APES Unit 9: Global Change
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
Stratosphere
Layer of the atmosphere that contains the ozone layer
Ozone Layer
Protective layer in atmosphere that shields earth from UV radiation.
Ozone
Atmospheric gas that contains three atoms of oxygen
O3 + UV-B --> O + O2
Natural decomposition of ozone by UV light (know the chemical reactions)
O2 + O + UV-C --> O3
Natural formation of ozone by UV light (know the chemical reactions)
Ozone Thinning/Depletion
The removal of ozone from the stratosphere by human produced chemicals or natural processes
CFCl3 + UV --> CFCl2 + Cl
Cl + O3 --> ClO + O2
Chemical decomposition of ozone by CFCs (know the chemical reactions)
Montreal Protocol
1987 international treaty that laid out plans to phase out ozone depleting chemicals like CFC
Tropospheric Ozone
Human produced "ground-level" ozone, a result of air pollution. Results from the interaction of sunlight, heat, nitrogen oxides (car exhaust), and volatile organic compounds (gasoline; solvents); causes photochemical smog
Ice Age
Any period of time during which glaciers covered a large part of the earth's surface
Interglacial Period
A period of warmer climate that is characterized by the retreat of glaciers
Greenhouse Effect
Important planetary function where certain atmospheric gases allow visible light to pass but traps infrared heat heat
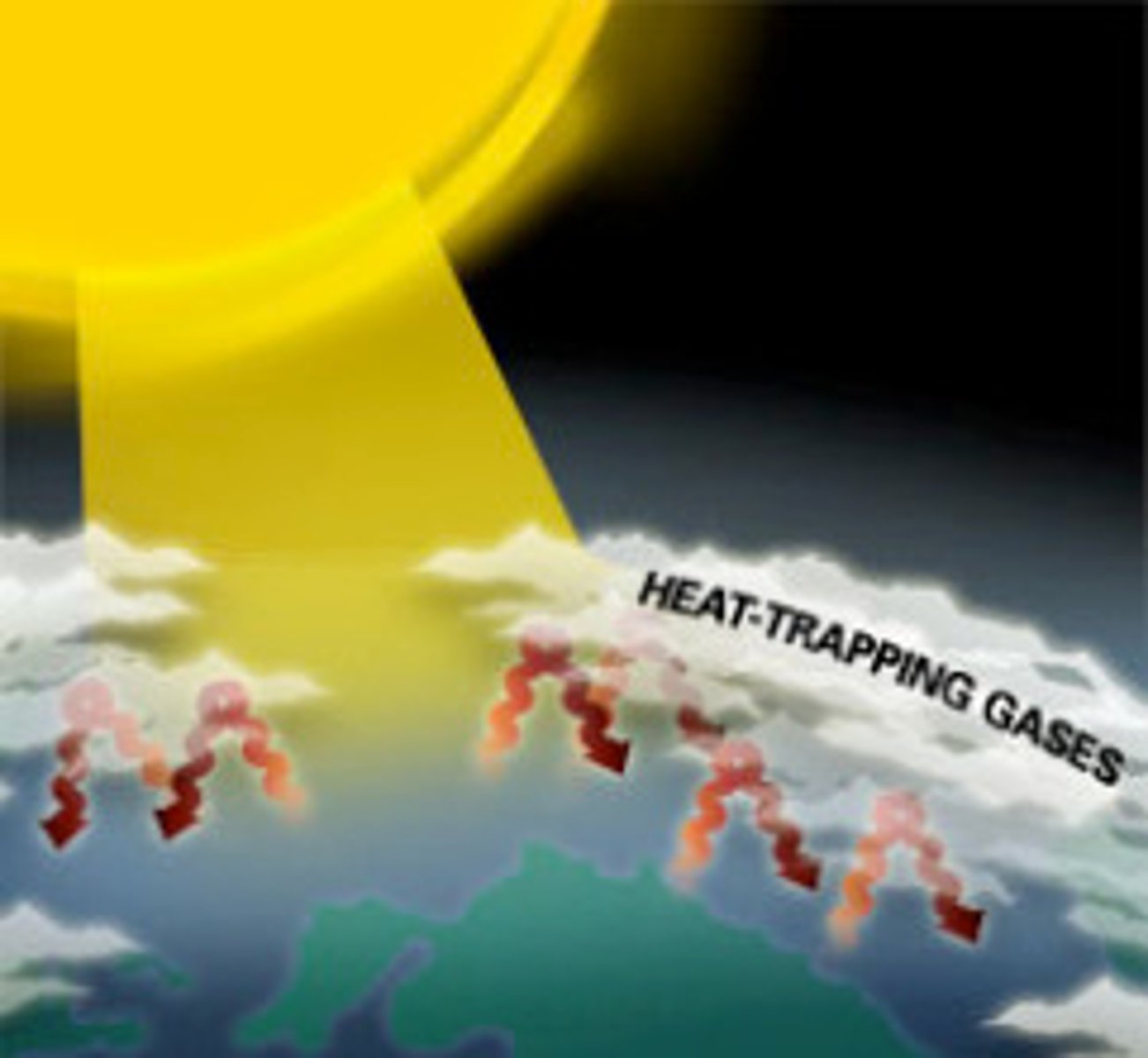
Greenhouse Gases
Gases such as water vapor, carbon dioxide, and methane that absorb heat leaving the Earth's surface.

Global Warming
An increase in the average temperature of the earth's atmosphere (especially a sustained increase that causes climatic changes)
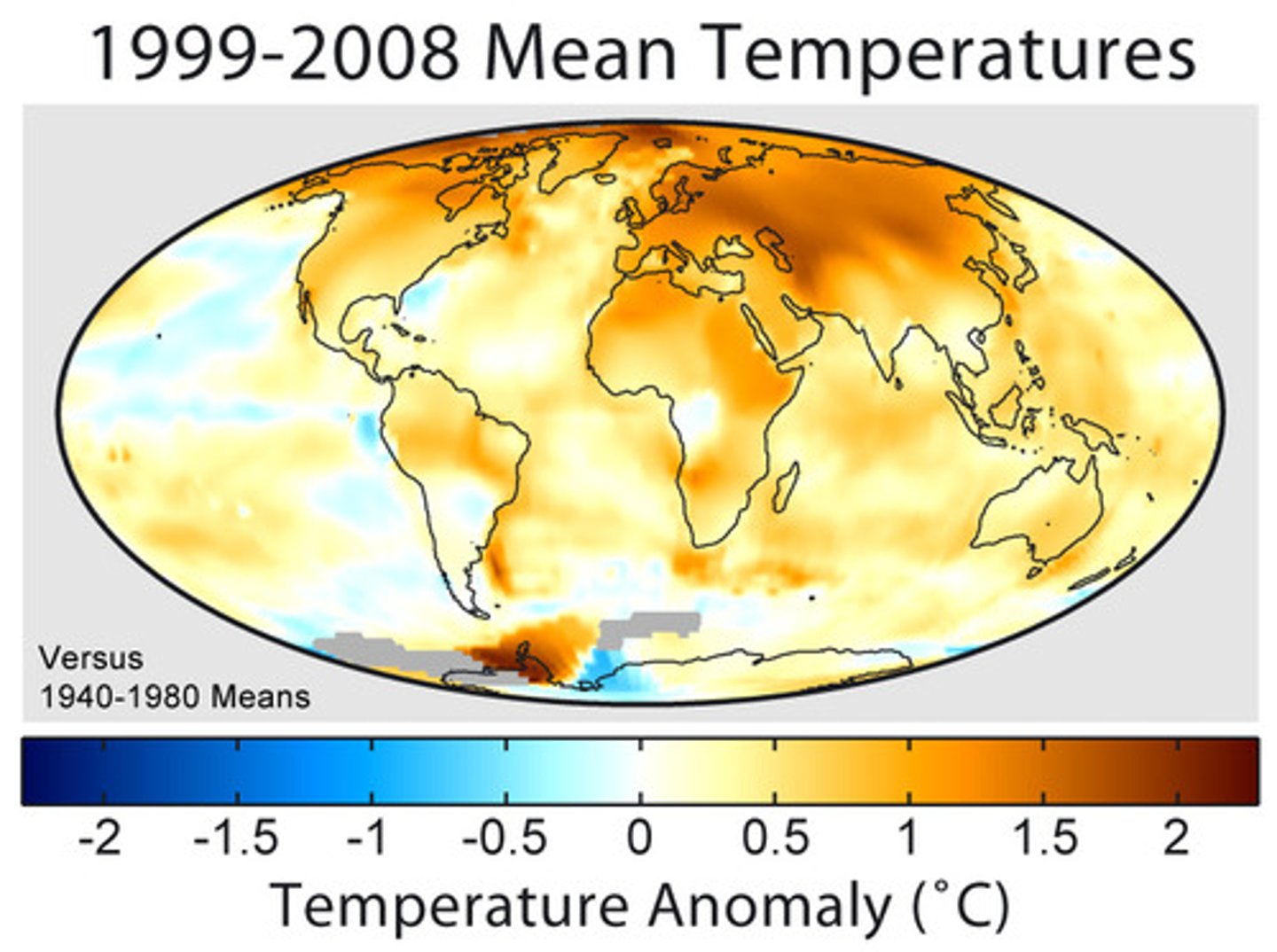
Climate Change
Change in the statistical properties of the climate system when considered over periods of decades
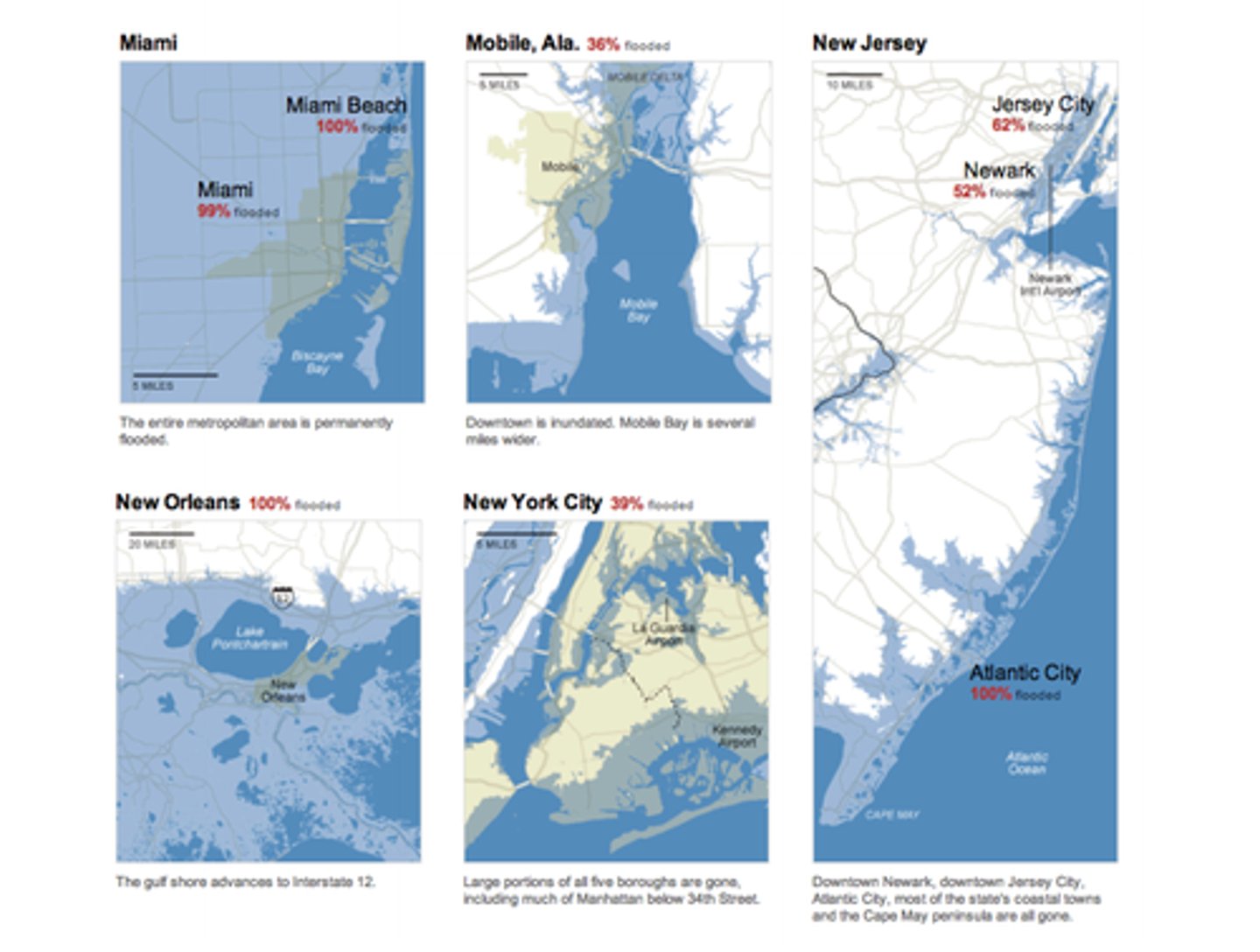
Sea Level Rise
Increase in average sea level over time. Caused by thermal expansion of seawater and melting of land-based glaciers. Results in coastal flooding and more severe storm surge.
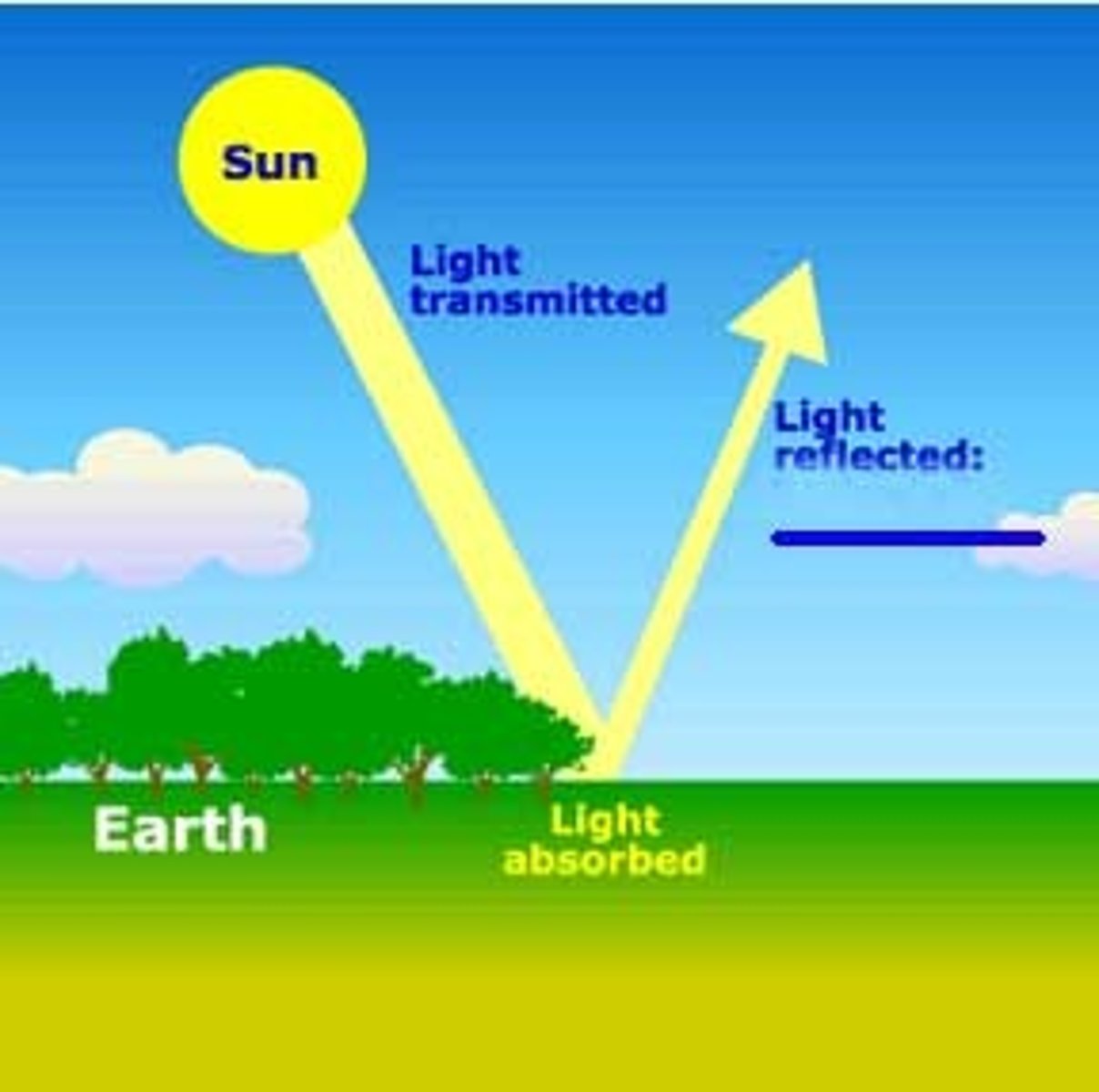
Albedo
The percentage of incoming sunlight reflected from a surface
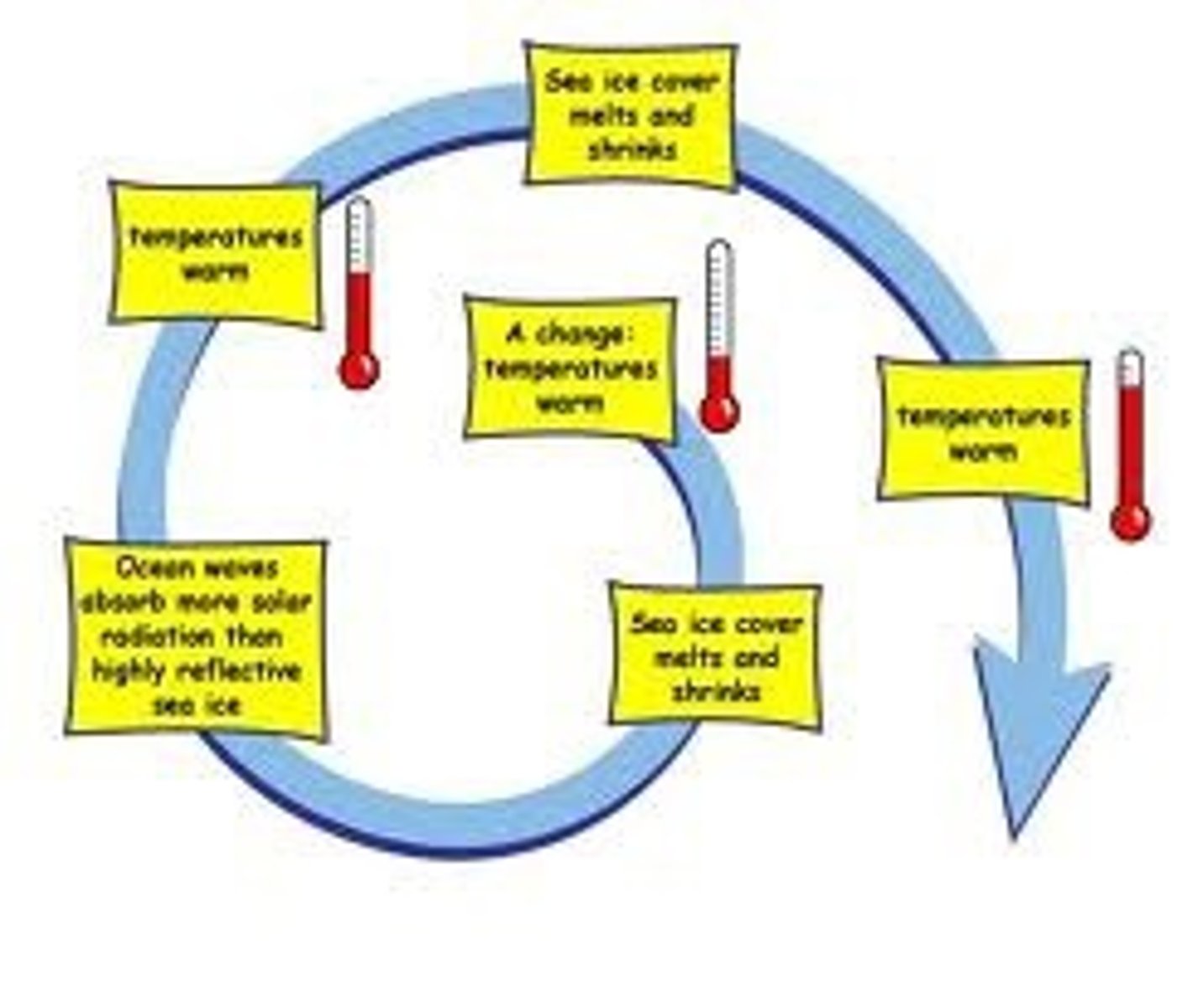
Positive Feedback Loop
Causes a system to change further in the same direction.
Kyoto Protocol
1997 treaty that calls for industrialized countries to reduce greenhouse gas emissions
Biodiversity
The number and variety of organisms in a given area during a specific period of time. Measured at ecosystem, species, and genetic levels.
Ecosystem Diversity
A measure of the diversity of ecosystems or habitats that exist in a particular region
Genetic Diversity
The range of genetic material present in a gene pool or population of a species.
Genetic Drift
Random change in allele frequencies that occurs in small populations
Inbreeding
Mating between closely related individuals; common in endangered species
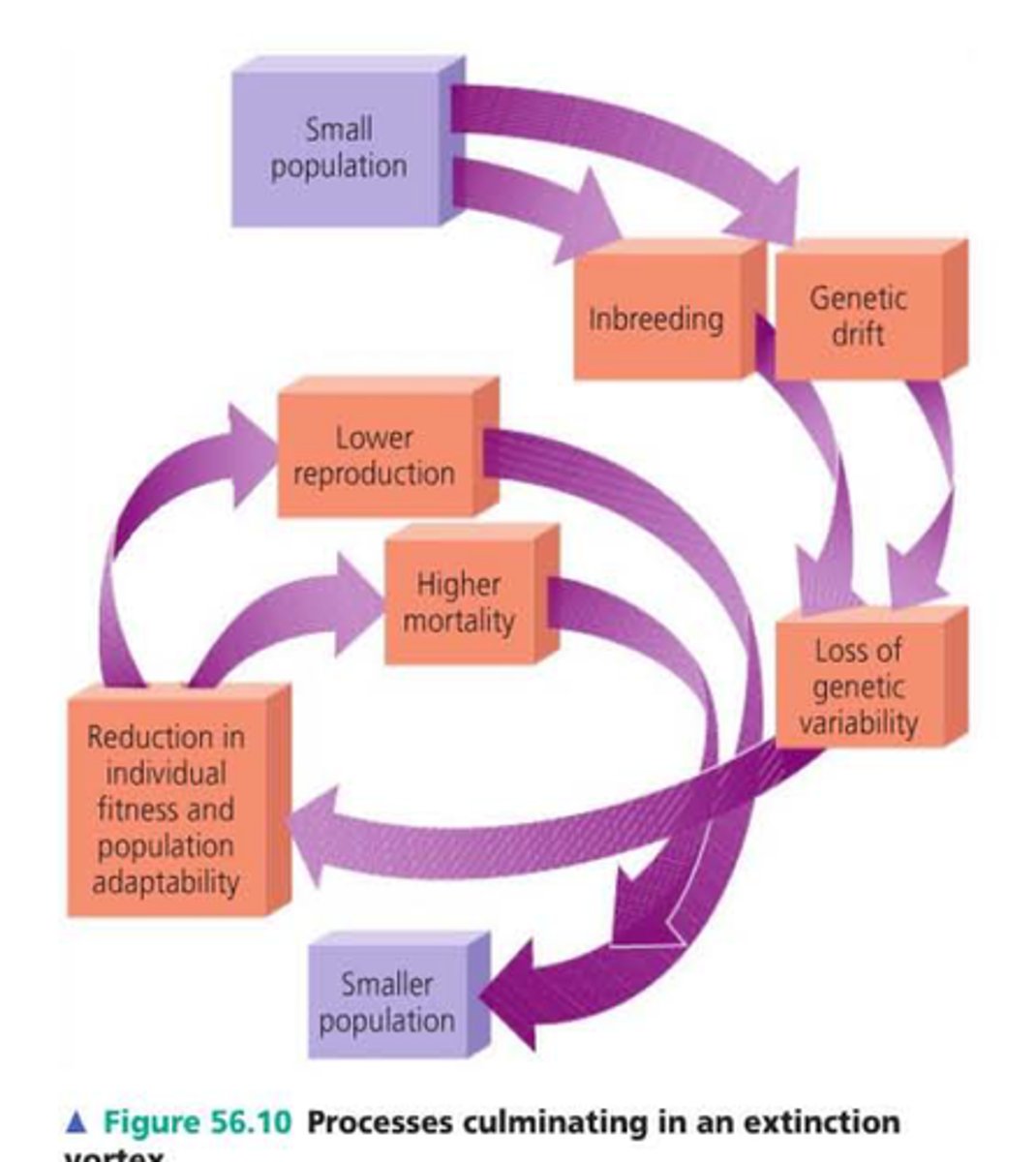
Extinction Vortex
Phenomenon experienced by endangered species. Small populations result in genetic drift and inbreeding, which decreases the fitness of individuals and causes the population to decrease even further.
Species Richness
The number of species in a given area
Species Evenness
The relative proportion of different species in a given area
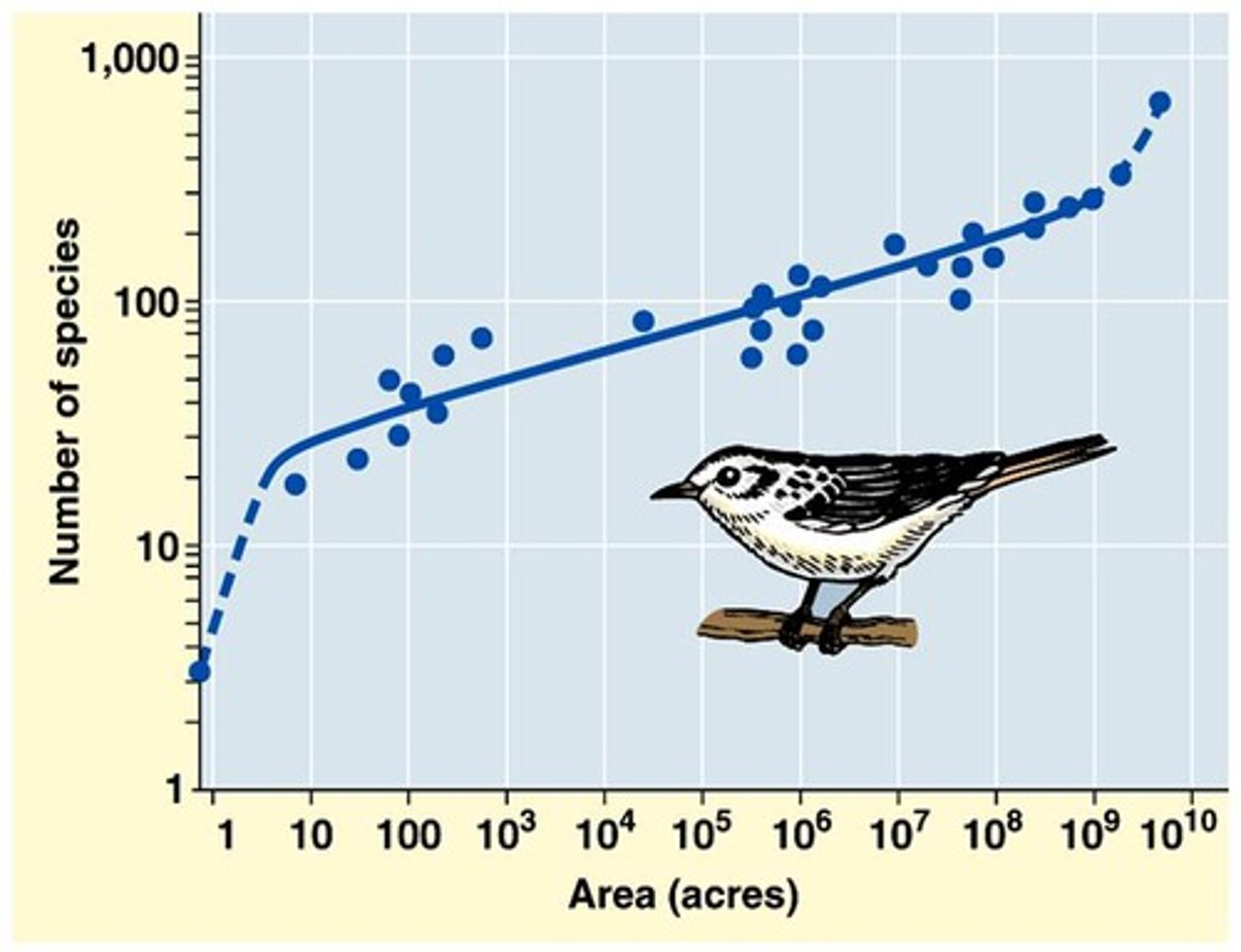
Species Area Curve
Relationship between the size of an area and the number of species that the area can support
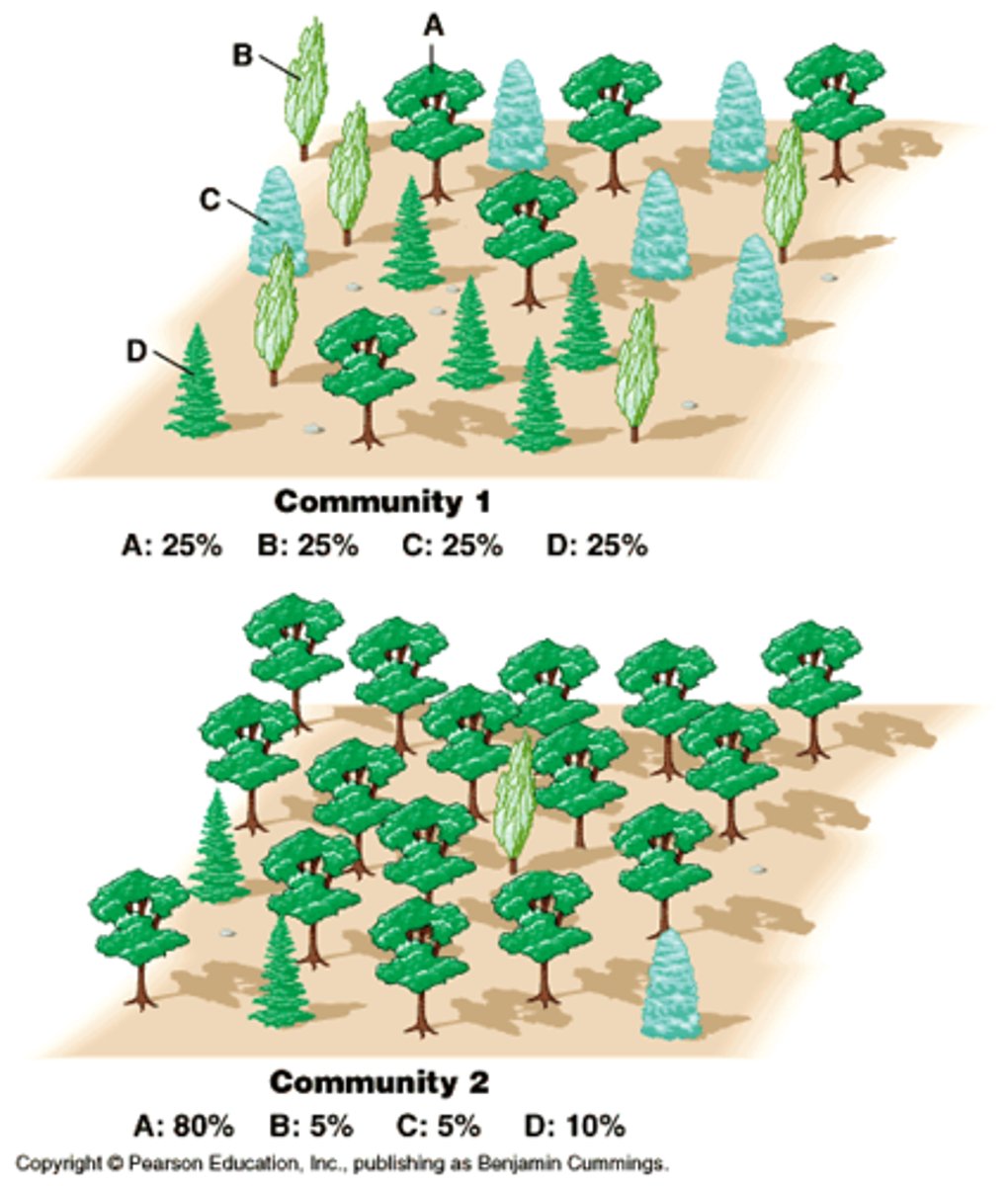
Ecosystem Stability/Resilience
The ability of an ecosystem to survive and maintain a balance among the organisms; depends on high biodiversity.
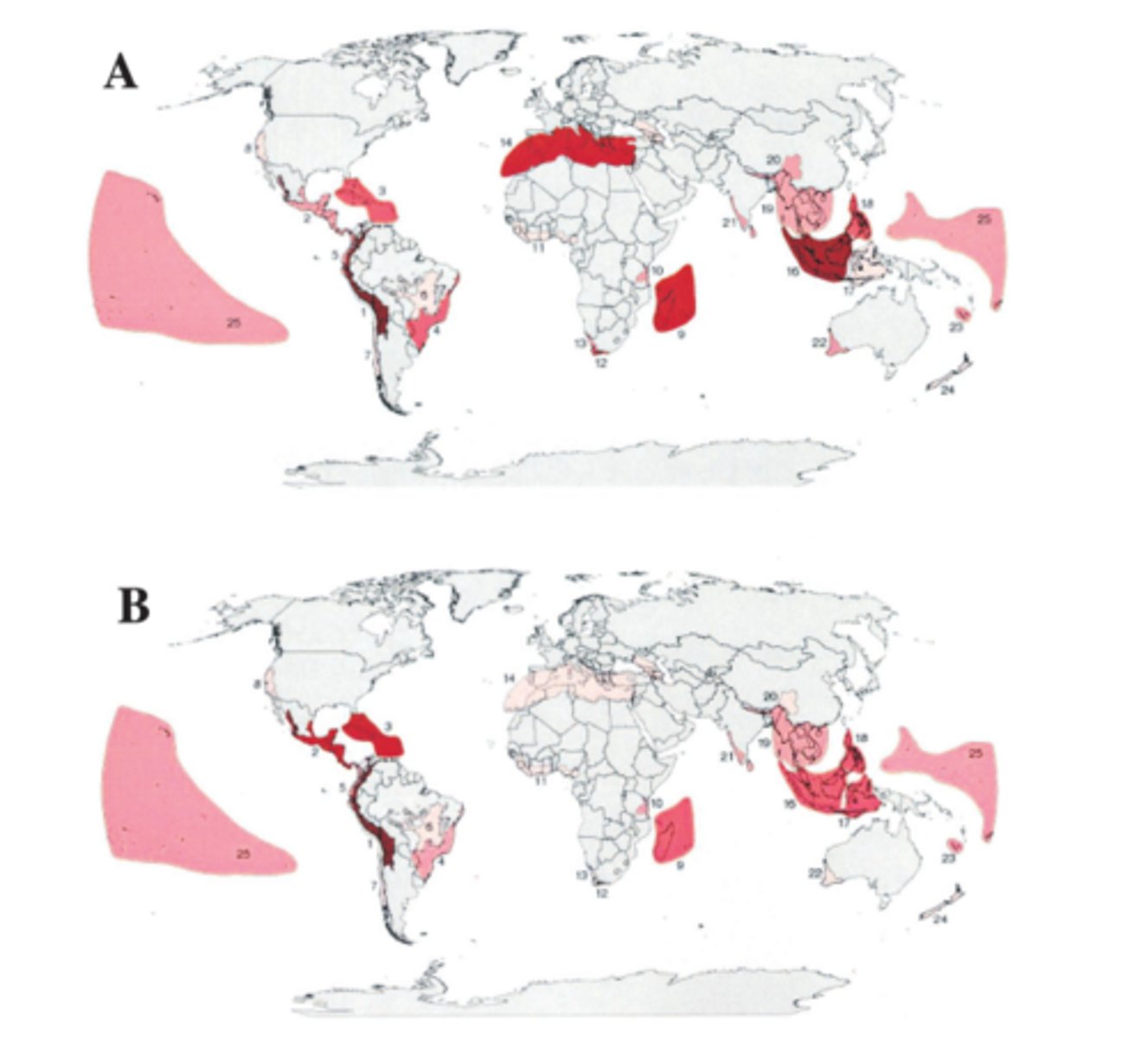
Biodiversity Hotspot
A place where there is an exceptionally large number of species in a relatively small area
Ecosystem Services
The process by which natural environments provide life-supporting resources; benefits we get from functioning ecosystems like clean water, soil, air, habitat, timber, pollination

Instrumental/Use Value
Value of an organism, species, ecosystem, or the earth's biodiversity based on its usefulness to humans.
Intrinsic/Existence Value
Worth of a species independent of any benefit they bring to humans.
Background Extinction
The continuous, low-level extinction of species that has occurred throughout much of history.
Mass Extinction
Event during which many species become extinct during a relatively short period of time
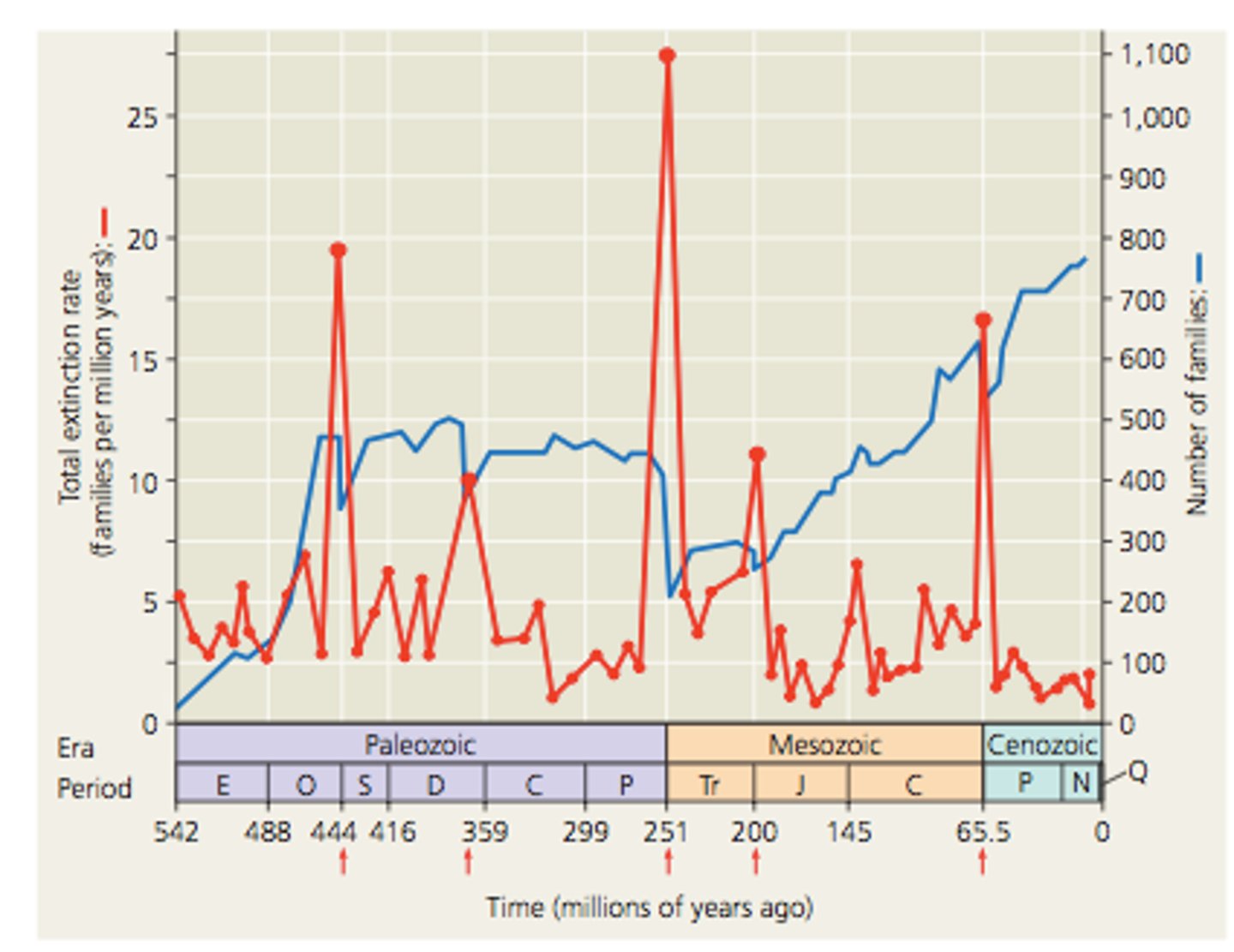
Extinction Rate
A percentage or number of species that go extinct within a certain time period; it is currently 100-1,000 times higher due to human impact.
Habitat Loss
The destruction of habitats that usually results from human activities
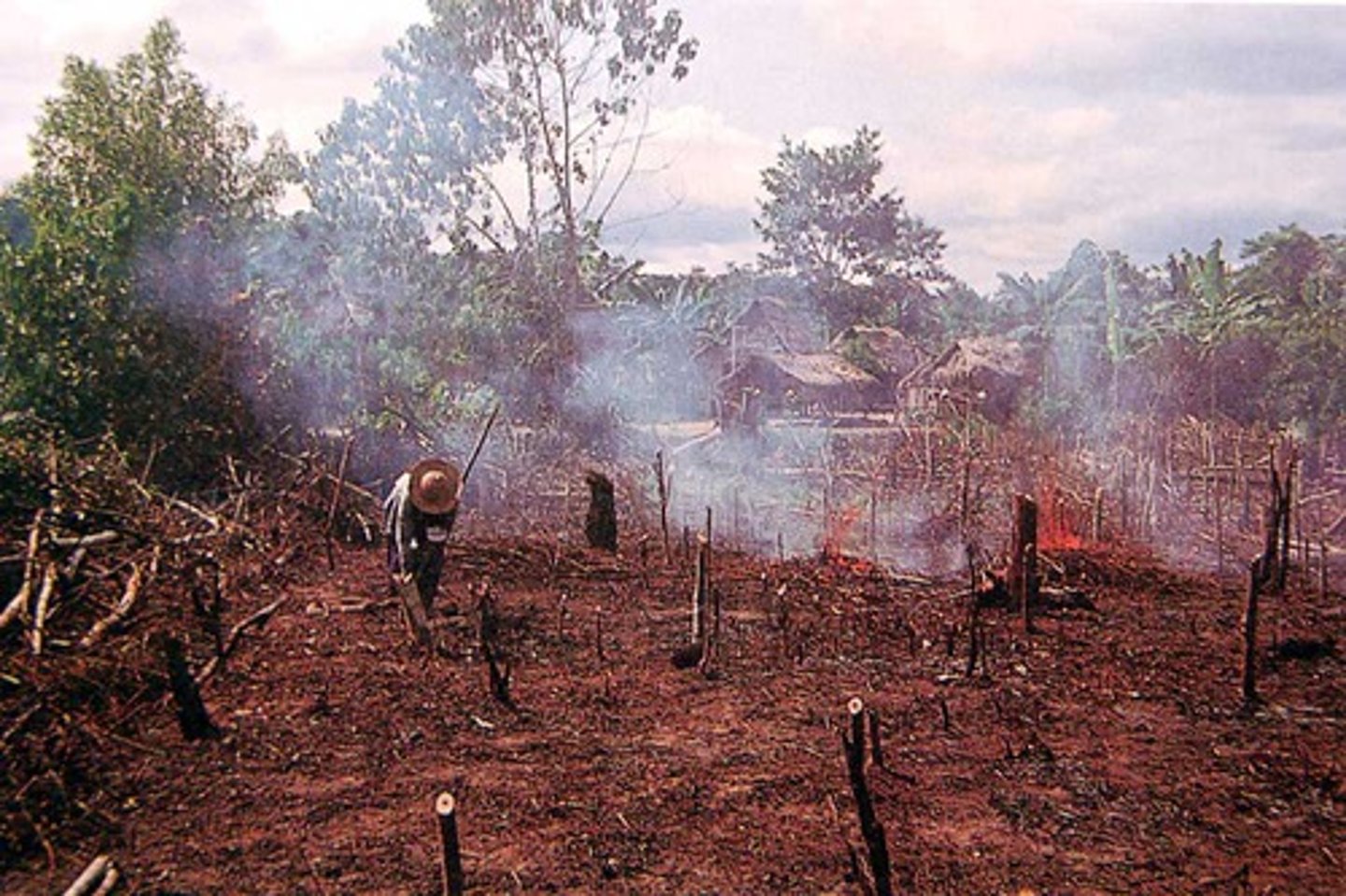

Habitat Fragmentation
Breakup of a habitat into smaller pieces, usually as a result of human activities.

Invasive Species
Species generally introduced by humans, that take hold outside of their native range. Typically decrease the biodiversity of native species.
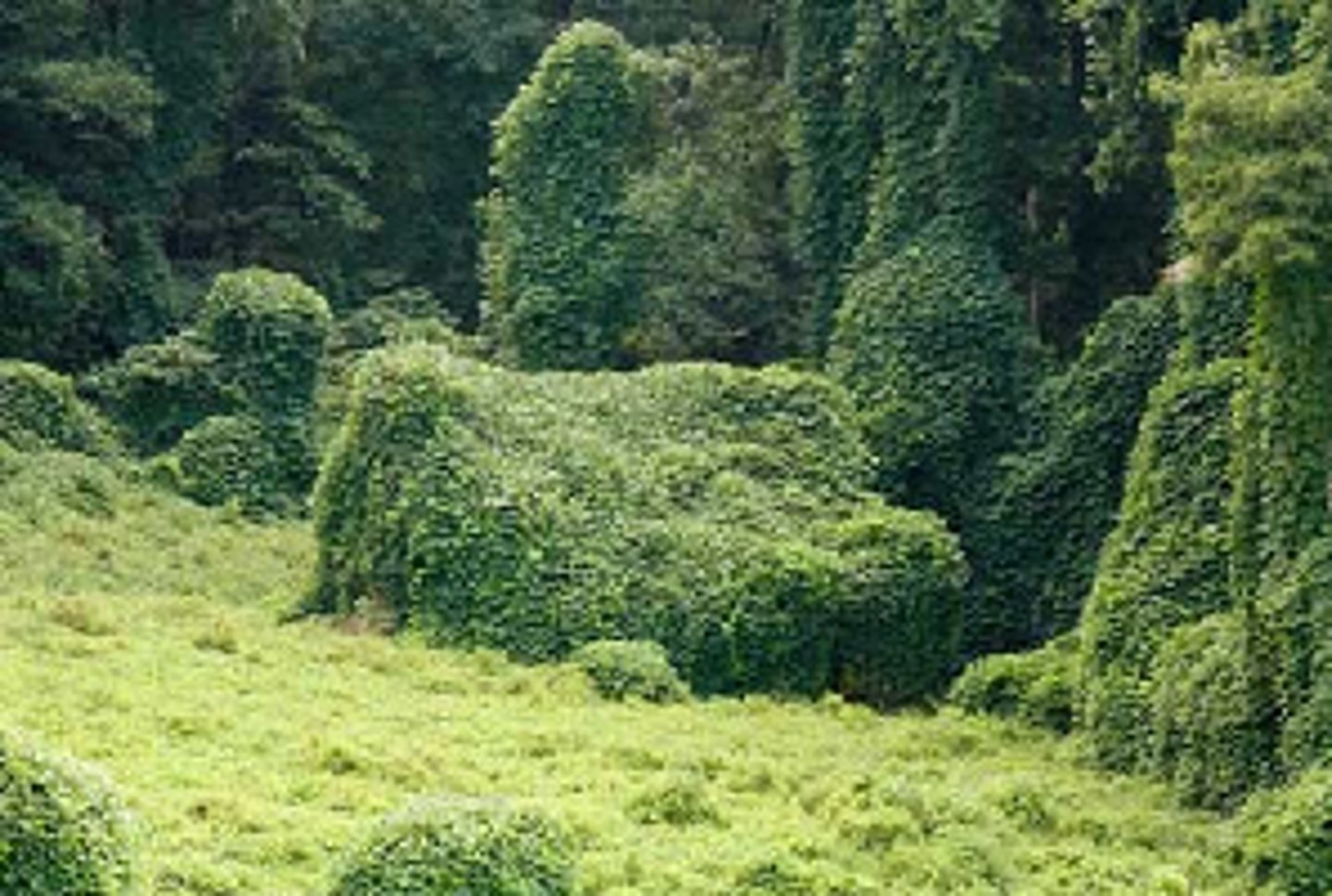

Overexploitation
Overuse of species with economic value--a factor in species extinction

Ocean Acidification
When CO2 dissolves in seawater, it reacts with water to form carbonic acid, which lowers ocean pH
Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species (CITES)
International treaty that lists species that cannot be commercially traded as live specimens or wildlife products.

Endangered Species Act
1973 U.S. legislation that implements CITES, designed to protect species from extinction; identifies/protects threatened and endangered species
Endangered Species
A species that is in danger of extinction throughout all or a significant portion of its range.

Threatened Species
A species that has been identified to be likely to become endangered in the foreseeable future.

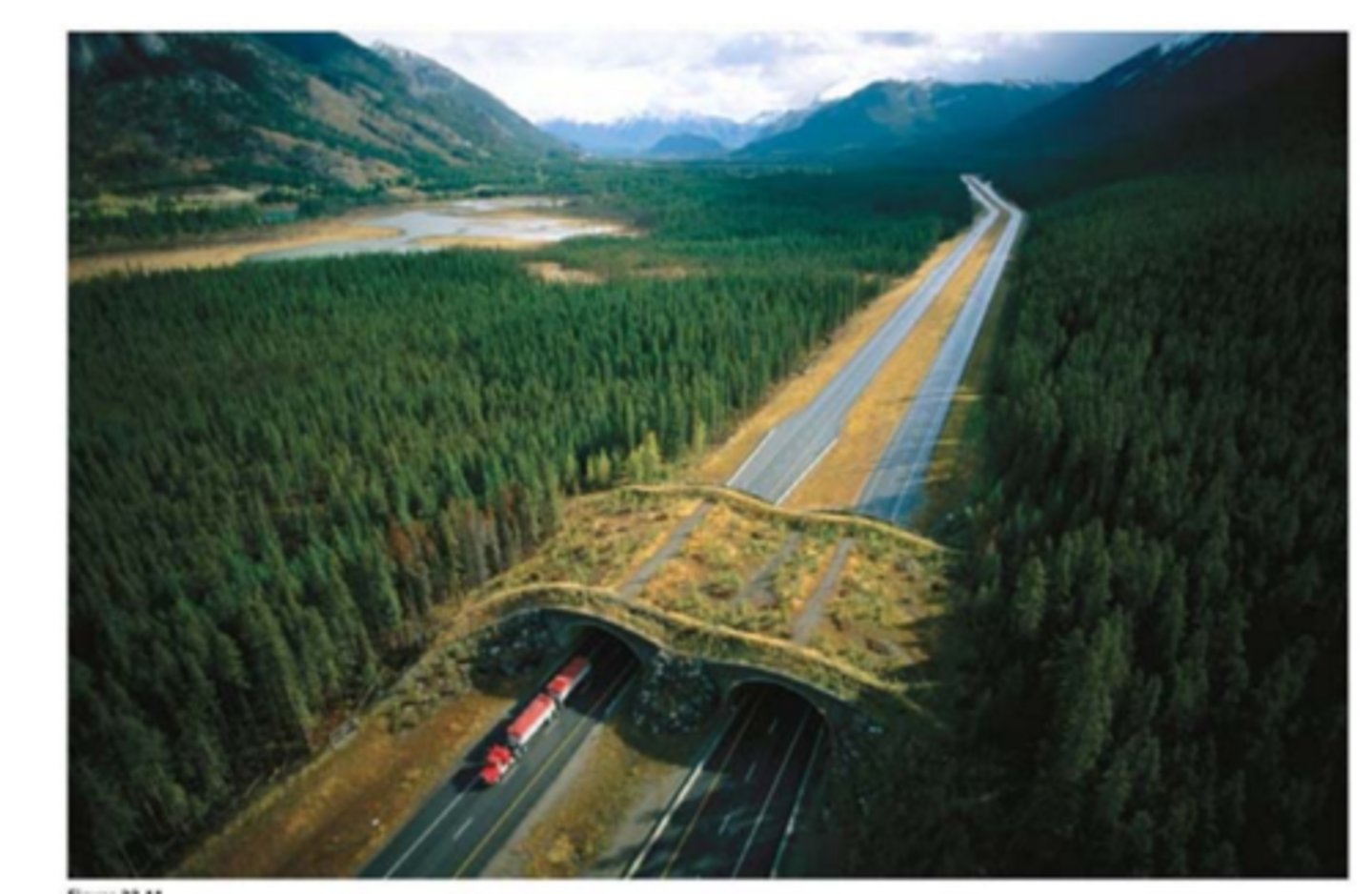
Habitat Corridors
Helps connect fragmented habitats used by different species

Wildlife Refuge/Reserve
An area of land or of land and water that is set aside for the protection of wildlife.
Marine Protected Area
A region in or near an ocean where human activity is limited in order to preserve marine life.

Captive Breeding
The process of breeding and raising organisms under controlled conditions so they can be reintroduced into the wild
