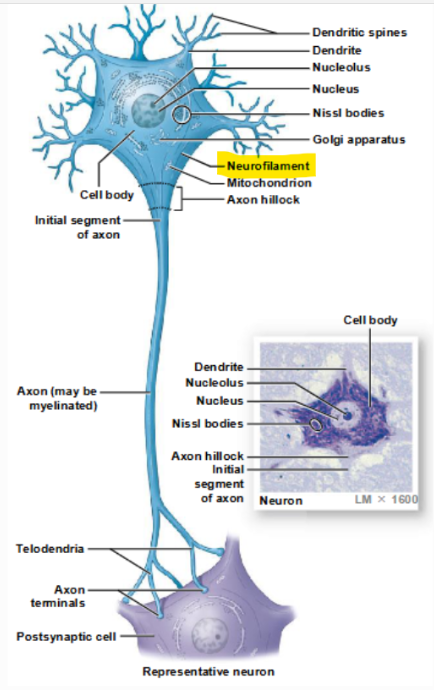
neurofilaments and neurotubules
make up the neuron cytoskeleton
neurofibrils
bundles of neurofilaments that extend into the dendrites and axons, providing internal support
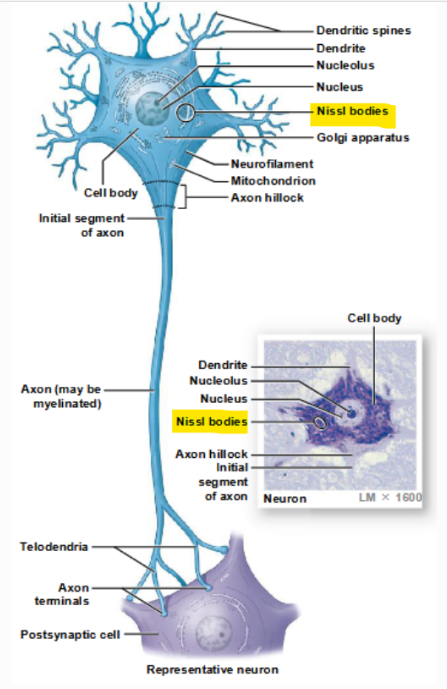
Nissl bodies
clusters of free ribosomes and RER, which stain a dark color in the perikaryon