Lecture 17: Minor Ailments & Responding to Symptoms in Community Pharmacy | Pain
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Pain
An unpleasant sensory & emotional experience assciated with, or resembling that associated with, actual or potential tissue damage
Nociception
When a noxious stimuli activate nociceptors and their pathways
Pain categories
Nociceptive - usually associated with acute injury or trauma
Neuropathic - arising from nervous system damage or dysfunction
Nociplastic - pain is real but not explained by tissue injury or nerve damage
Nociceptive pain
Somatic
Skin and musculoskeletal
Injury to skin, muscles, bone, joint and connective tissue
Characteristics
Pain may be described as dull or aching if in deep tissue, or sharp & pricking under the skin
Often localised and typically worsens with movement
Visceral
Injury to internal organs
Characteristics
Pain tends to be poorly localised and may be cramping or pressure-like
Neuropathic pain
Trauma, injury causing nerve damage or compression (peripheral or central) - changes in nervous system may sustain pain even after an injury heals
Different types of diseases or conditions:
Neuropathic pain syndromes
Diabetes
Shingles
Post stroke pain
Characteristics
Often described as unfamiliar feeling using terms like burning, electric shock like sensations, tingling, pins & needles
May persist long-term
May be associated with sensitivity of the skin
Frequently worsens at night possibly due to reduced distractions
Nociplastic pain
Pain that arises from altered nociception despite no clear evidence of actual or threatened tissue damage that causes peripheral nociceptors activation or evidence of disease or lesion of the somatosensory system causing pain
Characteristics
Typically more than 3 months duration
Pain tends to be poorly localised, often affecting multiple body regions
Deep, aching or burning
Persistent and unpredictable
Sensitive to touch or pressure
Made worse by stress, fatigue or poor sleep
Pain categorisation - duration
Acute (short-term) - less than 3 months, expectation that pain is time limited. Acute pain tends to be a warning to alert the body to prevent further tissue injury
Chronic (long-term) - persists beyond expected healing time or more than 3 months
Recurrent or Intermittent - comes and goes
Pain categorisation - cause
Musculoskeletal - arises from muscles, bones, joints or related soft tissues
Inflammatory - triggered by immune response to injury, infection or autoimmune condition
Mechanical pain - results from structural distortion or compression of tissues
Psychogenic pain - pain primarily influenced by psychological, emotional and behavioural factors
Pharmacological Management (OTC analgesics)
Encourage self-care for acute pain - treat with underlying cause where possible
Non-opioid (PO)
Paracetamol
Non-Steriodal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) - aspirin, ibuprofen, diclofenac, naproxen
Opioid (PO)
Codeine
Dihydrocodeine
Compound analgesics
Non-opioid & opioid e.g. co-codamol, ibuprofen
Topical preparations
NSAIDs
Rubefacients
Anti-inflammatories for local mouth pain
WHO 3 step analgesic ladder
Adjuvants = antodepressants, anticonvulsants, antispasmodics, muscle relaxant
Step 1 - mild pain
Non-opioid e.g. paracetamol, NSAIDs
Step 2 - moderate pain
Weak opioid e.g. codeine
Step 3 - moderate to severe pain
Strong opioid e.g. morphine
Paracetamol
Synthetic non-opioid acting in the CNS (CNS COX inhibitor)
Antipyretic analgesic - no peripheral COX inhibition, no anti-inflammatory activity
Mild to moderate pain - drug of choice for fever & pain for people with bleeding disorders, peptic ulcers
Avilable OTC as an oral (GSL, P) or rectal suppository (P) formulation
Well absorbed orally
Side effects are few/uncommon
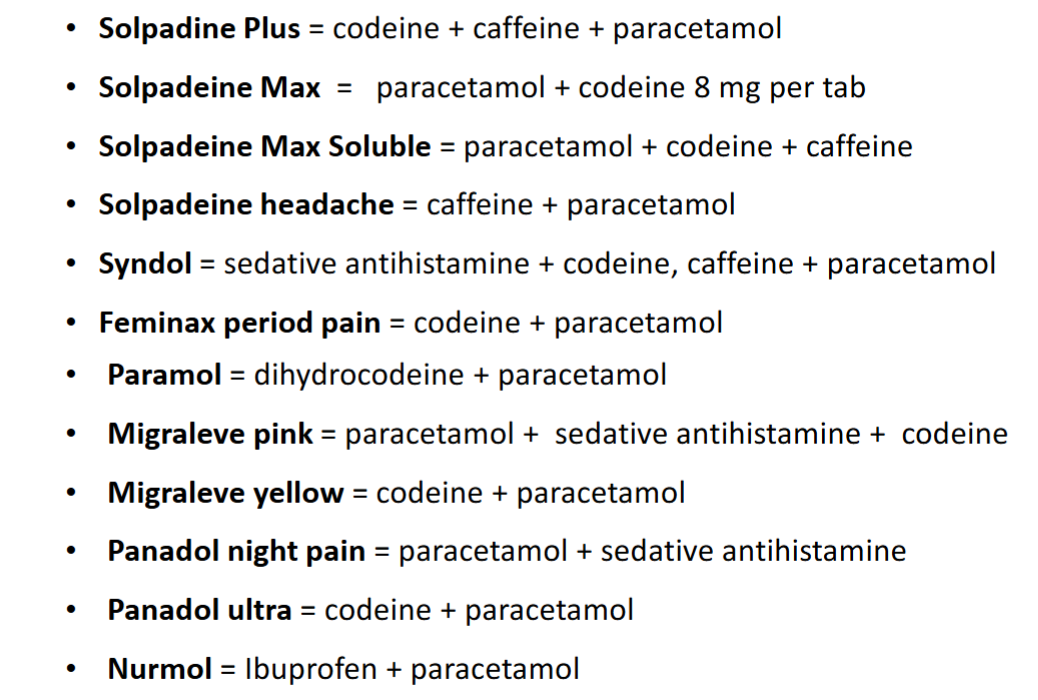
Paracetamol containing products
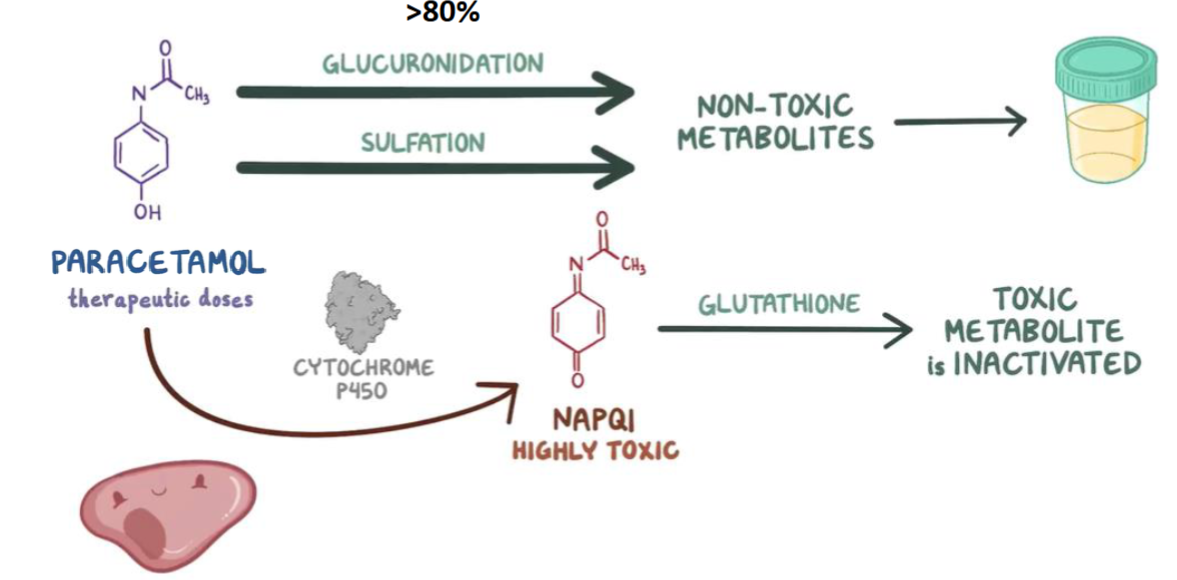
Paracetamol hepatoxicity
Hepatic metabolism
N-acetyl-P-benzoquinoneimine (NAPQI)
In overdose, more paracetamol is metabolised by CP450
NAPQI causes cell death & necrosis
Potential for live rfailure if untreated
OTC Paracetamol sales
The law says pharmacies may not sell more than 100 non-effervescent tablets/capsules to a person at one time
Most OTC pack sizes are 16 or 32 dose units = practically 96 is the maximum number that can be sold
Use professional judgement to decide the appropriate quantity to supply and what limits to impose
No legal limits on the quantity of OTC effervescent tablets, powders, granules or liquids
Non-Steriodal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
Widely used to reduce pain, inflammation and high temperature
Antipyretic analgesic (reduces fever) - peripheral COX inhibition, anti-inflammatory activity
Irreversible COX inhibitor (aspirin)
Reversible COX inhibitors (ibuprofen, diclofenac, naproxen)
Hypersensitivity - increased risk in people with asthma, trigger bronchospasm
NSAIDs sales
Available as OTC
Aspirin
Oral 300mg GSL (pack of 16)
Orall 300mg P (pack of 32)
By law - no more than 100 non-effervescent tablets or capsules can be sold to a person at 1 time
Diclofenac
Topical gel
Medicated plaster 140mg GSL
Ibuprofen
Oral 200mg GSL (pack of 16)
Oral 400mg (pack of 24, 48, 84)
Oral suspension 100mg per 5mL P & GSL
Naproxen
Oral 250mg P (pack of 9)
OTC Opioids
Strongest of the alagesics available OTC
Opioid analgesics bnd opioid receptors (mu, kappa, delta) in the brain, spinal cord and gastrointestinal tract
Antitussive - supresses coughs e.g. codeine
Antidiarrhoeal - acts on Mu receptors in gut, doesn’t cross BBB so not an analgesic e.g. loperamide
OTC Opioids analgesic
Codeine & dihydrocodeine available as compund oral formulations (P)
Combined with paracetamol
Only indication is short-term treatment of acute moderate pain not relieved by paracetamol or aspirin or ibuprofen alone
Codeine
Pro-drug of morphine
Some direct action
Morphine main analgesic effect
Hepatic CYP2D6
Drug-drug interactions
OTC Opioids: codeine & dihydrocodeine
Side effects:
Euphoria (less anxiety)
Sedation
Reduced gut motility (constipation)
Respiratory depression
Nausea & vomiting
Confusion (especially in elderly)
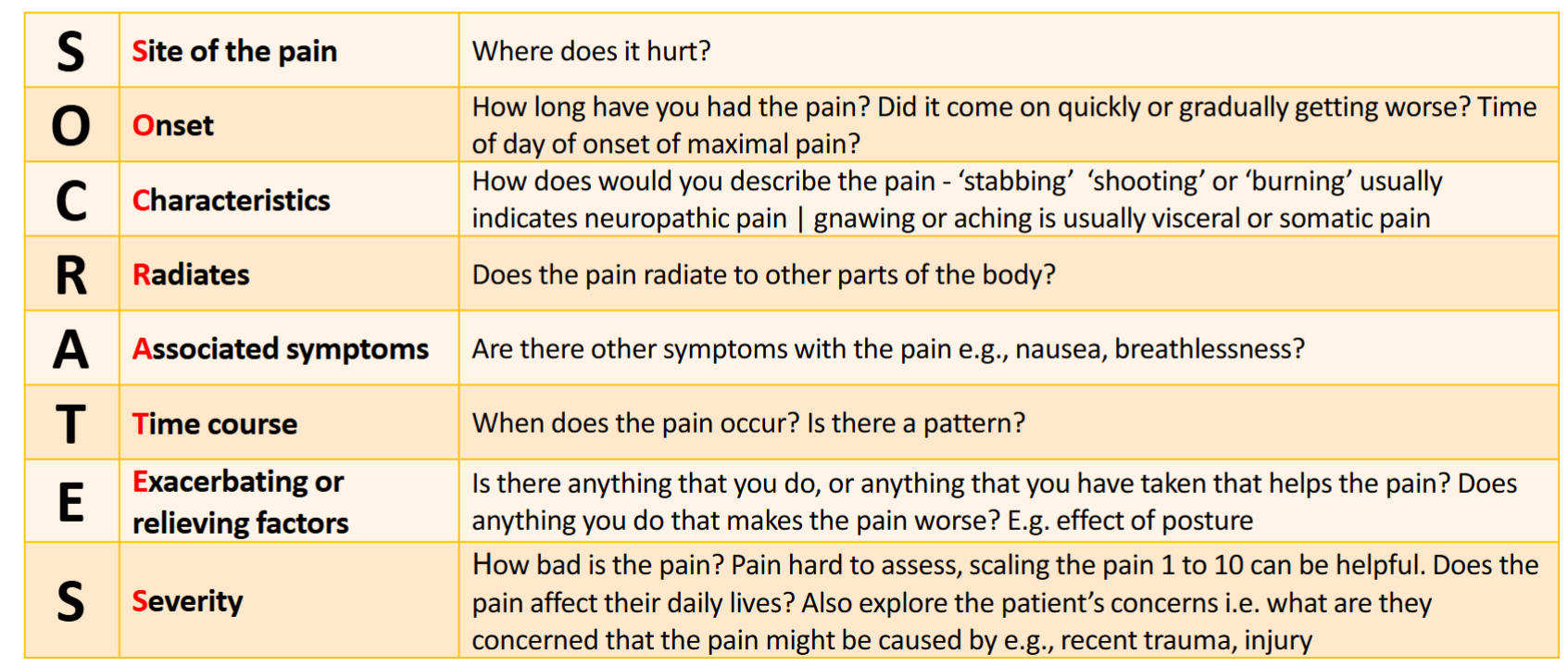
OTC Consultation questioning about Pain
OTC management of acute pain
Bleeding
Seizure, dizziness, impaired consciousness, numbness
Visual disturbance
Fever
Gradual onset
Neck pain or stiffness with photophobia
Progressive or persistent headache
Sudden onset severe headache
Weight loss
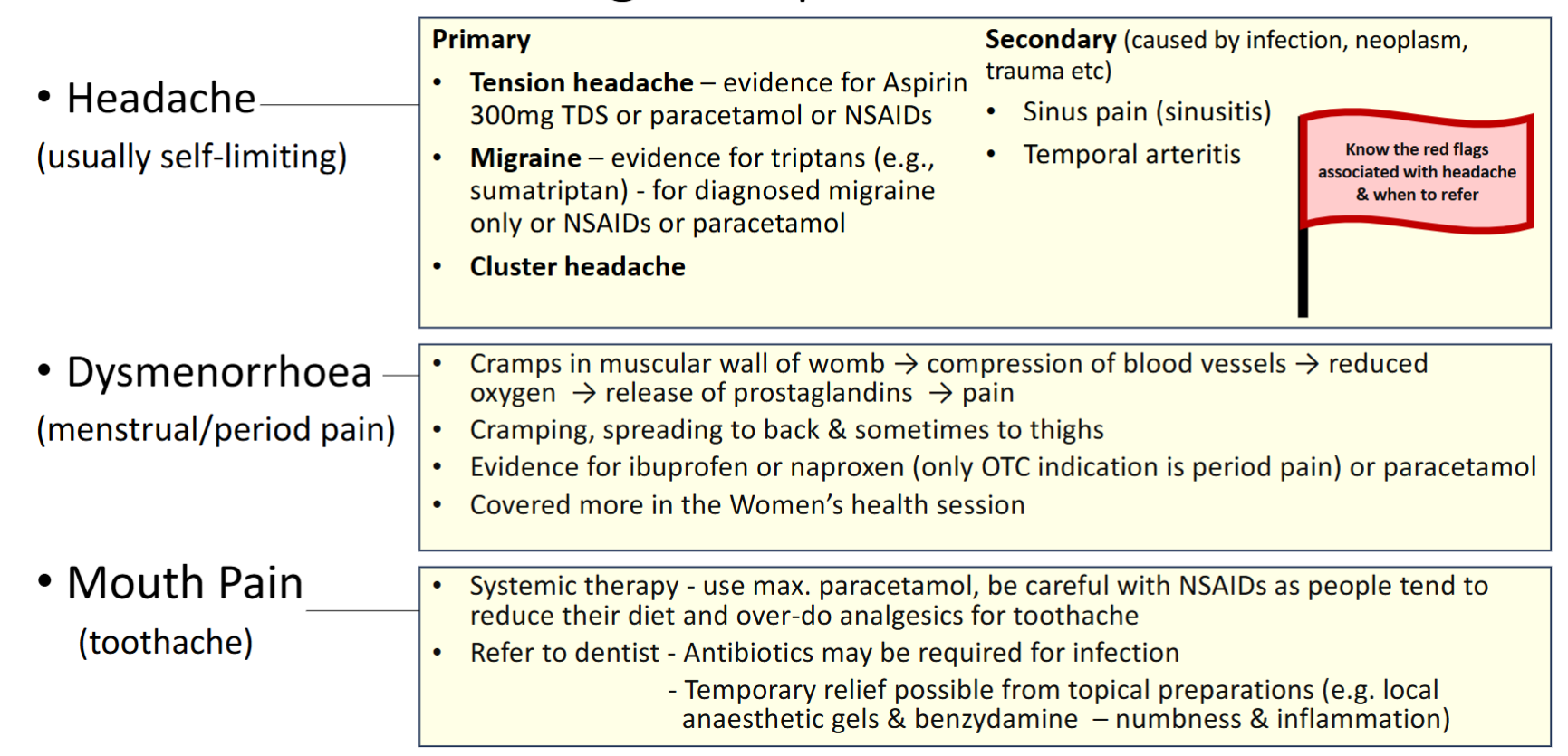
Common presenting complaints
Common presenting complaints
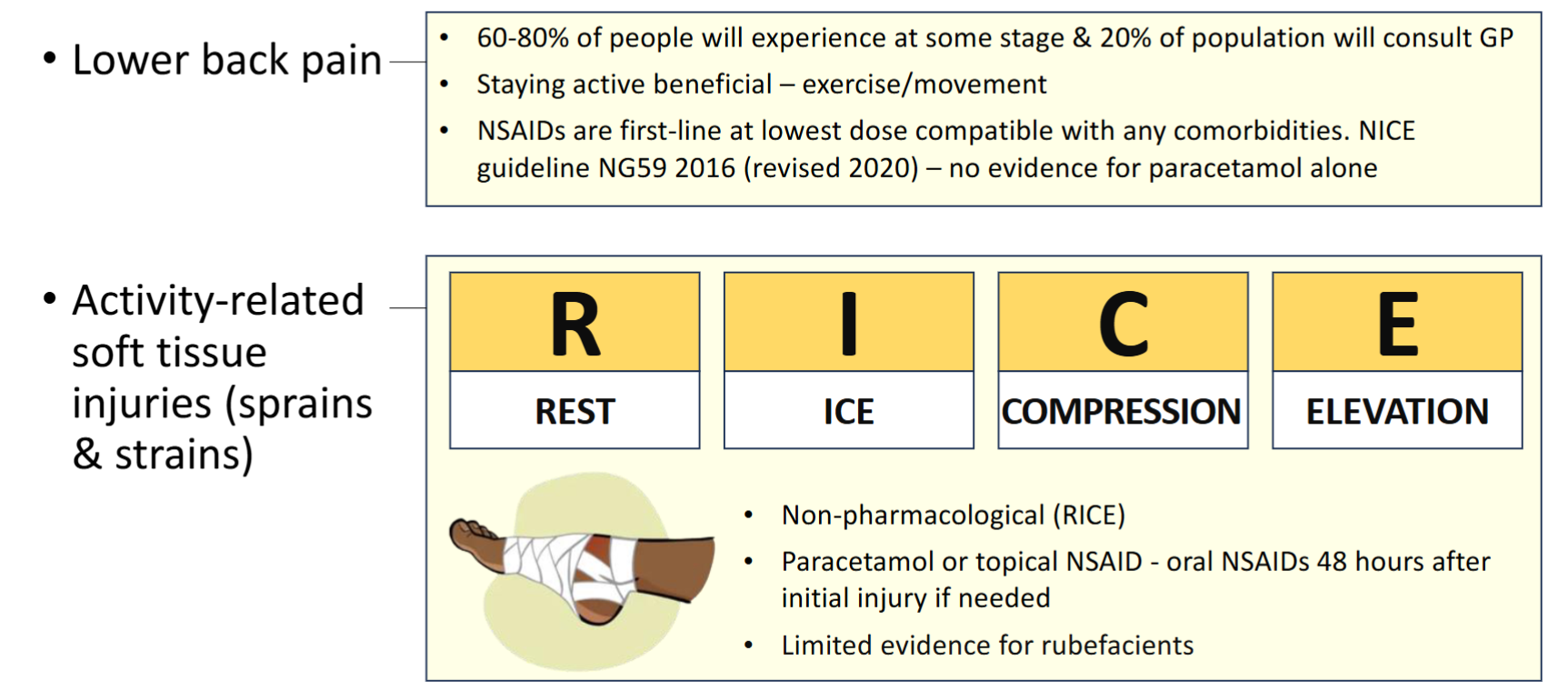
Topical Formulations
NSAID creams and gels
As effective as oral NSAIDs for musculoskeletal pain
Rubefacients - also known as counter-irritants
Cause vasodilation
Rare adverse effects