Plant Phys quiz 3 (unfinished)
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
What are the essential elements required by plants?
Hydrogen (H), Carbon (C), Oxygen (O), Nitrogen (N), Potassium (K), Calcium (Ca), Magnesium (Mg), Phosphorus (P), Sulfer (S), Silicon (Si), Chlorine (Cl), Iron (Fe), Boron (B), Manganese (Mn), Sodium (Na), Zinc (Zn), Copper (Cu), Nickel (Ni), Molybdenum (Mo).
What are dust seeds?
Microscopic seeds. That are made up of an embryo and a seed coat. They lack carbohydrates and mineral ions stored to aid in germination and growth. They lack an endosperm and have a tiny cotyledon allowing them to travel far by wind dispersal. They need mycorrhizae to germinate quickly as they provide the orchid with nutrients and carbon. The seeds are somewhat specific in choosing their fungal symbionts.
Orchids essentially serve as parasitic.
Similarities of C3, C4 and CAM carbon dynamics
They each the Calvin cycle to fix CO2 to create sugars. It is just that C4 and CAM plants have additional steps to capture and concentrate CO2 before the reaction starts.
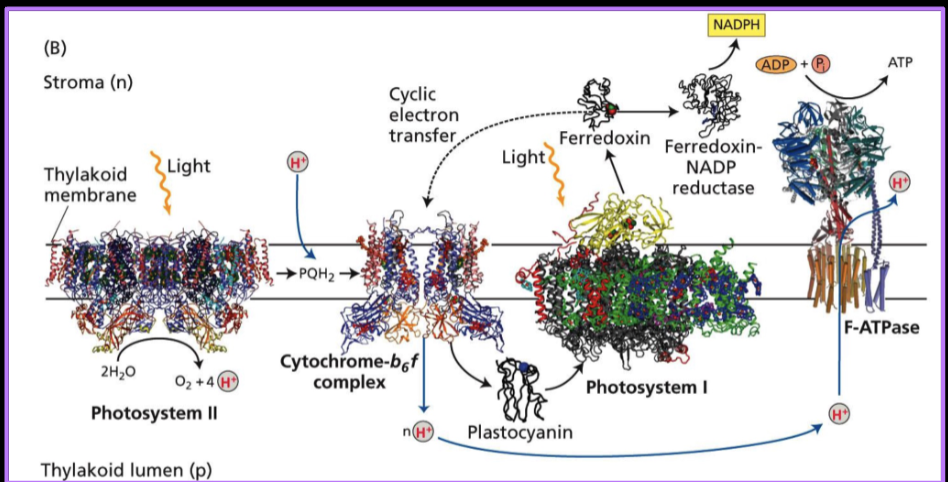
What is the Z scheme and draw it?
A model that takes place in the thylakoid membrane and is a part of the light dependent reactions. It is the source of electrons for the electron transport chain. The final electron acceptor is NaDH+ which becomes NADPH
The products of the s scheme include ATP and NADPH
What are the water dynamics for C3, C4, and CAM
CAM plants are the best at preserving water due to them opening their stomata at night. This is due to the lower respiration because of the lower temperature and higher humidity. C4 plants are ok at preserving water. They keep their stomata closed for longer durations than C3 just not as much as CAM plants. C3 plants are the worst at preserving water
C4 and CAM plants have the same processes just slightly changed based on the time their stomata are open, and where these processes take place.
What are the phases of respiration? Where do they occur and what are the final products?
Glycolysis (Cytoplasm + Plastid) carbohydrates are broken down. 6C sugar to 3C ( 2 pyruvate) produces 2 ATP, 1 NADH
Citric Acid Cycle (Mitochondria) Final products are 3 CO2, 4 NADH, 1 FADH2, 1 ATP
Electron Transport Chain (Inner membrane of mitochondria) Final product ATP.
Final products are 6CO2, 6H2O +ATP
What is phytochrome activity and shade avoidance response
Phytochrome is a photoreceptor which intercepts and responds to light by changing its configuration. This activity depends on photoreversibility which is based of the presence of Pfr (receptor for far-red light) or Pr (receptor for red light). Pfr is associated with kinase activity
Shade avoidance response: The response of stem elongation in leaves when phytochrome is in Pr form for long periods of time. Only adapted to plants where growing toward the sun would actually be useful.
What is In-situ plasticity vs. developmental plasticity
In-situ plasticity: Faster; regulates enzymatic activity, protein synthesis, etc. can occur within minutes to hours. e.g. up regulation of carotenoids.
Developmental plasticity: Plasticity that is transmitted to cells that can undergo division and expansion. requires the development of new tissues and is often delayed. Common among seedlings who detect light coming off neighbors in order to gain an advantage over them. Called asymmetric competition.
What are the three main phases of carbon reaction (Calvin cycle)
Carboxylation (Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate + 3CO2 + Rubisco = 2 3-phosphoglycerate)
Reduction (6ATP + 3-phosphoglycerate + PGA kinase = 1,3 biphosphoglycerate + 6ADP) also includes (6NADPH + 1,3 biphosphoglycerate + G3P dehydrogenase = 6NADP + 6G3P)
Regeneration ( 5 G3P + 3 ATP = 3 Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate)
net result of Calvin cycle is one molecule of G3P (glyceraldehye-3-phosphate)
What is rubisco and what is its function
the real name is Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase. and it has 8 binding sites.
Rubisco serves the purpose of carboxylation and oxygenation of Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate. Carboxylation yields two molecules of 3-phosphoglycerate, and oxygenation produces one molecule each of 3-phosphoglycerate and 2-phosphoglycolate.
What is photorespiration? What is it primarily effected by?
When O2 binds to rubisco instead of CO2. It is very energy inefficient. It is wasteful of energy and CO2. Despite it being considered bad it is essential for plant survival.
Effected primarily by an increased temperature. Though plants do have some adaptations to help prevent photorespiration
Summarize the difference between C3, C4, and CAM plants
The majority of plants are C3 plants, which have no special features to combat photorespiration. (stroma of mesophyll cells)
C4 plants minimize photorespiration by separating initial CO2 fixation and the Calvin cycle in space, performing these steps in different cell types. (bundle sheath cells)
Crassulacean acid metabolism (CAM) plants minimize photorespiration and save water by separating these steps in time, between night and day. ( Stores organic acid in vacuoles during day, and releases compound in mesophyll cells during night)
Remember C4 separates by space while CAM by time.
Differences between C3, C4, and CAM plants.
(Copy and pasted)
C₃ plants:
CO₂ enters the Calvin cycle directly.
The first stable product is a 3-carbon compound (3-phosphoglycerate).
C₄ plants: (differs in space)
CO₂ is first fixed by PEP carboxylase into a 4-carbon compound in mesophyll cells.
That 4-carbon compound is then transported to bundle-sheath cells, where CO₂ is released and enters the Calvin cycle.
CAM plants: (Differs temporally)
At night, CO₂ is fixed by PEP carboxylase into 4-carbon acids (malate) and stored in vacuoles.
During the day, CO₂ is released from malate and enters the Calvin cycle in the same cell.
What is zeaxanthin?
It is a photoreceptor for blue light that is heavily involved in heat dissipation.