AP Human Geography Semester 1 Final Exam
1/99
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
Human Geography
the study of people and their relationship to their physical surroundings
Types of Thematic Maps
tell a story by showing the density and distribution of quantitative data
ex. choropleth, dot distribution, graduated symbol, isoline, flow-line, cartogram
Hearth
place of origin
Physical Geography
focus on features of Earth’s surface like landforms, bodies of water, climate, natural resources
Map Scale
the level of detail and the amount of area covered on a map depends on map scale
Small scale of analysis
a lot of area but not much detail depicted
Large scale of analysis
less area but more detail depicted
Census
a survey conducted every 10 years on the American population to collect information about different distributions
Literacy
the ability to read and write
Density
the frequency of a feature occurring in space
Arithmetic Density
total number of people / total amount of land
Physiological Density
total number of people / total amount of arable land
Agricultural Density
total number of farmers / total amount of arable land
Distribution
the arrangement of a feature in space
GIS/GPS
technology systems that store data having to do with location
Cartography
the practice of drawing maps
Clustered
a type of concentration where something is distributed very close to each other
Dispersed
a type of concentration where something is distributed far from each other
Concentration
the extent of a feature’s spread over space
Formal/uniform region
an area of space with 1 common characteristic
Functional/nodal region
an area that has a central point/node
Vernacular/perceptual region
an area defined by a personal mental map
Graduated symbol map
map with different sized symbols
Cartogram
intentionally distorted map
Choropleth map
different colors
Dot Density map
same size dots that are clustered or disperse
Reference map
contain general information about places
Topographic/isoline map
shows similar characteristics within lines
Toponym
name of a place
Environmental determinism
theory that the physical environment controls human actions and culture
Possibilism
theory that the physical environment affects human actions, but humans can adapt
Absolute location
the exact location of something using latitude and longitude
Relative location
the location of a place relative to other places
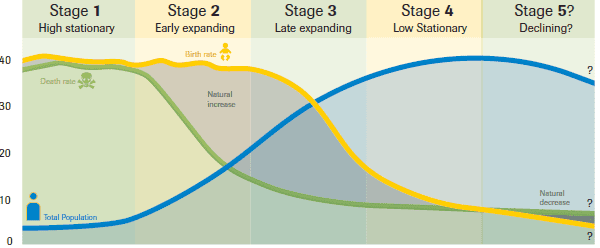
Demographic Transition Model
a process of change in a society’s population
Example of country in stage 1 of DTM
none
Example of country in stage 2 of DTM
The Gambia
Example of country in stage 3 of DTM
Mexico
Example of country in stage 4
Denmark
Crude birth rate (CBR)
number of live births / 1000 people
Crude death rate (CDR)
total deaths (annual) / 1000 people
Total fertility rate (TFR)
the average number of children a woman will have
MDC
high-developed country
LDC
low-developed country
Carrying capacity
the maximum population size of a species that the environment can sustain indefinitely
Chain Migration
migrating somewhere to reunite with family
Step migration
Migrating to different places until they get to a wealthy place
Remittances
the transfer of money by workers to their home country
Push factor
motivates people to move out
Pull factor
motivates people to move in
Brain drain
large-scale migration of talented people to one place
Ecumene
a place with permanent human settlement
Homogeneous
a uniform population of people that share one consistent characteristic
Heterogeneous
a mixed population that contains multiple different characteristics
Creolization
a mix of Native American, African, and European influences to create a new language
Assimilation
the process by which a group’s cultural features are altered to resemble those of another group
Acculturation
the process of changes in culture that result from the meeting of 2 groups
Ethnocentrism
using one’s own culture and beliefs to judge a different culture
Cultural landscape
the combination of the physical geography of a place and the actions of humans
Cultural trait
a particular thing a group does
Folk culture
practiced by small, homogeneous groups living in isolated rural areas
Popular culture
found in large, heterogeneous societies that share certain habits despite differences in other characteristics
Relocation diffusion
when people migrate from one place to another
Stimulus Diffusion
people in a culture adopt an idea from another culture but modify it
Syncretism
when two culture form an entirely new identity
Universalizing religion
actively seeks new members and believes it has a universal importance
Ethnic religion
specific to an ethnic group and not seeking new members
Judaism
ethnic religion that was first established in the Kingdom of Israel, followers were persecuted during WWII
Christianity
universalizing religion that was first established in Judea by Jesus, biggest religion practiced in the world
Islam
universal religion that was first established in Mecca by Mohammad and his Disciples, now mostly in Pakistan and Indonesia
Buddhism
universal religion first established in Lumbini by Siddartha Gautama (Buddha), mostly in Southeast Asia
Hinduism
ethnic religion first established in Indus River Valley by unknown person, mostly in India
Lingua franca
a language of international communication
Official language
used by government to enact legislation, publish documents, and conduct other public business
Racism
belief that race is the primary determinant of human traits and capacities; out of all races, one is better
Federal state
power is with local governments as well as central government
Unitary state
power is only within central government
Centripetal force
a factor that brings people together
Centrifugal force
a factor that pushes people apart
Supranational organization
an organization of more than two countries to achieve a common goal
State
an area organized into a political unit and ruled by an established government
Nation
a culture group
Nation-state
a state with one homogeneous culture group
Stateless nation
a culture group with no specific state
Enclave
a country that is completely surrounded by another state
Gerrymandering
redrawing legislative boundaries to benefit a political party
Neocolonialism
practice o using economic or political influence to indirectly control another area
Choke point
a geographical area on land or sea that you have to cross through in order to get to another location
Shatterbelt
a region caught between larger external powers
Theocracy
a form of government where priests are the rulers
Heartland-Rimland Theory
theory that if one empire controlled the Heartland, then they would be able to control the rest of the world (Rimland)
Containment (Domino) Theory
theory that if one country falls to Communism, then the ones surrounding would also fall
Constitutional monarchy
form of government where one monarchy is not alone when making decisions for the country
Relict boundary
a boundary that no longer exists but still has importance
Superimposed boundary
a boundary that is drawn by outside powers and ignores existing cultural differences
Antecedent boundary
a boundary that is drawn before people start living there and leads to cultural landscapes
Geometric boundary
a boundary that is a straight line, usually following longitude and latitude
Subsequent boundary
a boundary that is drawn after people have started living there
Consequent boundary
a kind of subsequent boundary that acknowledges the different ethnic/cultural groups
Autonomous region/republic
an area of a state that has a degree of self-government
Balkanization
the breakup of a large state into several independent states