Echo Test 1 Study Guide
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
79 Terms
pericardium
thin sac that houses the heart and root and great vessels
epicardium
outer visceral layer
myocardium
middle muscles contract
endocardium
inner epithelial layer
order of pericardium layers outer to inner
fibrous
parietal
pericardial cavity
visceral
superior border of the heart
RA LA
inferior border of the heart
RV
right border of the heart
RA
left border of the heart
LV
anterior border of the heart
RV
posterior border of the heart
LA LV
LCA arises from
left coronary cusp
LAD follows
AV sulcus
LCX follows
coronary sulcus
RCA arises from
right coronary cusp at sinuses
RCA feeds
RA
RV
inf portion LV
portion of IVS
order of blood flow through the heart
SVC/IVC
RA
TV
RV
PV
PulmA
Lungs
PulmV
LA
MV
LV
Ao Valv
Ao
Body
suprasternal window
suprasternal notch
subcostal window
midline beneath costal margin
apical window
over cardiac window
parasternal window
over area bounded superiorly by left clavicle, medially by sternum, inferiorly by apical region
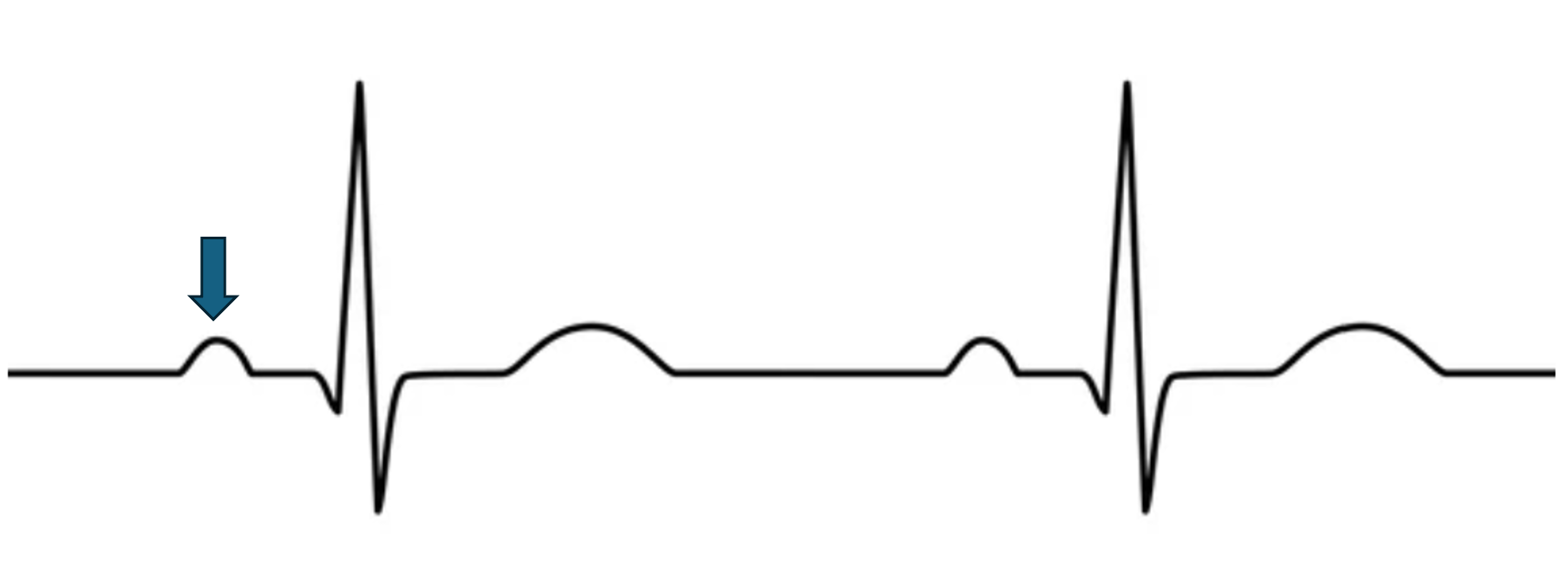
what does this represent?
atrial depolarization
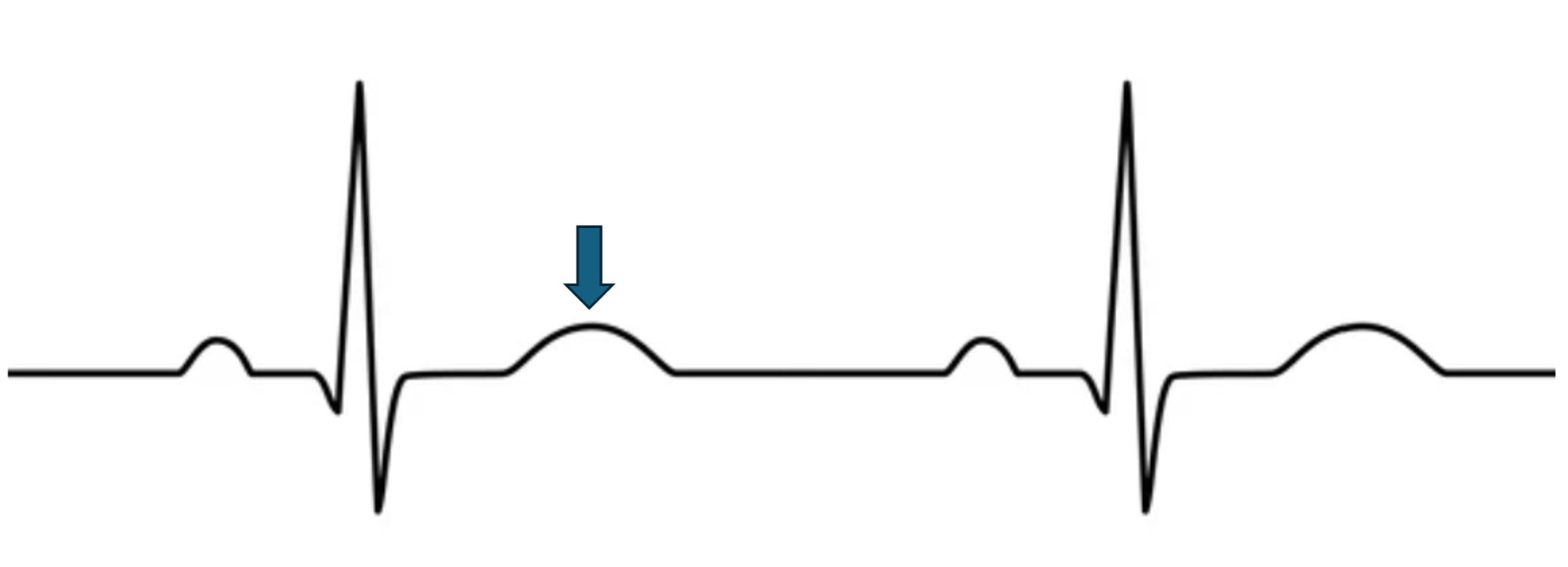
what does this represent?
ventricular repolarization
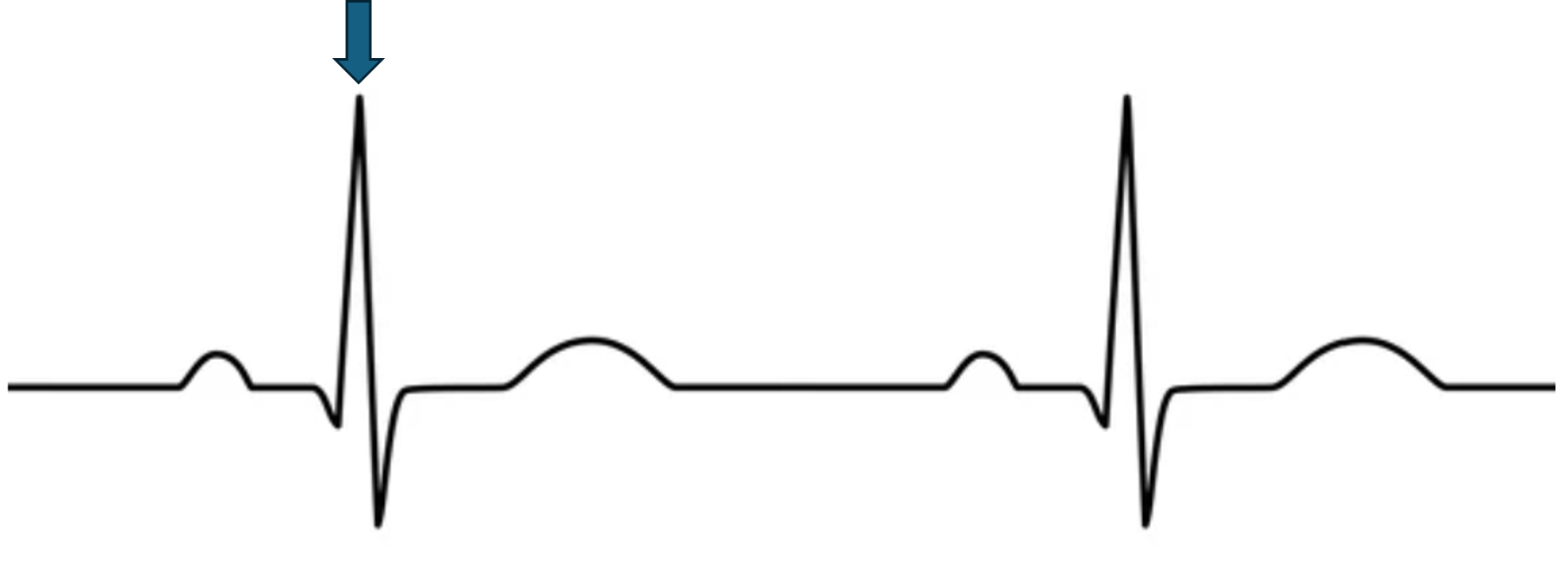
what does this represent?
ventricular depolarization
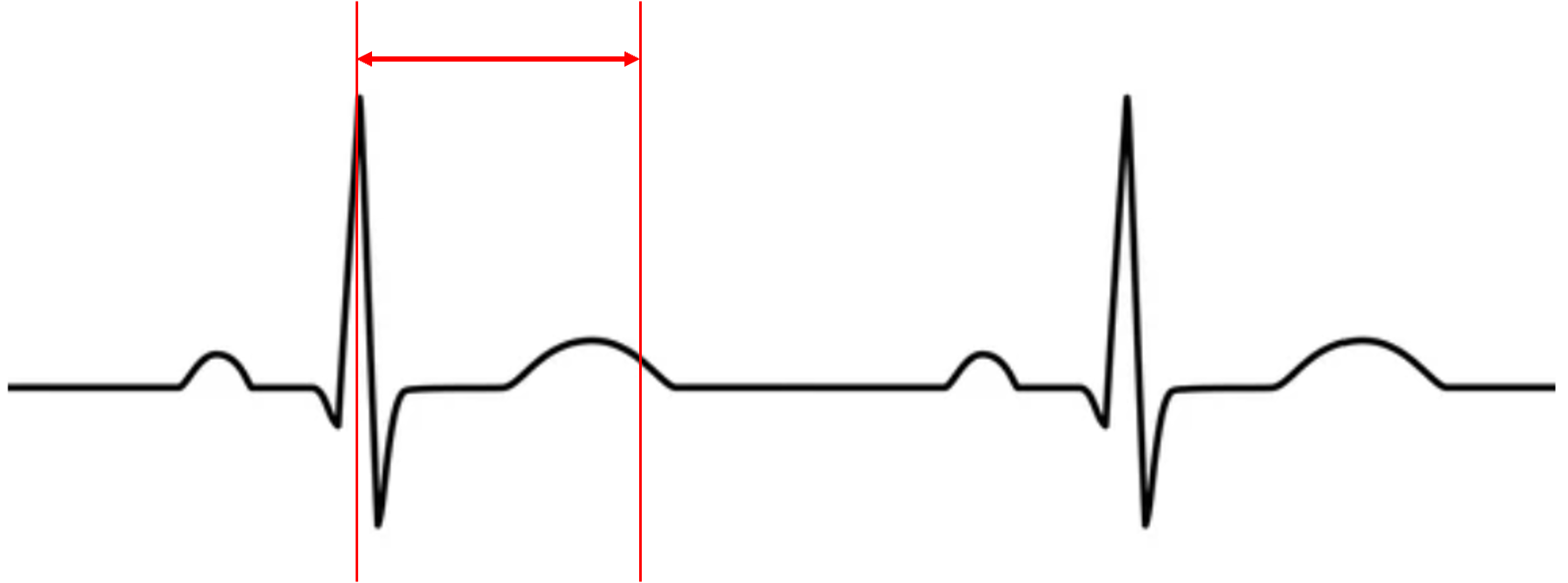
what does this represent?
systole
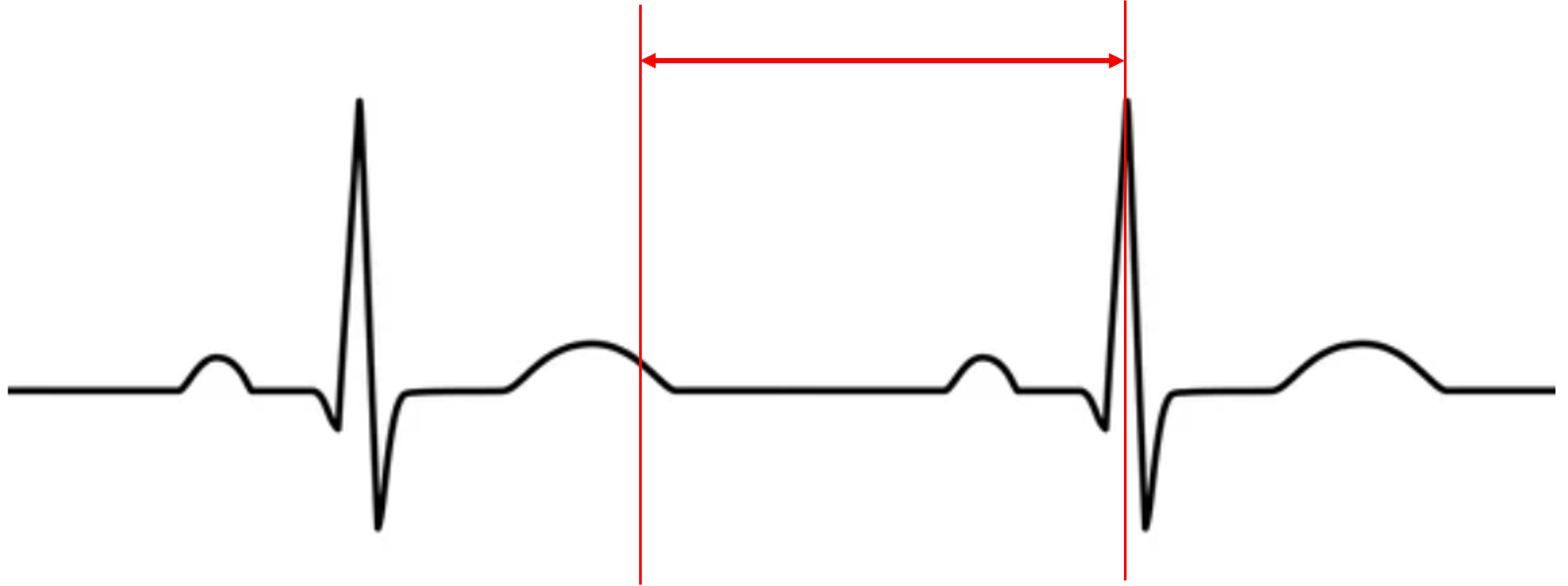
what does this represent?
diastole
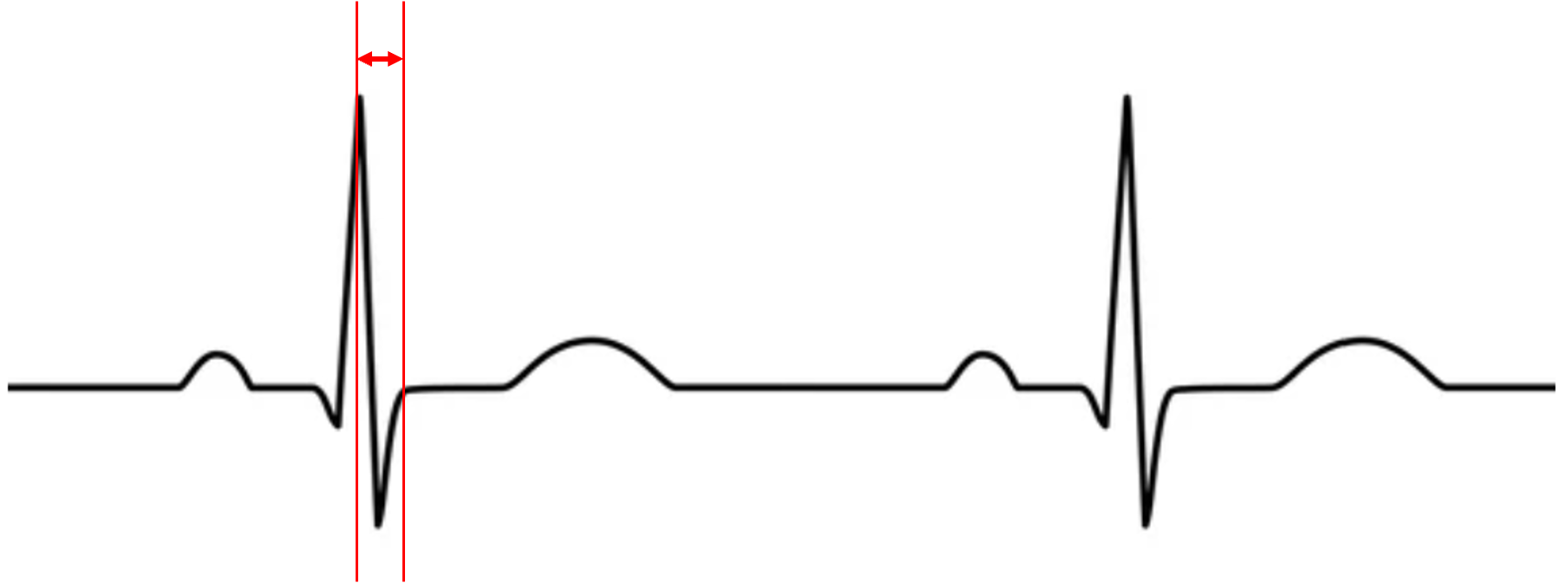
what does this represent?
iso contraction
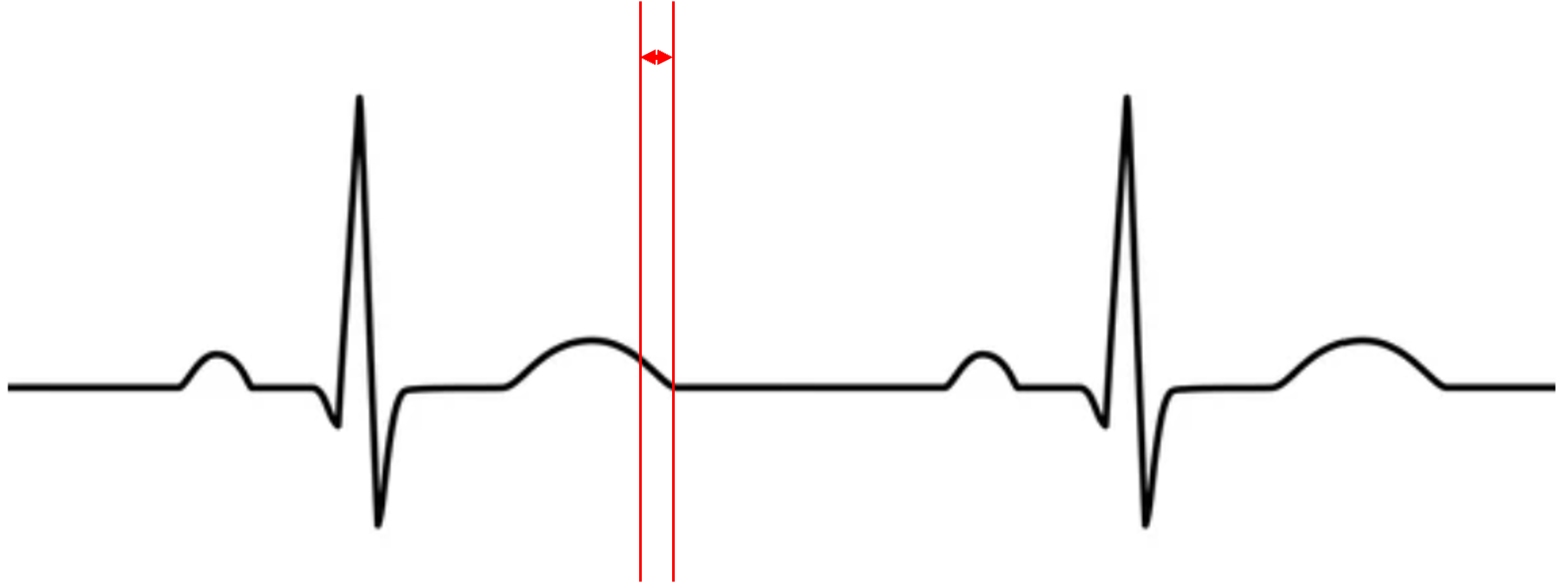
what does this represent?
iso relax
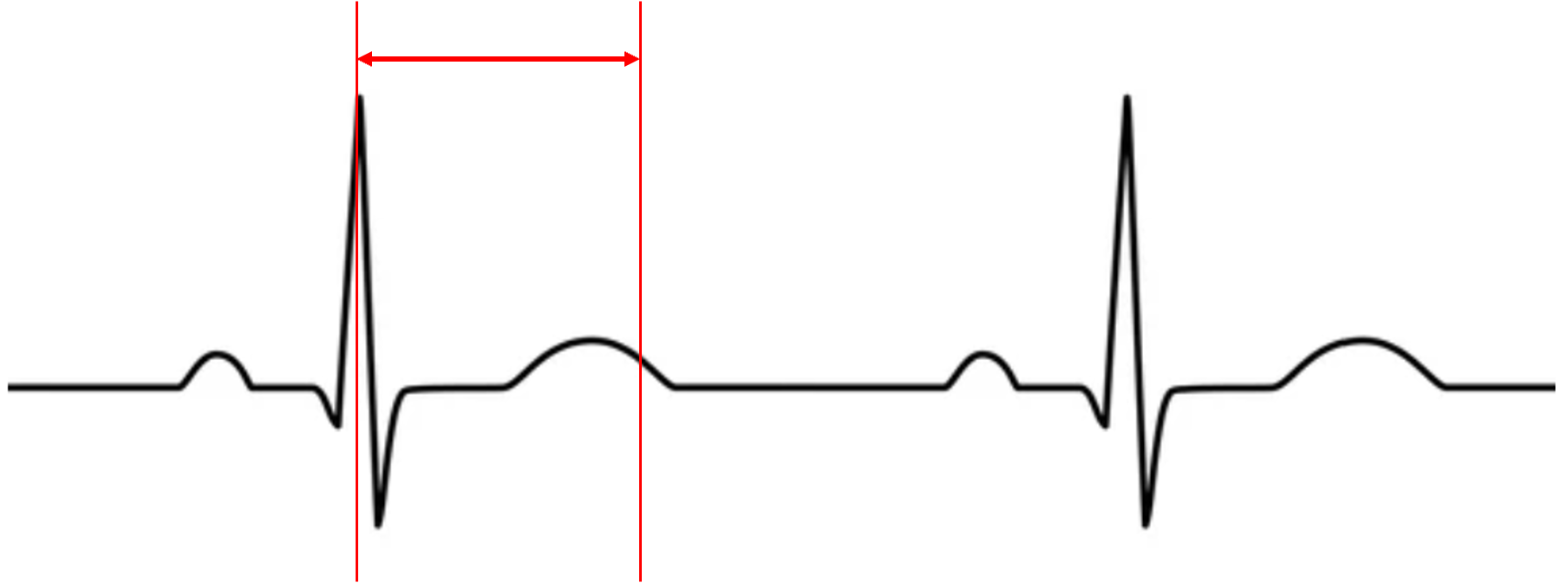
what is happening to ventricular volume and pressure?
pressure increase
volume decrease
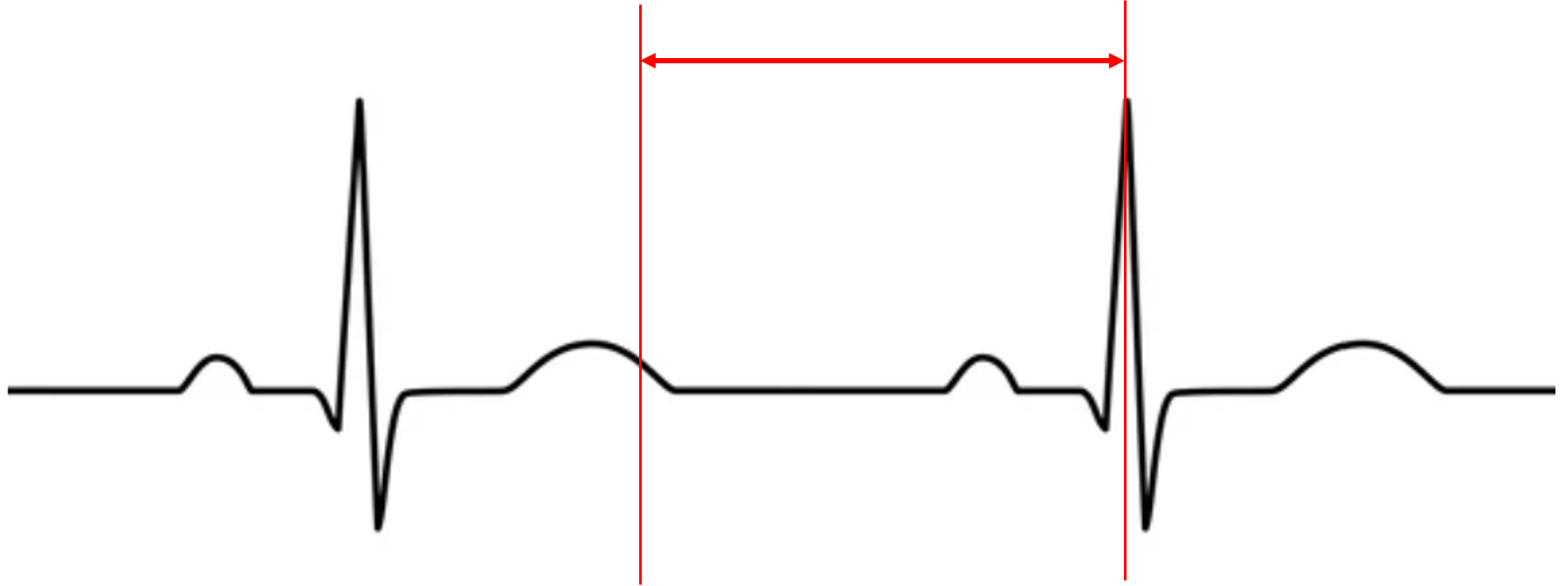
what is happening to ventricular volume and pressure?
pressure is stable
volume increase
which valve is closed during ventricular systole?
AV
Which valve is open after iso relax?
AV
during P wave the ventricles are in
mid-late diastole
during QRS the ventricles are in
systole
during T wave the ventricles are in
early diastole
During Systole the AV valves are ____ and Semilunar valves are _____.
closed, open
During Diastole the AV valves are ____ and Semilunar valves are _____.
closed, open
atrial depolarization is during which wave?
P
ventricular depolarization is during which wave?
QRS
ventricular repolarization is during which wave?
T
stroke volume
amount of blood ejected per beat
stroke volume formula
EDV - ESV
preload
stretch of the heart before it contracts
^ preload = ^ contraction during systole
afterload
the pressure that must be exceeded for LV contraction
contractility
the forcefulness of the contraction
common indications for an echo
enlarged heart, murmur, chest pain, heart failure, shortness of breath, TIA, A fib, Ao disease, Cardiac mass, pericardial disease, congenital heart disease, coronary artery disease
conduction system pathway
SA
AV
Bundle of HIS
right and left branches
purkinje fibers
SA node location
back of RA near entrance of SVC
AV node location
medial floor of RA
Bundle of HIS location
top of IVS
Purkinje Fibers stimulate
ventricular contraction that emerge from bundle branches and enter myocardium
AV node
delays impulse allowing for ventricular filling
SA node bpm
60-100
AV node bpm
40-60
normal sinus rhythm
60-100 bpm
Uniform shape with one wave in front of every QRS complex
bradycardia
less then 60 bpm
tachycardia
greater than 100 bpm
cardiac output
volume of blood pumped by bpm
ejection fraction
% of blood pumped out of ventricle with each beat
CO=
SV x HR
EF=
(SV/EDV) x 100%
fraction shortening
percentage change in the left ventricular (LV) internal diameter from end-diastole to end-systole
FS=
LVIDd-LIVDs / LVIDd
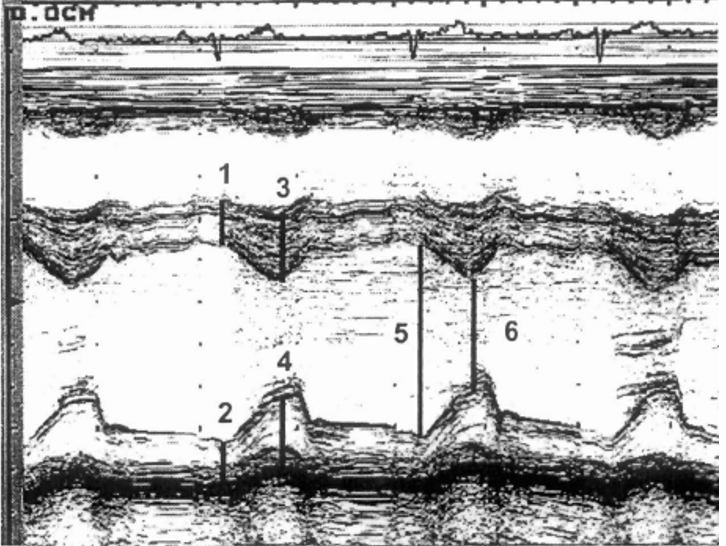
label LV size M-Mode
IVSd
PWDd
IVSs
PWDS
LVIDd
LVIDs
Doppler =
fd=fr-ft
fd= (2/c)(v)(ft)(cos <)
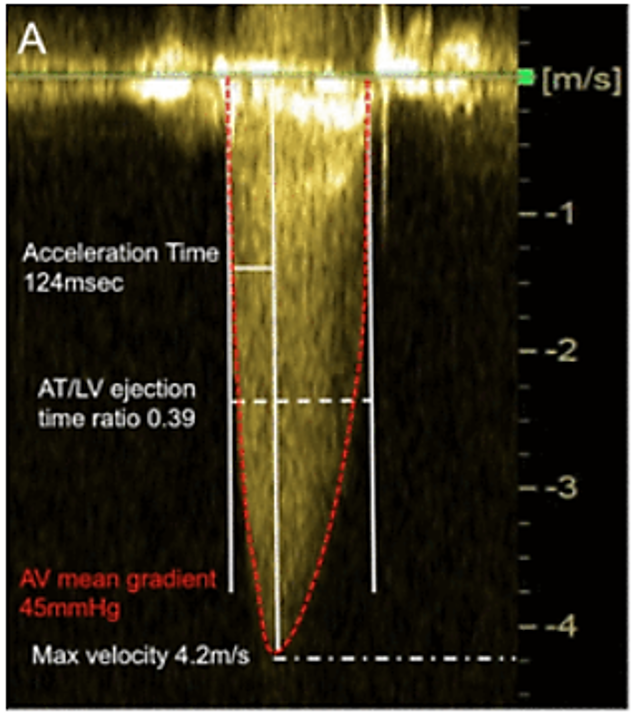
Acceleration time
Time from onset of flow to peak velocity
Deceleration time
Time from peak flow to end of flow
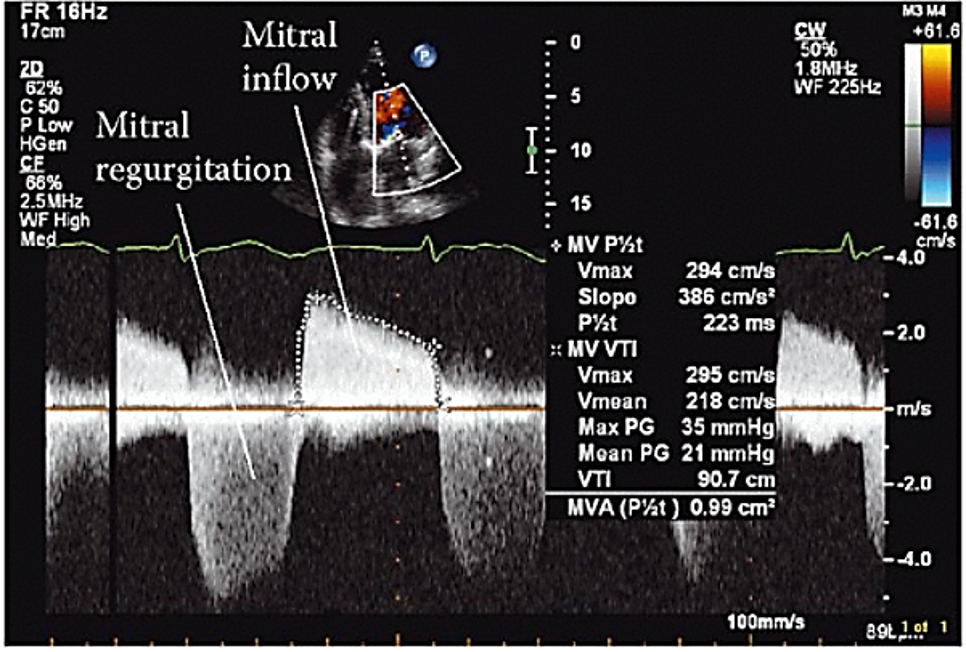
Pressure Half Time
The time it takes for the peak pressure to drop to half its original value
Velocity Time Integral (VTI)
The distance traveled by the blood cells in one cardiac cycle
VTI formula
trace the flow profile
(CSA lvot)(VTI lvot) = (CSA av)(VTI av)
Tracing the flow profile gives you:
VTI
Peak velocity
Mean velocity
Peak pressure gradient
Mean pressure gradient
Adjust ______ to maximize waveform w/o aliasing
scale
Use sweep speed of ____ mm/sec per ASE
100
Adjust _______ to receive adequate signal while reducing noise
sample volume size
Adjust ________ to remove unwanted noise w/o erasing flow info
Wall filter
Spectral Doppler _____ optimized for ability to measure accurately
gain
______ should be positioned to optimize the Doppler signal as large as possible
baseline
PW TDI is routinely used for assessing
LV diastolic function
TDI can be used for
Differentiation between constrictive pericarditis and restrictive cardiomyopathy
myocardial ischemia
resyncing pacemakers
transplant rejection