Nuclear Medicine (RNI) of the [adult] abdomen
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
what should you consider in NM
•Pregnancy & breastfeeding
•Distance from foetus/children
•Hydration for excretion
•Time, distance & shielding
•Contamination risks (injection site & bodily fluids)
•staff contamination and radiation monitoring
what are the abdomen scan types
•Renogram (kidneys)
•Gastric Emptying
•HIDA (gall bladder)
what in a renogram
Functional study to see how well each kidney is working and whether urine passes into the bladder without obstruction.
can assess for…
•Individual kidney function
•And/or bladder function (continue onto micturating cystogram)
•Detect urinary tract infections
•Detect/assess obstructed kidney(s)
•Detect/assess vesicoureteric reflux
•Assess kidney transplants
•Further assessment of “non functioning kidney” of other studies
what is the nucleotide in a renogram
•Tc99m Mag 3
•Up to 100MBq (ARSAC guidance) Administration of Radioactive Substances Advisory Committee
•Given as bolus injection IV via Cannula
•Scan begins immediately in synchronisation with injection
what happens in a renogram
30 minute dynamic acquisition (30 second frames 60 frames)
Furosemide (diuretic) usually at 15mins to encourage emptying of kidneys (Can have T-15, T0 or no frusemide depends on history and clinical information)
Full Bladder image at end
If necessary can continue to Micturating Cystogram (would need commode)
Presentation:
•Abdomen pain - on consultation, loin to groin pain.
•Sent for CT…Result hydronephrosis
•Clinical question? PUJ obstruction
Patient preparation:
•Letter: where/when to come
•Eat as normal but well hydrated because Dehydration can delay renal excretion and interfere with scan accuracy and it encourages frequent urination for radiation protection purposes
•Questionnaire to assess suitability for diuretic
•Empty bladder before scan
•(catheter if not continent or requires assistance to void)
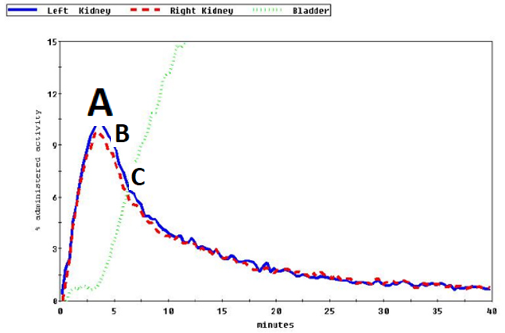
whats the normal result on a renogram
Peak around 3 minutes (A) (Vascular phase)
Spontaneous emptying (B) (Secretory phase)
Low level at end of examination (C) (excretory phase)
what does hydronephrosis look like on a renogram
•Obstructive hydronephrosis of the right kidney
•Arrow indicates no response to IV diuretic
•Normal scan seen for left kidney
Image not annotated which is imperative in N/M
what is gastric emptying
A study to demonstrate the emptying of the stomach after a meal
A dynamic study (functional information) may be supported by delayed static images
Solid and liquid meals behave differently – No agreed national protocol for choice of food (porridge/ scrambled eggs etc)
Useful to diagnose dumping syndrome and stasis (gastroparesis)
•These patient ingest/eat the Radionuclide
•Meal is made up in the department
•dose is measured via syringe and mixed into the porridge
•Tc99m colloid up to Max 40MBq as per ASRAC guidance
•The patient eats the porridge in the first 10 mins of the exam
what is the gastric emptying scan parameters
Imaged sitting up. Gamma camera facing out into room
Dynamic imaging: 1 minute frames for 30 minutes
Static images every 30 minutes until there is emptying of the stomach
Patient presentation:
•Unable to eat: feeling of fullness and can only eat small amounts
•Clinical question: delayed gastric emptying or dysmotility?
Patient preparation:
•Letter to tell patient where/when to come
•No food/drink on the morning of the examination
•Questionnaire to assess suitability for meal
•Appropriate clothing
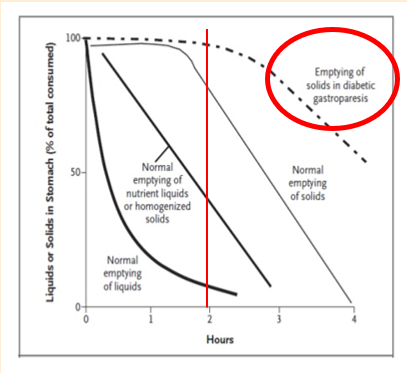
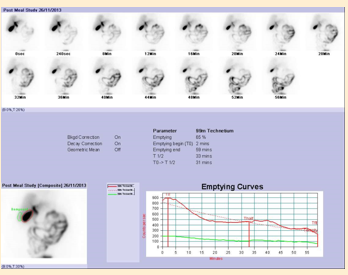
normal result gastric emptying
•Rapid filling
•Spontaneous emptying by approximately:
•30% after 30 mins
•50% within 40 mins
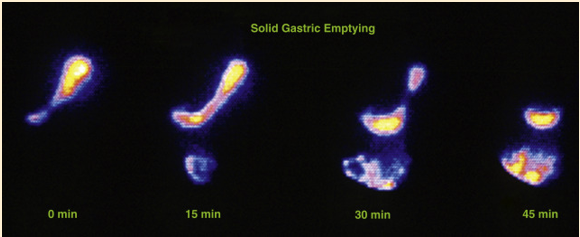
abnormal gastric emptying
Delayed gastric emptying with food still in the stomach after 4 hours post meal
what are the possible pathologies of abnormal gastric emptying
Possible pathologies:
•Delayed filling
•Evidence of Reflux
•Delayed emptying
what is a HIDA scan
Hepatobiliary iminodiacetic acid scan
Functional imaging of the Gall bladder
Can assess for:
•Acute (or chronic) cholecystitis
•Calculation of gallbladder ejection fraction
•Evaluation of enterogastric reflux (bile reflux)
•Evaluation of the biliary system after surgery
•Jaundice (obstructive Vs non-obstructive)
•Biliary leak
•Further evaluation of any cold spots on (Radiolcolloid) Liver Imaging
Paeds:
•Biliary atresia Vs neonatal hepatitis
•Presence of Choledochal cyst
HIDA: injection of radionuclide
•Tc99m IDA (iminodiacetic acid)
•HIDA Product no longer used but the test has kept its original name
•Maximum of 150MBq (ARSAC, 2023)
•Given via cannula or butterfly needle
•Imaging begins immediately after injection
•90 minute dynamic acquisition
•1 minute frames 90 frames
•Sincalide (CCK) infusion but supply limitations many sites have moved to
•Calogen drink at 45 minutes (or when Gall Bladder is full)
•Some centres use chocolate
HIDA scenario
Patient presentation:
•Right sided abdominal pain.
•On and off for months, worse after consuming meal.
•Previous ultrasound, no evidence of gallstones.
•Clinical question: gall bladder dysfunction
Preparation:
•Letter to tell patient where/when to come
•No Food/Drinks from midnight on day of the exam
•Calogen food supplement: (35ml) 40% fat emulsion drink
•Warning that test is 90 minutes in length
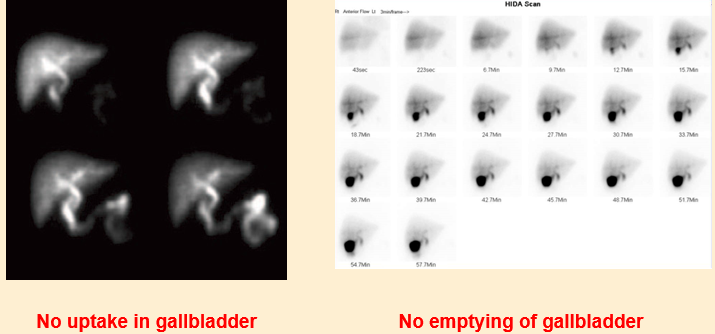
HIDA: normal result
•Prompt spread of isotope through liver and ducts
•GB filling at 20 minutes
•Between 35-75% empty at end of examination
HIDA – abnormal result
other abdomen scans
DMSA Kidneys- For scar tissue/ split function
Liver/Spleen – for location of active tissue
Meckel diverticulum – to locate ectopic stomach tissue
Red cell imaging – to identify sites of bleeding
Infection imaging – to identify sites of infection