Chapter 4-Three Dimensional Structure of Proteins
1/111
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
112 Terms
3
protein molecules adopt a _______ dimensional configuration. each structure is able to fulfill a specific function
native fold
what is the structure of a protein called ?
entropy cost
there is an _______ _________ to folding the protein into one specific native fold
hydrophobic effect
___________ is the release of water molecules from the structured solvation layer around the molecules as protein folds incresses net entropy
hydrogen bonds
_________ ________ is the interaction of N-H and C=O of the peptide bond leads to local regular structures such as alpha helices and beta sheets
london dispersion
__________ ____________ is a medium range attraction between all atoms and contributes significantly to the interior of the protein
electrostatic interactions
__________ _____________ are long-range interactions between permanently charged groups. creates salt bridges
primary, secondary, tertiary, quaternary
what are the 4 levels of protein structure?
primary amino acid
what is shown?

properties of peptide bond
what is the structure of the primary structure dictated by?
rigid, planar
the peptide bond in a primary structure is __________ and nearly __________
rotation around peptide bond
what is not permitted due to the resonance structure of primary structure?
around bonds connected to alpha carbon
what rotation is permitted in primary structure?
amide nitrogen bond
what bond goes with the phi angle?
carbonyl carbon bond
what bond goes with the psi angle?
180 degrees
in a fully extended polypeptide both y and f are __________
planes
the polypeptide is made up of a series of __________ linked at alpha carbons
antiparallel
is antiparallel beta plated sheets stronger or parallel?
steric crowding
some f and y combinations are very unfavorable because of _______ _________ of backbone atoms
favorable H-bonding interactions
some f and y combinations are more favorable because of a chance to form what along the backbone?
ramachandran plot
what is shown?
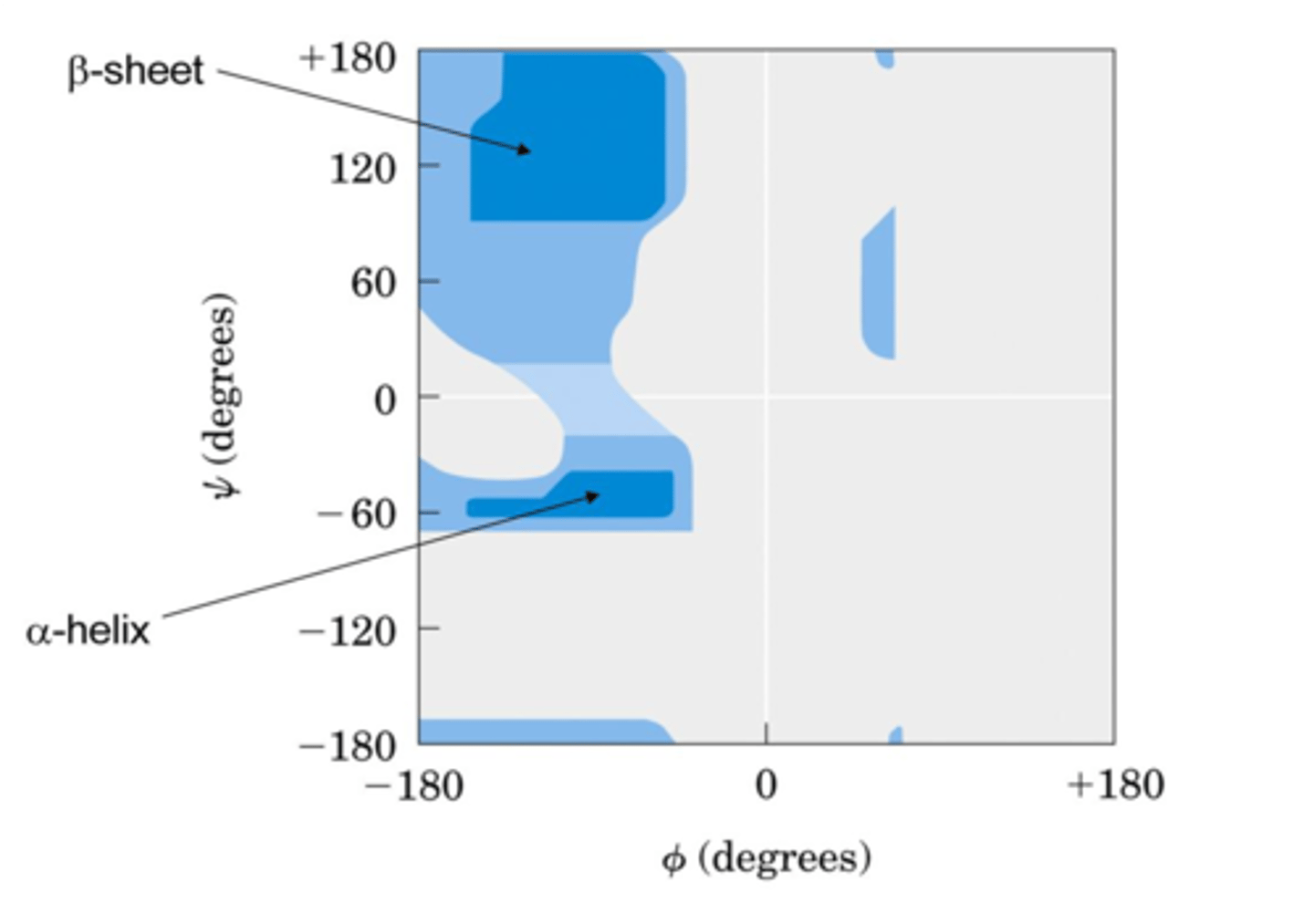
distribution of f and y dihedral angles that are found in a protein
what does a ramachandron plot show?
ramachandran plot
_________________ shows common secondary structure elements and reveals regions with unusual backbone structure
secondary amino acid
what is shown?
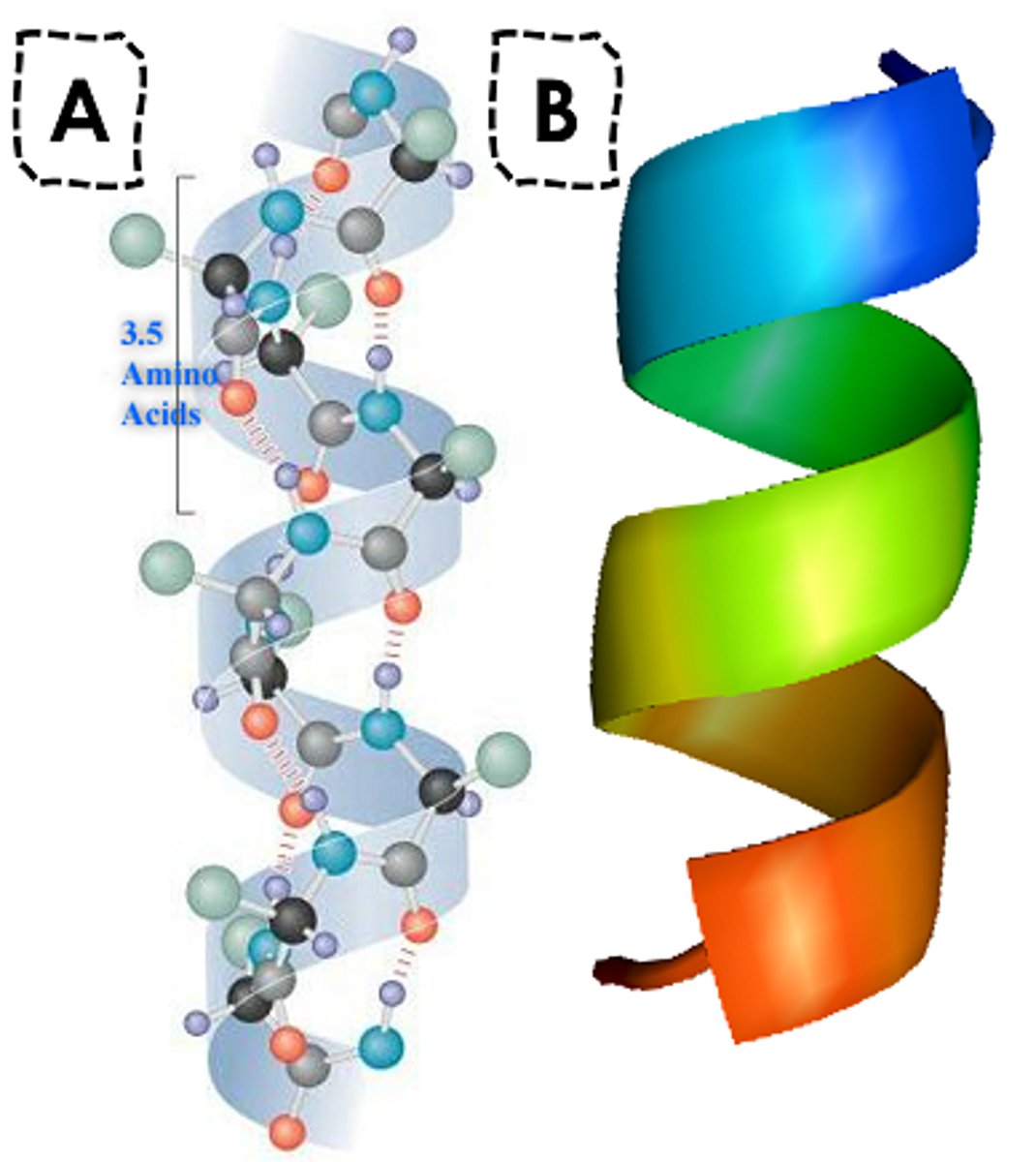
alpha helix and beta pleated sheet
what are the two arrangements for secondary structures?
hydrogen bonds between nearby residues
what are alpha helixes stabled by?
hydrogen bonds between adjacent segments that may not be nearby
what are beta pleated sheets stabilized by?
random coli
irregular arrangement of the polypeptide chain is called the __________ _______
n, n+4
helical backbone is held together by hydrogen bonds between the backbone amides of an ______ and ___________ amino acids
right
the alpha helix is a _______- handed helix with 3.6 residues per turn
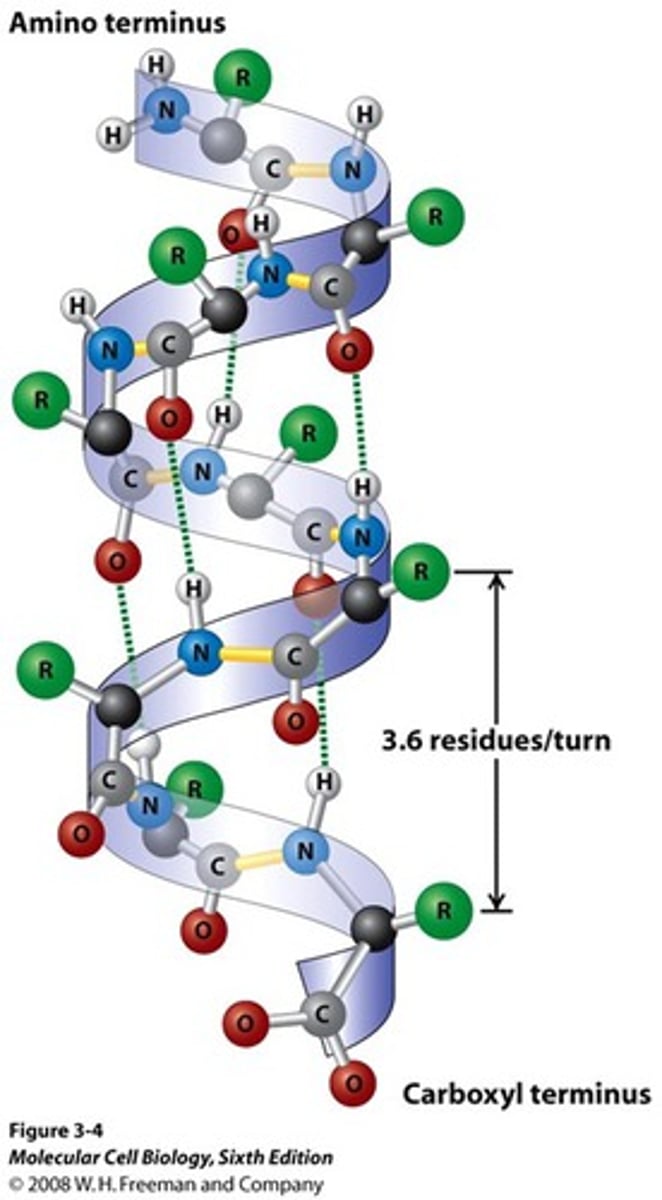
4-5 A
what is the inner diameter of the helix (no side chains)?
10-12 A
what is the outer diameter of the helix (with side chains)?
Alanine and Leucine
what are the two strong helix formers?
Proline and Gylcine
what are the two helix breakers?
rotation around N-Ca bond is impossible, too rigid
why is proline a helix breaker?
too flexible, it supports other conformations
why is glycine a helix breaker?
attractive or repulsive interactions
what two things with side chains can affect the formation of amino acids in an alpha helix?
peptide
__________ bond has a strong dipole moment in a helix
negative
C-O (carbonyl)= ______________
positive
N-H (amide)= ____________
large macroscopic diploe moment
what is enhanced by unpaired amides and carbonyls near the ends of the helix?
beta pleated sheet
what is shown?
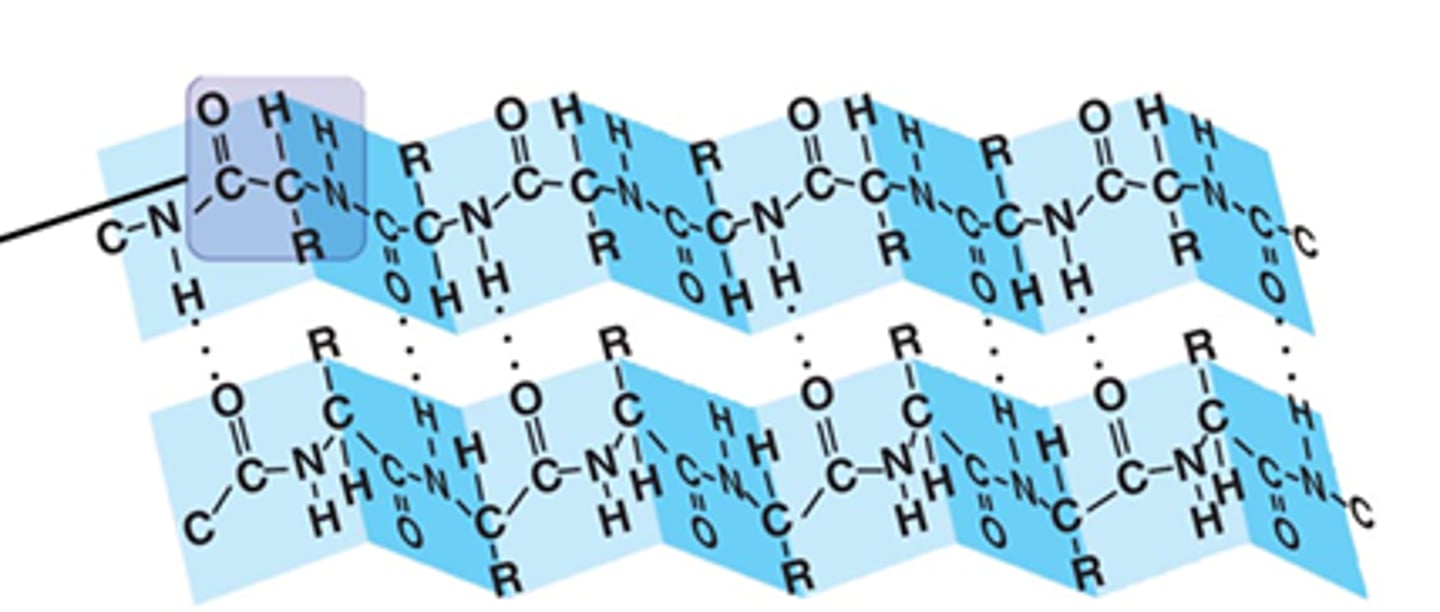
pleated sheet like
the planarity of the peptide bond and tetrahedral geometry of the alpha carbon creates a ______________ like structure
hydrogen bonds
what is the sheet like structure held together by?
parallel beta sheet
what is shown?
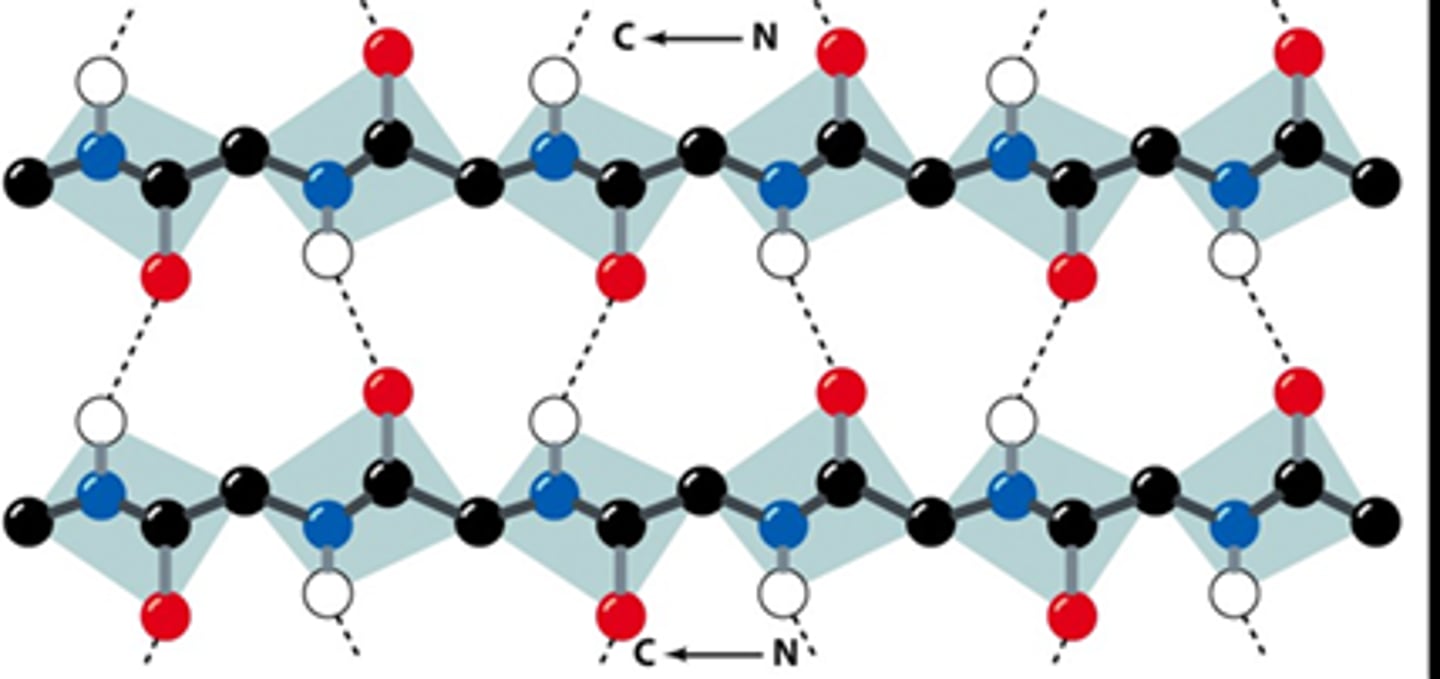
same
H bonded strands run in the _______ direction in parallel sheets
antiparallel beta sheet
what is shown?
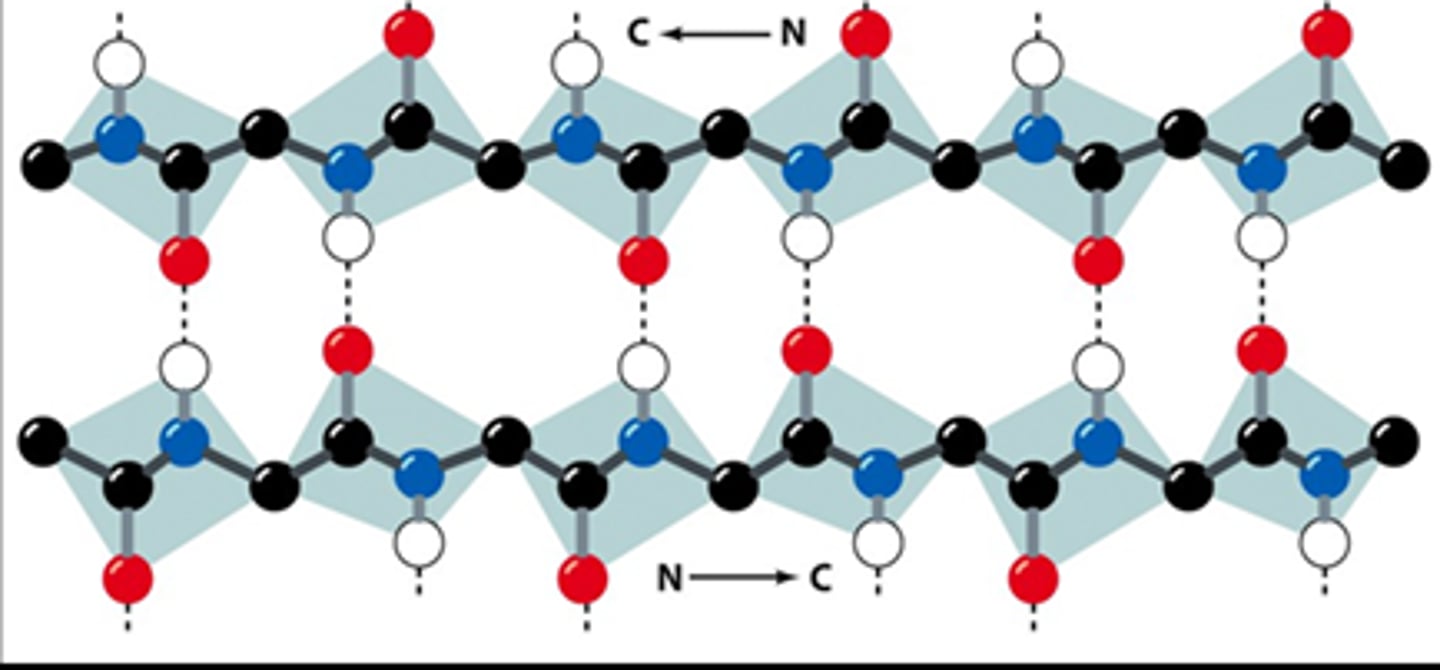
opposite
H bonded structures run in the ___________ directions for antiparallel beta sheets
b turns
___________ occurs frequently whenever the b sheets change direction
180 degree
what degree turn do beta sheets accomplish over 4 amino acids?
proline and glycine because proline is rigid while glycine is flexible
what two amino acids are common in beta turns and why?
trans configuration
most peptide bonds not involving proline are in the _______ ___________ (greater than 99.95%)
cis
for peptide bonds involving proline, about 6 percent are in the ________ configuration. most of the 6 percent involve beta turns
circular dichroism analysis
what can be used to determine secondary structure?
molar absorption difference of left and right circularly polarized light
what does circular dichroism measure?
chromophores in the chiral environment
____________ produces characteristics signals in circular dichroism analysis
conformation
CD signals form peptide bonds depend on the chain ____________ for circular dichroism
CD analysis
_____________ can be used to identify motives in secondary structures of proteins
tertiary structure
what is shown?
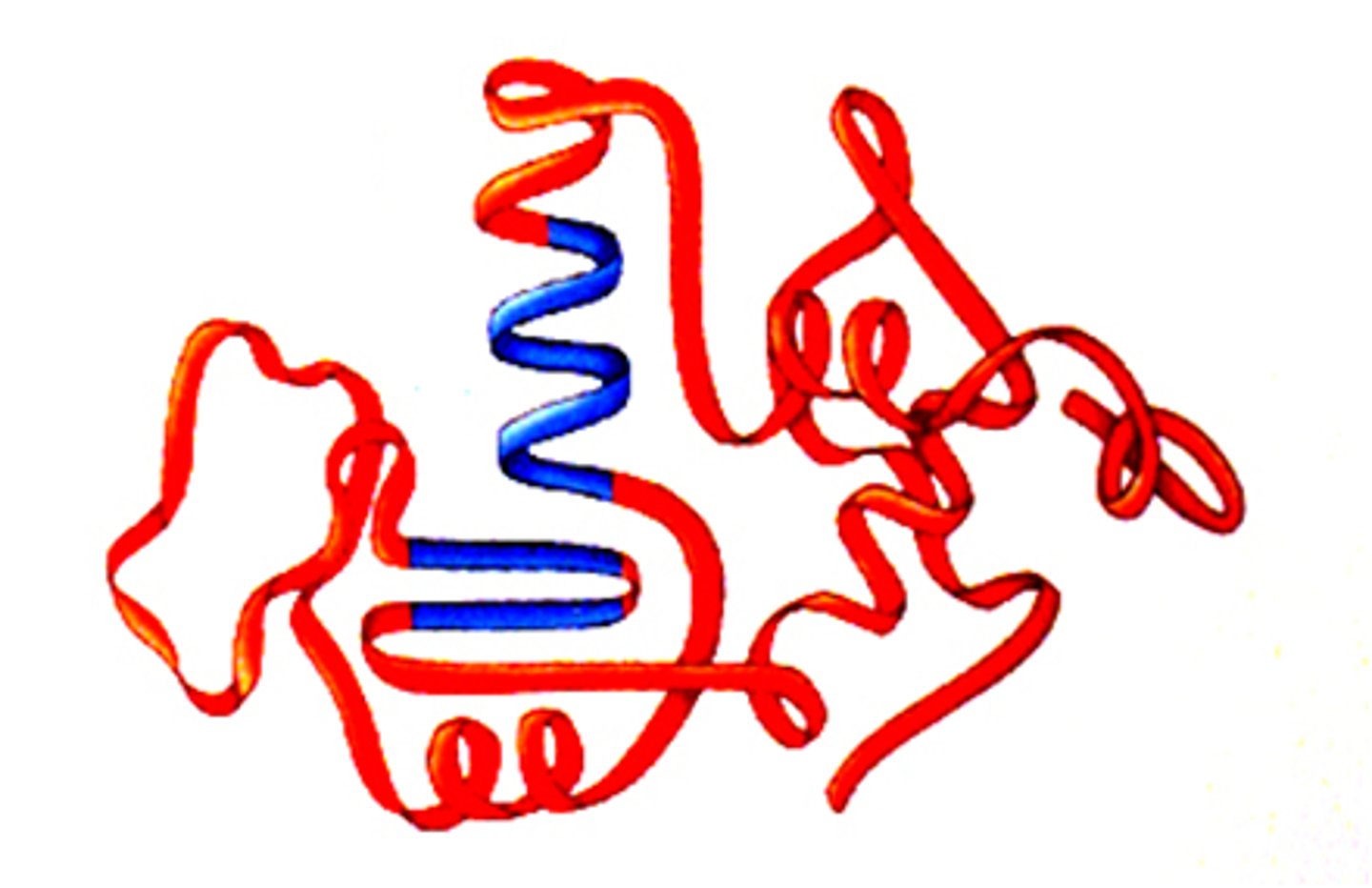
native fold
what is the tertiary structure also called?
numerous weak interactions between amino acid side chains
what is a primary tertiary structure stabilized by?
fibrous and globular
what are two major classes of protein tertiary structures?
disulfide bond
what is the only type of strong bond with tertiary structures that maintains its structure?
disulfide bond
what is the only covalent bond that you can find in tertiary structures?
peptide bonds
what bonds do you find in primary structures? (1)
hydrogen bonding between hydrogens and oxygens
what bonds do you find in secondary structures?
hydrogen bonds between different r groups, disulfide bonds, 3 nonpolar covalent bonds
what bonds do you find in tertiary structures? (3)
keratin, collagen, silk fibroin
what are three examples of tertiary structure proteins?
right handed alpha helix
what is the secondary structure of keratin?
left handed alpha helix
what is the secondary structure of collagen?
glycine and proline
what is a collagen chain rich in? (2)
collagen fibril
what do many collagen triple helices assemble into to form?
vitamin C
collagen fibrils will be brittle if they lack what?
cross links, covalent bonds
strands of collagen fibrils are based on ________ ______ and determined by modified amino acids. Modified amino acids create what type of bonds?
anti parallel beta pleated sheets
what is the secondary structure of fibroin?
left handed double helix
what is the quaternary structure of keratin?
right handed triple helix
what is the quaternary structure of collagen?
no
does fibroin have a quaternary structure?
fibroin
__________ is the main protein in silk from moths an spiders
alanine and glycine
what small side chains allows for the close packing of beta pleated sheets? (2)
hydrogen bonding within sheets, London dispersion interactions between sheets
what is silk fibroin stabilized from? (2)
flexible, resistant
silk fibroin is very __________ and _________
proteins that are folded into a compacted spherical shape. this enables them to carry our biological functions
what are globular proteins?
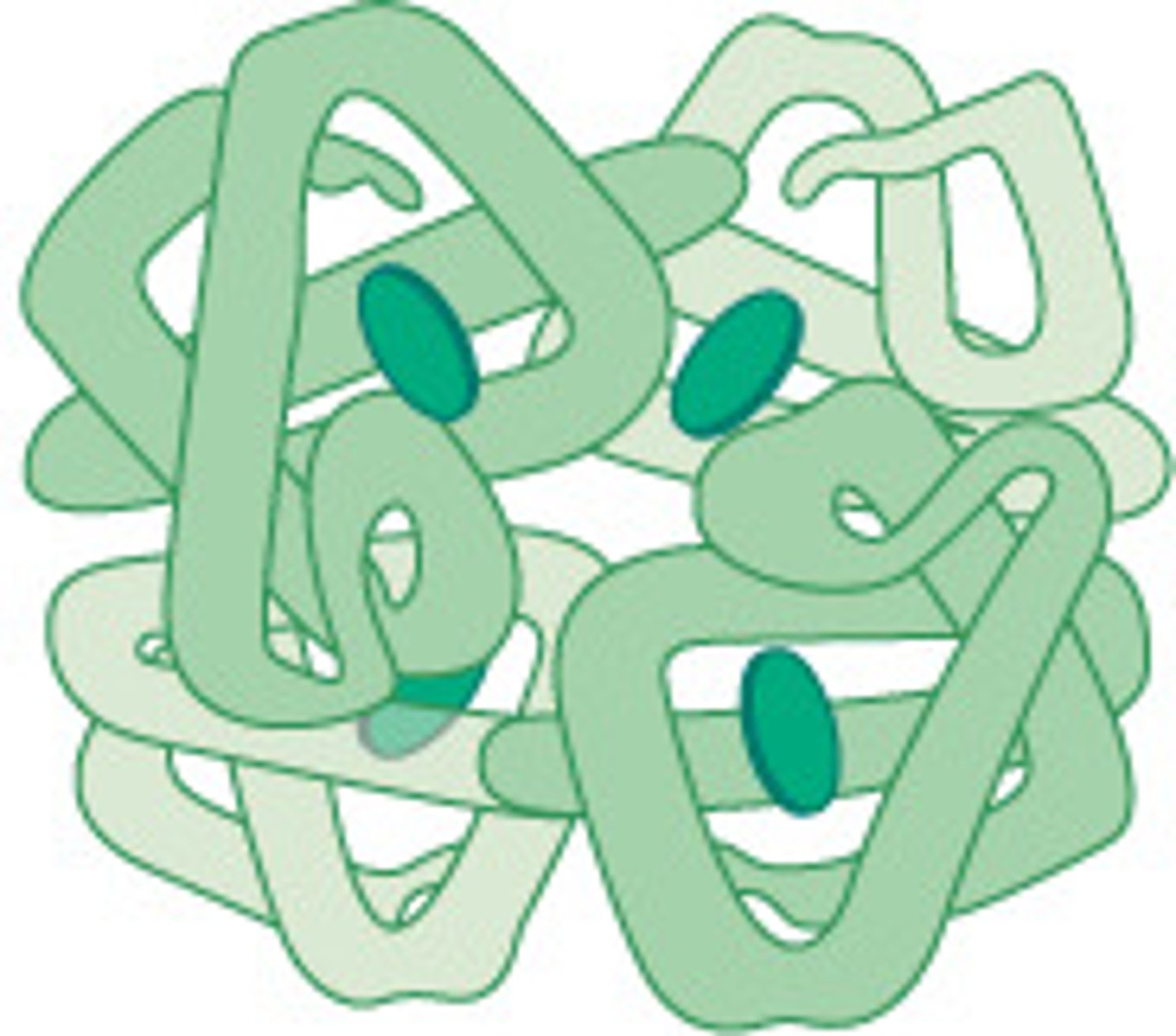
specific arrangements of several secondary structure elements
what are motifs/ folds?
alpha helix and beta pleated sheets
what are two examples of motifs in proteins?
motifs
globular proteins are composed of different ________ folded together
motifs
a beta barallel and a beta alpha beta loop is an example of what?
lysine, arginine, glucose, proline
what are 4 amino acids that intrinsically disordered proteins use whose higher concentration forces less defined structure?
more than 1 polypeptide chain
what forms a quaternary structure?
disulfide
__________ bonds are important for antibodies
x- ray crystallography, and biomolecular NMR
what are the two tests to run on quaternary structures?
figuring out 3 dimensional shape of protein
what is x-ray crystallography and biomolecular NMR used for?
for x-ray crystallography you need to crystalize the protein first but for biomolecular NMR you do not
what is the major difference between x-ray crystallography and biomolecular NMR?
flexible
biomolecular NMR can show what regions of the protein are more __________/ Ridgid
lowest
proteins always fold into the native fold because it always has the _________ energy
protein that helps another protein to fold
what is a molecular chaperone?
denaturation
loss of structural integrity with accompanying loss of activity is called ___________
heat/cold, ph extremes, organic solvents, chaotropic agents
what are 4 things that can denature a protien?
secondary, tertiary, quaternary, primary
what structures does denaturation destroy? (3) what does it leave you with?
hydrolysis
what activity would break down primary-quaternary?