AP Psychology: Learning Theories and Conditioning Concepts
1/114
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
115 Terms
What is the behavioral perspective in psychology?
It examines how observable behaviors are learned and reinforced through interactions with the environment.
How does operant conditioning work?
It shows how behaviors can be learned and modified based on the reinforcements and consequences that follow them.
What is associative learning?
A process of learning in which an individual forms connections between events that occur together.
What is classical conditioning?
A learning method where two stimuli are associated, enabling anticipation of events.
Provide an example of classical conditioning.
A child develops a fear of dogs after being bitten, associating all dogs with pain and fear.
What is habituation?
A form of non-associative learning where organisms exhibit a diminished response to a repeated stimulus.
How does habituation manifest in an office environment?
An employee becomes accustomed to the sound of a ringing phone and no longer reacts strongly to it.
What is an unconditioned stimulus (UCS)?
A stimulus that naturally and automatically triggers a response without any learning needed.
In the classroom example, what is the unconditioned stimulus?
The pop quizzes that provoke a stress response.
What is an unconditioned response (UR)?
A natural and automatic reaction to a stimulus that occurs without prior learning.
What is the unconditioned response in the quiz scenario?
The immediate stress and nervousness experienced when quizzes are announced.
What is a conditioned stimulus (CS)?
A previously neutral stimulus that, after being paired with an unconditioned stimulus, evokes a conditioned response.
What becomes the conditioned stimulus in the classroom scenario?
The classroom itself, which triggers anxiety due to its association with pop quizzes.
What is a conditioned response (CR)?
A learned response that occurs when a conditioned stimulus is presented, resulting from its association with an unconditioned stimulus.
What is the conditioned response in the classroom example?
The anxiety felt by the student when entering the classroom, even without a quiz.
What does acquisition refer to in learning?
The initial learning of an association between a stimulus and a response.
What is the difference between unconditioned and conditioned stimuli?
Unconditioned stimuli trigger responses naturally, while conditioned stimuli become associated with responses through learning.
What is the difference between unconditioned and conditioned responses?
Unconditioned responses are automatic reactions, while conditioned responses are learned reactions to stimuli.
How does classical conditioning affect emotional responses?
It can shape emotional responses by associating neutral stimuli with significant emotional events.
What role does reinforcement play in behavior modification?
Reinforcement increases the likelihood of a behavior being repeated in the future.
What is an example of reinforcement in training a pet?
Giving treats and praise to a dog when it successfully fetches a ball.
What is the significance of the environment in behavioral psychology?
The environment provides stimuli and consequences that shape and reinforce behaviors.
What is the outcome of repeated exposure to a non-threatening stimulus?
The individual's response to that stimulus diminishes over time, demonstrating habituation.
How can classical conditioning lead to anticipatory anxiety?
By associating a neutral environment with stress-inducing events, leading to anxiety in similar contexts.
What is the role of the unconditioned response in classical conditioning?
It serves as the natural reaction that is paired with a conditioned stimulus to form a learned response.
What does 'acquisition' refer to in the context of learning?
The phase of learning where a student associates the classroom (conditioned stimulus) with the anxiety of pop quizzes (unconditioned stimulus).
How does the acquisition phase strengthen the conditioned response?
Each time the student enters the classroom and a pop quiz occurs, the association between the classroom and the quizzes strengthens.
What is 'extinction' in classical conditioning?
The process where the conditioned response weakens and eventually disappears when the conditioned stimulus is presented without the unconditioned stimulus.
How does extinction apply to a student anxious about pop quizzes?
Extinction occurs when the classroom is presented without pop quizzes, leading to a decrease in the anxiety response.
What is 'spontaneous recovery'?
The reappearance of a previously extinguished conditioned response after a period of rest.
How might spontaneous recovery manifest for a student with quiz anxiety?
The student may suddenly feel anxiety upon returning to the classroom after a break, despite no recent quizzes.
What is 'stimulus discrimination'?
The ability to differentiate between similar stimuli and respond differently based on past experiences.
How does stimulus discrimination work in the context of classroom anxiety?
The student feels anxious in the math classroom but not in the science classroom, as the latter is not associated with unexpected quizzes.
What is 'stimulus generalization'?
The tendency to respond to stimuli that are similar to the conditioned stimulus.
How might stimulus generalization affect a student's anxiety?
The student may feel anxious in other classrooms or settings that share characteristics with the math classroom.
What is 'higher-order conditioning'?
A process where a previously conditioned stimulus is used to create further associations with new neutral stimuli.
Can you give an example of higher-order conditioning?
If a bell in the math classroom becomes associated with anxiety, it can evoke the same response even in a different context.
What does 'counterconditioning' involve?
Changing a learned response by pairing it with a different, more preferred experience.
How might counterconditioning be applied to a student with quiz anxiety?
The student learns relaxation techniques that are practiced in the classroom to replace anxiety with calmness.
What is 'taste aversion'?
A learned association between the taste of a food and feeling sick, often occurring after just one pairing.
Can you provide an example of taste aversion?
A person develops an aversion to a type of seafood after experiencing food poisoning shortly after eating it.
What is 'one-trial conditioning'?
Learning that occurs quickly after just one pairing of two stimuli.
How does one-trial conditioning relate to taste aversion?
A strong aversion can develop after one pairing of seafood with the sickness caused by food poisoning.
What role does the conditioned stimulus play in classical conditioning?
It is the stimulus that is paired with the unconditioned stimulus to elicit a conditioned response.
What is the unconditioned stimulus in the context of classroom anxiety?
The pop quizzes that cause stress and anxiety for the student.
What is the conditioned response for a student experiencing anxiety about pop quizzes?
The anxiety and stress felt when entering the classroom.
How does repeated exposure to the conditioned stimulus affect the conditioned response?
It strengthens the association, leading to a more pronounced conditioned response.
What might be a long-term effect of extinction in a classroom setting?
The student may eventually feel comfortable in the classroom without experiencing anxiety.
What is the significance of the unconditioned response?
It is the natural reaction to the unconditioned stimulus, such as anxiety to pop quizzes.
How can a therapist help a student using counterconditioning?
By introducing positive stimuli like relaxation techniques to replace anxiety.
What is the relationship between the conditioned stimulus and the conditioned response?
The conditioned stimulus elicits the conditioned response due to prior associations.
What might trigger spontaneous recovery in a student with quiz anxiety?
Returning to the classroom after a break may trigger a resurgence of anxiety.
What is the impact of a strong unconditioned stimulus on learning?
It can lead to quicker and more lasting associations with the conditioned stimulus.
What is biological preparedness?
The innate tendency of organisms to quickly learn associations between certain stimuli and responses relevant to their survival.
How does biological preparedness relate to taste aversion?
It explains why taste aversion develops quickly, often after just one exposure to a food that causes illness.
What is operant conditioning?
A type of learning where behavior is strengthened or weakened by consequences, such as reinforcement or punishment.
Give an example of operant conditioning in a classroom.
A teacher gives stickers for timely homework submissions, increasing the likelihood of students submitting on time.
What does the Law of Effect state?
Behaviors followed by favorable outcomes are more likely to be repeated, while those followed by unfavorable outcomes are less likely to be repeated.
How does the Law of Effect apply to weight loss tracking?
Positive outcomes from tracking food intake encourage continued logging of habits.
What is reinforcement?
Any consequence that increases the likelihood of a behavior occurring again in the future.
How can a teacher use reinforcement to encourage class participation?
By giving extra credit points for thoughtful contributions, reinforcing the behavior of participation.
What are primary reinforcers?
Things we naturally like, such as food or water.
What are secondary reinforcers?
Things we learn to like because they are connected to primary reinforcers, such as money or grades.
What is reinforcement discrimination?
The ability to distinguish between different stimuli and respond appropriately based on reinforcement.
Give an example of reinforcement discrimination.
A dog learns to respond to 'sit' and 'stay' commands differently based on receiving treats for correct responses.
What is reinforcement generalization?
The tendency to respond similarly to different stimuli associated with the same reinforcement.
How does reinforcement generalization manifest in a classroom?
A student applies the behavior of raising their hand to speak in various settings, expecting similar praise.
What is positive reinforcement?
Presenting a desirable stimulus after a behavior to increase the likelihood of that behavior happening again.
How can positive reinforcement be used in education?
Teachers can praise students immediately after correct answers to encourage active participation.
What is negative reinforcement?
Removing an aversive stimulus after a behavior to increase the likelihood of that behavior happening again.
Give an example of negative reinforcement.
Fastening a seat belt to stop the annoying beeping sound in a car.
What is punishment in behavioral terms?
Any consequence that decreases the likelihood of a behavior occurring again in the future.
How can punishment be applied in a classroom setting?
A teacher takes away a student's phone for using it during class to discourage that behavior.
What is positive punishment?
Adding an aversive stimulus after a behavior to decrease the likelihood of that behavior happening again.
How might parents use positive punishment with screen time limits?
Imposing additional chores if a child exceeds their screen time limit.
Give an example of positive punishment.
Requiring a child to do extra household tasks after exceeding screen time limits.
What is negative punishment?
Removing a desirable stimulus after a behavior to decrease the likelihood of that behavior happening again.
Provide an example of negative punishment.
Taking away a teenager's privilege to use the family car for coming home past curfew.
What is reinforcement in operant conditioning?
A process that increases the likelihood of a behavior recurring.
What is shaping in operant conditioning?
Gradually reinforcing behaviors that are closer to the desired behavior, leading to the development of a complex behavior or skill.
How is shaping exemplified in dog training?
A trainer rewards a dog for successive approximations to the desired behavior of fetching a ball.
What is instinctive drift?
The tendency of animals to revert to their natural instincts instead of learned behaviors.
Give an example of instinctive drift.
Killer whales trained to perform tricks may exhibit natural behaviors like aggression or refusal to follow commands.
What is superstitious behavior?
Accidental reinforcement of behaviors, leading to the belief that those behaviors cause desired outcomes.
Provide an example of superstitious behavior.
A basketball player believes wearing a specific pair of socks leads to better performance after winning games while wearing them.
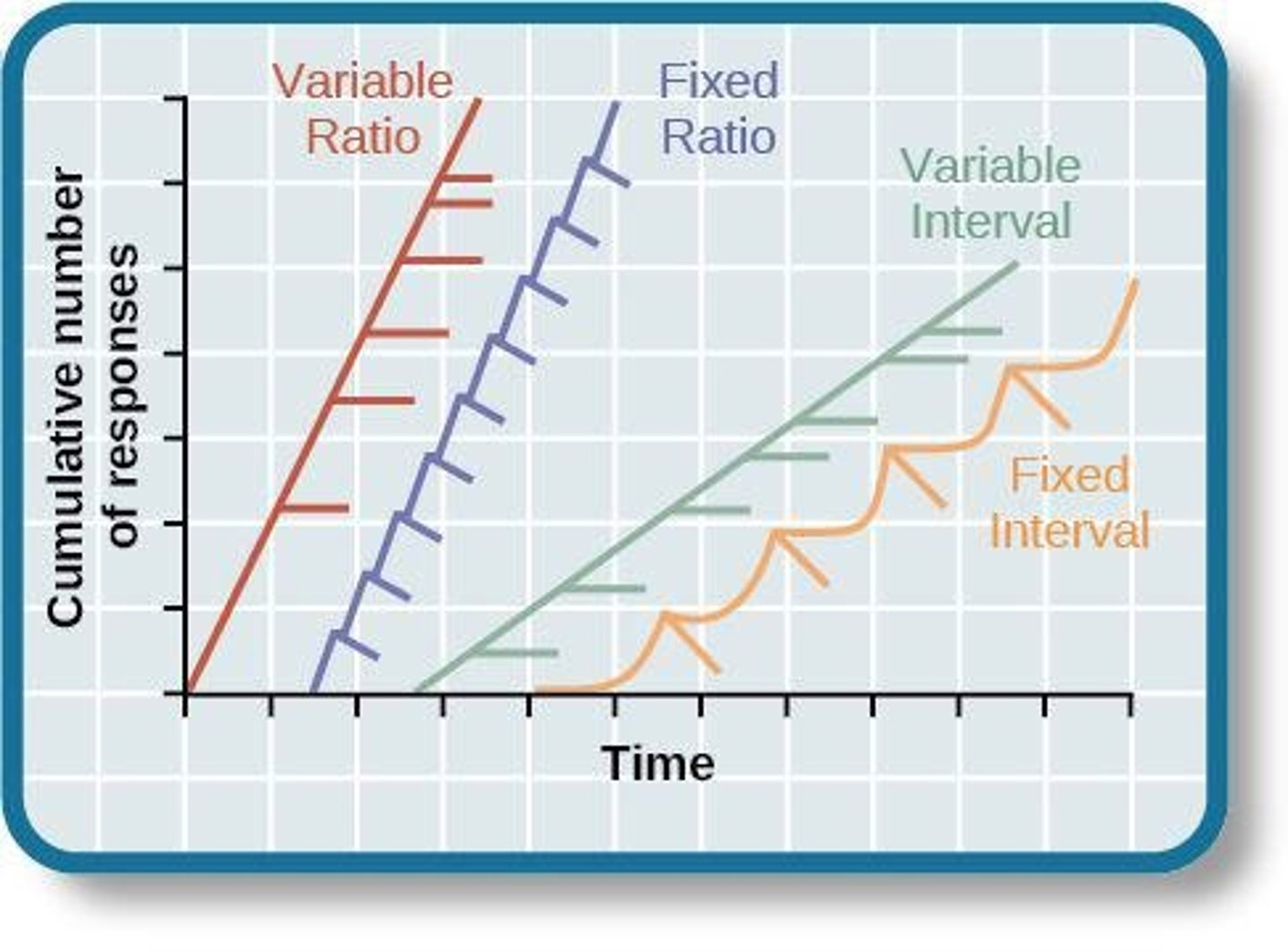
What are reinforcement schedules?
Patterns determining when and how often reinforcement is given for a behavior, influencing the rate and persistence of that behavior.
What is continuous reinforcement?
Reinforcing a behavior every time it occurs.
What is partial reinforcement?
Reinforcing a behavior only some of the time it occurs, leading to slower extinction.
What is a fixed interval schedule?
Reinforcement is delivered after a fixed amount of time has passed since the last reinforcement.
Give an example of a fixed interval schedule.
A student receives grades at the end of each semester, encouraging study efforts as the grading period approaches.
What is a variable interval schedule?
Reinforcement is delivered after varying amounts of time have passed since the last reinforcement.
Provide an example of a variable interval schedule.
Social media notifications that arrive at unpredictable times, encouraging users to check their accounts regularly.
What does 'fixed' mean in the context of reinforcement schedules?
It refers to a constant or unchanging amount of time or number of responses required for reinforcement.
What does 'variable' mean in the context of reinforcement schedules?
It refers to a changing or unpredictable amount of time or number of responses required for reinforcement.
What does 'interval' refer to in reinforcement schedules?
It refers to time-based reinforcement, indicating the passage of time between reinforcements.
What does 'ratio' refer to in reinforcement schedules?
It refers to response-based reinforcement, indicating the number of responses required for reinforcement.
What is a variable interval schedule of reinforcement?
A reinforcement schedule where rewards are given at unpredictable times, encouraging repeated engagement.
How does social media illustrate a variable interval schedule?
Users receive likes and comments at unpredictable times, compelling them to check their apps frequently.
What is fixed ratio reinforcement?
Reinforcement delivered after a fixed number of responses, leading to high response rates with pauses after rewards.
Give an example of fixed ratio reinforcement.
A coffee shop punch card system where customers earn a free coffee after purchasing ten coffees.