P15: Electromagnetism (1/2, motor effect)
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
What are the 2 ends of a bar magnet called?
Poles

2 types of poles
North
South
Where are the magnetic forces strongest?
At the poles of a magnet
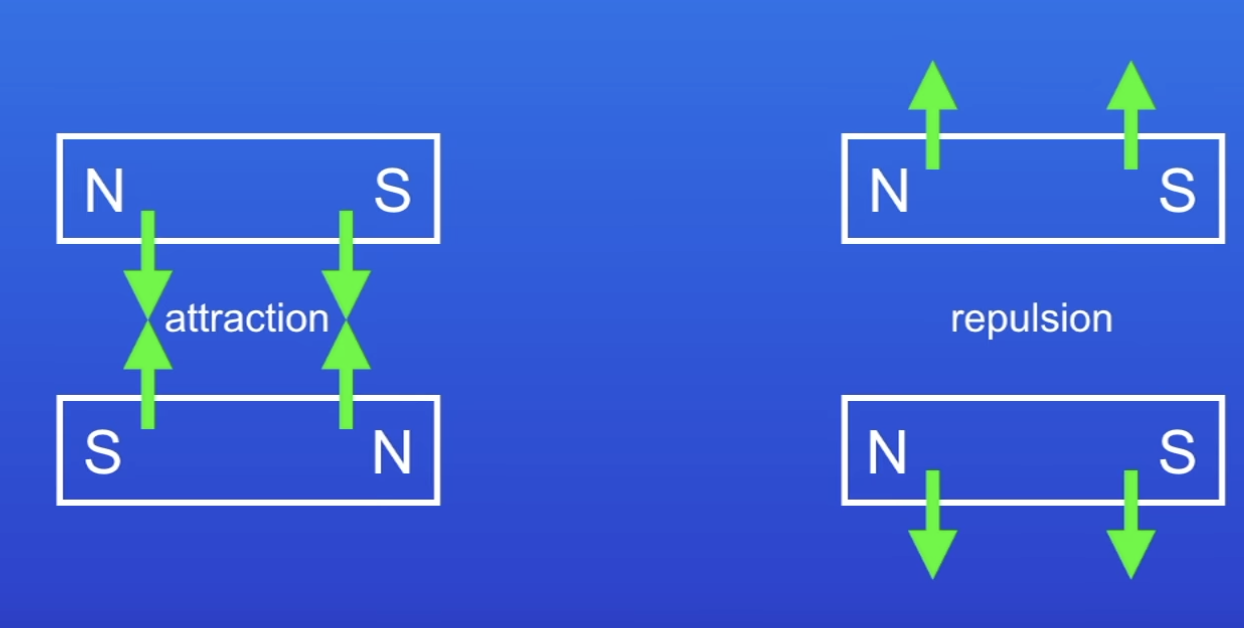
What happens when 2 magnets are brought close tog?
They exert a force on each other
Force when 2 like poles are brought tog
Repulsion
Eg 2 North poles close tog
What does the force of repulsion between 2 like poles do?
Forces the magnets apart
Force when 2 unlike poles are brought together
Attraction
N + S pole close tog
What type of forces are the attraction + repulsion of 2 magnetic poles and why?
Non contact forces
Magnets don’t have to touch to experience the force
Permanent magnet
Produces its own magnetic field
Example of permanent magnets
Bar magnets
What happens when 2 permanent magnets are brought close together?
Attract or repel each other depending on the direction
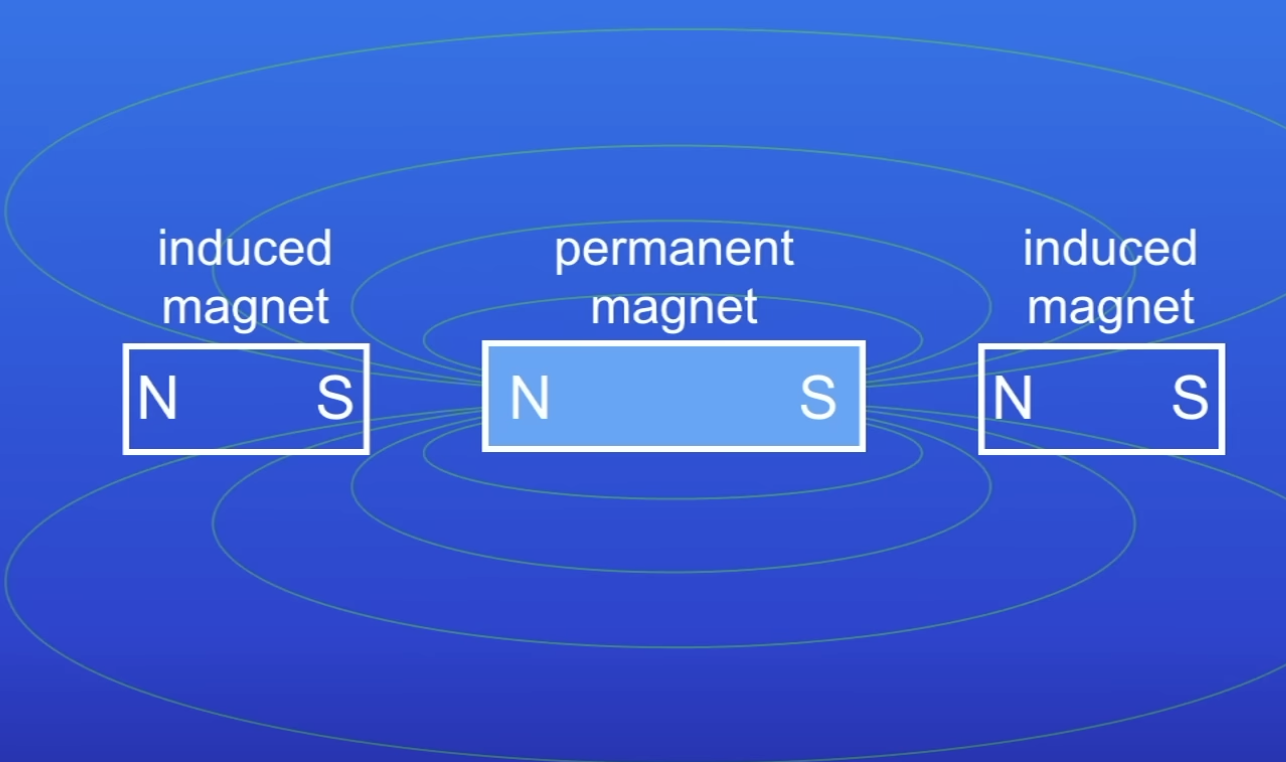
Induced magnet
Material that becomes a magnet when it is placed in a magnetic field
The object isn’t magnetic
What force does induced magnetism always cause?
Attraction
What happens when the permanent magnet is removed from an induced magnet?
(when the induced magnet is removed from the magnetic field?)
The induced magnets lose most / all of its magnetism quickly
How to create an induced magnet?
Place a permanent magnet betw 2 non-magnetic objects
There is a MF around the permanent magnet
MF causes the 2 objects to become magnets
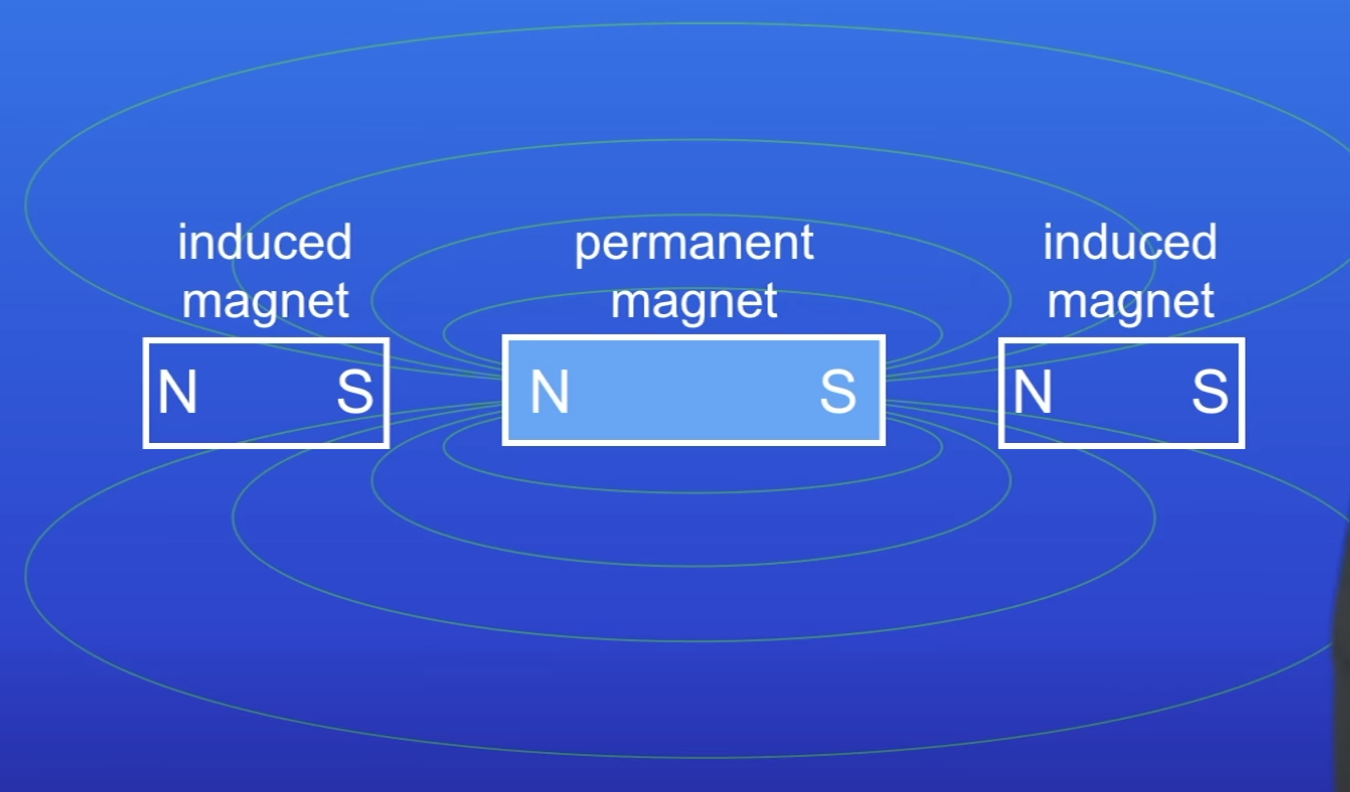
Like poles…
Unlike poles…
Repel
Attract
4 types of magnetic material
Iron
Steel (alloy of iron)
Cobalt
Nickel
What types of magnets can the 4 magnetic materials be made into
Permanent
Induced
Magnetic field
A region around a magnet where a force acts on another magnet / magnetic material
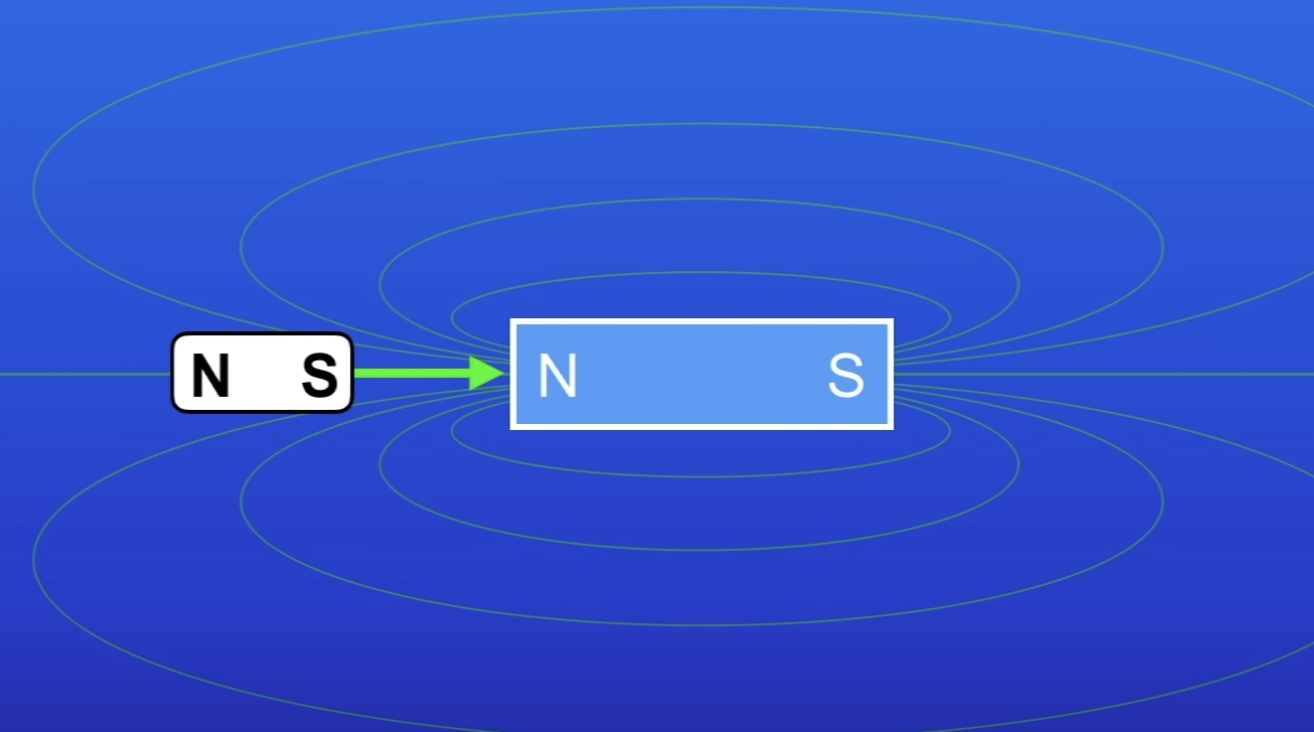
What happens if a magnetic material eg iron is placed into this field?
Becomes an induced magnet
Will experience a force of attraction towards the magnet
What does the strength of a magnetic field depend on?
Distance from the magnet
Is the force of attraction between 2 unlike poles strongest as the magnets are closer or further apart?
Closer
Where is the magnetic field strongest at?
Poles of the magnet
What equipment can you use to find the direction of a magnetic field?
Compass
What does a compass contain?
Small bar magnet
How to plot the magnetic field of a bar magnet using a compass placed near a bar magnet
Place compass near the N pole of the bar magnet
Draw a cross at the N pole of the compass
Move the compass so the S pole of the compass is on the cross
Draw another cross at the N pole of the compass
Continue doing so until a complete magnetic field line is plotted
Connect all dots with a line
Show direction of the field line using an arrow
Repeat all steps starting at different points around the N pole of the bar magnet
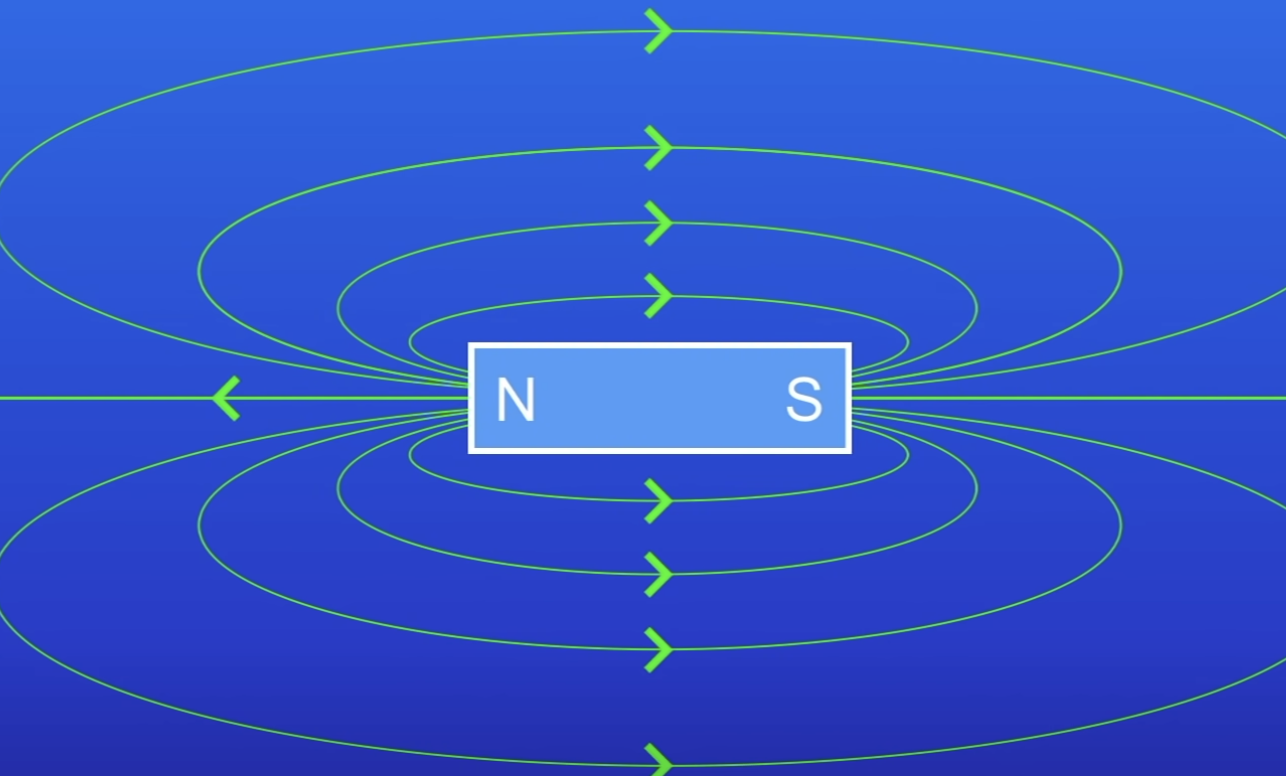
What directions do field lines run in?
North pole to South pole
When plotting field lines, where is the field strongest?
Where the lines are closer tog
What happens when you hold a compass away from any magnets?
Needle always points in the North - South direction
What does it show if the compass needle always points in the N-S direction, even when away from a magnet?
The Earth has its own magnetic field
What is the Earth’s magnetic field due to?
Compass always points in direction of Earth’s MF
The Earth’s core
The force between a magnet and magnetic material is always…
Attraction
The direction of the magnetic field at any point is given by the…
Direction of the force that would act on another north pole placed at that point
The direction of a magnetic field line is from the north pole of a magnet is to the…
South pole of a magnet
A compass needle points in the…
Direction of the Earth’s magnetic field
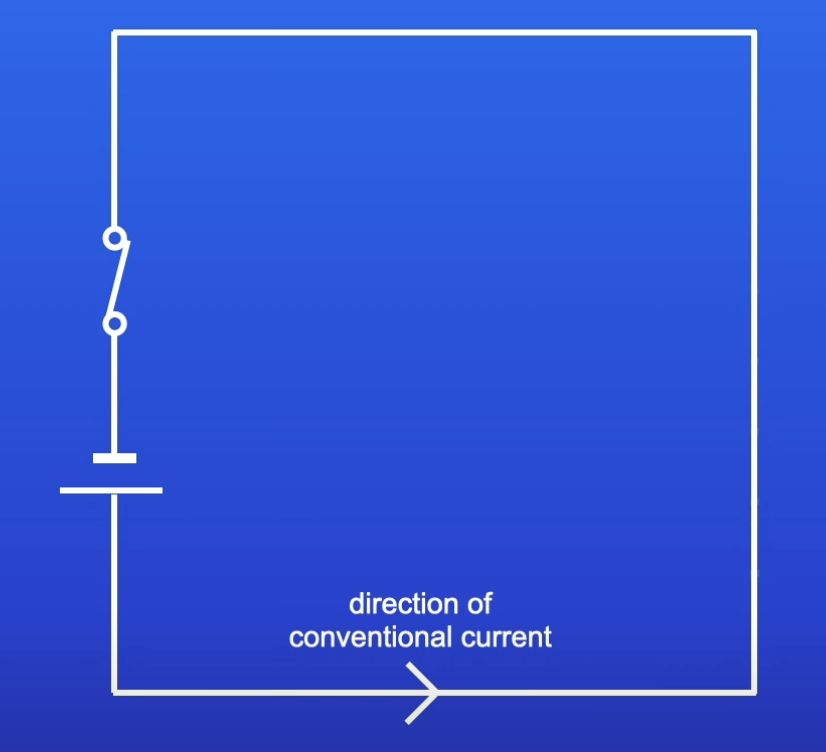
What happens when a switch is closed in a circuit?
Electric current flows around the circuit
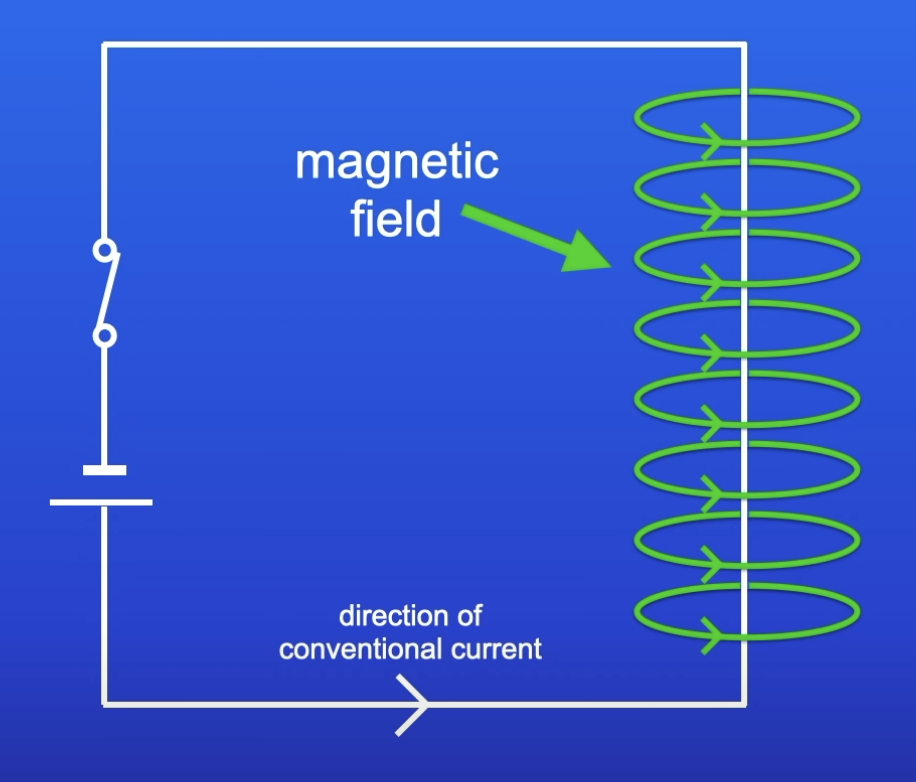
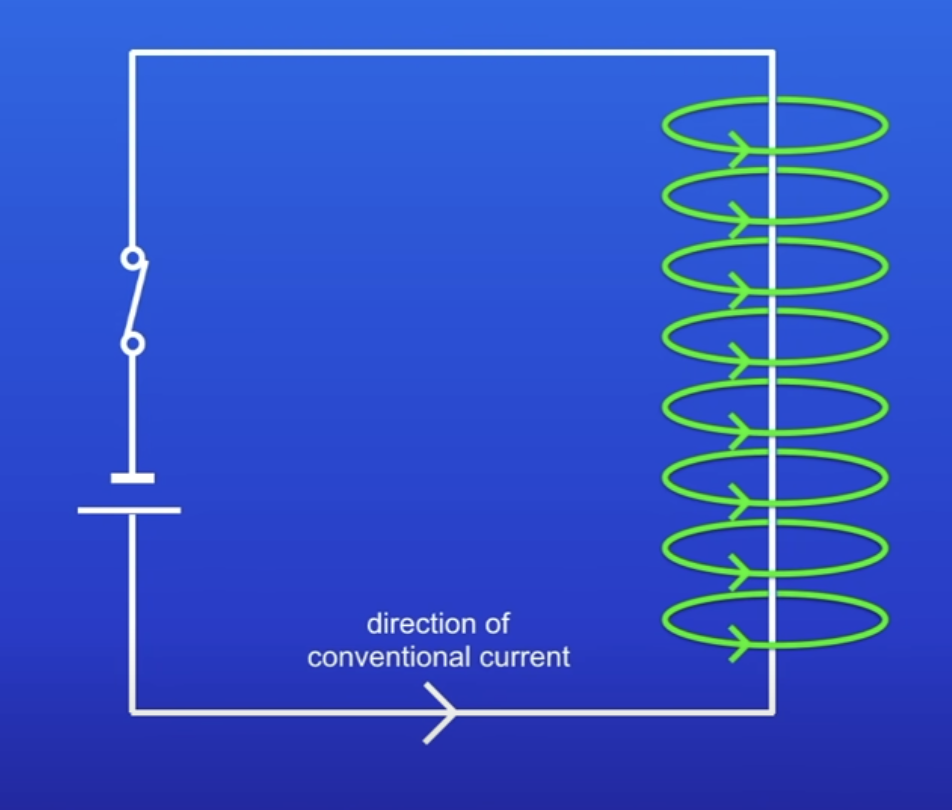
What happens when current flows through a conducting wire?
Magnetic field produced around the wire
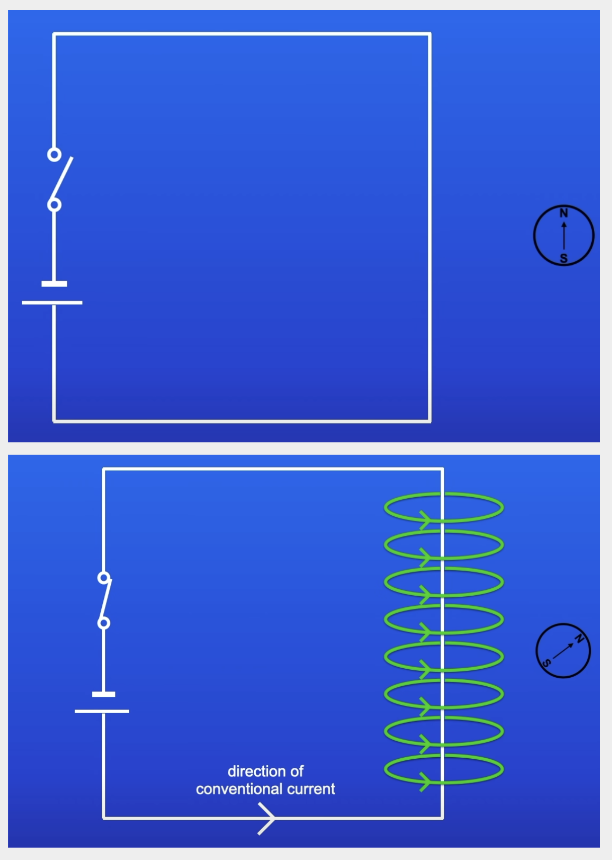
How can you prove there is a magnetic field around a wire using a compass?
Current turned off = compass needles lines up with Earth’s magnetic field
Current turned on = compass needle deflects
Proof of MF around wire
What does the strength of the magnetic field by a wire depend on?
Size of current thru wire
Distance from wire
Larger current produces…
Stronger magnetic field
Move further from wire…
Strength of MF decreases
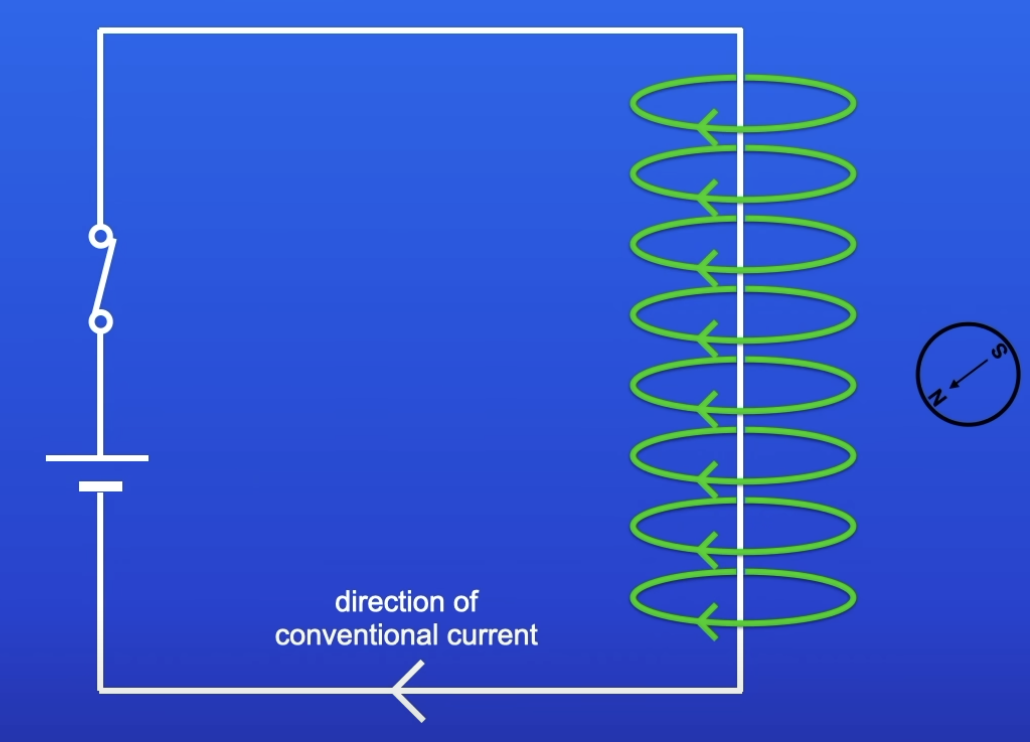
What happens to the MF if the direction of current is changed?
Direction of MF is changed
Reverse direction of CC = reverse direction of MF
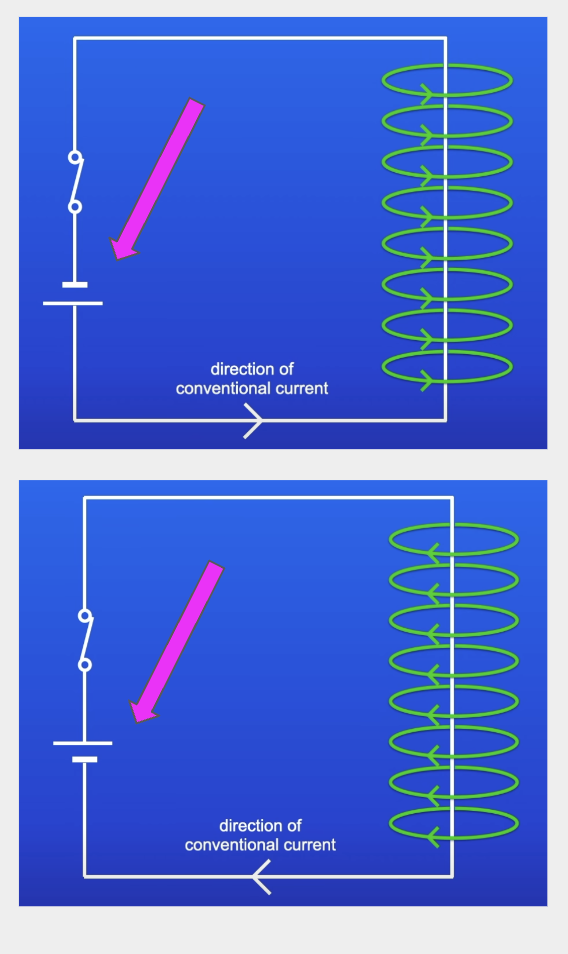
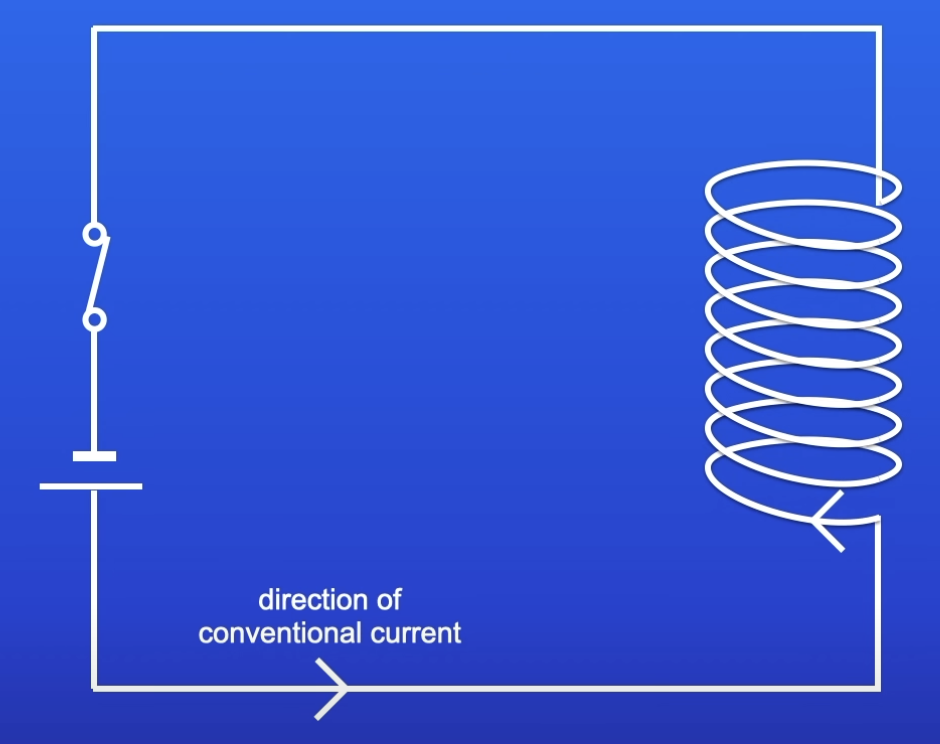
Conventional current
Flow of current from the positive terminal to negative
What happens if you place a compass near a wire that has had the direction of current reversed?
Deflects in the opposite direction to before
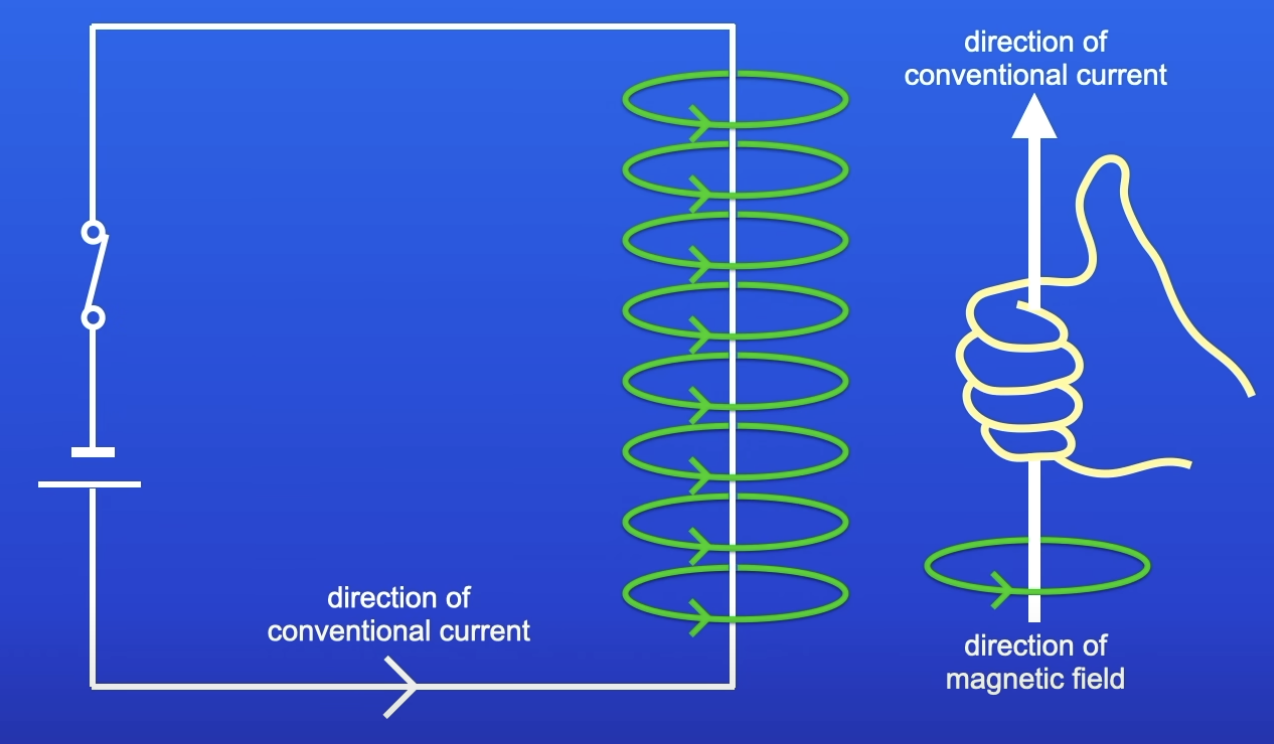
How to work out the direction of the MF produced by a wire?
Right hand rule
Place right hand so thumb is pointing in the direction of conventional current
Fingers are pointing in the direction of MF
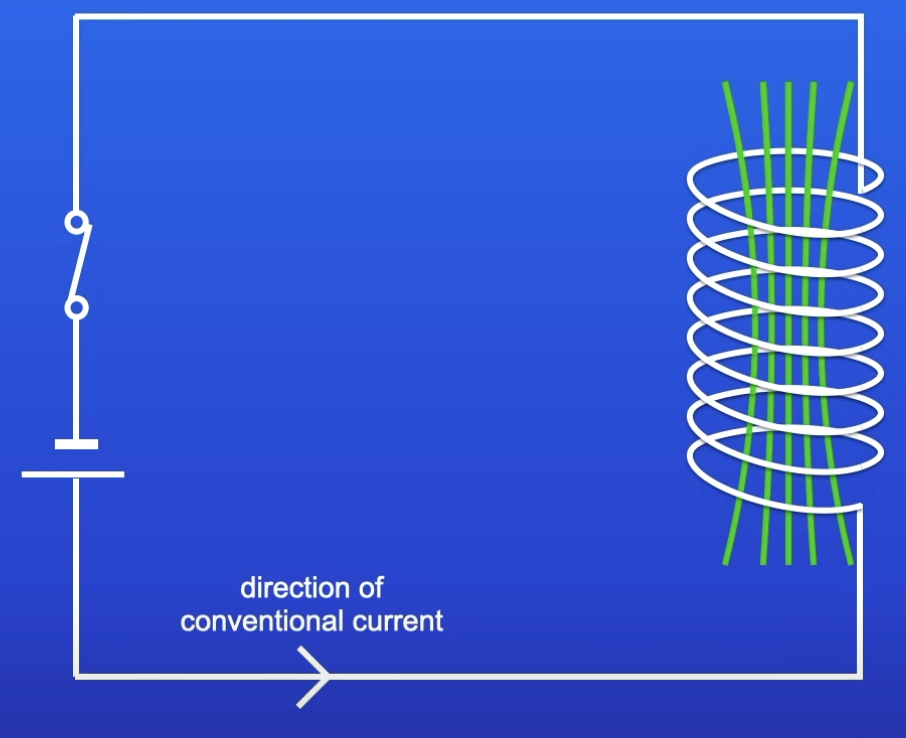
Shaping a wire to form a solenoid increases the strength of the magnetic field created by a current through the wire. The magnetic field inside a solenoid is strong and uniform
Solenoid
The shape of a coiled wire

How to increase the strength of a MF created by current through the wire regarding the shape of a wire?
Shaping the wire in a coil
To form a solenoid
Features of the MF created when current is turned on in a solenoid?
Strong + uniform MF inside solenoid
What creates a MF in a circuit?
Current through the wire
The magnetic field around a solenoid has a similar shape to…
MF around bar magnet
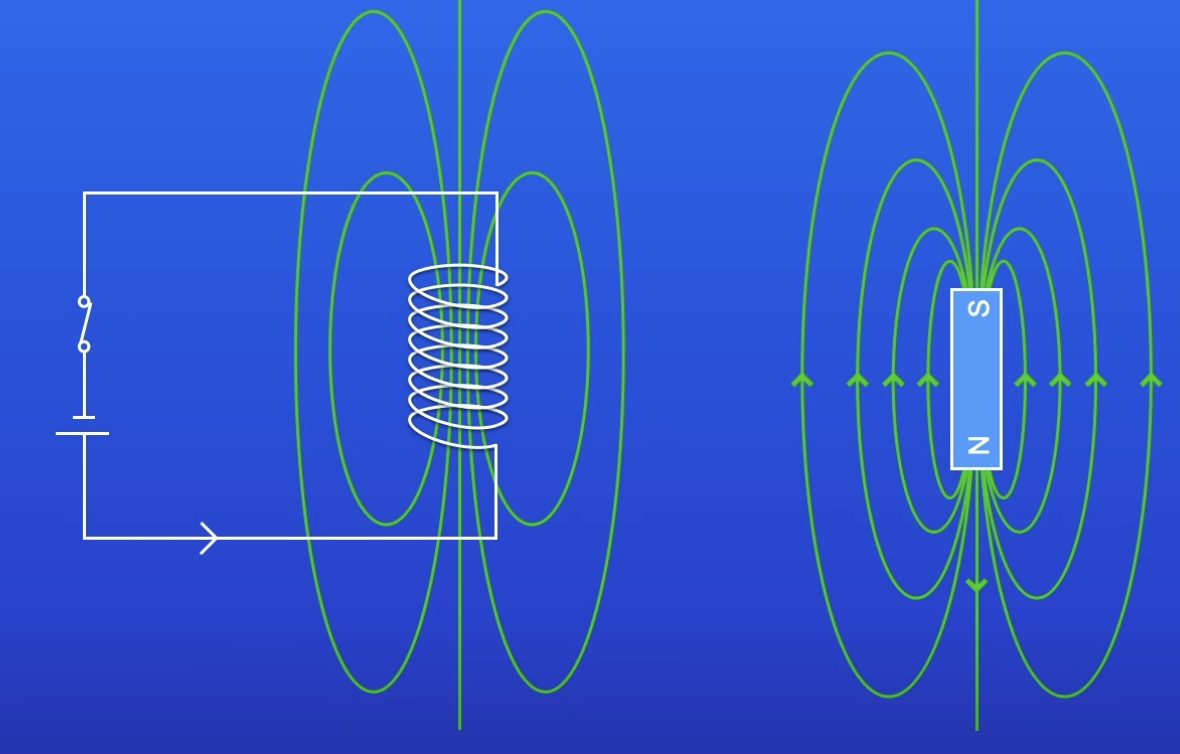
How to work out the direction of the MF in a solenoid
RH rule
Place fist of RH so fingers curl in the same direction as conventional current
Thumb points in direction of North pole (in this eg)
Thumb = MF, fingers = current
3 ways to increase the strength of a MF produced by a solenoid
Increase size of current
Increase no. of turns of the coil
Place piece of iron inside solenoid
Iron core
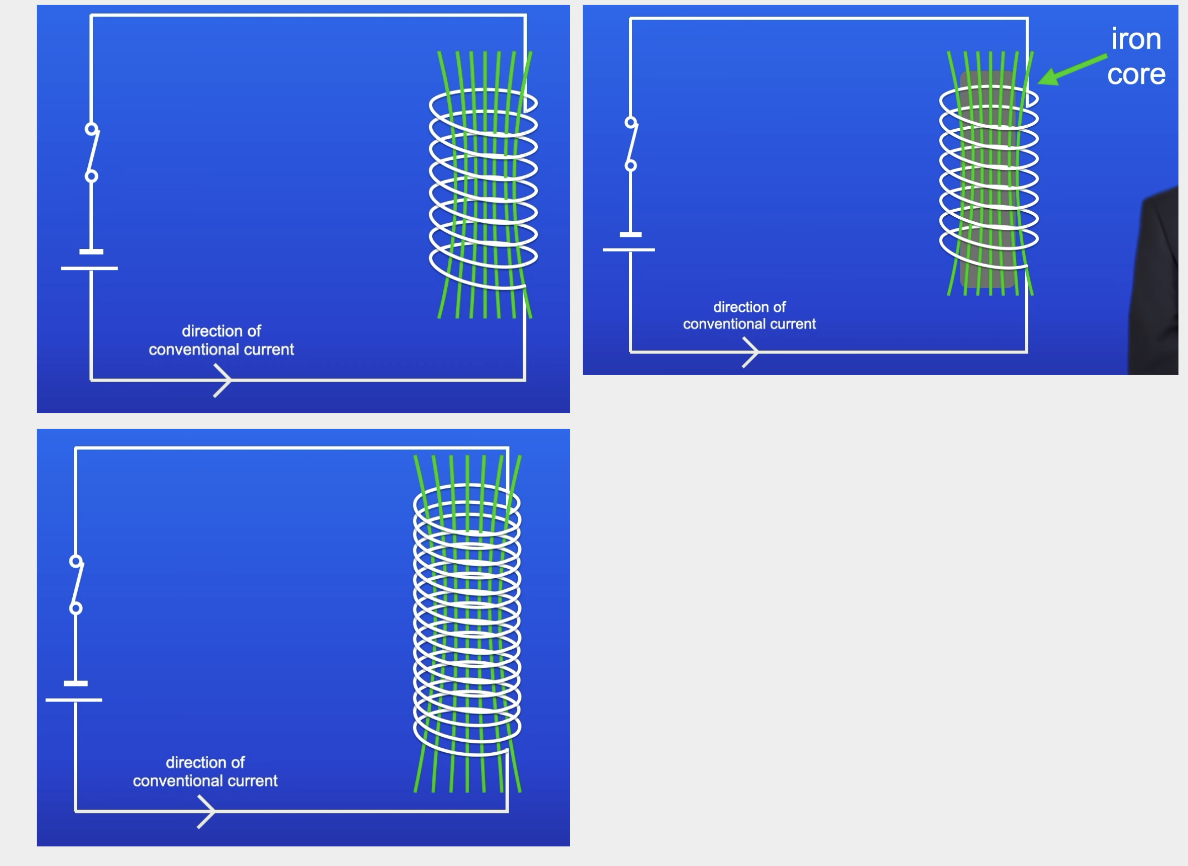
Electromagnet
Solenoid containing an iron core
Why are electromagnets useful?
Can change strength of MF by changing size of current
Can turn electromagnet on or off
What devices contain electromagnets?
Relay
Electric doorbell
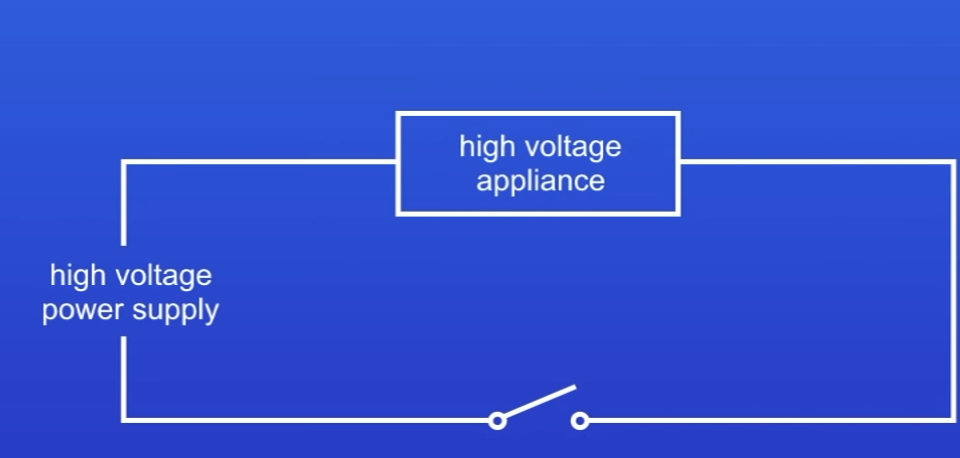
In high voltage circuit why is using a switch to turn it on + off dangerous?
Can get sparking
Risk of electrocution
In high voltage circuits, what is used instead of a switch to turn it on and off?
Relay
What does a relay contain?
2 separate circuits
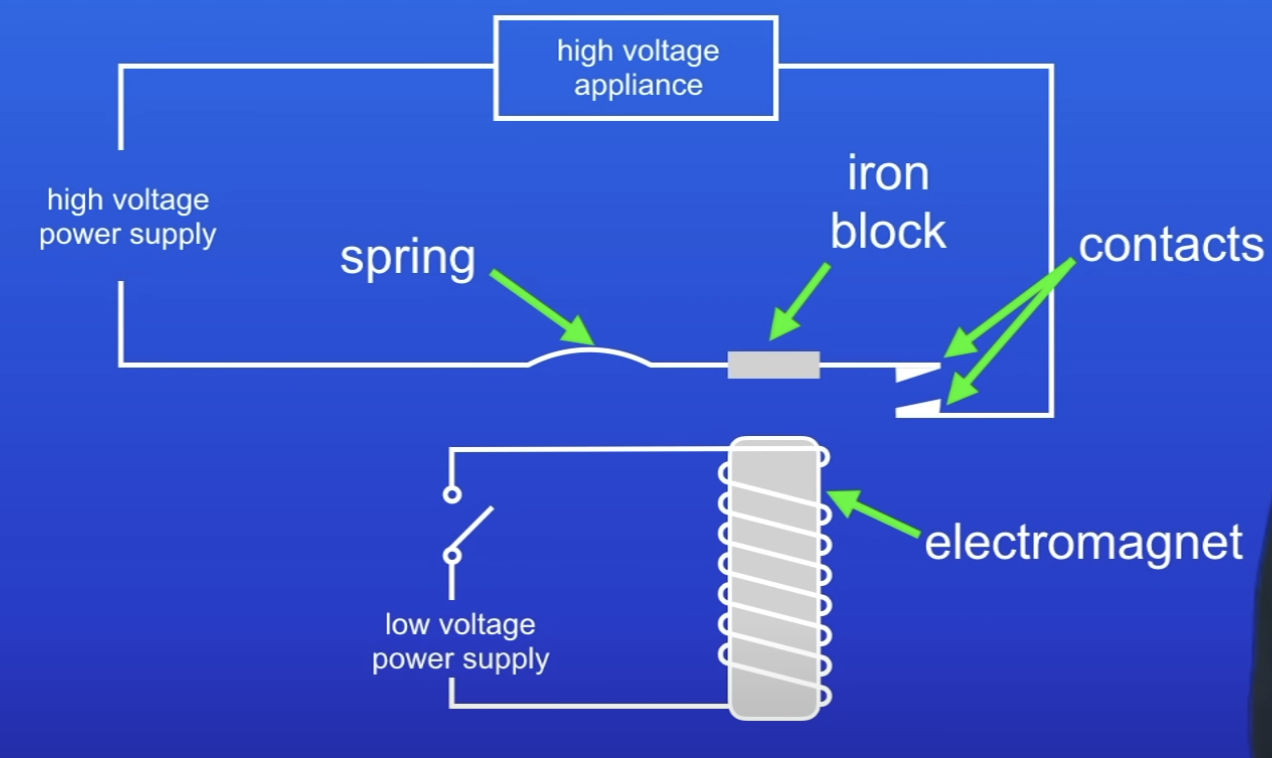
How are the 2 circuits in a relay different?
Low voltage circuit containing electromagnet
High voltage circuit
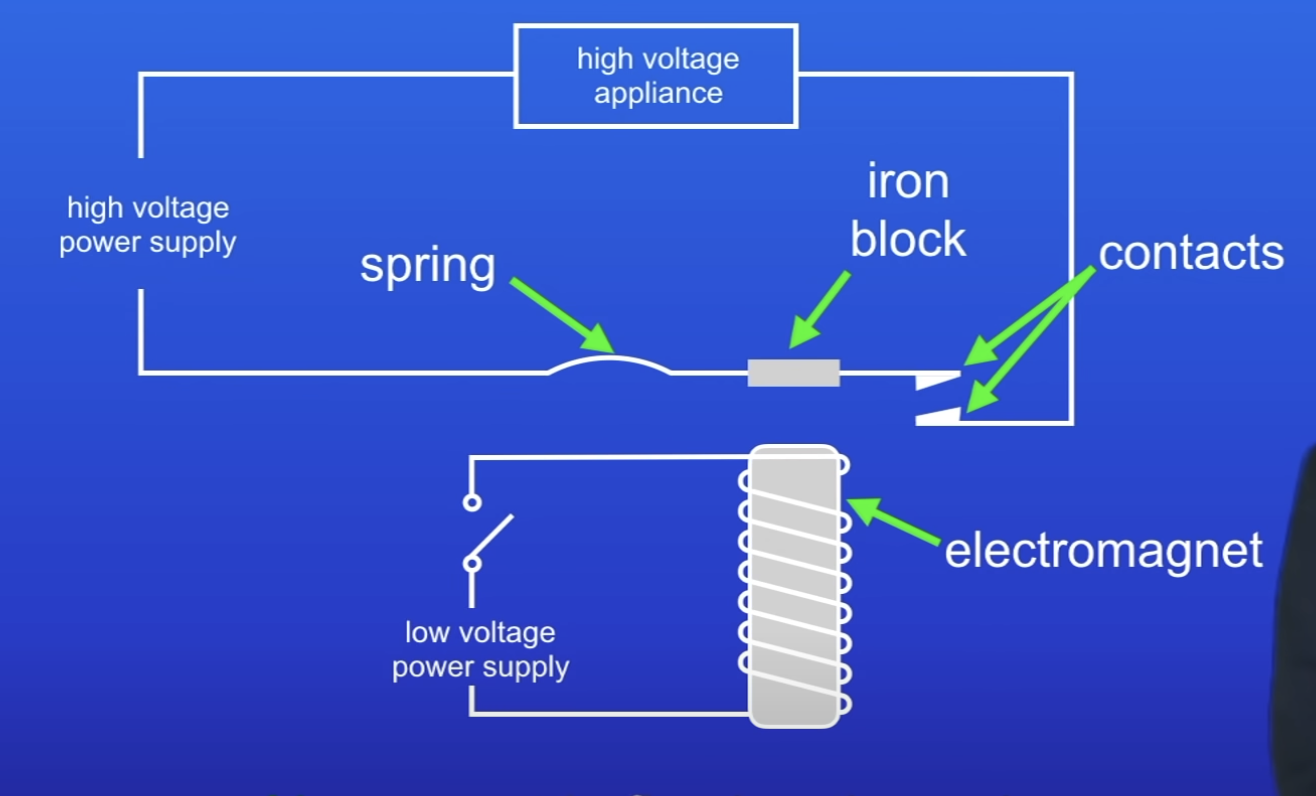
Why does a relay contain a low voltage circuit with an electromagnet?
Circuit is safe to be switched on + off
What is the switch replaced with on the high voltage circuit in a relay + why?
2 metal contacts
1 contact connected to spring → keeps contacts apart
When is a magnetic field produced?
When current moves through a wire
What happens if a wire (w a current through it, ao it has a MF) is placed in another MF?
Motor effect
MF around the wire interacts with MF between the magnets
So wire experiences a force (eg upwards)
Upwards force causes wire to move upwards
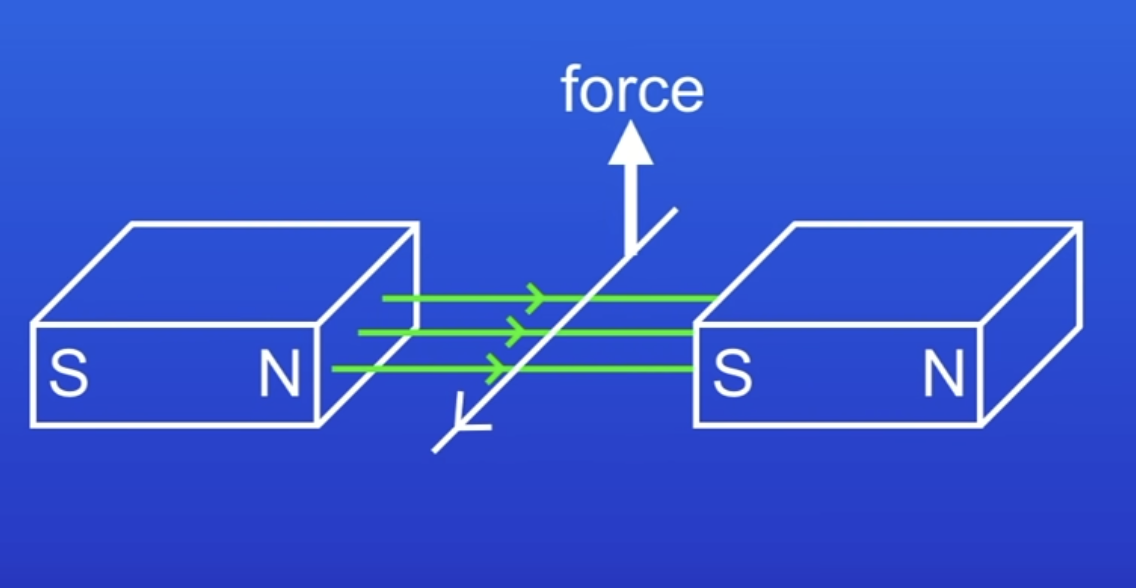
Motor effect
When a conductor carrying a current is placed in a MF, the magnet producing the MF + the conductor exert a force on each other
When the wire is NOT PARALLEL to the lines of the MF
Magnetic flux density
Measure of the strength of a MF
Size of force equation (produced by motor effect)
F = BIl

Which wire does the size of force equation apply to?
Wires at right angles to the MF
Factors affecting the size of the force
Magnetic flux density (of MF)
Current (in conductor)
Length of conductor
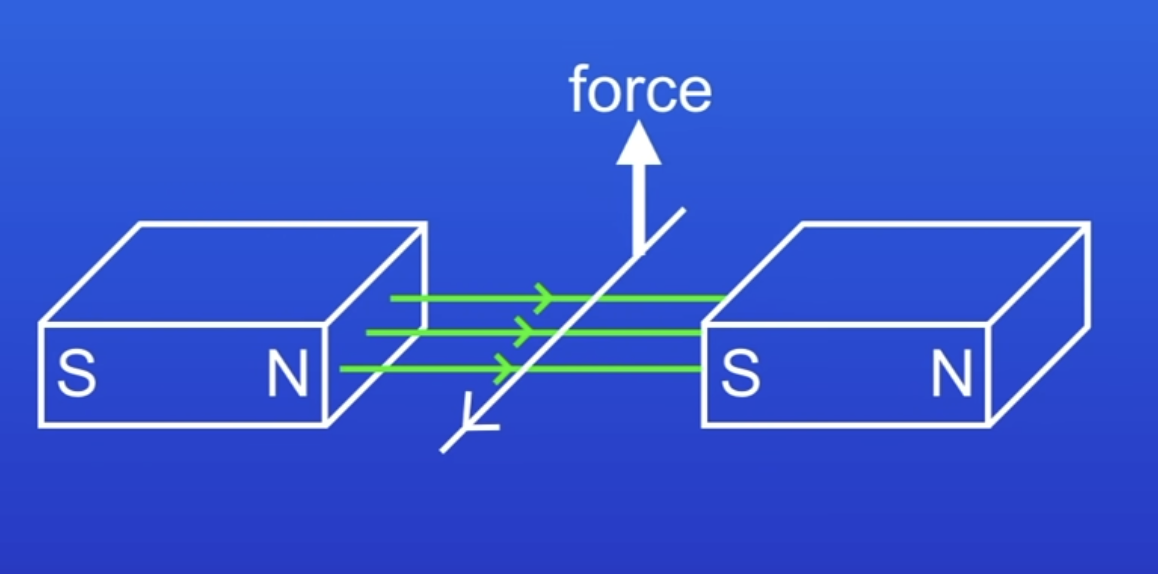
How to determine the direction of the force experienced by a wire?
Fleming’s left hand rule
Place thumb, 1st, + 2nd finger so they are at right angles
Point 1st finger in direction of MF (from N to S)
Point 2nd finger in direction of conventional current (+ to -)
Direction thumb is pointing shows direction of motion (the force)
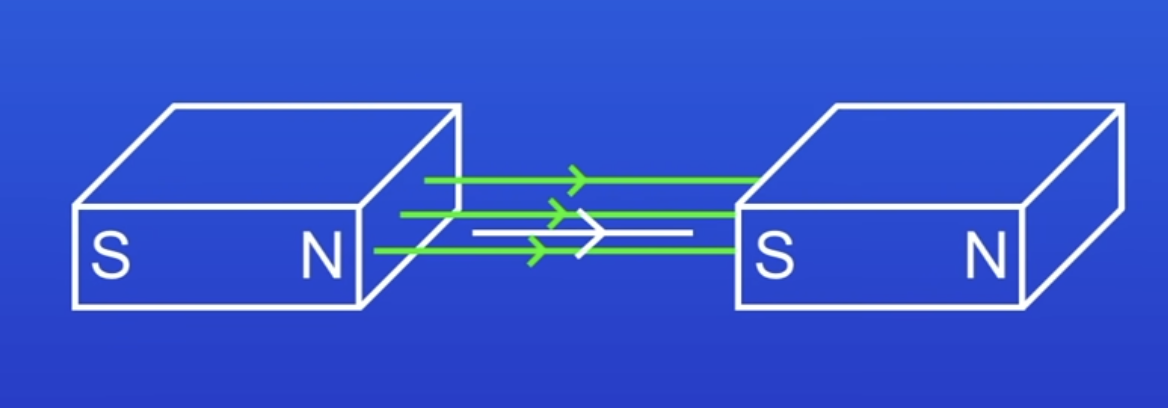
When will the conductor not experience a force?
When the conductor is parallel to the MF
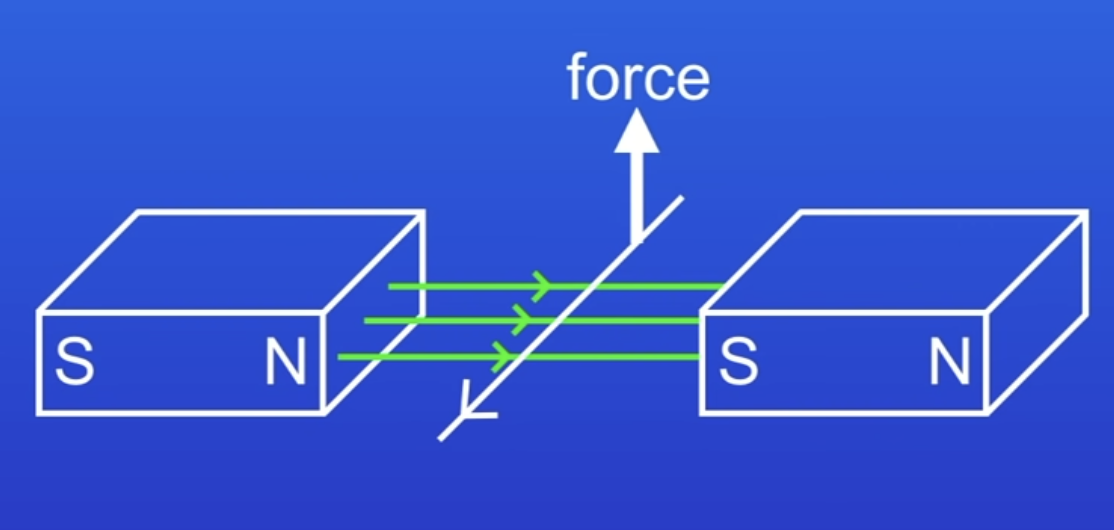
When will the conductor experience a force (movement)?
When the conductor is at right angles to the MF
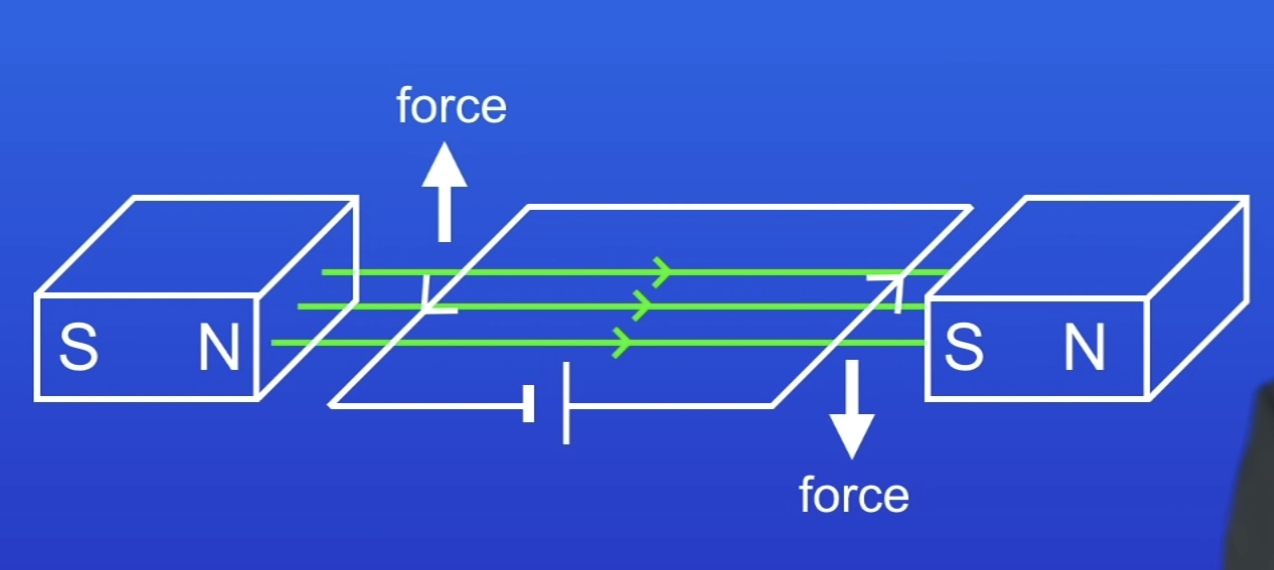
Where is the motor effect used?
In electric motors
Basis of an electric motor
A coil of wire carrying a current in a MF tends to rotate (due to motor effect)
Summary of what causes a coil to rotate
As the current flows (from - to +), the force produced in each side of the coil acts in opp directions
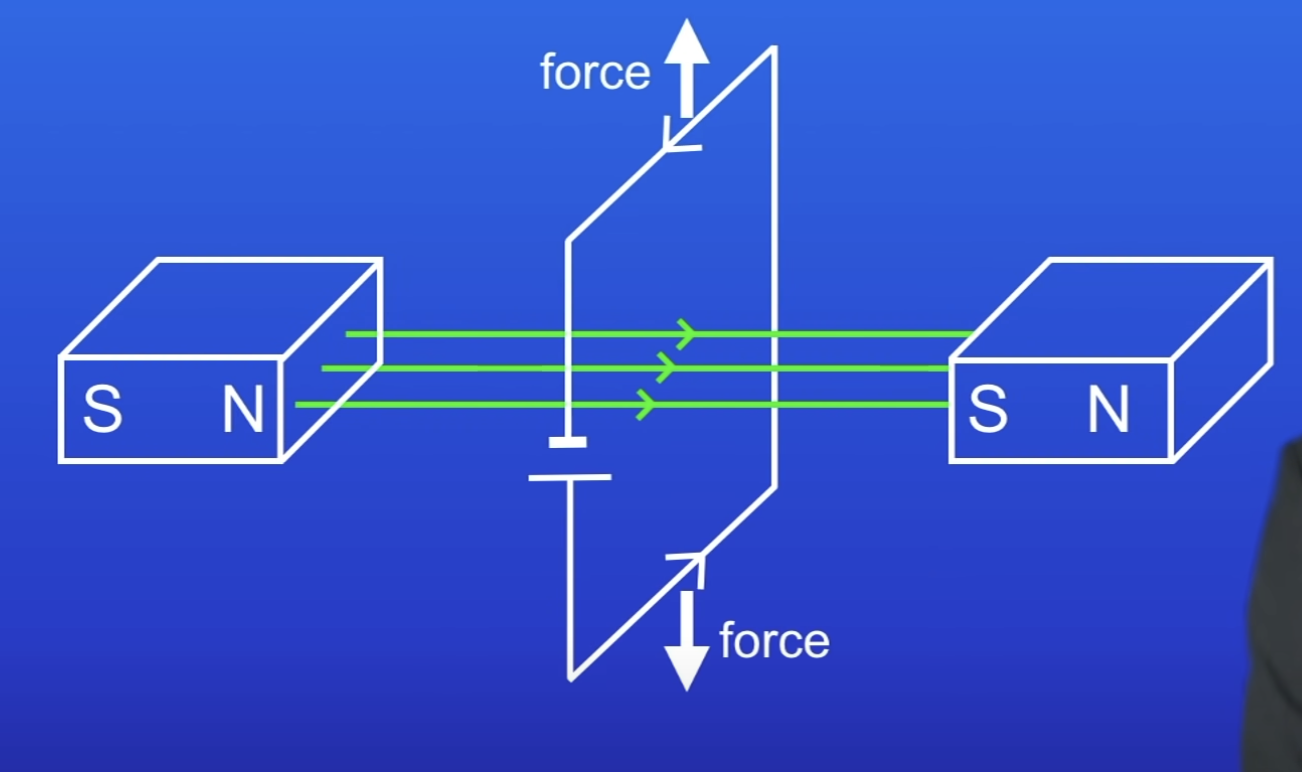
Why does the motor stop rotating when the coil reaches 90° position?
Force produced is now parallel to the MF line → would be 0
Why are graphite brushes used in a split ring commutator?
Conducts electricity
V slippery = v little friction when in contact with SRC
When current passed through a coil why does it spin?
Force acts on each side of the coil due to the motor effect
Force on 1 side is in the opp direction to force on the other side
What does a split ring commutator do every half turn of the coil?
Reverses current around the coil
In the motor effect, how can you increase the size of the force produced?
Increase current
Use stronger magnet
So increased strength of MF
In the motor effect, how can you change the direction of the force produced?
Switch MF
Switch direction of current
How can you increase motor speed?
Increase current
Increase magnetic field
What do loudspeakers and headphones do?
Use the motor effect to convert variations in current in electrical circuits to the pressure variations in sound waves
Where are loud speakers found?
Speakers on a stereo
Inside headphones
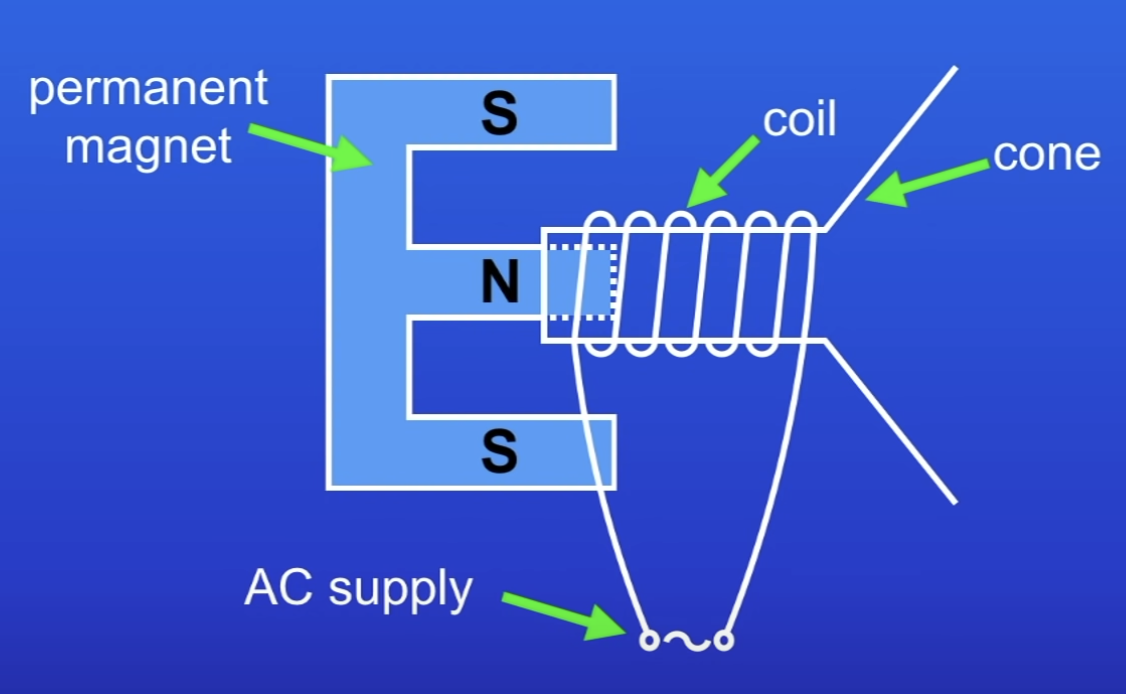
Describe the set up of a loudspeaker / headphones (3 points)
Cone with coil of wire wrapped around 1 end
Coil of wire connected to AC electrical supply
Permanent magnet which goes inside the coil of wire
How do loudspeakers and headphones work?
As an AC passes through the coil, it generates a MF (around the wire)
The MF from the coil interacts with the MF from the permanent magnet
ie the MFs attract or repel each other
→ Produces a RF (ME) → causes the cone to move
When current switches direction, the direction of the force on the cone reverses
Causes the cone to move in and out → generates sound waves
Changing the frequency of the AC supply changes…
The freq the cone vibrates at
Higher frequency produces a …
Higher pitch sound
Increase size of current…
Increases amplitude of the vibration → increases volume of sound
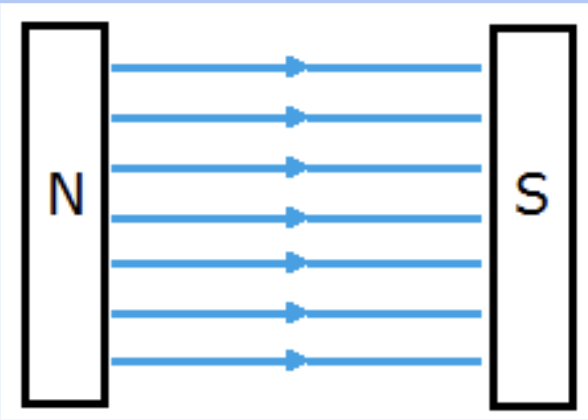
What is this field called?
Uniform magnetic field
The MF is the space IN BETWEEN the lines, not the lines
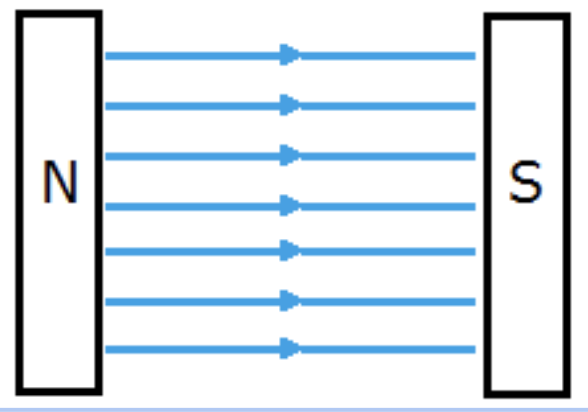
Describe a uniform magnetic field
Field lines are:
Straight
Evenly spaced
Parallel
Arrows point towards south