Muscle Physiology
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
Muscles are — tissues able to contract
soft
Name three different muscle types:
Skeletal
Smooth
Cardiac
Skeletal muscles are usually attached to —- on each end by —
bones;tendons
Connective tissue within the tendons forms the:
epimysium
The epimysium subdivides the muscle into —, which are surrounded by the —
muscle fascicles;perimysium
A muscle fascicle is made of several muscle cells, also named:
muscle fibers
The plasma membrane of the muscle fibers is called the —- and their cytoplasm is the —
sarcolemma;sarcoplasma
Muscle fibers are surrounded by a thin layer of connective tissue called the:
endomysium
True or false: muscle fibers are multinucleated
true
Muscle fibers contain —, which are made up of —, responsible for muscle contraction
myofibrils; myofilaments
Skeletal muscle fibers are —
striated
Dark bands are called —bands and the light bands are called —bands. In the middle of the I bands, dark lines are visible: they are named — bands.
A;I;Z
Each muscle fiber receives a single terminal bouton from a somatic motor neuron, or —
motor neuron
The motor end plate is rich in ACh receptors and voltage-gated Na+ channels (VGSCs). The depolarization is called — —- potential
end plate
Each motor neuron and its innervated muscle fibers is called a — —
motor unit
The A band contains — filaments primarily made of myosin. The I band contains thin filaments primarily made of —
thick; actin
The central region is called the — band and it only contains thick filaments
H
In the middle of the A bands, in the center of each H band is an - line. Produced by protein filaments made of myomesins and titin
M
Sliding of the filaments is produced by the action of numerous —- — extending out from the thick filaments towards the thin filaments
cross-bridges
Describe the cross-bridge cycle:
Myosin heads are able to hydrolyze ATP into ADP and inorganic phosphate (Pi)
Then, Pi is released and the myosin head becomes unphosphorylated, triggering a power stroke
After the power stroke, the bound ADP is released: myosin and actin are tightly bound to each other
Rigor state
Then, a new ATP molecule can bind to the myosin head, allowing it to break its bond with actin
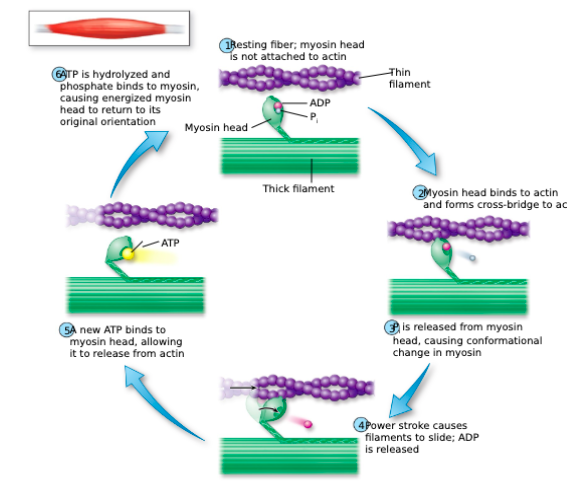
True or false: In order for a muscle to relax, cross-bridge formation must be prevented
true
Troponin complex proteins:
Troponin I. Inhibits the binding of myosin to actin
Troponin T. Binds to Tropomyosin
Troponin C. Binds to Ca2+
In a relaxed muscle, —- physically blocks the myosin heads from bonding to actin
tropomyosin
In order for a —- —— to occur, troponin C binds to Ca2+
Conformational change
The — — is made of interconnected tubules and terminal cisternae
sarcoplasmic reticulum
Muscle fibers have extensions of the cell membrane called — —-
transverse tubules
For muscle contraction regulation, the receptors open and Na+ enters the cell, causing a depolarization:
end plate potential
For muscle contraction regulation, the T tubules have —- —- that respond to action potentials.
They undergo a conformational change and they are coupled to the —— —- — in the sarcoplasmic reticulum
This process is called: —- —- —-
voltage-gated Ca2+ channels; Ca2+ release channels; excitation-contraction coupling
To stop muscle contraction, the production of action potentials muscle cease, closing the Ca2+ release channels.
Ca2+ now needs to be pumped back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum by — —
SERCA pumps
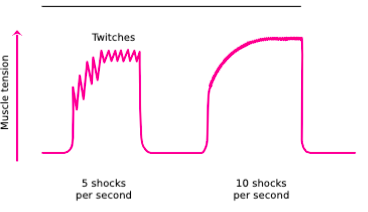
Name
Incomplete tetanus
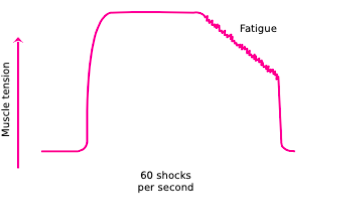
Name
Complete tetanus
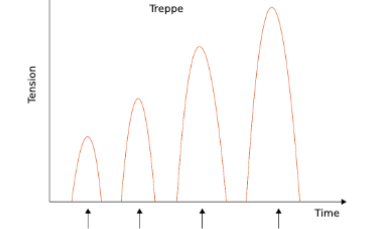
Name
Treppe or stairway effect
Muscle contraction strength is influenced by:
Number of stimulated fibers
The frequency of the stimulation
The thickness of each muscle fiber
In skeletal muscles, the maximum relative tension is achieved when the muscle is — to — of its resting length
100%;120%
Exercise stimulates the production of — — into the sarcolemma
glucose transporters
Muscle cells combine ADP with a Pi derived from a high energy molecule called ——
phosphocreatine/creatine phosphate
Describe slow-twitch fibers:
Also known as type I fibers, reach their maximal tension in up to 100 msec
Slow oxidative fibers or red fibers
Describe fast-twitch fibers:
AKA type II fibers, reach their tension in 7.3 msec
White fibers
Type II fibers can be subdivided into two categories:
Fast glycolytic, or type IIX fibers. They have the greatest rate of ATP and phosphocreatine consumption.
Fast oxidative-glycolytic, or type IIA fibers. They have a high oxidative capacity and are more resistant to fatigue.
Sensory feedback is provided by the —— and —-
Golgi tendon organ; muscle spindle
Muscle spindles are stretch receptors (—-) located in the muscles
proprioceptors
— — —-, loosely arranged nuclei and — — —, nuclei arranged in rows
nuclear bag fibers; nuclear chain fibers
Skeletal muscles are mainly innervated by two types of neurons:
Alpha motor neurons, innervating the extrafusal fibers
Gamma motor neurons that innervate the intrafusal fibers
Stimulation by gamma neurons, causes an — — in the spindle
active stretch
Alpha and gamma neurons are usually stimulated simultaneously by upper motor neurons, this is termed:
coactivation
Stretch and activation of the spindles triggers a reflex contraction to maintain a normal resting muscle length:
the muscle tone
The simplest type of reflex is:
monosynaptic
Neurons from the Golgi tendon organ synapse between a sensory neuron and a spinal interneuron: —-. This system prevents any dangerous tension on a tendon from excessive muscle contraction
disynaptic reflex
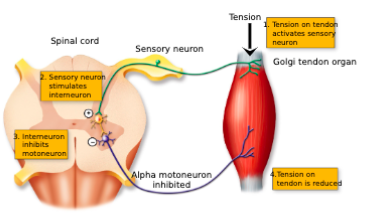
During a stretch reflex, — — takes place
reciprocal innervation
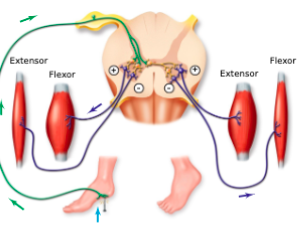
On the opposite limb, the extensor muscles contract and the flexor relax to support weight:
Contralateral reflex
Unlike skeletal muscles, cardiac and smooth muscles are —- and are regulated by autonomic motor neurons
Involuntary
— cells are short, branched and interconnected
cardiac muscle
In skeletal muscle cells, —— —- are mechanistically coupled to the —- —- —
the voltage-gated Ca2+ channels; Ca2+ release channels
True or false: in myocardiac cells, the two channels DO interact
False
— — can be found in the walls of hollow organs. They can be arranged in circular and longitudinal layers
Smooth muscles
Smooth muscles are —- and involuntary
non-striated
Thin filaments attach their ends to the plasma membrane or to structures called — —
Dense bodies
In skeletal muscles, the myosin proteins of the thick filaments are stacked
horizontally
In smooth muscles, the myosin proteins of the thick filaments are stacked
vertically
Smooth muscles can be grouped in two functional categories:
Single-unit
Multiunit
In smooth muscle, neurotransmitters are released from regions of the autonomic axon named:
varicosities
Unlike single-unit smooth muscles, the cells of the multiunit must be stimulated —- by neurons
individually
True or false: In smooth muscles, Ca2+ does not bind to troponin: smooth muscle cells do not express that protein
True
—- phosphorylates the myosin light chains, allowing them to interact with actin filaments and cause contractions in smooth muscles
MLCK
To relax a smooth muscle, — cytoplasmic levels are brought back to their basal concentration
Ca2+