Delirium
1/113
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
114 Terms
Delusions
- Fixed, false beliefs, cannot be corrected by logic and are not consistent with culture and education of the patient.
- Ex. Getting robbed.
Hallucinations
- False sensory perception experienced without real external stimulus.
- They are usually experienced as originated in the outside world not within the mind as imagination.
- Ex. Seeing angels with no birds outside of the window.
*Not just visual (ex. taste, smell, sounds).
Illusions
- Misperception of real external stimulus. Most likely to occur when general level of sensory stimulation (consciousness) is reduced.
- Ex. Seeing angels, but their are birds outside of the window.
DSM-F-TR Criteria
- A: Represents change from baseline.
- C: Visuospatial - Reach for things, but miss cause of altered spatial ability.
- E: Decline in health/delirium = A direct physiological consequence.

CAM Instrument
Must Have:
–Acute onset of symptoms.
–Inattention.
–Fluctuating symptoms.
Plus, One of:
–Disorganized thinking.
–Altered level of consciousness.
*Cannot be used to rate severity of delirium.
*Brain is most times the first organ system to show signs of problems/inflammation.
Dementia vs. Delirium
- Differentiating delirium (acute disorder) from dementia (chronic disorder) is not always easy.
- The adult with dementia is more likely to become delirious.
- The onset of delirium in this population could be mistaken for an exacerbation of dementia and then Tx may not be targeted to cause.
- Delirium has a high 1-year mortality rate 35 - 40% (in those 65+).
- Decreased albumin = 4x likely for delirium = risk for hemorrhage.
*Dementia = Brain.
*Delirium = Changed cognition due to issue in the body.
*Mange delirium by finding the pathophysiology problem in the body.
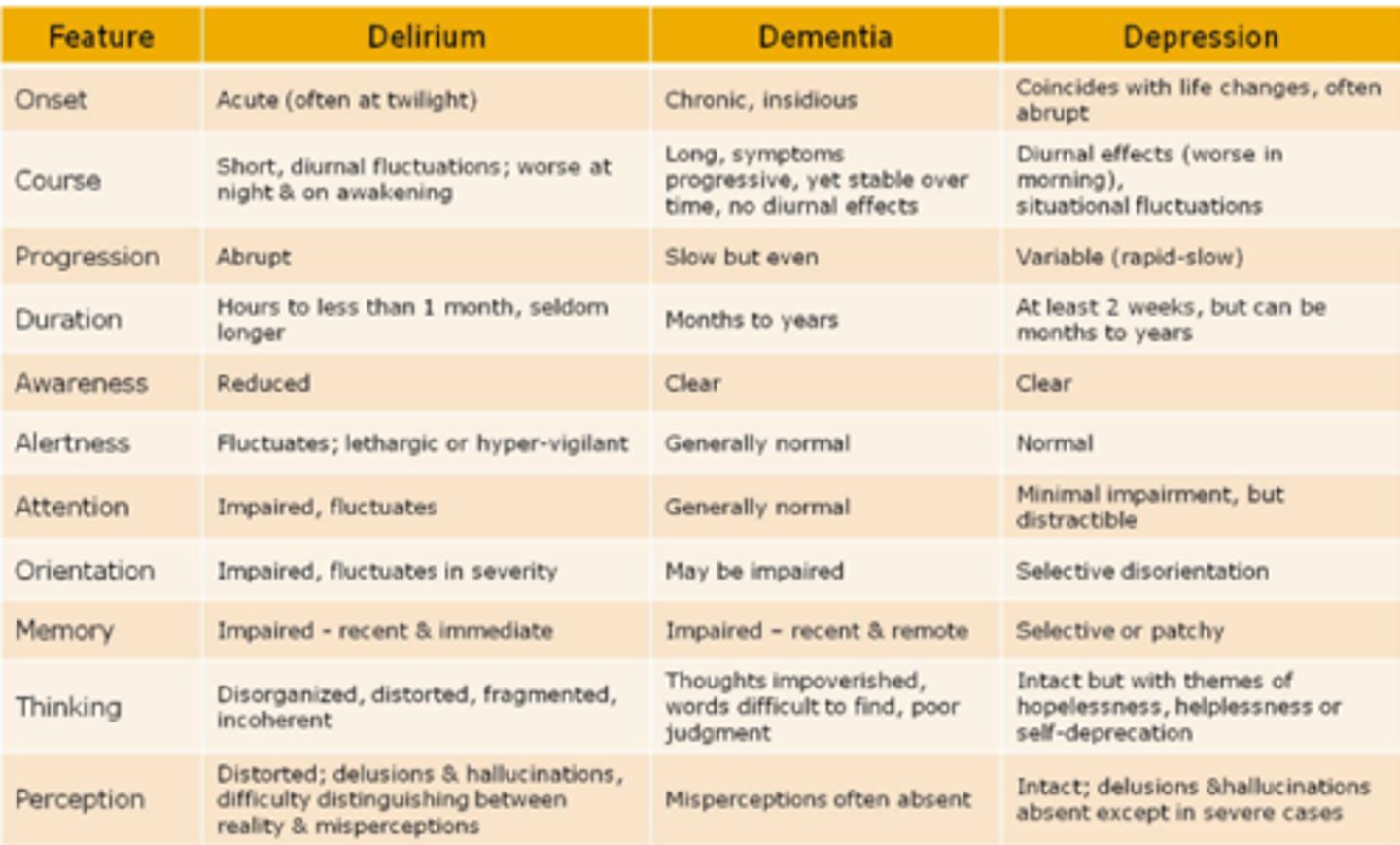
Delirium vs. Dementia vs. Depression
Insidious
- Unclear of what's fault.
- It is not directly linked to anything.
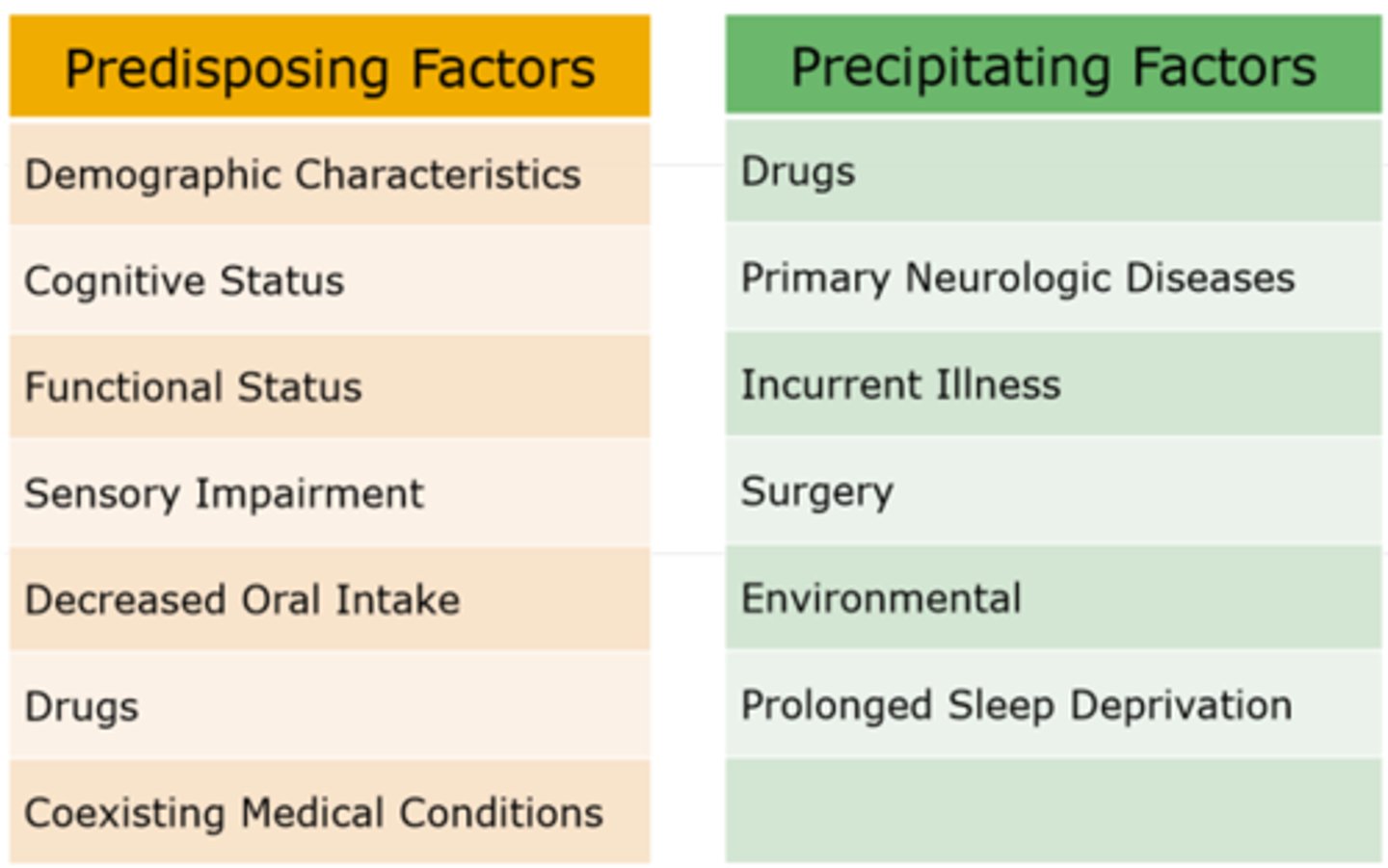
Predisposing vs. Precipitating Factors
Mental Status Assessment
- Mental status is a bedside or interview assessment that dramatically fluctuates.
- It includes the patient's appearance, affect (mood), thoughts (especially the presence of hallucinations and delusions), inquiry into self-destructive behavior, homicidal behavior, judgment and, in this diagnosis, orientation, immediate, recent, and long-term memory.
Management of Delirium
- Patient safety is key!
- The nurse must be knowledgeable of the
risk factors of delirium.
- Continuous use of delirium assessment tools must be implemented (i.e., HHS uses the CAM instrument).
- Prevent any chance of infection (aseptic tech, catheters) and hypovolemia (monitoring ins & outs, assess for signs of swelling, edema, congestion; monitor for dehydration).
- When the patient is in a state of delirium, the primary role of the nurse is to monitor patient safety and to advocate for the patient (implementing a safe environment which would include having 24hr watch by a PSW).
Important Fact's About Delirium
- Delirium is a complex clinical syndrome associated with significant morbidity and mortality.
- A clients' overall health and fitness status greatly determines their risk for delirium.
- Neither the neuroinflammatory or cholinergic hypothesis can explain all symptoms of delirium.
- Delirium may indicate a patient who is entering the early stages of dementia.
- It is important to treat the underlying disease and provide symptomatic relief (nutrition, hydration, rest, comfort, emotional support).
D.E.L.I.R.I.U.M.
- D = Drugs.
- E = Electrolyte disturbances.
- L = Lack of drugs.
- I = Infection.
- R = Reduced sensory input.
- I = Intracranial disorders.
- U = Urinary and fecal disorder.
- M = Myocardial and pulmonary disorders.
Delirium Definition
- Acute decline in the cognitive processes of the brain (i.e. attention and cognition).
- Most commonly associated with hospitalized patients aged 65 years and older (affects 20% of patients).
- Cognitive function fluctuates throughout the day.
- Wide range of symptoms and patient characteristics.
- 2/3 of cases go unreported.
- Linked to poor clinical outcomes.
- Marker for severe illness and mortality (1 year mortality rate of 35 - 40%).
- Experience changes in attention, disorganized thinking, LOC, disorientation, delusions, perceptual disturbances, and impaired memory, speech, and psychomotor activity.
*Only 40% of health care workers routinely screen for delirium in at risk patient.
Pathophysiological Changes due to Delirium
- Loss of independence.
- Increased risk of morbidity and death.
- Increased health care costs.
Diagnostic Criteria for Delirium
Disturbance must be over a short period of time

Clinical Features of Delirium
- Acute Onset (occurs abruptly, usually over a period of hours or days; reliable information often needed to ascertain the time course of onset).
- Fluctuating Course (symptoms tend to come and go or increase and decrease in severity over a 24-hour period; characteristic lucid intervals).
- Inattention (difficulty focusing, sustaining, and shifting attention; difficulty maintaining conversation or following commands).
- Disorganized Thinking (manifested by disorganized or incoherent speech; rambling or irrelevant conversation or an unclear or illogical flow of ideas).
- Altered level of consciousness (clouding of consciousness, with reduced clarity of awareness of the environment).
- Cognitive deficits (typically global or multiple deficits in cognition, including disorientation, memory deficits, and language impairment).
- Perceptual Disturbances (illusions or hallucinations in about 30% of patients).
- Psychomotor Disturbances (hyperactive = marked by agitation and vigilance; hypoactive = marked by lethargy, with a markedly decrease level of motor activity; mixed).
- Altered sleep-wake cycles (characteristic sleep-cycle disturbances; typical daytime drowsiness, nighttime insomnia, fragmented sleep, anxiety, depression, irritability, apathy, anger, or euphoria).
- Emotional disturbances (common; manifested by intermittent and labile symptoms of fear, paranoia, anxiety, depression, irritability, apathy, anger, or euphoria).
Delirium Features
Onset:
- Acute (often at twilight).
Course:
- Short, diurnal fluctuations; worse at night & on awakening.
Progression:
- Abrupt.
Duration:
- Hours to less than 1 month, seldom longer.
Awareness:
- Reduced.
Alertness:
- Fluctuates; lethargic or hyper-vigilant.
Attention:
- Impaired, fluctuates.
Orientation:
- Impaired, fluctuates in severity.
Memory:
- Impaired - recent & immediate.
Thinking:
- Disorganized, distorted, fragmented, incoherent.
Perception:
- Distorted; delusions and hallucinations, difficulty distinguishing between reality and misperceptions.
*Can be caused by surgery or medication change.
*Much different than schizophrenia that is over a extended period of time and has a social isolation phase.
Dementia Features
Onset:
- Chronic, insidious.
Course:
- Long, symptoms progressive, yet stable over time, no diurnal effects.
Progression:
- Slow but even.
Duration:
- Months to years.
Awareness:
- Clear.
Alertness:
- Generally normal.
Attention:
- Generally normal.
Orientation:
- May be impaired.
Memory:
- Impaired – recent & remote.
Thinking:
- Thoughts impoverished, words difficult to find, poor judgement.
Perception:
- Misperceptions often absent.
*Most cognition is not intact, unlike delirium where it is.
Depression Features
Onset:
- Coincides with life changes, often abrupt.
Course:
- Diurnal effects (worse in morning), situational fluctuations.
Progression:
- Variable (rapid-slow).
Duration:
- At least 2 weeks, but can be months to years.
Awareness:
- Clear.
Alertness:
- Normal.
Attention:
- Minimal impairment, but distractible.
Orientation:
- Selective disorientation.
Memory:
- Selective or patchy.
Thinking:
- Selective or patchy Intact but with themes of hopelessness, helplessness or self-deprecation.
Perception:
- Intact; delusions and hallucinations absent except in severe cases.
*Gradual onset and the cognitive factors look more like disinterest unlike delirium.
Types of Delirium
- Hyperactive.
- Hypoactive.
- Mixed.
Hyperactive Delirium
- Restlessness, constant movement, agitation.
- Insomnia, hyper-vigilance, irritability, rapid speech.
- May be mistaken for schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, or agitated dement.
Hypoactive Delirium
- Slowing or lack of movement, paucity of speech (with or without prompting), unresponsiveness.
- May be mistaken for depression.
- Most common form of delirium.
- Associated with a higher mortality.
- Common form for the elderly.
- Difficult for clinicians to identify.
- Often mistaked for something else.
- Lowest survival rate (6 months).
Mixed Delirium
- Alternating hyperactive and hypoactive states.
-
Confusion Assessment Method Instrument (CAM) - Screening for Delirium Part #1
1. Acute Onset: Is there evidence of an acute change in mental status from the client's baseline?
2. Inattention: Did the client have difficulty focusing attention, for example, being easily distractible, or having difficulty keeping track of what was being said? (if present or abnormal: Did this behavior fluctuate during the interview, that is, tend to come and go or increase and decrease in severity; as well as describe the behavior).
3. Disorganized Thinking: Was the client's thinking disorganized or incoherent, such as rambling or irrelevant conversation, unclear or illogical flow of ideas, or unpredictable switching from subject to subject?
4. Altered Level of Consciousness: Overall, how would you rate this client's level of consciousness? (alert, vigilant, lethargic, stupor, coma, uncertain).
5. Disorientation: Was the client disoriented at any time during the interview, such as thinking that their was somewhere other than the hospital using the wrong bed, or misjudging the time of day?
6. Memory Impairment: Did the client demonstrate any memory problems during the interview, such as inability to remember events in the hospital or difficulty remembering instructions?
7. Perceptual Disturbances: Did the client have any evidence of perceptual disturbances (ex. hallucinations, illusions, or misinterpretations).
Confusion Assessment Method Instrument (CAM) - Screening for Delirium Part #2
8. Psychomotor Agitation & Retardation: A = At any time during the interview did the client have an unusually increased level of motor activity (ex. restlessness, picking bedclothes, tapping fingers, frequent sudden changes in position); B = At any time during the interview did the client have an unusually decreased level of motor activity (ex. sluggishness, staring into space, staying in one position)?.
9. Altered Sleep-Wake Cycle: Did the client have evidence of disturbance of the sleep-wake cycle (i.e. excessive daytime sleepiness with insomnia at night)?
*CAM ICU for patient's that can not respond.
*Scoring:
To have a + CAM result, the client must have:
1. Presence of acute onset and fluctuating course,
AND
2. Inattention,
AND EITHER
3. Disorganized thinking.
OR
4. Altered LOC.
Predisposing Factor's for Delirium (on admission)
- Demographic Characteristics (age of 65 or older; male sex).
- Cognitive Status (dementia, cognitive impairment, history of delirium, depression).
- Functional Status (functional dependence, immobility, low level of activity, history of falls0.
- Sensory Impairment (visual impairment, hearing impairment).
- Decreased Oral Intake (dehydration, malnutrition).
- Drugs (treatment with multiple psychoactive drugs, treatment with many drugs, alcohol abuse).
- Coexisting Medical Conditions (severe illness, multiple coexisting conditions, chronic renal or hepatic disease, history of stroke, neurological disease, metabolic derangements, fracture or trauma, terminal illness, infection with HIV).
Precipitating Factors of Delirium (developed due to hospitalization)
- Drugs (sedative hypnotics, narcotics, anticholinergic drugs, treatment with multiple drugs, alcohol or drug withdrawal).
- Primary Neurologic Diseases (stroke, intracranial bleeding, meningitis or encephalitis).
- Incurrent Illness (infections, latrogenic complications, severe acute illness, hypoxia, shock, fever or hypothermia, anemia, dehydration, poor nutritional status, low serum albumin level, metabolic derangements such as electrolyte, glucose, acid-base).
- Surgery (orthopedic surgery, cardiac surgery, prolonged cardiopulmonary bypass, noncardiac surgery).
- Environmental (admission to an intensive care unit, use of physical restraints, use of bladder catheter, use of multiple procedures, pain, emotional stress).
- Prolonged Sleep Deprivation.
Predisposing vs. Precipitating Factors for Delirium
*Can determine what patient's are at risk for delirium in the first 9 days of their stay.
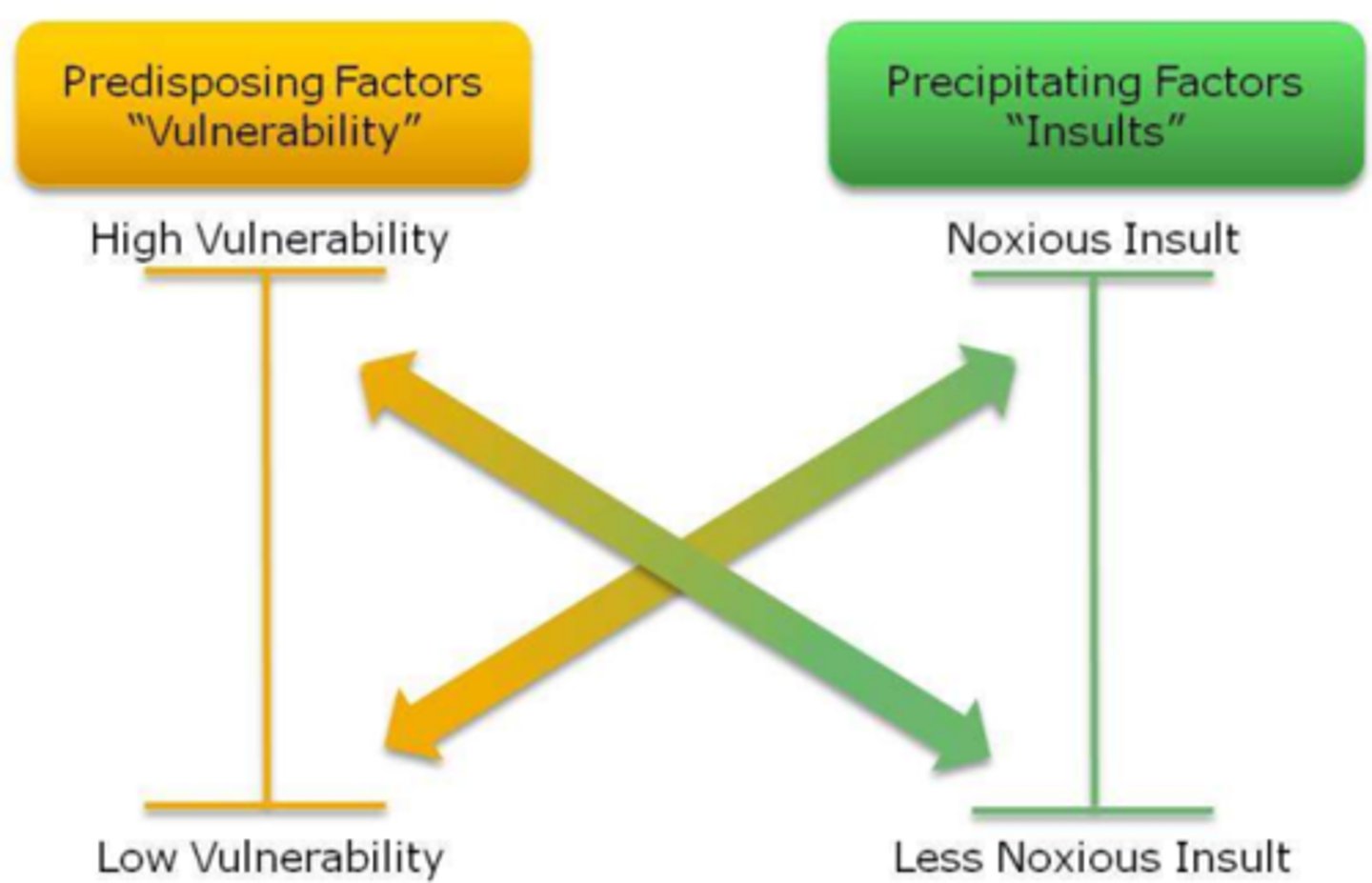
Multifactorial Model of Delirium
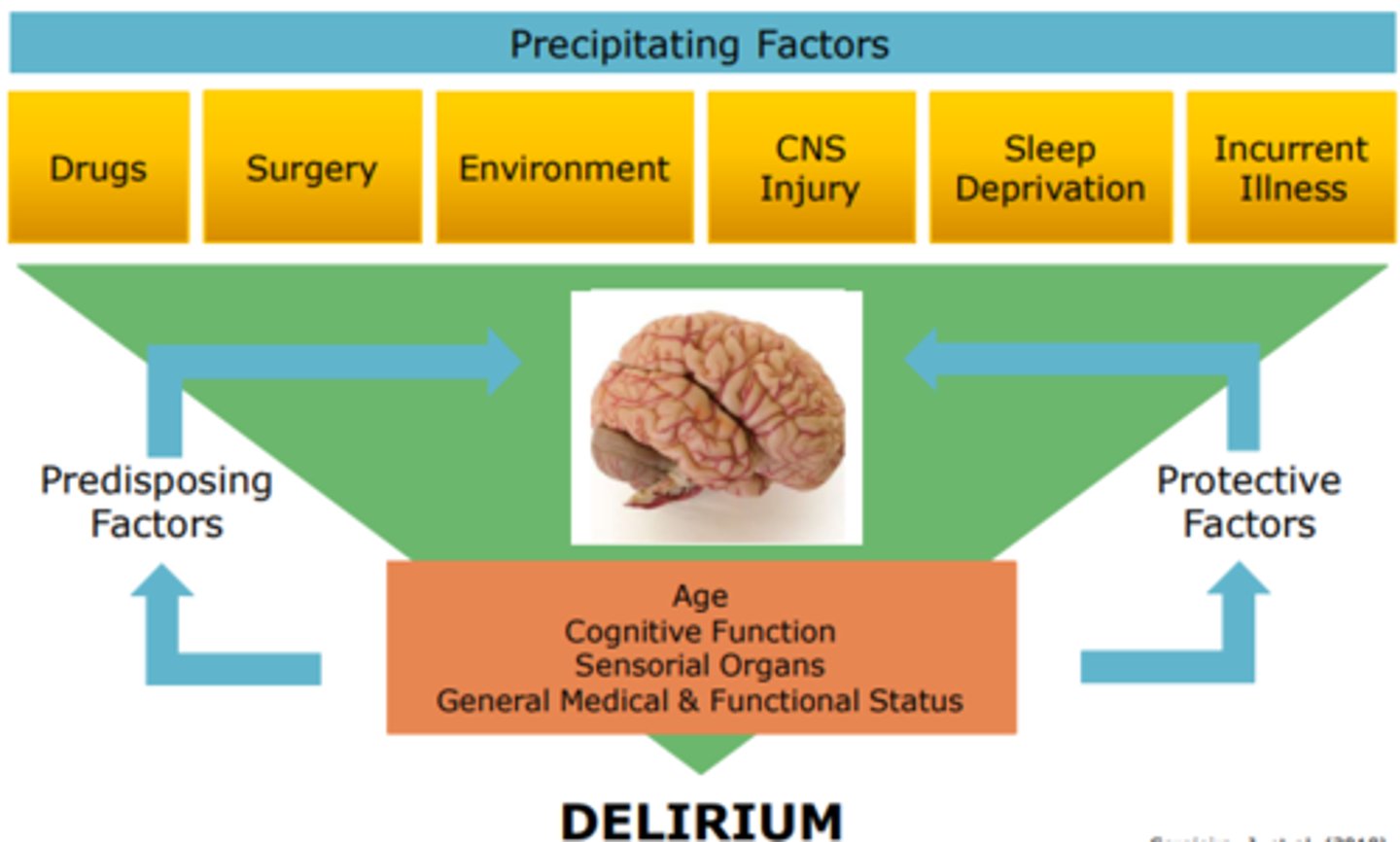
Pathophysiology of Delirium
*Poorly understood.
- Inattention and impaired cognition are difficult to define.
- Fluctuating course is a hallmark feature of the disease.
- Multiple and interacting risk factors.
- Inaccessibility of the central nervous system to scientific investigation.
- Link between physical stressors and delirium.
Hypothesis:
- Neuroinflammatory.
- Neurotransmitter dysregulation.
- Physiological stressors (ex. cortisol, hypoxia).
- Metabolic derangements (ex. metabolic acidosis such as elevated lactate, hyper/hypo glycemia, IGF1 such a neurotrophic peptide/decreased levels, hypercapnia).
- Electrolyte disorders (ex. sodium, calcium, magnesium).
- Genetic factors (ex. apolipoprotein E, glucocorticoid receptor, dopamine transporter or receptor, TLR-4).
*Pathophysiology of delirium remains unknown, however it is likely to involve more than one neurobiological mechanism*
Systemic Inflammation - Neuroinflammatory Hypothesis of Delirium
- Predominant feature of many surgical and medical conditions associated with delirium.
- Especially when tissue destruction or infection is involved.
Delirium - Neuroinflammatory Hypothesis of Delirium
- Clinical feature of sepsis, urinary tract infections, pneumonia, myocardial infarctions, fractures, etc.
All of these conditions share a common thread:
- Release and production of pro-inflammatory mediators into the systemic circulation.
- Strong link between delirium and inflammation.
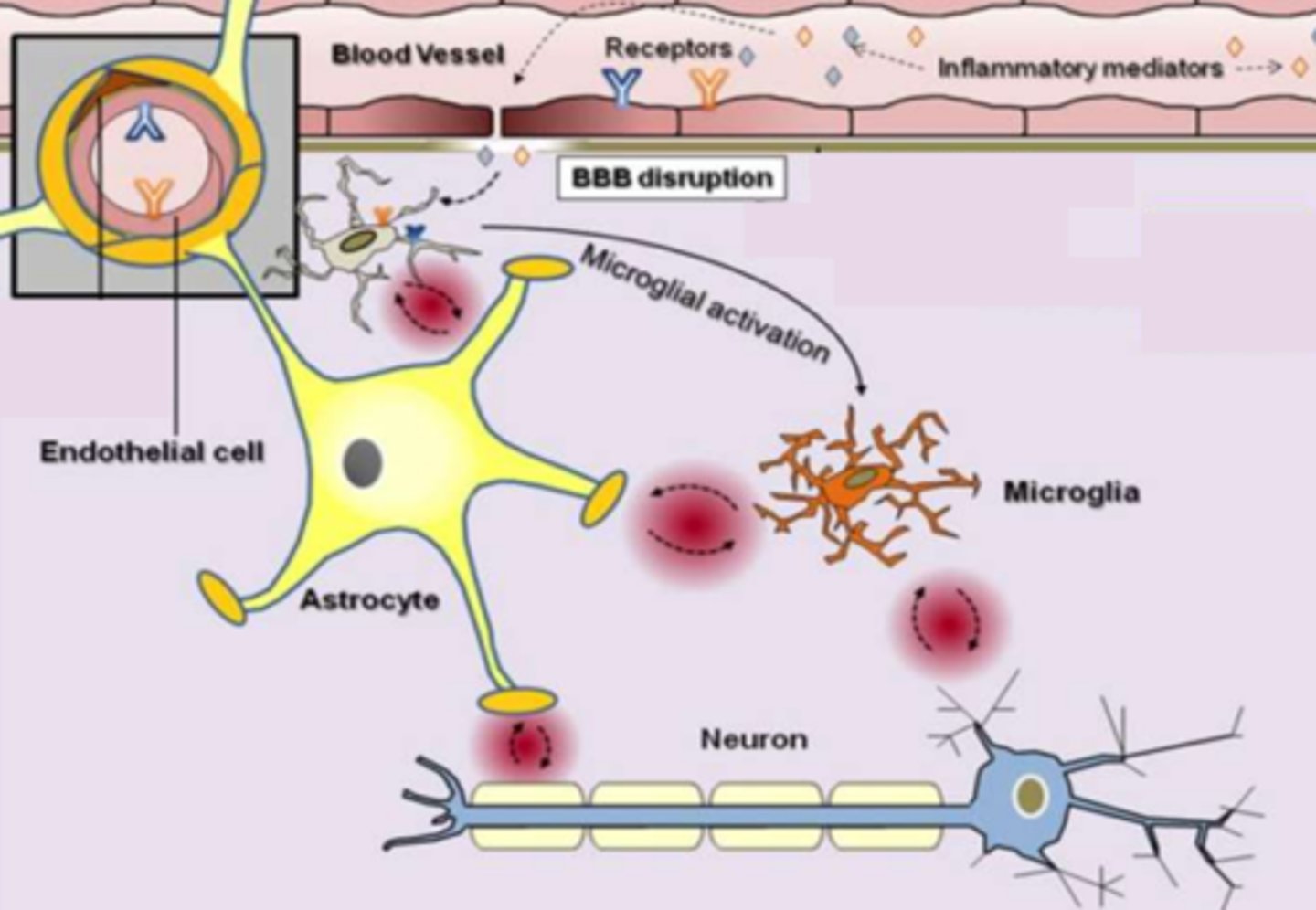
Neuroinflammatory Hypothesis of Delirium
- Delirious patients have higher blood plasma levels of inflammatory cytokines than patients without delirium.
- Provides an explanation as to how peripheral changes in the body may affect brain function and increase a patient's risk for developing delirium.
Offers insight as to why elderly patients are more vulnerable to delirium:
- Neuroanatomical studies revealed the presence of enlarged and damaged microglia in elderly non-delirious patients.
- Elderly brain may exist in a pro-inflammatory state that is "primed" and vulnerable to noxious insults.
Neuroinflammatory Hypothesis of Delirium Diagram
Acetylcholine - Cholinergic Hypothesis of Delirium
- Memory & cognition.
- Patients with delirium show reduced brain cholinergic activity.
- Anticholinergic drugs cause delirium in healthy adults and the elderly population.
Dopamine - Cholinergic Hypothesis of Delirium
- Inhibitory effect on cholinergic activity.
- Dopamine agonists induce delirium.
- Dopamine antagonists treat some of the symptoms associated with delirium.
Cholinergic Hypothesis of Delirium
- Many precipitating factors for delirium decrease acetylcholine synthesis in the brain (ex. hypoxia).
- High levels of serum anticholinergic activity are associated with an increased risk of delirium.
Neuroinflammatory & Cholinergic Hypothesis of Delirium
- Provide insight into the biological mechanisms that underlie delirium.
- However neither hypothesis can fully explain all of the characteristic features of delirium.
- This is because their are a combined heterogenous of factors affecting delirium, so it is unlikely that one neuro pathway is involved in it's development.
Delirium Prevention
*Targeted interventions reduce the risk of delirium in elderly hospitalized patients by 40%.
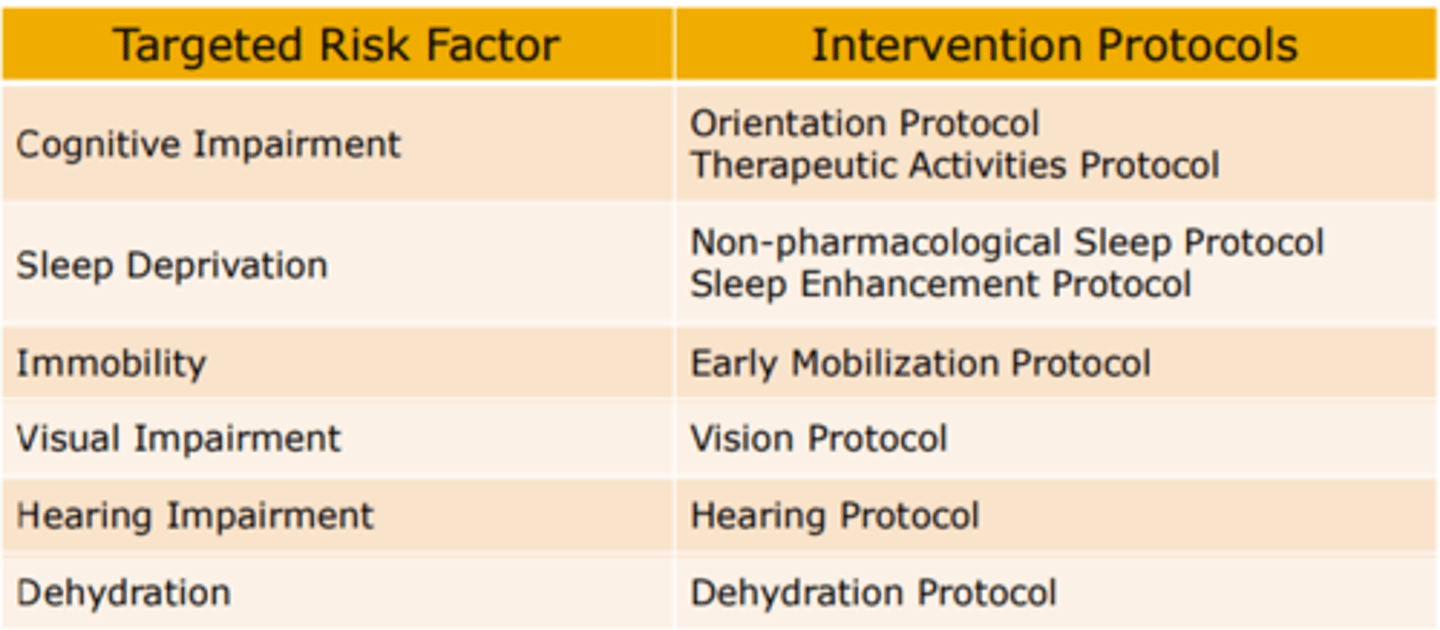
Cognitive Impairment - Delirium Prevention
Orientation Protocol:
- Board with names of care-team members and day's schedule; communication to reorient to surroundings.
Therapeutic Activities Protocol:
- Cognitively stimulating activities 3 times daily (ex. discussion of current events, structured reminiscence, or word games).
Sleep Deprivation - Delirium Prevention
Non-Pharmacological Sleep Protocol:
- At bedtime, warm drink (milk or herbal tea), relaxation tapes or music, and back massages.
Sleep Enhancement Protocol:
- Unit-wide noise-reduction strategies (ex. silent pill crushes, vibrating beepers, and quiet hallways) and schedule adjustments to allow sleep (ex. rescheduling of medications and procedures).
Immobility - Delirium Prevention
Early-Mobilization Protocol:
- Ambulation or active range-of-motion exercises 3 times daily; minimal use of immobilizing equipment (ex. bladder catheters or physical restraints).
Visual Impairment - Delirium Prevention
Vision Protocol:
- Visual aids (ex. glasses, magnifying lenses) and adaptive equipment (ex. illuminated telephone key pads, large print-books, and fluorescent tape on call bell), with daily reinforcement of their use.
Hearing Impairment - Delirium Prevention
Hearing Protocol:
- Portable amplifying devices, earwax dis-impaction, and special communication techniques, with daily reinforcement of these adaptions.
Dehydration - Delirium Prevention
Dehydration Protocol:
- Early recognition of dehydration and volume repletion (i.e. encouragement of oral intake of fluids).
Hospital Elder Life Program (HELP)
- Many seniors have problems with their memory, thinking and mobility while in hospital.
- The Hospital Elder Life Program (HELP) helps keep the mind and body as active as possible as a way to prevent delirium, a mental state that can cause confusion and restlessness.
- The HELP team consists of elder life specialists, elder life clinical nurse specialists, doctors, and specially-trained volunteers who engage with senior patients aged 75 or older who are at risk of delirium.
*At HHS
Common Modifiable Contributors - D.E.L.I.R.I.U.M.
- Drugs.
- Electrolyte disturbances.
- Lack of drugs.
- Infection.
- Reduced sensory input.
- Intracranial disorders.
- Urinary and fecal disorders.
- Myocardial and pulmonary disorders.
Drugs - Common Modifiable Contributors
Evaluation/Treatment:
- Newly initiated drugs, increased doses, interactions, OTC drugs, ETOH? Lower dose, discontinue or substitute.
Electrolyte Disturbances - Common Modifiable Contributors
Evaluation/Treatment:
- Assess and Tx dehydration, sodium imbalance and thyroid abnormalities.
Lack of Drugs - Common Modifiable Contributors
Evaluation/Treatment:
- Assess for withdrawal symptoms; minimize use of opioids.
Infection - Common Modifiable Contributors
Evaluation/Treatment:
- Evaluate and Tx urinary tract, resp and soft-tissue infections.
Reduced Sensory Input - Common Modifiable Contributors
Evaluation/Treatment:
- Address issues with vision and hearing.
Intracranial Disorders - Common Modifiable Contributors
Evaluation/Treatment:
- Consider infection, hemorrhage, stroke or tumor.
Urinary & Fecal Disorders - Common Modifiable Contributors
Evaluation/Treatment:
- Assess and Tx urinary retention and fecal impaction.
Myocardial & Pulmonary Disorders
Evaluation/Treatment:
- Assess and Tx MI, arrhythmia, HF, hypotension, anemia, exacerbation of COPD, hypoxia and hypercapnia.
Delirium Management Flowchart
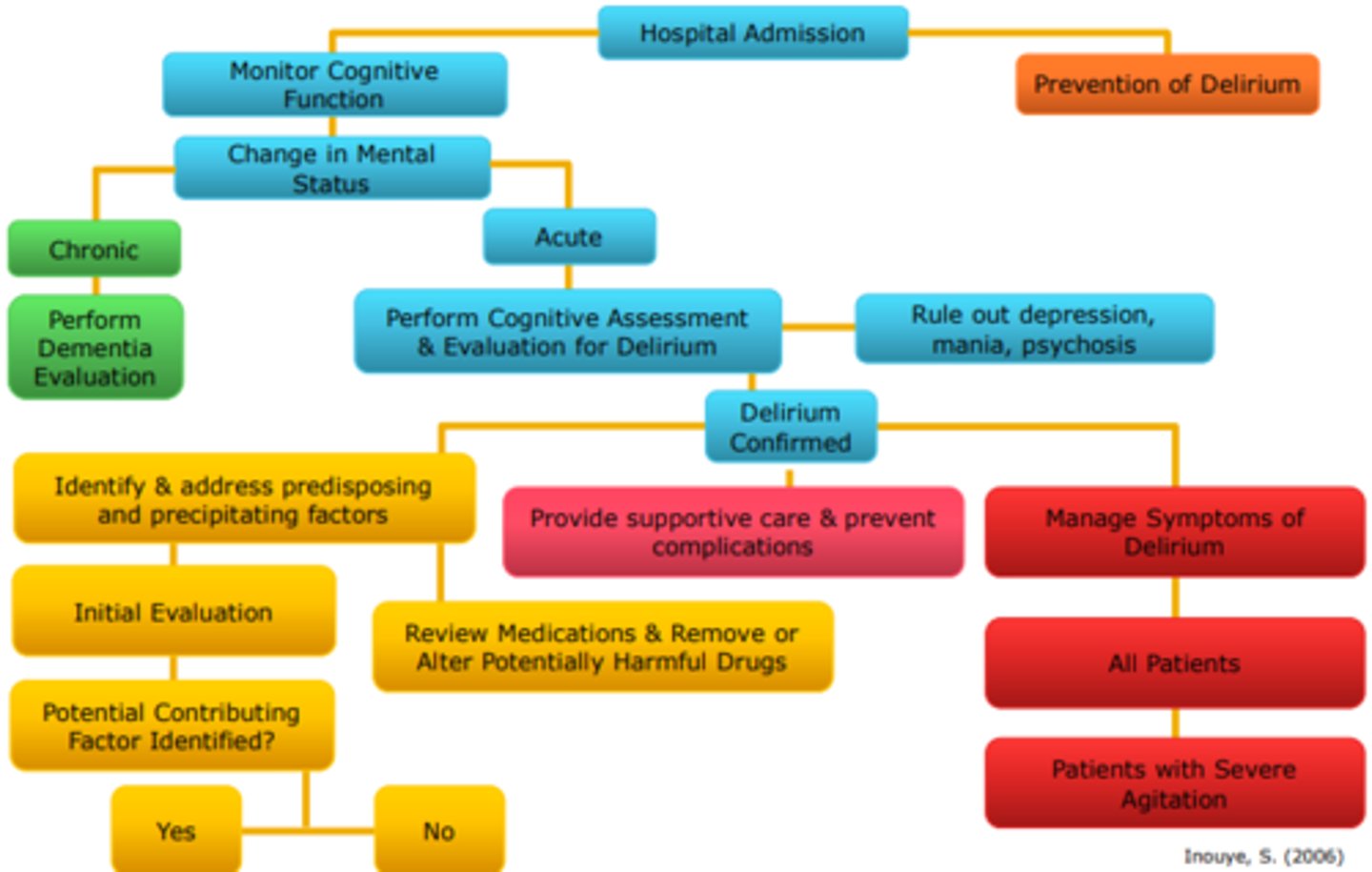
Delirium Management Flowchart Explanation
*Key strategies to prevent and control delirium in the elderly hospitalized admission.
*All patient should be woken at anytime to be evaluated for delirium.
Monitor Cognitive Function:
- Perform formal cognitive assessment.
- Establish baseline cognitive function and recent changes.
- Monitor patient for changes in mental status.
Prevention of Delirium:
- Address risk factors for delirium.
- Provide orienting communication.
- Encourage early mobilization.
- Use visual and hearing aids.
- Prevent dehydration.
- Provide uninterrupted sleep time.
- Avoid psychoactive drugs.
Prevent Complications:
- Protect airway, prevent aspiration.
- Maintain volume status.
- Provide nutritional support.
- Provide skin care, prevent pressure sores.
- Use mobilization, prevent deep venous thrombosis, pulmonary embolus.
Initial Evaluation:
- Obtain history (including alcohol and benzodiazepine use).
- Obtain vital signs.
- Perform physical and neurologic examination.
- Order selected laboratory tests.
- Search for occult infection.
Potential Contributing Factors Identified?
- Yes: Evaluate and treat as appropriate for each contributing factor.
- No: order laboratory tests (thyroid, drug levels, toxicology, ammonia and cortisol levels, vitamin B12, arterial blood gas levels; electrocardiography, neuroimaging, lumbar puncture, electroencephalography.
Nonpharmacologic Treatment Strategies for Delirium
- Continue delirium prevention.
- Reorient patient, encourage family involvement.
- Use sitters.
- Avoid use of physical restraints and Foley catheters.
- Use nonpharmacologic approaches for agitation: music, massage, relaxation techniques.
- Use of eyeglasses, hearing aids, interpreters.
- Maintain patient's mobility and self-care ability.
- Normalize sleep-wake cycle, discourage naps, aim for uninterrupted period of sleep at night.
- At night, have patient sleep in quiet room with low-level lighting.
Review Previous Medications
- Review the use of prescription drugs, as-needed drugs, over-the-counter drugs, herbal remedies.
- Identify psychoactive effects and drug interactions.
- Change to less noxious alternative for drugs.
- Lower their dose.
- Non-pharmacologic approaches for potentially harmful drugs.
Pharmacological Management of Delirium
Antipsychotic Drugs:
- Low dose haloperidol.
- Atypical antipsychotics (need to use careful judgement for dose and duration of this drug due to high death results with various populations).
- Increased risk of mortality with atypical antipsychotic drug use (physicians should prescribe with caution).
- Non-pharmacological therapies should always be attempted first.
- Reserve this approach for patients with severe agitation at risk for interruption of essential medical care (ex. intubation) or for patients who pose safety hazard to themselves or staff.
- Start low doses and adjust until effect achieved.
- Maintain effective dose for 2-3 days.
Delirium & Dementia
- Dementia is the leading predisposing risk factor for delirium.
- Dementia and delirium are associated with decreased cerebral blood flow, cholinergic deficiency and inflammation.
- 50% of delirium cases persist after discharge, from months to years.
- Delirium worsens dementia and accelerates the patient's loss of independence.
- May serve as an early warning sign of dementia.
- Use of restraints increases the risk for delirium in older people, especially with those with dementia.
Pathophysiology Textbook Chapter 15 Reading
Agnosia
- Defect of pattern recognition.
- It is a failure to recognize the form and nature of objects.
- Agnosia can be tactile, visual, or auditory, but generally only one sense is affected.
- Although agnosia is associated most with cerebrovascular accidents, it may arise from any pathological process that injures specific areas of the brain.
- Ex. An individual may be unable to identify a safety pin by touching it with a hand but is able to name it when looking at it.
Dysphasia
- Impairment of comprehension or production of language with impaired communication.
- Comprehension or use of symbols, in either written or verbal language, is disturbed or lost.
- Aphasia is a more severe form of dysphasia and an inability to communicate using language.
- Dysphasia results from dysfunction in the left cerebral hemisphere (i.e., Broca area [inferior frontal gyrus] and Wernicke area [superior temporal gyrus]) and the subcortical and cortical connecting networks; often due to cerebrovascular accident or vascular, neoplastic, traumatic, degenerative, metabolic, or infectious causes.
Area's of the Brain Mediating Cognitive Function
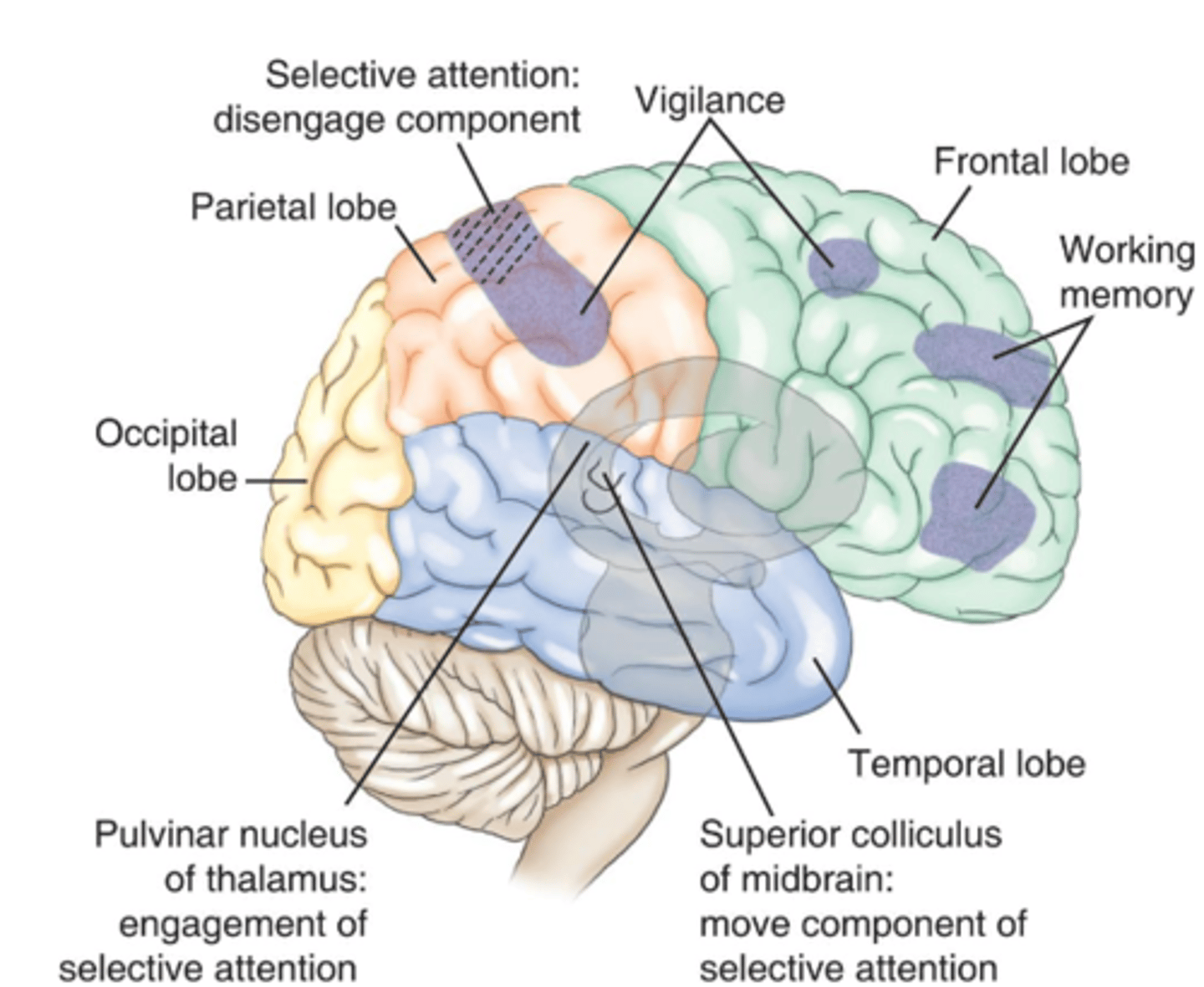
Expressive (Broca, non-fluent or motor aphasia) Dysphasia
Expression:
- Cannot find words, difficulty writing.
Verbal Comprehension:
- Relatively intact.
Repetition:
- Impaired.
Reading Comprehension:
- Variable.
Writing:
- Impaired.
Location of Lesion:
- Left posteroinferior frontal lobe (Broca area).
Cause of Lesion:
- Occlusion of one or several branches of left middle cerebral artery supplying inferior frontal gyrus.
Expressive (Transcortical motor, non-fluent dysphasia) Dysphasia
Expression:
- Halting speech.
Verbal Comprehension:
- Intact.
Repetition:
- Intact.
Reading Comprehension:
- Impaired.
Writing:
- Impaired.
Location of Lesion:
- Anterior superior frontal lobe.
Cause of Lesion:
- Occlusion at the border zone between two arterial territories.
Receptive (Wernicke, receptive fluent or sensory dysphasia) Dysphasia
Expression:
- Meaningless verbal language, inappropriate words or unable to monitor language for correctness so errors are not recognizedIntonation, accent, cadence, rhythm, and articulation normal.
Verbal Comprehension:
- Impaired; disturbance in understanding all language.
Repetition:
- Impaired.
Reading Comprehension:
- Impaired.
Writing:
- Impaired.
Location of Lesion:
- Left posterosuperior temporal lobe (Wernicke area).
Cause of Lesion:
- Occlusion of inferior division of left middle cerebral artery.
Receptive (Conductive dysphasia) Dysphasia
Expression:
- Difficulty repeating words, phrases spoken to them; naming is impaired.
Verbal Comprehension:
- Intact.
Repetition:
- Severely impaired.
Reading Comprehension:
- Variable.
Writing:
- Variable.
Location of Lesion:
- Inferior and posterior temporal lobe; parietotemporal junction.
Cause of Lesion:
- Occlusion in distributions of left middle cerebral artery.
Receptive (Anomic dysphasia) Dysphasia
Expression:
- Hesitancy, difficulty recalling names, objects, or numbers.
Verbal Comprehension:
- Intact.
Repetition:
- Impaired.
Reading Comprehension:
- Variable.
Writing:
- Intact except for anomia.
Location of Lesion:
- Left temporoparietal zones; arcuate fasciculus.
Cause of Lesion:
- Diffuse left hemisphere brain disease.
Receptive (Transcortical sensory, fluent dysphasia) Dysphasia
Expression:
- Repeats words and phrases spoken to them.
Verbal Comprehension:
- Poor.
Repetition:
- Intact.
Reading Comprehension:
- Impaired.
Writing:
- Impaired.
Location of Lesion:
- Posterior temporal lobe.
Cause of Lesion:
- Occlusion at the border zone between two cerebral arterial territories.
Transcortical (mixed motor and sensory, non-fluent) Dysphasia
Expression:
- Repeats words and phrases spoken to them.
Verbal Comprehension:
- Impaired.
Repetition:
- Intact.
Reading Comprehension:
- Impaired.
Writing:
- Impaired.
Location of Lesion:
Left cerebral hemisphere; spares the perisylvian cortex.
Cause of Lesion:
- Occlusion at the border zone between two cerebral arterial territories.
Global (non-fluent, summation of motor and sensory aphasia) Dysphasia
Expression:
- Mute.
Verbal Comprehension:
- Impaired.
Repetition:
- Impaired.
Reading Comprehension:
- Impaired
Writing:
- Impaired.
Location of Lesion:
- Large areas of the left cortex and subcortical regions.
Cause of Lesion:
- Occlusion of left middle cerebral artery of left internal carotid artery, tumours, other mass lesions, hemorrhage, embolic occlusion of ascending parietal or posterior temporal branch of middle cerebral artery.
Types of Dysphagia
- Expressive dysphasia (also known as Broca, motor, or non-fluent dysphasia) involves loss of ability to produce spoken or written language, with slow or difficult speech. Verbal comprehension is usually present.
- Dysarthria: Words cannot be spoken clearly because of cranial nerve damage or muscle impairment.
- Receptive dysphasia (also known as Wernicke, sensory, or fluent dysphasia) involves an inability to understand written or spoken language. Speech is fluent, flowing at a normal rate, but words and phrases have no meaning.
- Anomic aphasia is a sensory aphasia distinguished by difficulty finding words and naming a person or object.
- Conductive Dysphasia: Auditory comprehension is present in conductive dysphasia, but there is impaired verbatim repetition.
- Transcortical Dysphasia's: Are rare and can be motor, sensory, or mixed. They involve areas of the brain that connect into the language centers.
- Global Dysphasia: The most severe dysphasia and involves both expressive and receptive dysphasia. The individual is non-fluent or mute; cannot read or write; and has impaired comprehension, naming, reading, and writing.
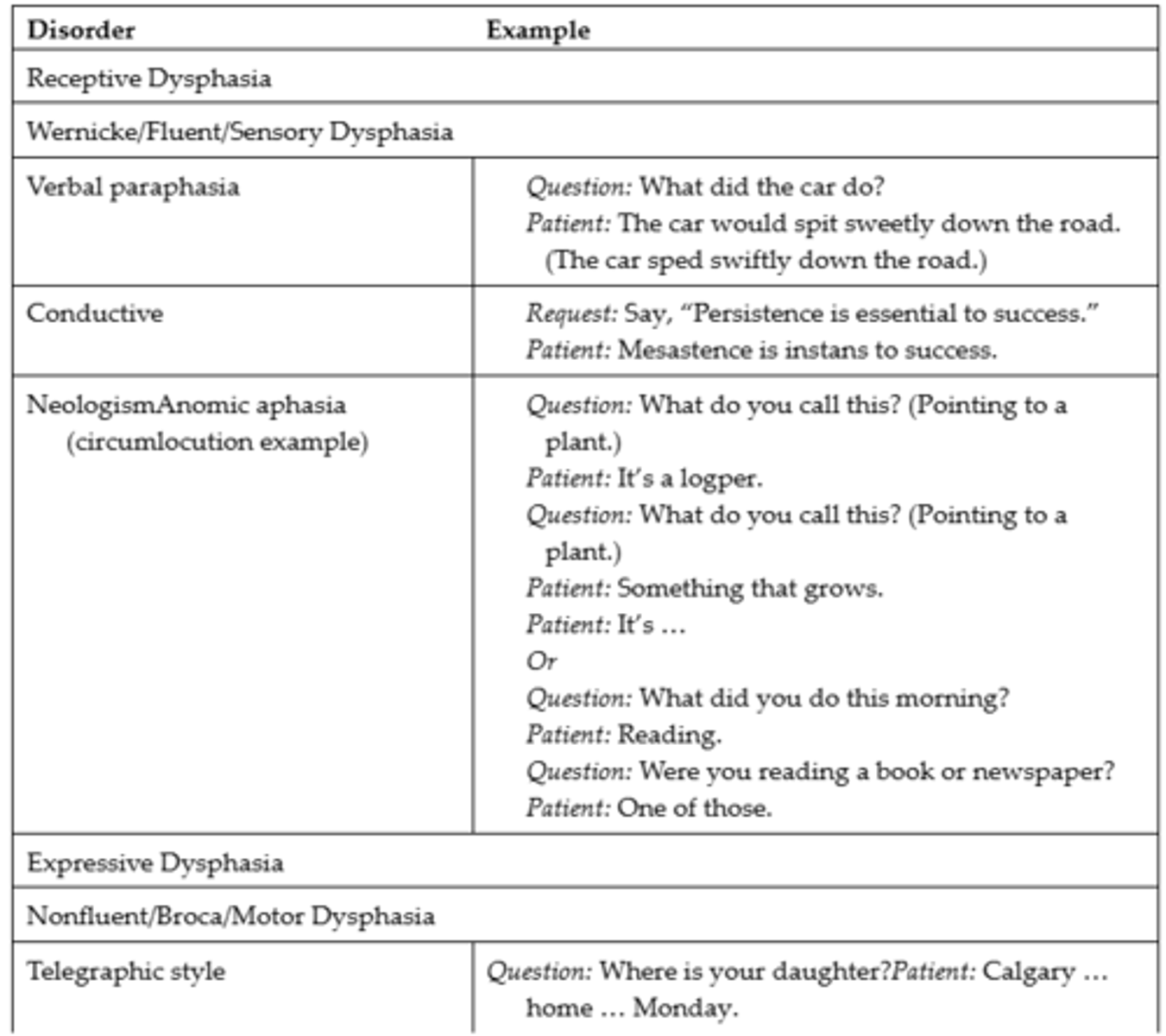
Expressive Dysphasia

Examples of Dysphasia
Acute Confessional States
- Acute organic brain syndromes.
- Are transient disorders of awareness and may have either a sudden or a gradual onset.
- Delirium is a type.
- Causes include drug intoxication, alcohol or drug withdrawal; metabolic disorders (e.g., hypoglycemia, thyroid storm); brain trauma or surgery; post anesthesia; febrile illnesses or heat stroke; electrolyte imbalance, dehydration; heart, kidney, or liver failure.
- Acute confusional states arise from disruption of a widely distributed neural network. This network involves the reticular activating system of the upper brainstem and its projections into the thalamus, basal ganglion, and specific association areas of the cortex and limbic areas.
Delirium
- Hyperactive confusional state.
- Associated with autonomic nervous system overactivity.
- This condition typically develops over 2 to 3 days.
- It most commonly occurs in Critical Care Units, following surgery, or during withdrawal from CNS depressants (i.e., alcohol or narcotic agents).
- Delirium is associated with right-upper middle-temporal gyrus or left temporal-occipital junction disruption, and several neurotransmitters (i.e., acetylcholine and dopamine) are involved.
- Most metabolic disturbances (i.e., hypoglycemia, thyroid disorders, liver, or kidney disease) that produce delirium interfere with neuronal metabolism or synaptic transmission.
- Many drugs and toxins also interfere with neurotransmission function at the synapse.
Excited Delirium Syndrome (ExDS)
- Agitated delirium.
- A type of hyperkinetic delirium that can lead to sudden death.
- Its symptoms include altered mental status, combativeness, aggressiveness, tolerance to significant pain, rapid breathing, sweating, severe agitation, elevated temperature, noncompliance, or poor awareness in following direction, inability to become fatigued, unusual or superhuman strength, and inappropriate clothing for the current environment.
Hypoactive Delirium
- Hypoactive confusional state.
- More likely to be associated with right-sided frontal-basal ganglion disruption.
- This condition may occur in individuals who have fevers or metabolic disorders (i.e., chronic liver or kidney failure) or who are under the influence of CNS depressants.
- The individual exhibits decreases in mental function, specifically alertness, attention span, accurate perception, interpretation of the environment, and reaction to the environment.
- Forgetfulness and apathy are prominent, speech may be slow, and the individual dozes frequently.
Clinical Manifestations of Delirium
- Delirium initially manifests as difficulty in concentrating, restlessness, irritability, insomnia, tremulousness, and poor appetite.
- In a fully developed delirium state, the individual is completely inattentive, and gross alteration of perceptions occurs with extensive misperception and misinterpretation.
- The person appears distressed and often perplexed. Conversation is incoherent. Frank tremor and high levels of restless movement are common. Violent behaviour may be present. The individual cannot sleep, experiences flushing, has dilated pupils, a rapid pulse rate (tachycardia), elevated temperature, and profuse sweating (diaphoresis).
*Normally lasts 2-3 days, but can last weeks.
Goals for Treatment of Delirium
- Establish that the individual is confused.
- Determine the cause of the confusion (organic or functional).
- The next step is to differentiate whether the confusion is delirium or an underlying dementia (individuals with dementia are at increased risk of developing delirium).
- A complete history, physical examination, and laboratory tests (electrocardiogram and blood, urine, cerebrospinal fluid [CSF], and radiological studies) are needed.
- Several assessment scales are available to guide evaluation (such as Clinical Assessment of Confusion A and B, Confusion Assessment Method for the Intensive Care Unit [CAM-ICU], and Intensive Care Delirium Screening Checklist).
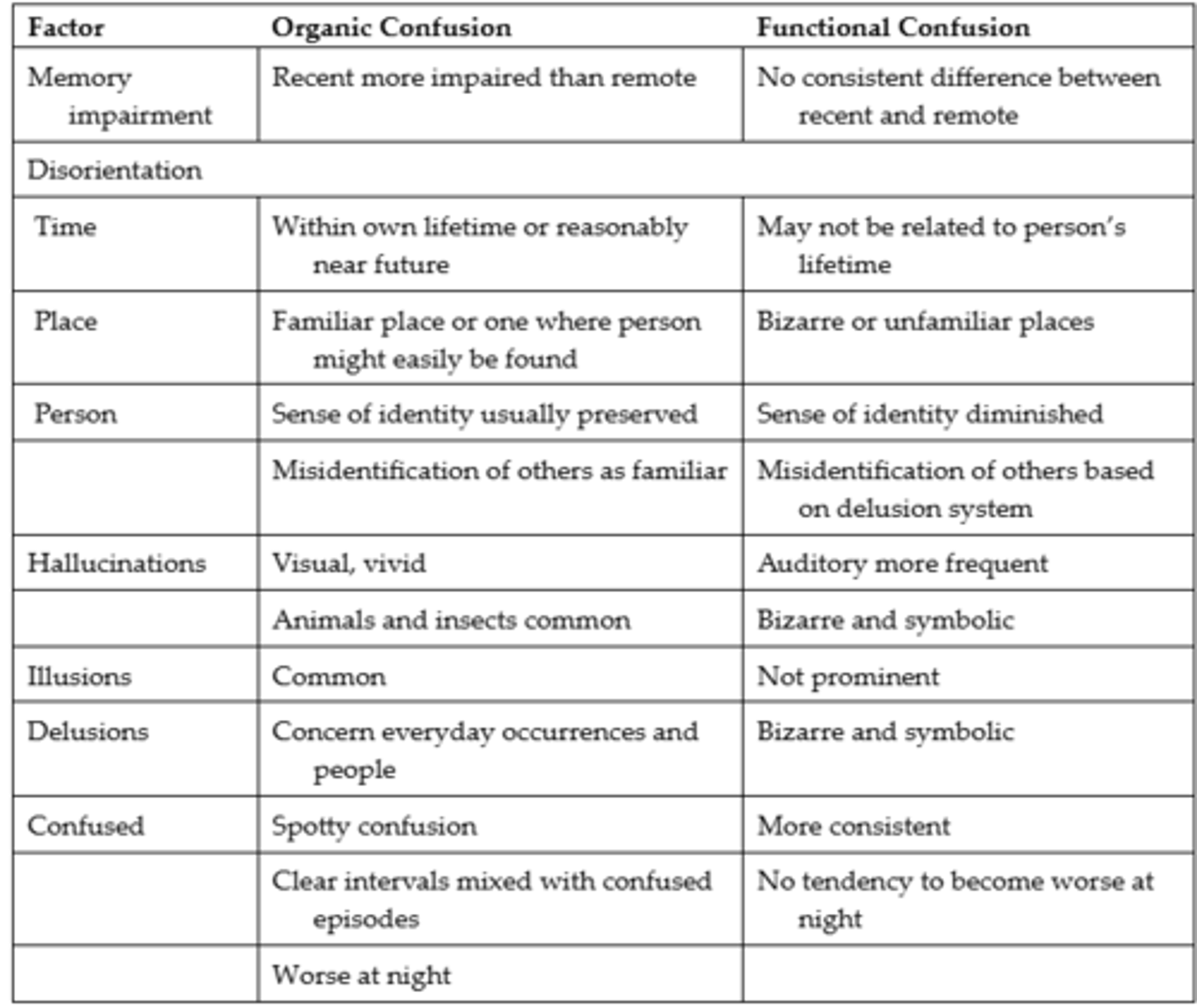
Differences Between Organic & Functional Confusion
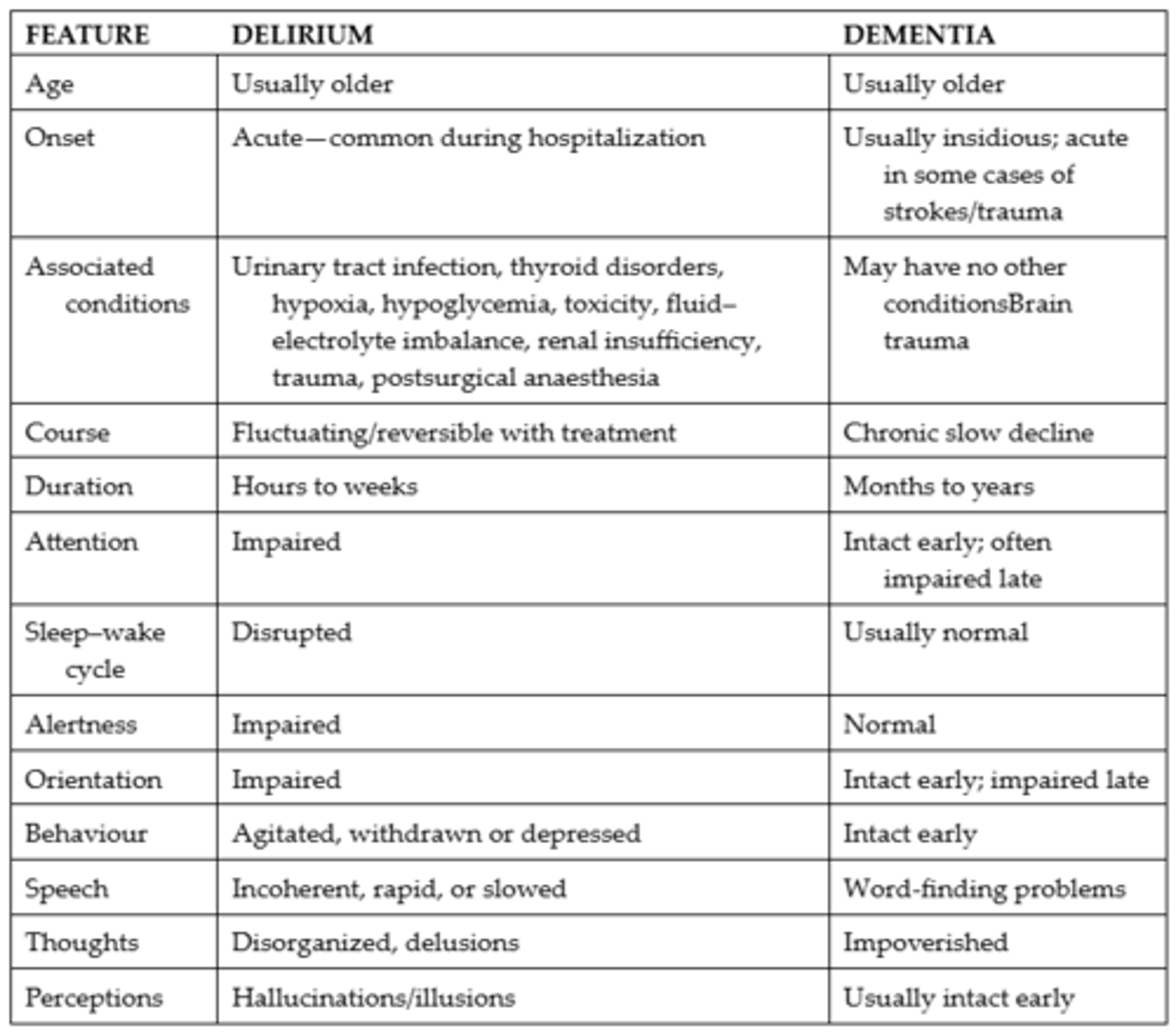
Delirium vs. Dementia
Dementia
- An acquired deterioration and a progressive failure of many cerebral functions.
- Symptoms include impairment of intellectual processes with a decrease in orienting, memory, language, judgement, and decision making.
- Examples of these alterations include agitation, wandering, and aggression.
- Mechanisms leading to dementia include neuron degeneration, compression of brain tissue, atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels, brain trauma, Alzheimer's. Huntington's, Parkinson's, HIV, and Creutzfeldt-Jakob.
- Evaluation of individuals with clinical manifestations of dementia should include laboratory and neuropsychological testing to identify underlying conditions that may be treatable.
Alzheimer's Disease - Clinical Manifestations of the Major Degenerative Dementia's
First Symptom:
- Memory loss; impaired learning.
Mental Status:
- Episodic memory loss.
Neurobehaviour:
- Initially normal, progressive cognitive impairment.
Neurological Examination:
- Initially normal.
Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease - Clinical Manifestations of the Major Degenerative Dementia's
First Symptom:
- Dementia, mood, anxiety, movement disorders.
Mental Status:
- Variable, frontal/executive, focal cortical, memory.
Neurobehaviour:
- Depression, anxiety.
Neurological Examination:
- Myoclonus, rigidity, parkinsonism.
Dementia with Lewy Body - Clinical Manifestations of the Major Degenerative Dementia's
First Symptom:
- Visual hallucinations; delusions that family members/friends are someone else; REM sleep disorder; delirium; parkinsonism.
Mental Status:
- Drawing and frontal/executive; spares memory; delirium prone.
Neurobehaviour:
- Visual hallucinations, depression, sleep disorder, delusions.
Neurological Examination:
- Parkinsonism.
Frontotemporal Dementia - Clinical Manifestations of the Major Degenerative Dementia's
First Symptom:
- Apathy; poor judgement/reasoning, speech/language.
Mental Status:
- Frontal/executive, language; spares drawing.
Neurobehaviour:
- Apathy, decline in person or social conduct, euphoria, depression.
Neurological Examination:
- Due to PSP/CBD overlap; vertical gaze palsy, axial rigidity, dystonia, alien hand.
Vascular Dementia - Clinical Manifestations of the Major Degenerative Dementia's
First Symptom:
- Often but not always sudden, usually within 3 months of a stroke; variable: apathy, falls, focal weakness.
Mental Status:
- Frontal/executive, cognitive slowing; memory can be intact.
Neurobehaviour:
- Apathy, delusions, anxiety.
Neurological Examination:
- Usually motor slowing; can be normal.
Alzheimer's Disease (AD)
- The leading cause of severe cognitive dysfunction in older adults. The three forms of AD are nonhereditary sporadic or late-onset AD (70 to 90%), early-onset familial AD (FAD), and early-onset AD (very rare).
- Early-onset FAD has been linked to three genes with mutations on chromosome 21.
- Late-onset AD may be related to the involvement of chromosome 19 with the apolipoprotein E gene-allele 4.
- Sporadic late-onset AD is the most common form and does not have a specific genetic association.
- Failure to process and clear amyloid precursor protein results in the accumulation of toxic fragments of amyloid beta protein. This accumulation leads to formation of diffuse neuritic plaques, disruption of nerve impulse transmission, and death of neurons.
- The loss of neurons results in brain atrophy with widening of sulci and shrinkage of gyri.
- Loss of synapses, acetylcholine, and other neurotransmitters contributes to the decline of memory and attention, and to the loss of other cognitive functions associated with AD.
- The clinical history, including mental status examinations (Mini-Mental Status Examination, clock drawing, and Geriatric Depression Scale), laboratory tests, brain imaging of structure, blood flow and metabolism, and the course of the illness (which may span 5 years or more), is used to assess progression of the disease.
Cognitive Stage - Progression of Alzheimer's Disease
Mild Cognitive Impairment:
- Mild memory loss.
Early Stage:
- Measurable short-term memory loss; difficulty with word finding; other cognition problems compared with previous behaviour.
Middle Stage:
- Moderate to severe cognitive problems: impaired reasoning, judgement, and problem solving; disorientation to time, place, and person; difficulty planning and organizing; progressive memory loss.
Late Stage:
- Little cognitive ability; language not clear.
End Stage:
- No significant cognitive function; loss of orientation to self.
Functional Stage - Progression of Alzheimer's Disease
Mild Cognitive Impairment:
- Possibly depression (versus apathy); mild anxiety.
Early Stage:
- Mild IADL problems.
Middle Stage:
- IADL-dependent; some ADL problems.
Late Stage:
- ADL-dependent; incontinent.
End Stage:
- Nonambulatory/bedbound; unable to eat related to failure to sense hunger or thirst, difficulty swallowing.
Risk Factors Associated with Alzheimer's Disease
- Diabetes.
- Hypertension.
- Obesity.
- Smoking.
- Depression.
- Cognitive inactivity or low education.
- Physical inactivity.
- Poor diet.
- High alcohol intake.
- Head injuries.
- Hearing loss.
- Social isolation.
*Main characteristics include the person, the lifestyle, the environment, and genetic background.
Treatment for Impaired Cognitive Function
- These devices include memory aids; maintaining unimpaired cognitive functions; and maintaining or improving the general state of hygiene, nutrition, and health.
Frontotemporal Dementia (FTD)
- Known as Pick Disease.
- A degenerative disease of the frontal and anterior frontal lobes.
- Most cases involve mutations of genes encoding tau protein.
- There are three distinct clinical syndromes identified in frontotemporal degeneration, depending on the site of atrophy: (1) behavioral variant of FTD, (2) progressive non-fluent aphasia, and (3) semantic dementia.
- No specific treatment.
Seizure
- A sudden, transient disruption in brain electrical function caused by abnormal excessive discharges of cortical neurons.
- Causes for seizures includes metabolic disorders, congenital malformations, genetic predisposition, perinatal injury, postnatal trauma, myoclonic syndromes, infection, brain tumour, vascular disease, and medication or alcohol abuse.
- Factor's that lower the threshold for seizures include hypoglycemia, fatigue, or lack of sleep, emotional or physical stress, fever, large amounts of water ingestion, constipation, use of antipsychotic medications (i.e., chlorpromazine [Largactil] and clozapine [Clozaril]) especially when combined with alcohol, withdrawal from depressant medications (including alcohol), or hyperventilation (respiratory alkalosis).
Epilepsy
- The recurrence of seizures and a type of seizure disorder for which no underlying, correctable cause for the seizure can be found.
Convulsion
- Used to describe seizures and refers to the tonic-clonic (jerky, contract-relax) movement associated with some seizures.