W7 L1 - Link-State Routing & OSPF
1/3
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
4 Terms
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)
Goal: Dynamically obtain IP address from network server when it joins a network
Process:
Client broadcasts for DHCP until it receives ACK and usable IP address
Client accepts IP address
Network Address Translation (NAT)
All datagrams leaving local network have the same source NAT ip address, but different source port numbers.
In a network, NAT hides private IPs behind one public IP
NAT translates the internal IPs and Ports to a public IP port for outgoing traffic
Maintains “translation table” for routing replies back to the correct device
OSPF routing
Uses Dijkstras and adds to it for a real-world application for routing
Each router learns about its neighbors
Routers flood link-state advertisements (LSAs)
Each router builds a full map of network
Dijkstras algoithm runs
Routing table updated
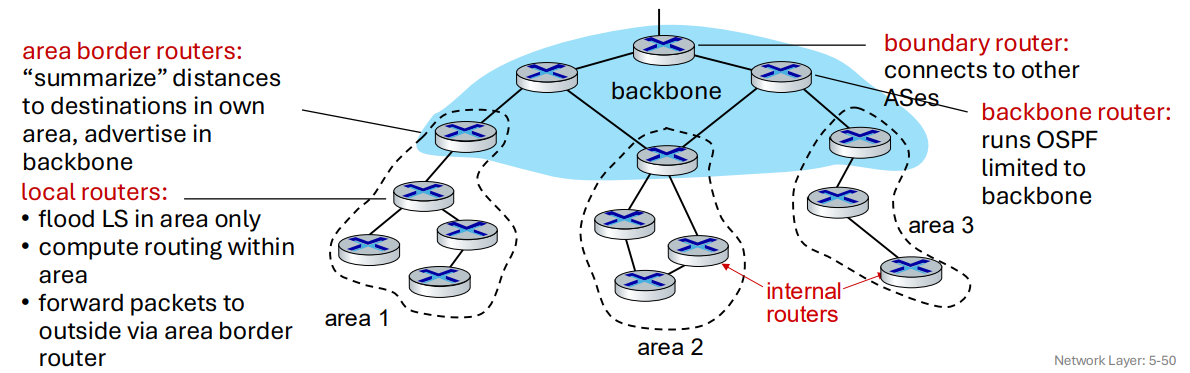
Hierarchical OSPF
Two-level hierarchy - local area, backbone
LSAs only flooded in one area
Each node has detailed area topology