Public Health Planning Exam 3: Key Terms & Definitions
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
4 P's of marketing
Product
Price
Place
Promotion
What we're offering people for product
Commodity (Tangible good or service)
Idea
Attitude
Behavior
Service
Product Must Be
Solution to a problem
Unique
Cognizant of the competition
Deigned in terms of the user's beliefs, practices, and values
The cost of adopting the product (price)
Money
Time
Pleasure
Loss of self esteem
Embarrassment
Others
Place or Channels
Where tangible products are purchased
Where service is provided
Media aspect
Where people will act
Media aspect
Delivery of message
Frame of mind
Important Considerations for place
Available
Easy to find and use
Appropriate
Timely
Place where decisions are made
Healthcare settings
Family/friends
Advertising reminders
Promotion
Creation of educational messages that are memorable and persuasive
Message design elements for promotion
Type of appeal
Tone
Spokesperson
consumer orientation
Understand consumers' perceptions:
Benefits
Barriers
Self-efficacy
Social norms
Program Implementation Defined
the act of converting planning, goals, and objectives into action through administrative structure, management activities, policies, procedures, and regulations, and organizational actions of new programs
Setting up, managing, and executing a project
Program diffusion - adoption, implementation, sustainability
Efforts involved per phase of program development
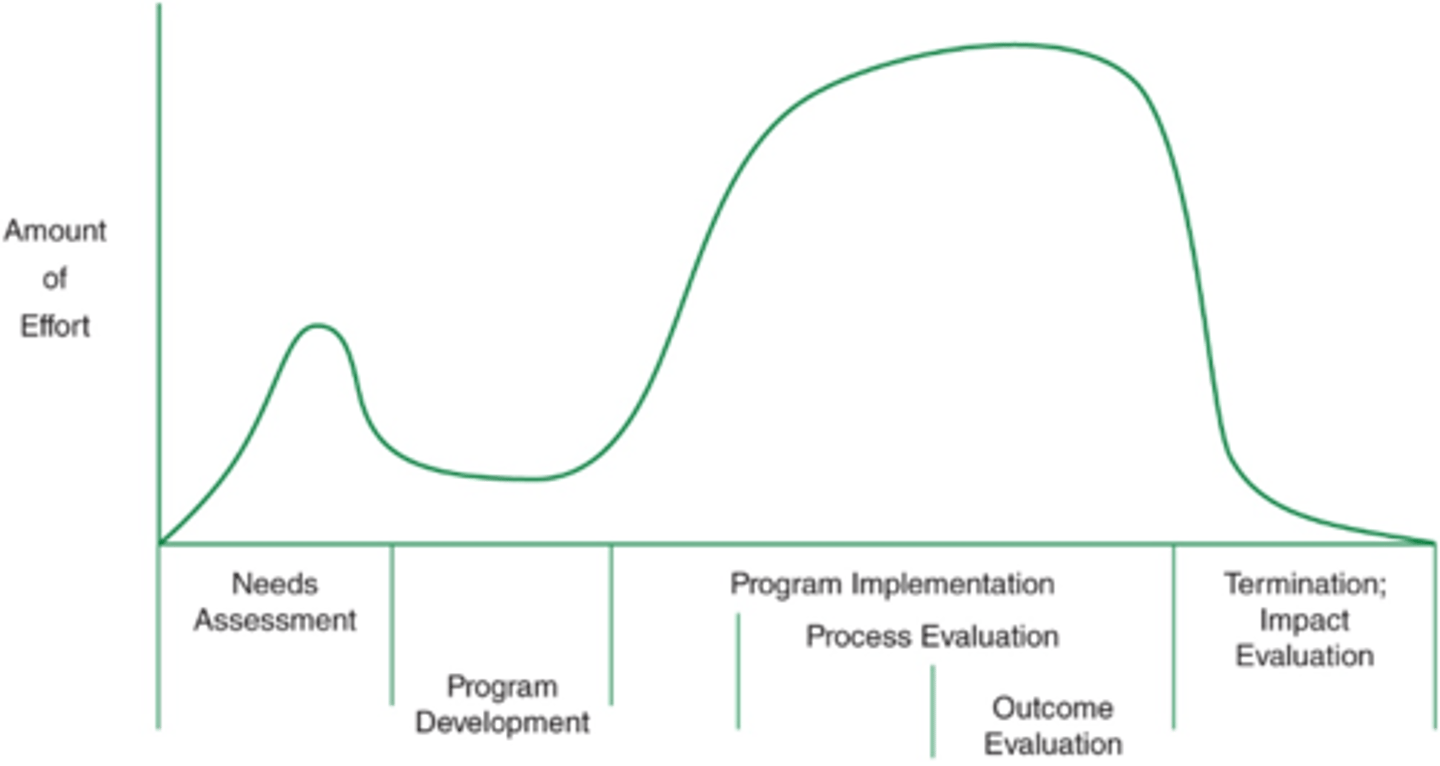
Effort needed for needs assessment
about half
Effort needed for program development
little
effort needed for program implementation and process evaluation
a lot
effort needed for outcome evaluation
Most effort needed
effort needed for termination; impact evaluation
Least effort needed
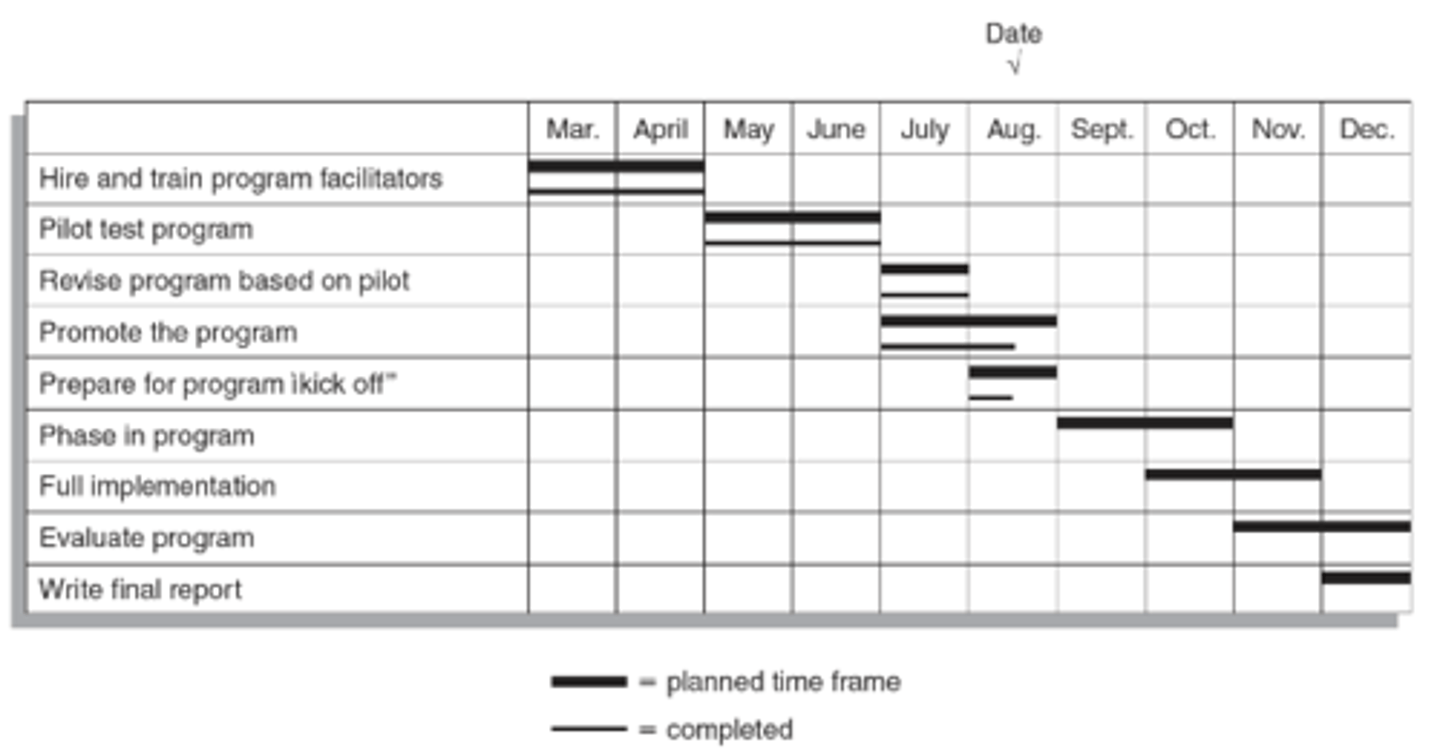
Grant Chart
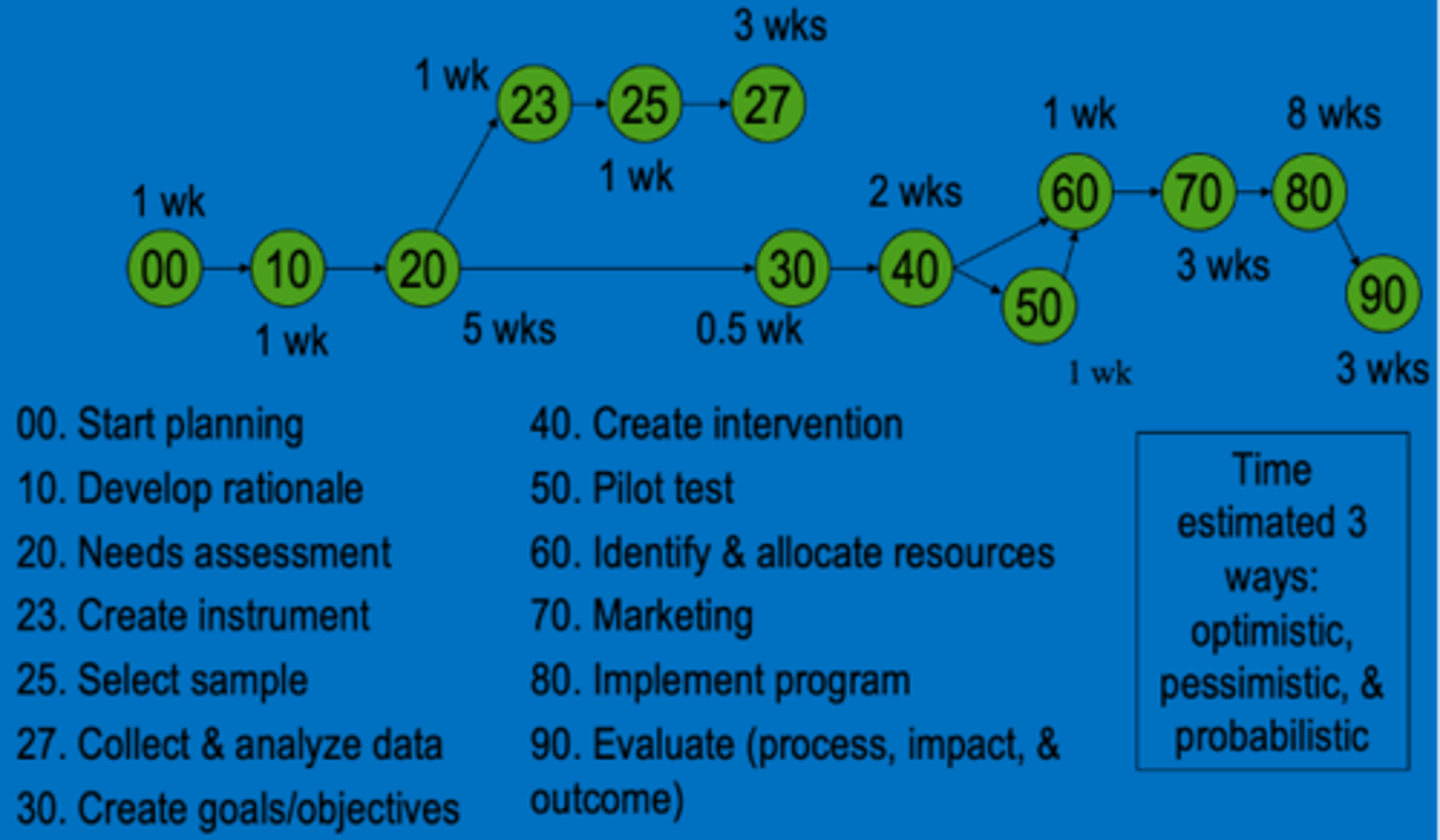
Program Evaluation and Review Technique
Pilot Testing
trying the program out with a small group from the priority population to identify any problems
Pilot Testing questions
1. Were strategies implemented as planned?
2. Did the intervention strategies work as planned?
3. Adequacy of resources
4. Evaluation of pilot activities
Phasing in
limiting the number of people who are exposed then gradually increasing the numbers.
Phasing in questions
1. Especially if there is a large target population
2. Can phase in by location, program offering, and number of participants.
Total Program
All in priority population exposed at the same time.
Pilot advantages
Opportunity to test program
Close control of program
Pilot disadvantages
Very few involved
Not meeting all needs
Hard to generalize about results
Phased-in advantages
easier to cope with workload
gradual investment
Phased-in Disadvantages
fewer people involved
Total program advantages
more people involved evaluation more meaningful with larger group
Total program disadvantages
big commitment
no chance to test program
Safety and Medical Concerns
Most programs are to improve health, thus do not put participants in danger.
Informed consent (waiver of liability or release of liability) do not protect planners from being sued
Medical clearance signed by a physician
Ensure safety & health
Ensure safety & health
Program Location; appropriate security
Building codes met and facilities free from any hazards
Qualified instructors
Plan in case of emergency
Informed Consent
Explain nature of program
Inform participants of risk and discomfort
Explain expected benefits
Inform of alternative programs
Indicate that they are free to discontinue participation at any time.
Allow participants to ask questions
Reducing liability
Key to avoiding liability
Aware of legal liabilities
Qualified instructors
Good judgement
Medical clearance
Limit work to expertise
Safe environment
Insurance
Negligence
Failing to act in a prudent (reasonable) manner
Omission
Commission
Purpose of the logic model
To determine if objectives were met
To improve program implementation
To provide accountability to stakeholders
To increase public support for initiatives
To contribute to the scientific base
To inform policy decision
Two critical purposes of program evaluation
assessing & improving implementation quality
determining program effectiveness
The logic model
A picture of your program: what you are putting into the program, what you are doing, and what you are trying to achieve
Clarifies the strategy underlying your program
Builds common understanding, especially about the relationship between actions and results
Communicates what your program is (and is not) about
Forms a basis for evaluation
Inputs
The inputs dedicated to our consumed by the program.
Can include non-physical investments, such as staff time
Activities
The actions that the program takes to achieve desired outcomes.
Each activity should begin with an action verb to demonstrate that it is something your organization is doing.
Outputs
The measurable product of a program's activates
Should be the direct, physical result of activities. Should be measurable and/or tangible
Outputs examples
Number of communications materials printed (posters, flyers)
Number of staff trained
Educational materials developed for target population
Outcomes
The benefits to clients, communities, systems, or organizations
Usually related to changes in knowledge, attitudes, beliefs, behaviors, or health outcomes of the populations of focus for the program. Should be measurable
Outcomes examples
Increased knowledge of the topic (short-term outcome)
Increased delivery of health care service (intermediate outcome)
Increased utilization of health care services (long-term outcome)
How logic models help with evaluation
Provides the program description that guides our evaluation process
Helps us match evaluation to the program
Helps us know what and when to measure
Are you interested in process and/or outcomes?
Helps us focus on key, important information
Prioritize: Where will we spend our limited evaluation resources?
What do we really need know?
Process Evaluation
Examines whether program activities are being implemented as intended
Impact/Outcome Evaluation
Measures program short term and long-term effects in the population.
Reason for process evaluation
when expected outcomes are not observed, process evaluation can suggest reason
when outcomes are positive, process evaluation may help understand which components are especially important
when an activity is newly implemented, and it is too early to expect changes in outcomes
when an outcome evaluation is not feasible due to resource constraints
5 common process evaluation measures
reach
quality of implementation
appropriateness
satisfaction
barriers
reach
Degree to which intended audience participates in intervention
reach questions
What percent of target population were aware of the intervention?
What was the percent of persons attending influenza vaccination clinic that do not usually get vaccinated?
What percent of mothers were contacted by peer-to-peer counselors?
Quality of implementation
Was activity implemented properly, according to standards or protocol
Quality of implementation questions
Was the curriculum implemented per guidelines?
Were protocols followed?
Was the training standardized?
Fidelity: What % of the intervention was implemented (100%, 70%, 30% ??)
Appropriateness
Interventions or messages that are delivered may only be effective if judged appropriate by target population.
Appropriateness questions
Did messages "speak" to target audience?
Culturally appropriate?
Reading level appropriate?
Age appropriate?
Addressed the target concern of the population?
Satisfaction
The extent to which staff are satisfied with training.
Satisfaction questions
Are staff satisfied with the intervention?
Are target population participants satisfied with the intervention?
Barriers
This attempts to understand why something didn't happen, and may identify key environmental variables
Barriers questions
Reasons not attending a clinic or intervention
Reasons for low fidelity
quantitative
survey participants
survey providers of the intervention
qualitative
focus groups
observation of intervention implementation
Impact and Outcome Evaluation purpose
assess objectives
assess goals
requires a comparison group to judge success
what can be evaluated---almost anything
Direct service interventions
Community mobilization efforts
Research initiatives
Surveillance systems
Policies
Outbreak investigations
Laboratory diagnostics
Communication campaigns
Infrastructure-building projects
Training and educational services
Administrative systems
Impact Evaluation
focuses on short term/intermediate endpoints
knowledge
attitudes
behaviors-short term
behavioral intent
skills
awareness
Outcome Evaluation
focuses on long term endpoints
morbidity
mortality
disability
behaviors-long term
Purpose of control/comparison group
To judge success
phases of implementation
1. adoption of the program part of marketing
2. Identifying and prioritizing the task to be completed
3. establishing a system of management
4. putting the plans into action
5. ending or sustaining a program
Identifying and prioritizing the task to be completed (Phase 2)
many tasks need to be completed when implementing a program (eg. reserving space, ordering equipment, hiring staff)
task needs to be identified and prioritized
planning timetables and timelines can help with this process
establishing a system of management (Phase 3)
Establishing a system of management
management
the efficient, satisfactory management of a health promotion program is vital to its long-term success.
Key personnel
delegation of responsibilities
Advisory Boards
putting the plans into action (Phase 4)
putting plans into action
pilot testing
phasing in
total program
ending or sustaining a program (Phase 5)
ending or sustaining a program
how long to run a program
ending a program
sustainability of a program
management
the process of achieving results through controlling human, financial, and technical resources
Key personnel
credentials
ending a program
goals and objectives met?
Are resources available?
need to re-focus?
sustainability of a program
work to institutionalize
advocating for the program
partnering with others
revisiting and revising the rationale
other sources of funding