Lecture 6- Occipital Lobe
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
sensation vs perception
sensation: process of our sense organs receiving information abt the world
raw information (meaningless)
perception: experience of information, compiled by brain
unified & meaningful
characteristics of receptive fiels for eyes
some receptor cells detect change & constancy
rapidly/ slowly adapting receptors
some distinguish self from other
exteroceptive/ interoceptive
rapidly adapting receptors
detect change
slowly adapting receptors
detect constancy
exteroceptive
respond to external stimuli
interospective
respond to internal stimuli
processing steps
receptors connect to cortex through intervening neurons
some neural relays in each sensory system are in the spinal cord, others in the brainstem, neocortex, defining the hierarchy of motor cortex
at each relay point, behaviour related to that sensory system can be evoked
messages that sensory systems carry can be gated or modified
all sensory info from systems is encoded by AP that travel along PNS, until they enter brain
every bundle carries same kind of signal
region of processing & neuronal activation rates distinguish types of stimuli from each other in brain
perception
can be embodied or embedded
embodied: influenced by other bodily states
embedded: influenced by env and past experiences
sensory impressions affected by contexts in which they take place
human eye
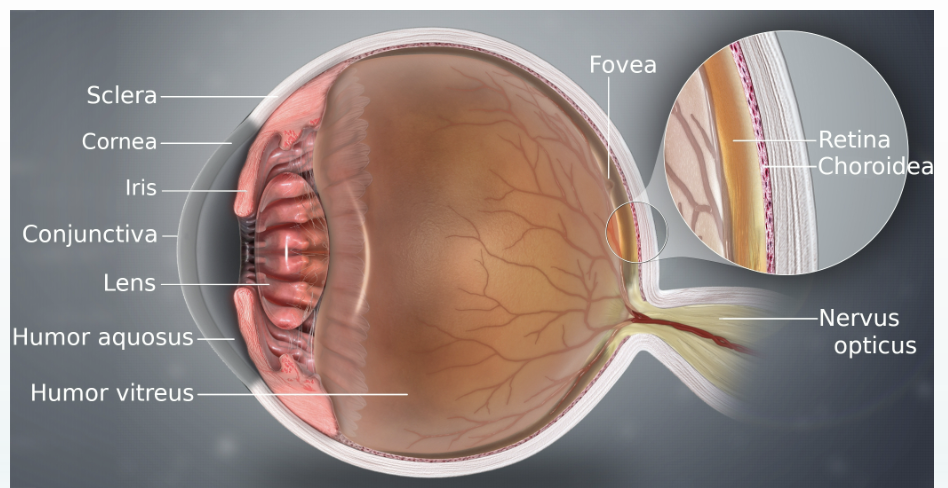
outside to inside order
conjunctiva > cornea > sclera > iris > lens > fovea > nervus opticus
cornea
clear membrane covering visible part of eye
helps gather & direct incoming light
iris
color part of eye
muscle that controls pupil size
pupil
opening in middle of iris
changes size to allow diff amounts of light to enter eye
lens
transparent structure located behind pupil
actively focuses or bends light as it enters the eye
what is accomodation in terms of the eye
process by which the lens changes shape to focus incoming light, so that it falls on the retina
retina
thin, light-sensitive membrane located at back o feye
contains sensory receptors for vision
rods
long, thin, blunt light receptors
sensitive to light, not colour
for peripheral & night vision
cones
short, thick, pointed receptors
detect colour
for colour vision & acuity
from photoreceptors to optic nerve
light striking retina converted into neural energy by photochemical process
info from rods & cones collected by bipolar cells then ganglion cells
ganglion cell axons bundled together to form optic nerve, transmits information to brain
binocular vision
two overlapping fiels of view create perception of depth
why do we see in 3D? Depth cues
texture gradient
stereopsis
motion parallax
texture gradient
elements tend to appear more closely packed together as the distance from the view increases
stereopsis
ability to perceive 3D bc two eyes receive slightly different view of the world
motion parallax
provides 3D information when an object is in motion
points further from the retina will move more slowly than those nearer to the retina
astigmatism
when your cornea/lens has different shape than normal, creating two or more image points on back of eye
eye to occipital lobe
optic nerves from left & right eyes meet at optic chiasm, then partly cross over
left/right visual hemifield
anatomical subdivisions of occipital lobe
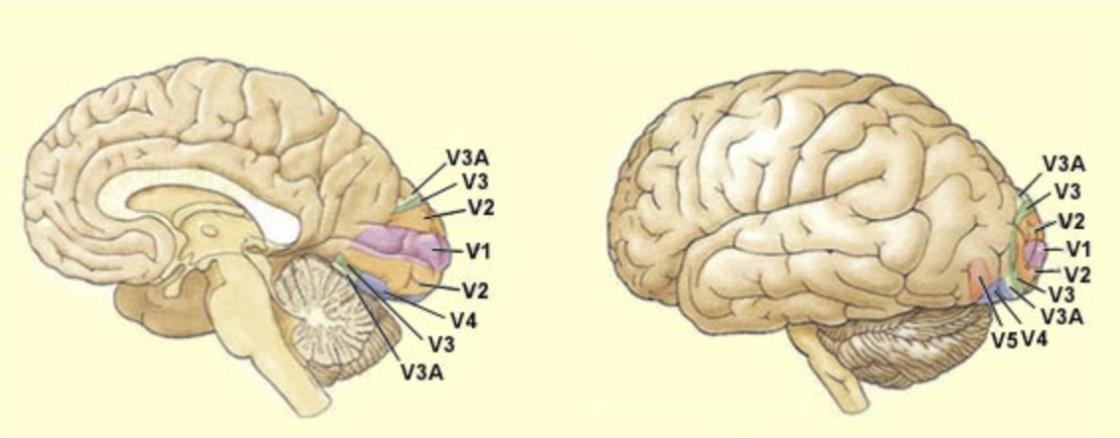
areas of visual cortex
V1, V2, V3, V4, V5
V1
segregates pattern vision from motor signals
V2
3D vision/ seeing camouflage/ more complex patterns
V3
shape perception
V4
colour area & shape perception
V5
motion area
what & where pathways
what- ventral
where- dorsal
early phase of visual perception
shapes & objects extracted from visual scene
features, position, orientation, movement
later phase
shapes and objects are recognised
bottom-up processing
eye-to-brain
top-down processing
brain-to-perception
context & pattern recognition- bottom-up processing
info from physical stimulus used to help recognise stimulus
start with small bits of info & combine them to form perception
context & pattern recognition- top-down processing
information from general context used to help recognise stimulus
high level general knowledge contributes to interpretation of low-level perceptual units
greebles
when participants are shown figures that sort of resemble humans, their face area is activated
gestalt principles
proximity
similarity
good continuation
closure
Helmholtz’s theory
how does the perceptual system perceive patterns?
likelihood principles
unconscious inference
environmental regularities
characteristics in the environment that occur frequently
physical regularities
oblique effect
light-from-above assumption
oblique effect
horizontals & verticals occur more often, so oblique angles are harder to perceive
light-from-above assumption
we always assume that the light is shining from above (in terms of lighting and shadowing)
semantic regularities
functions common to a scence
scene schema
knowlege of what a scene typically contains
bayesian inference
prior probability: our beliefs about the probability of an outcome
based on likelihood of that outcome occurring
specialised neurons in occipital lobe
respond only to horizontals & verticals
object recognition
feature analysis
template model
feature analysis
detecting features and their combinations
stimuli are thought of as combinations of elemental features
we can perceive an object bc we store their features in our LTM
we compare retinal image and see what object in LTM has most features that match object
template model
comparing whole images to past experiences
features are simpler
computationally less intensive
flexible in terms of real variation
visual processing styles
field-dependence
field- independency
field-dependence
tendency to derive info from context as primary means of learning
field- independency
a tendency to derive focal information as primary means of learning
culture influences processing style
SEA cultures are more context-dependent
blindsight
lacking conscious awareness of visual experience, but being able to respond to those experiences anyways
caused by damage to V1
visual agnosia
inability to recognise visual objects, which is neither a function of general intellectual loss, nor loss of basic sensory abilities
apperceptive agnosia
associative agnosia
prosopagnosia
visuospatial agnosia
apperceptive agnosia
unable to recognise objects, draw, or copy a figure
associative agnosia
difficulty understanding meaning of what they are seeing
can draw or copy, but don’t know the meaning
prosopagnosia
face blindness
affected FFA
visuospatial agnosia
difficulty with spatial relationship between objectss