Chapter 33: Invertebrates
1/114
Earn XP
Description and Tags
This set of flashcards covers key vocabulary and concepts from the lecture on invertebrates, including various phyla, anatomical features, and developmental processes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
115 Terms
Invertebrates
Animals that lack a backbone and account for 95% of known animal species.
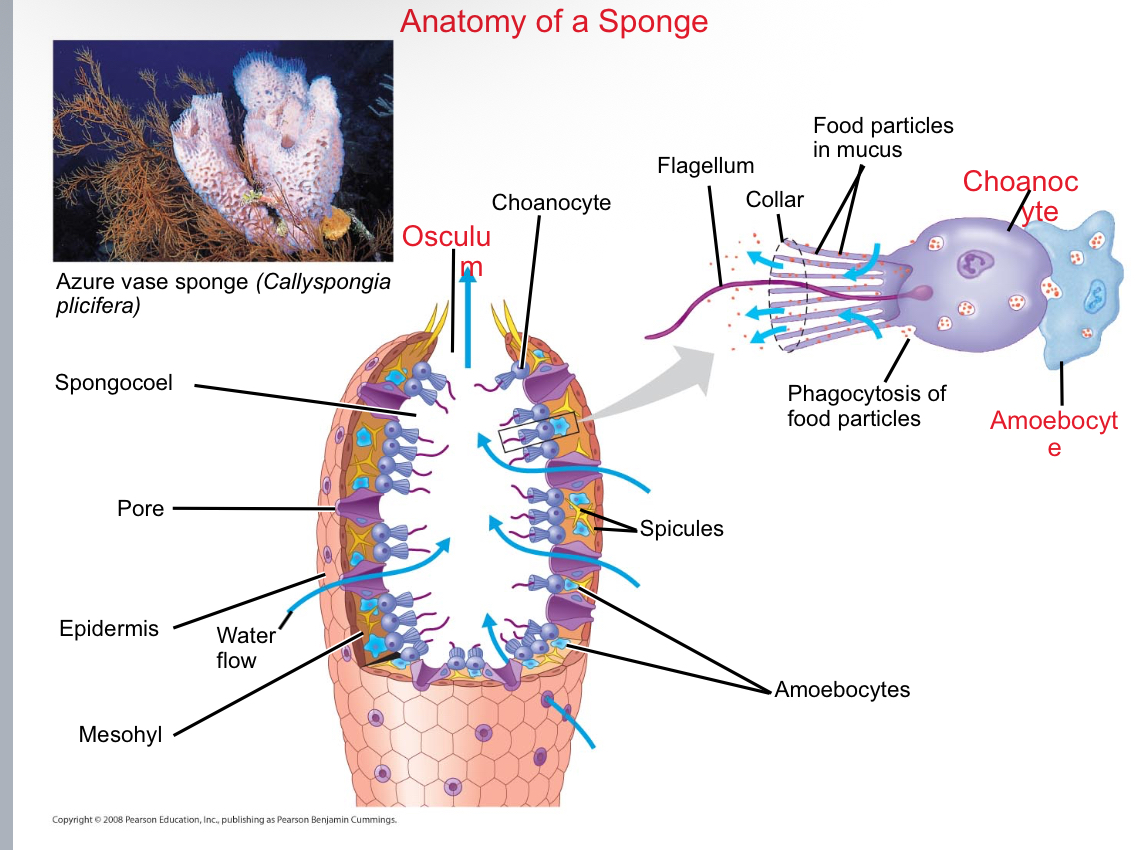
Sponges
Sedentary animals from the phyla Calcarea and Silicea with no true tissues or body symmetry
What type of feeders are sponges?
Suspension feeders
Suspension feeders
Capturing food particles suspended in the water that pass through their body
Ambeocytes
Found in the mesohyl and play roles in digestion and structure within a sponge
Hermaphrodites
The ability of an individual to function as both male and female
Cnidaria
An ancient phylum of eumetazoans characterized by a sac-like body plan with a central digestive cavity.
What are included in Cnidarians?
Jellies, corals, and hydras,
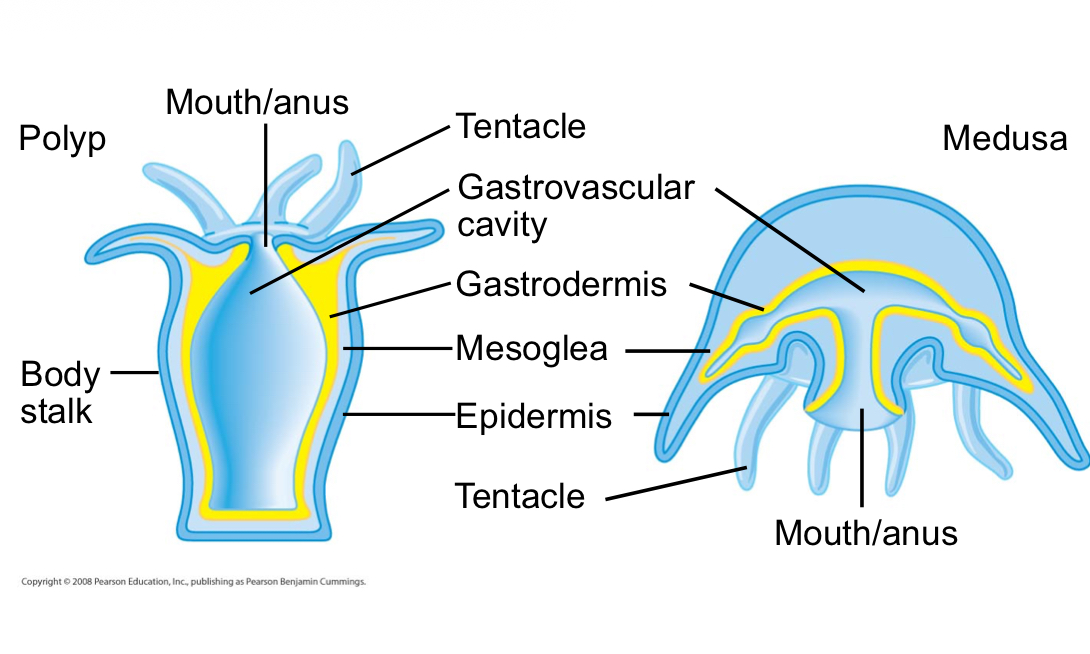
The two variations on the body plan of a cnidarian are:
The sessile polyp and motile medusa
Phylum Cnidaria is divided into four major classes:
Hydrozoa, Scyohozoa, Cubozoa, Anthozoa

Hydrozoa
Mostly marine, few freshwater, both polyp (often colonial) and medusa stages in most species
What are examples of Hydrozoans?
Portuguese man-of-wars, hydras, Obelia, some corals

Scyphozoa
All marine, polyp stage is absent or reduced, free-swimming, medusae up to 2 m in diameter
What are included in Scyphozaos?
Jellies (prevalent form of the life cycle), sea nettles

Cubozoa
All marine, box-shaped medusae, complex eyes, potent venom
What are examples of Cubozoa?
Box jellies, sea wasps

Anthozoa
All marine, medusa stage is completely absent, most sessile, many colonial
What are examples of Anthozoa?
Sea anemones, most corals, sea fans (only occurring as polyps)
Spongocoel
A central cavity in sponges through which water flows.
Choanocytes
Flagellated collar cells in sponges that generate a water current and capture food particles.
Osculum
The opening of a cavity
Ectoprocta
A phylum of lophophorates that comprises colonial animals resembling plants.
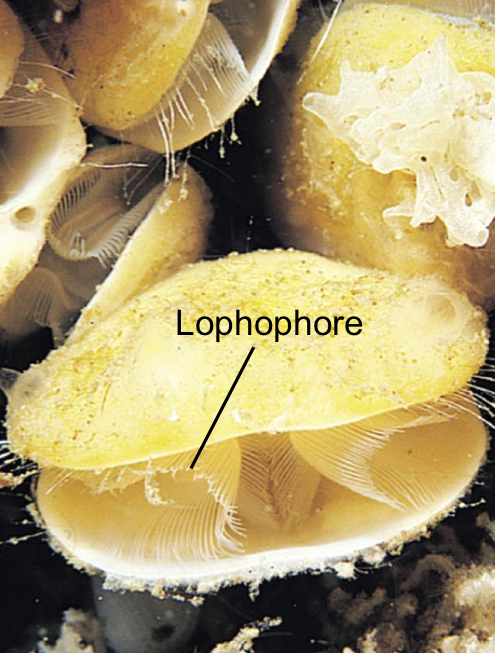
Lophophore
A horseshoe-shaped, suspension-feeding organ with ciliated tentacles found in lophophorates.
Lophophorates include two phyla:
Ectoprocta, Brachiopoda
What encases the colony of Lophophorates?
A hard exoskeleton and some are reef builders
Flatworms
Soft-bodied invertebrates (acelomates) that are flattened dorsoventrally and have a gastrovascular cavity
Where does gas exchange take place in Flatworms?
Across the surface
Protonephridia
Regulating the osmotic balance in a flatworm
Where do members of phylum Platyhelminthes (flatworms) live?
Marine, freshwater, and damp terrestrial habitats
Flatworms are divided into four classes:
Turbellaria, Monogenea, Trematoda, Cestoda
Turbellaria
Marine, mostly free-living flatworms
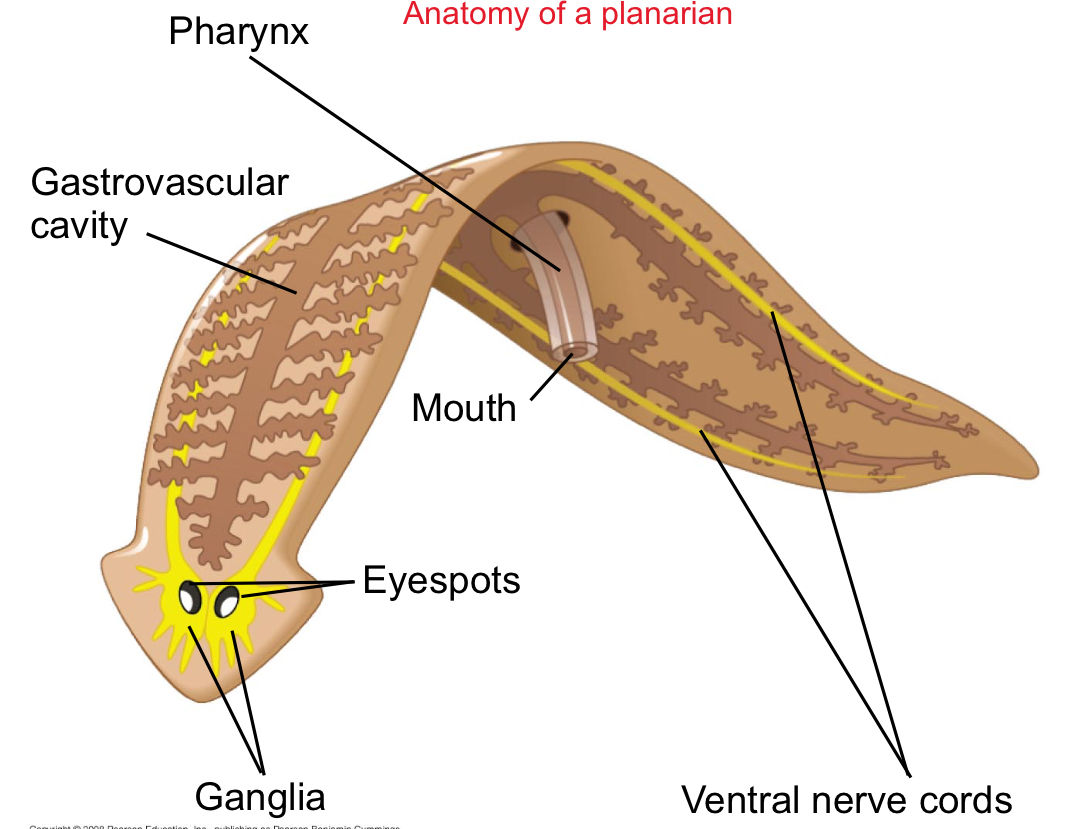
Planarians
Best-known turbellarians that have light-sensitive eye spots and centralized nerve nets
Planarians can reproduce:
Sexually or asexually through fission
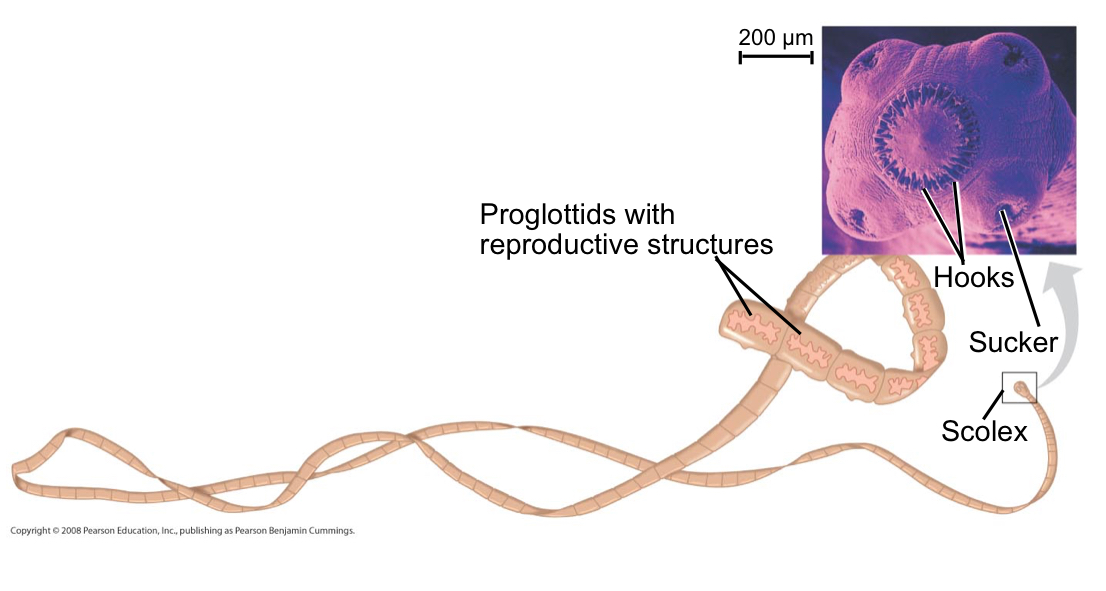
Tapeworms
Parasites of vertebrates that lack a digestive system
Tapeworms absorb nutrients from:
The host’s intestine
What leaves the host’s body in feces from tapeworm?
Fertilized eggs produced by sexual reproduction
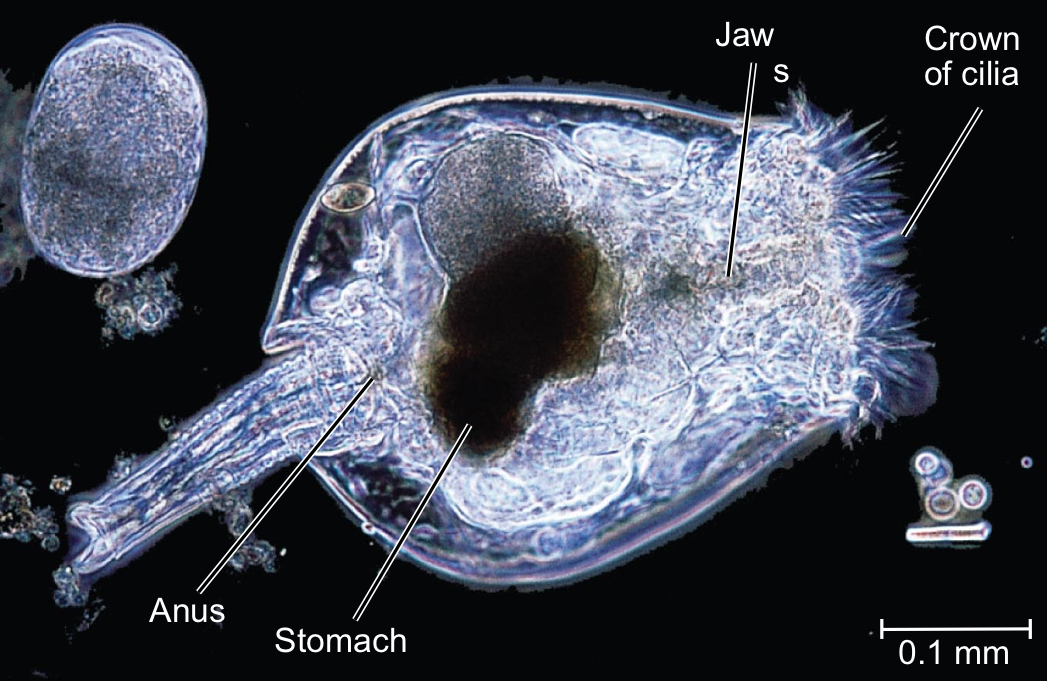
Rotifere (phylum Rotifera)
Tiny animals that inhabit fresh water, the ocean, and damp soil and are multicellular with specialized organ systems
Alimentary canal
A digestive tube with a separate mouth and anus that lies within a fluid-filled pseudocoelom in Rotifers
Rotifers reproduce by:
Parthenogenesis
Parthenogenesis
Females producing offspring from unfertilized eggs
Molluscs
Soft-bodied animals, most protected by a hard shell, are marine, inhabit freshwater, or are terrestrial
Which of the following is a typical characteristic of molluscs?
A rasping organ called the radula
Phylum Mollusca include:
Snails and slugs, oysters and clams, and octopuses and squids
All molluscs have a similar body plan with three main parts are:
Muscular foot, Visceral mass, Mantle (water-filled)
Four major classes of molluscs:
Polyplacophora, Gastropoda, Bivalvia, Cephalopoda
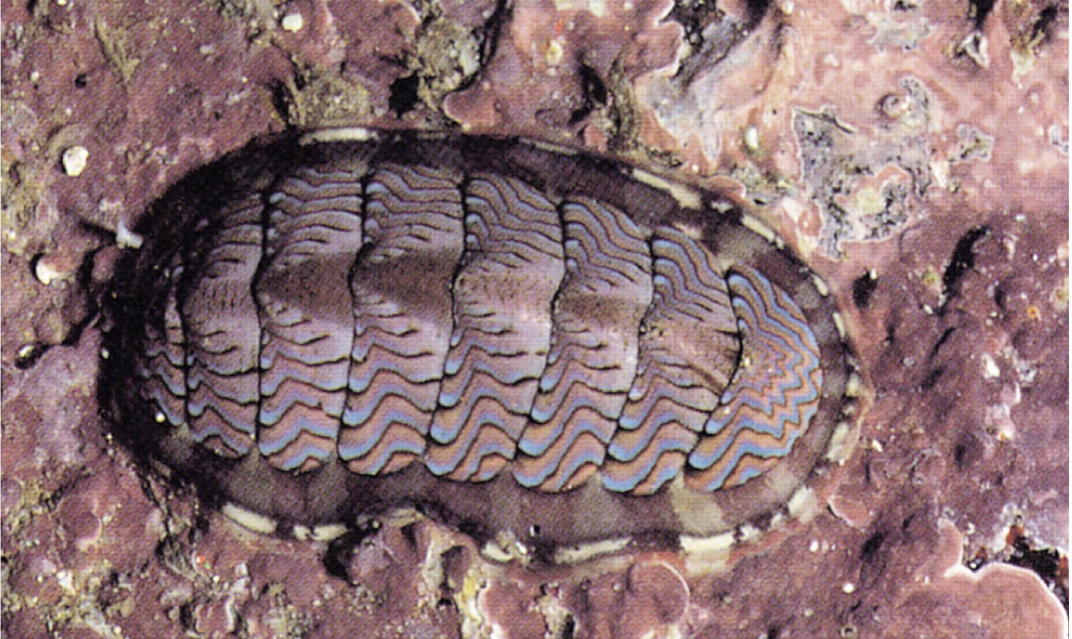

Polyplacophora
Chitons
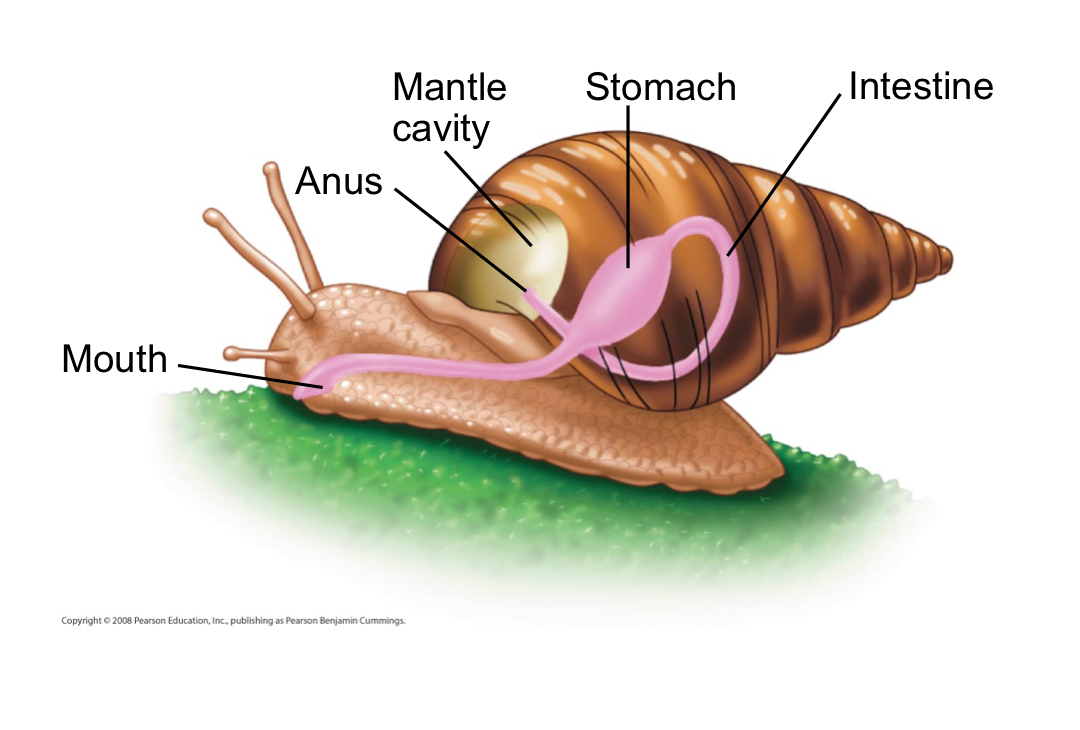
Gastropods
Mostly marine, but many are fresh water and terrestrial species, most have a single, spiraled shell
Torsion
The most distinctive characteristic of gastropods that causes the animal’s anus and mantle to end up above its head
Hirudin
A chemical secreted by leeches that prevents blood from coagulating.
Ecdysis
The process of molting the outer cuticle in ecdysozoans as they grow.
Metamorphosis
A developmental process in insects where they undergo changes in body form, including larval and adult stages.
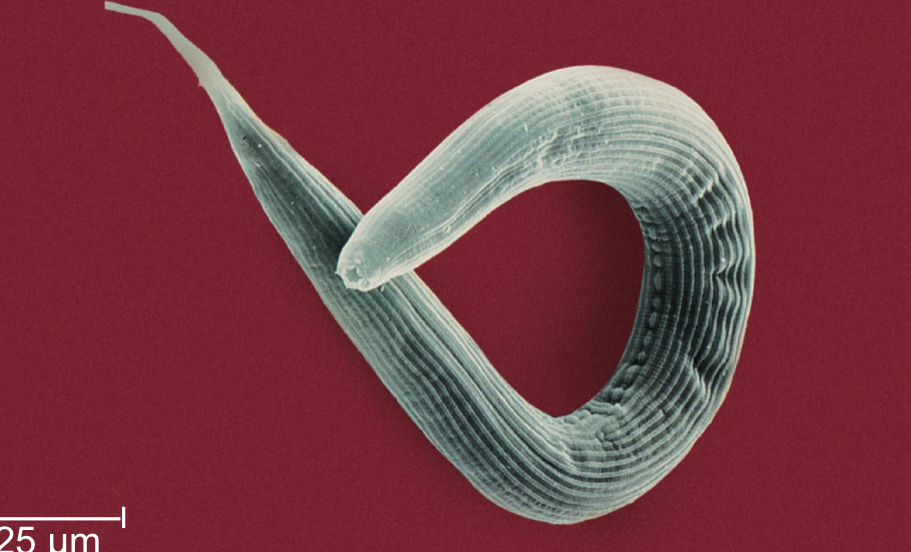
Nematodes
Roundworms that are typically found in various habitats
Where are nematodes found in?
Most aquatic habitats, in the soil, moist tissues of plants, body fluids, and tissues of animals
Nematodes have a:
An alimentary canal but no circulatory system.
How do Nematodes reproduce?
Through sexual reproduction by internal fertilization
Where are the parasitic nematode Trichinella spiralis located?
Usually encysted in human muscle tissue
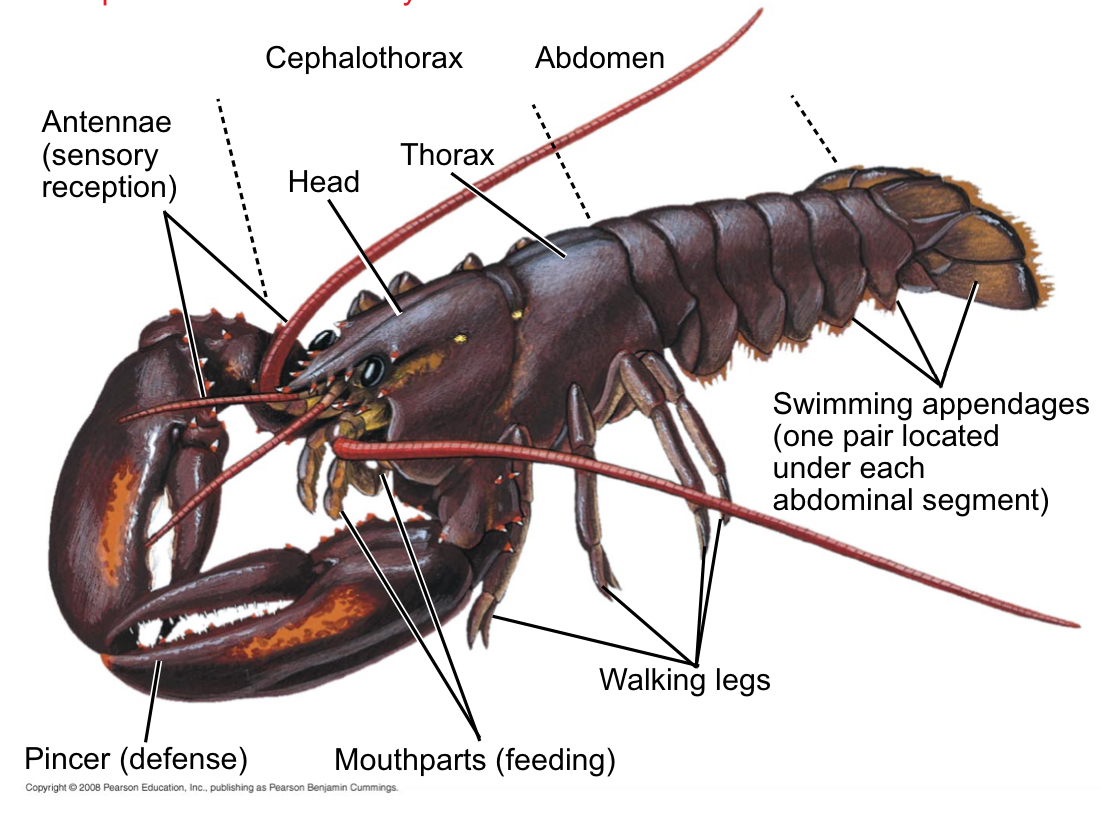
Arthropoda
The largest phylum in the animal kingdom, found in nearly all habitats of the biosphere
What are Arthropods characterized by?
A segmented body, hard exoskeleton, and jointed appendages, early arthropods show little variation
What type of system do Arthropods have?
An open circulatory system
Hemolymph
A fluid circulated into spaces surrounding the tissues and organs
What are the four major lineages of arthropods?
Cheliceriforms, Myriapods, Hexapod, Crustaceans
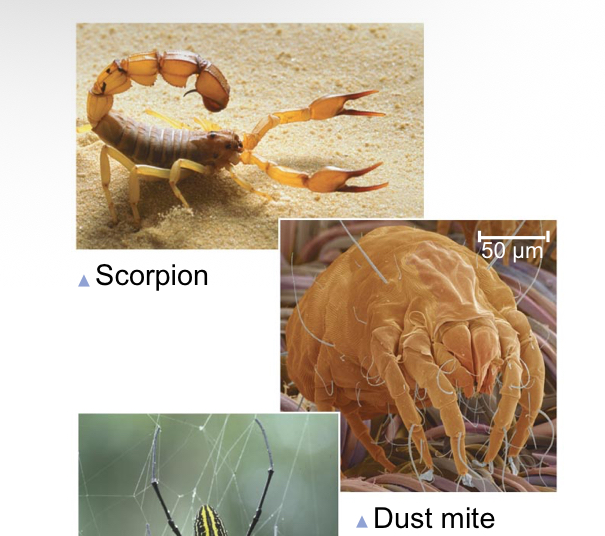

What do most chelicerforms include?
Spiders, scorpions, ticks, and mites
Arachnids are composed of:
An abdomen and a cephalothorax, six pairs of appendages, and the chelicerae (the most anterior)
Where does gas exchange in spiders occur?
Book lungs (respiratory organs)
What do many spiders produce?
A liquid protein silk from specialized abdominal glands
Myripods
Terrestrial, and have jaw-like mandibles
Subphylum Myriapoda includes:
Millipedes and centipedes
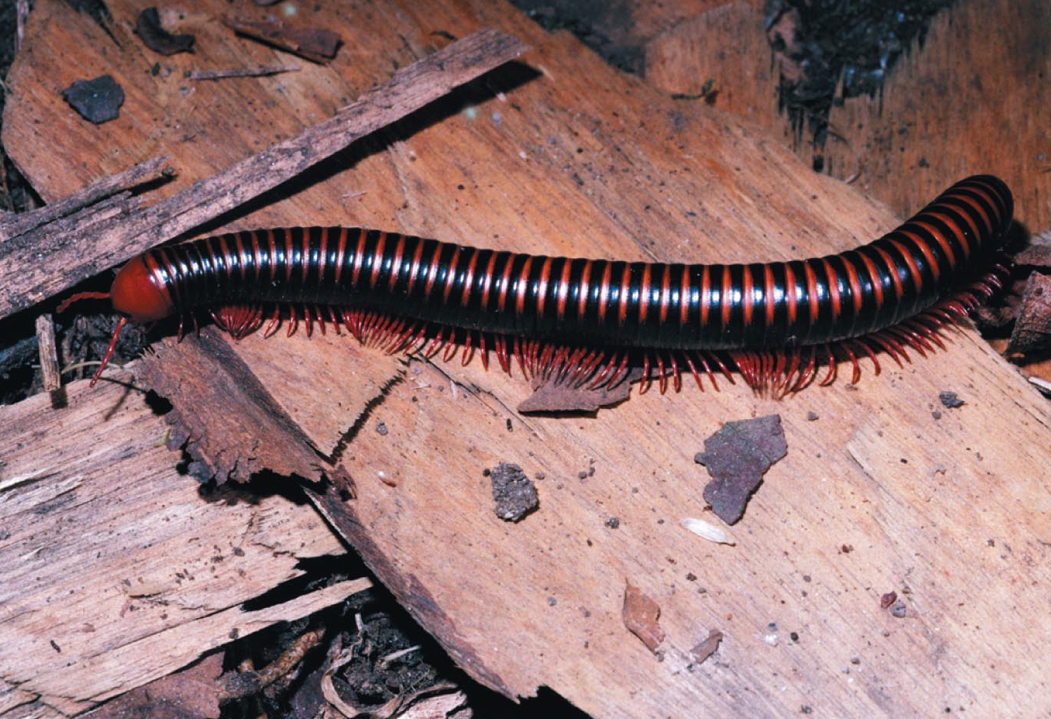

Millipedes (class Diplopoda)
Contain trunk segments that have two pairs of legs
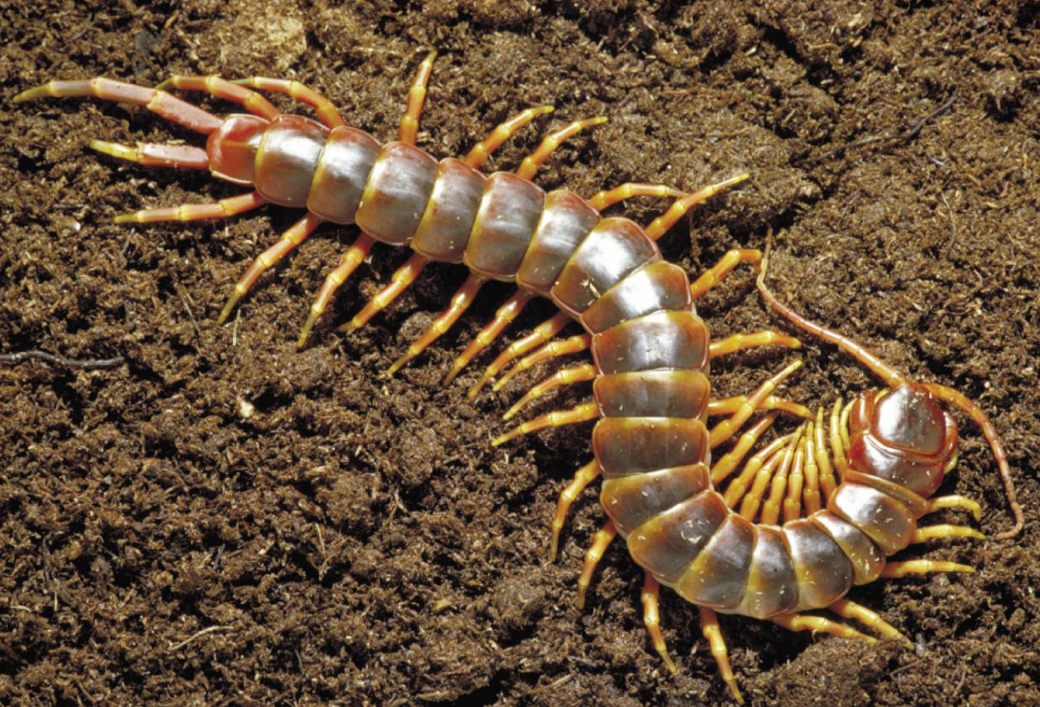

Centipedes (class Chilopoda)
Carnivores with one part of legs per trunk segment
What are included in the Subphylum Hexapoda?
Insects and relatives
Where do the insects live?
In almost every terrestrial habitat and in fresh water
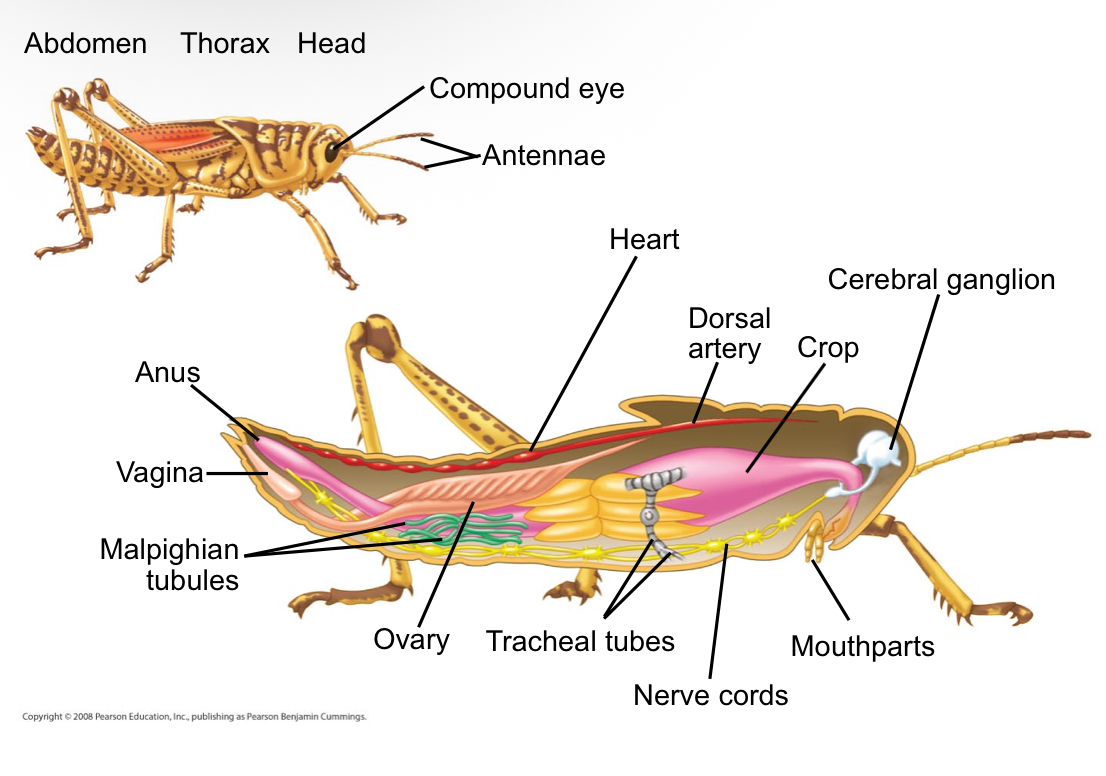
What does the internal anatomy of an insect include?
Several complex organ systems
Insect diversification of evolution:
Flight, adaptation to feeding on gymnosperms, and the expansion of angiosperms
Incomplete metamorphosis
Nymphs (young) that resemble adults but are slightly smaller and go through series of molts until reaching full size

Complete metamorphosis
Insects with larval stages known by such names as maggot, grub, or caterpillar and look different from adult stage
How do insects reproduce?
Through sexual reproduction of separate males and females
How do individual insects recognize members of their own species?
Bright colors, sound, or odors
How are insects beneficial?
As pollinators
How are insects harmful?
As carriers of diseases, or pests of crops

Where do Crustaceans usually live?
In marine and freshwater environments
What do Crustaceans (subphylum Crustacea) typically contain?
Branched appendages specialized for feeding and locomotion
Isopods
Terrestrial, freshwater, and marine species
Decapods
Relatively large crustaceans that include lobsters, crabs, crayfish, and shrimp
Tube feet
Hydraulic structures in echinoderms used for locomotion, feeding, and gas exchange.
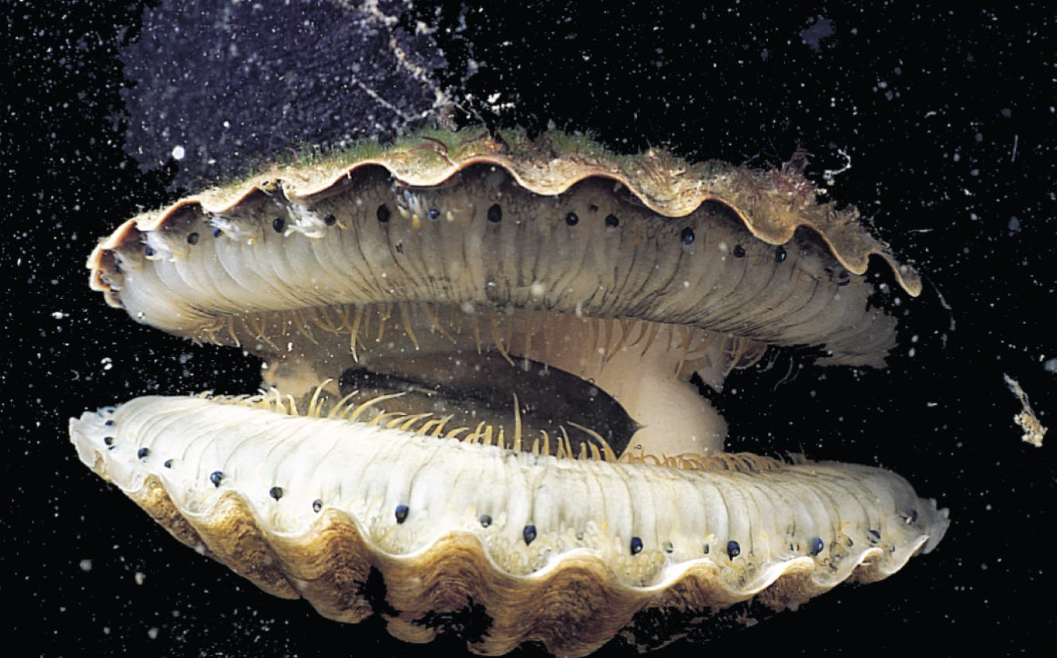

Bivalvia
A class of molluscs that includes clams and oysters, characterized by a two-part shell.
The mantle cavity of a bivalve contains:
Gills that are used for feeding, gas exchange
Cephalopoda
Carnivores with beak-like jaws surrounded by tentacles of their modified foot
What are included in Cephalopods?
Squids, octopuses
Where do most octopuses search for their prey?
Along the sea floor
What allows squids to swim quickly?
Their siphon to fire a jet of water
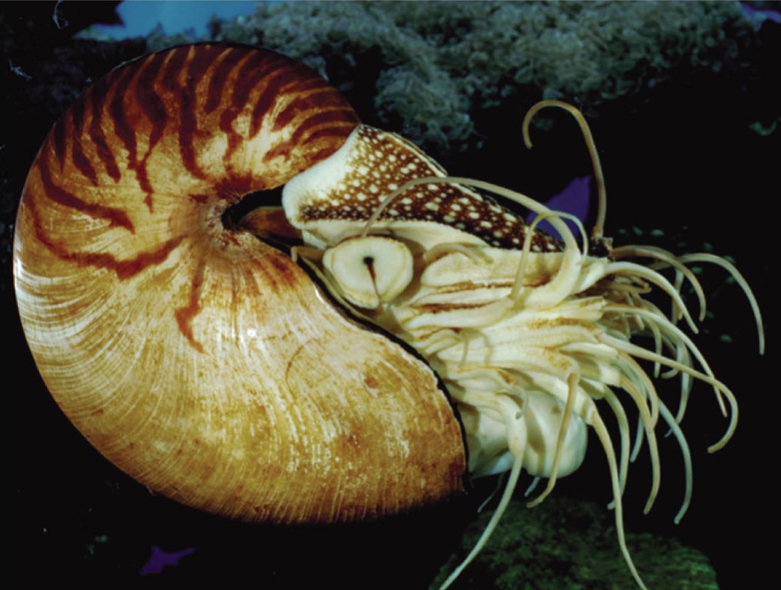

Which group of cephalopods survive today?
Nautiluses
What type of system do Cephalopods have?
A closed circulatory system, well-developed sense organs, and a complex brain
Ammonites
Common shelled cephalopods before the end of Cretaceous
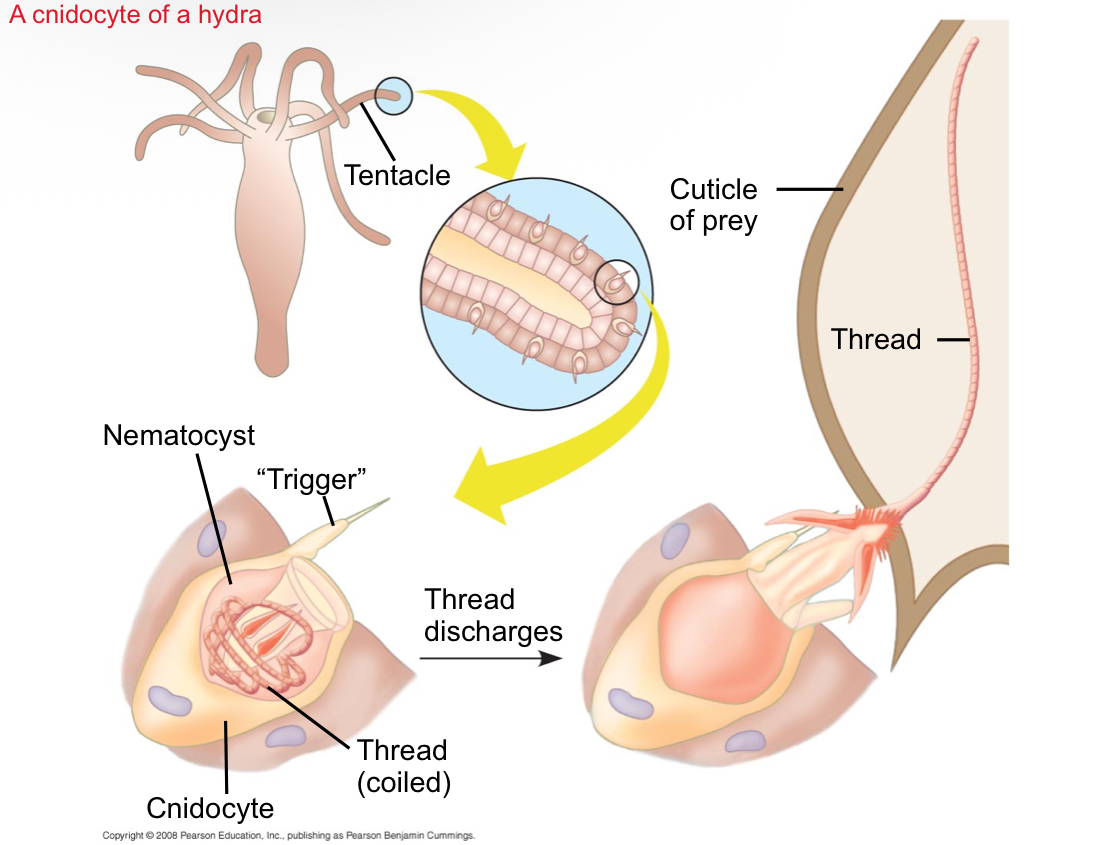
Cnidocytes
Specialized cells in cnidarians used for defense and capturing prey, containing stinging nematocysts.
Annelida
A phylum of segmented worms that have bodies composed of a series of fused rings
The phylum Annelida is divided into three classes:
Oligochaeta, Polychaeta, Hirudinea
Olgiochaetes
A class of earth worms that are named for relatively sparse chaetae, bristles made of chitin
What do Oligochaetes include?
Earthworms and a variety of aquatic species
How do earthworms obtain their nutrients?
Through soil as it moves through the alimentary canal
Earthworms are:
Hermaphrodites but cross-fertilize