hearing rehabilitation - exam 1 study guide
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
89 Terms
air conduction
the process by which sound waves enter the ear through the pinna
bone conduction
occurs as the eardrum vibrates and moves the auditory ossicles
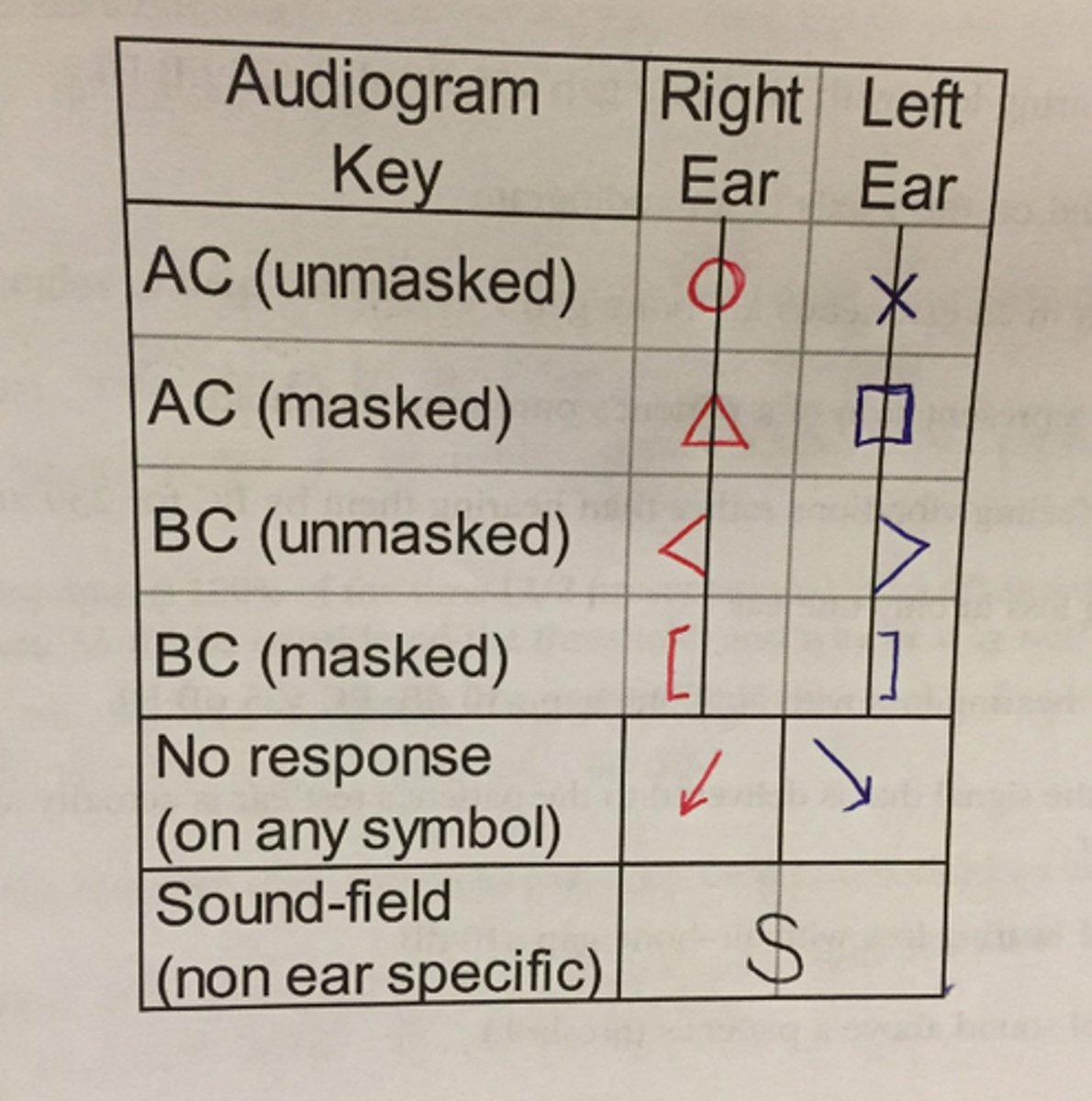
audiogram key
Three types of hearing loss
conductive, sensorineural, mixed
conductive HL
HL that occurs in the outer and middle ear
what causes conductive HL?
excess wax
presence of foreign object
external otitis
otitis media
serous otitis
otosclerosis
sensorineural HL
HL that occurs in the inner ear
what causes sensorineural HL?
meniere's disease
noise exposure
ototoxicity
mixed HL
HL that occurs in a combination of outer, middle, and inner ear
what causes mixed HL?
combination of otitis media and noise exposure
combination of ossicular chain disruption and age
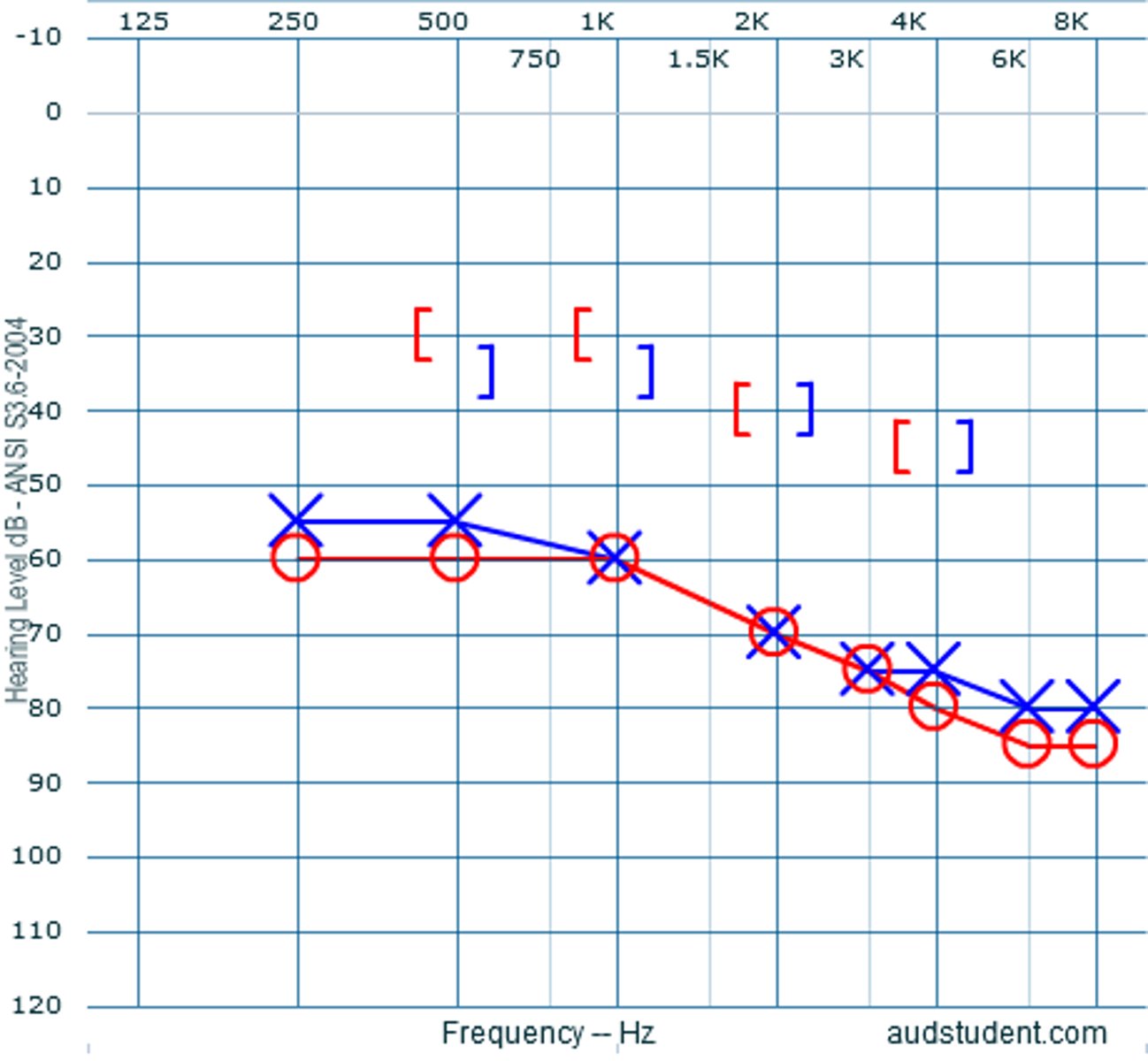
what type of hearing loss is shown in this audiogram?
normal hearing
3 multiple choice options
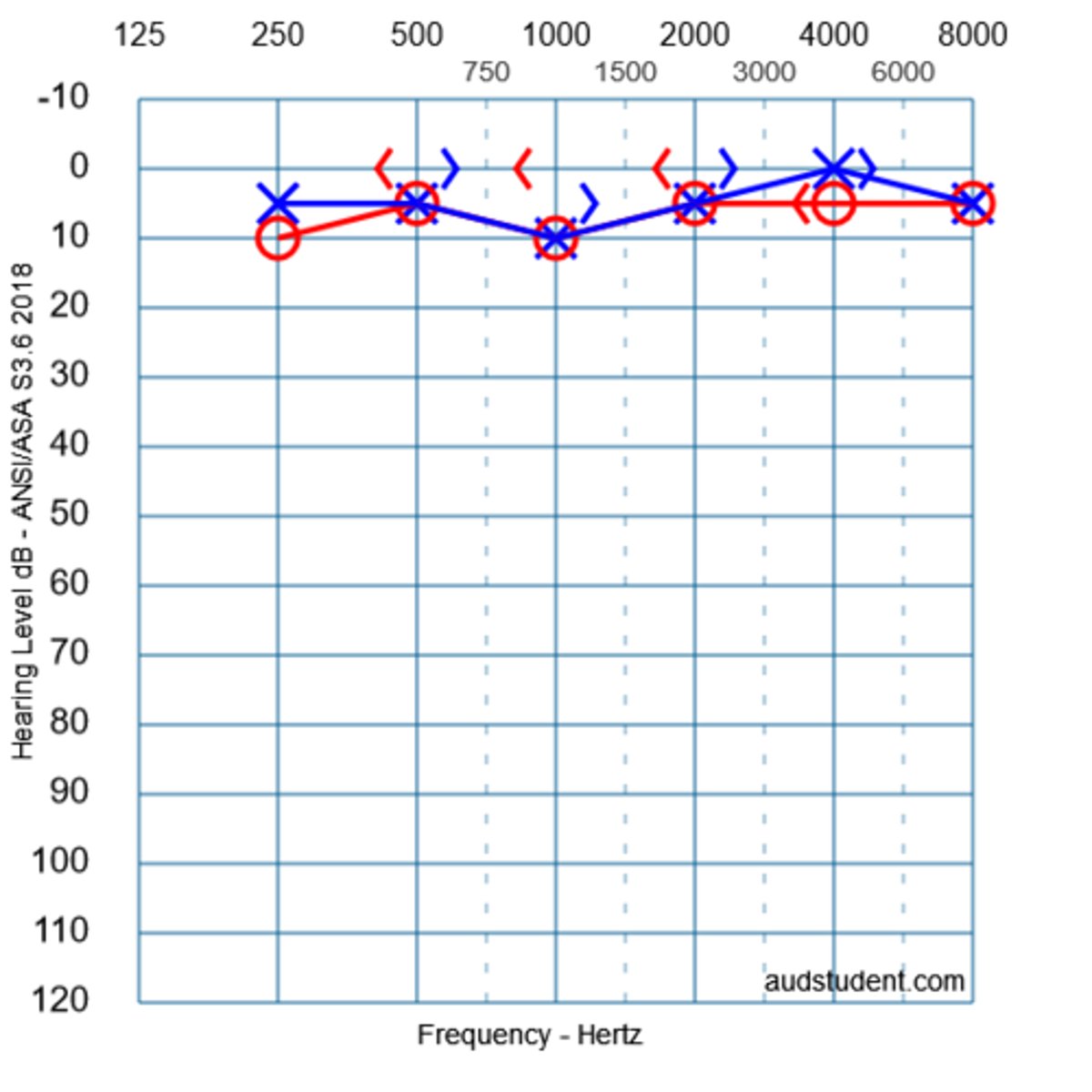
what type of hearing loss is shown in this audiogram?
conductive HL
3 multiple choice options
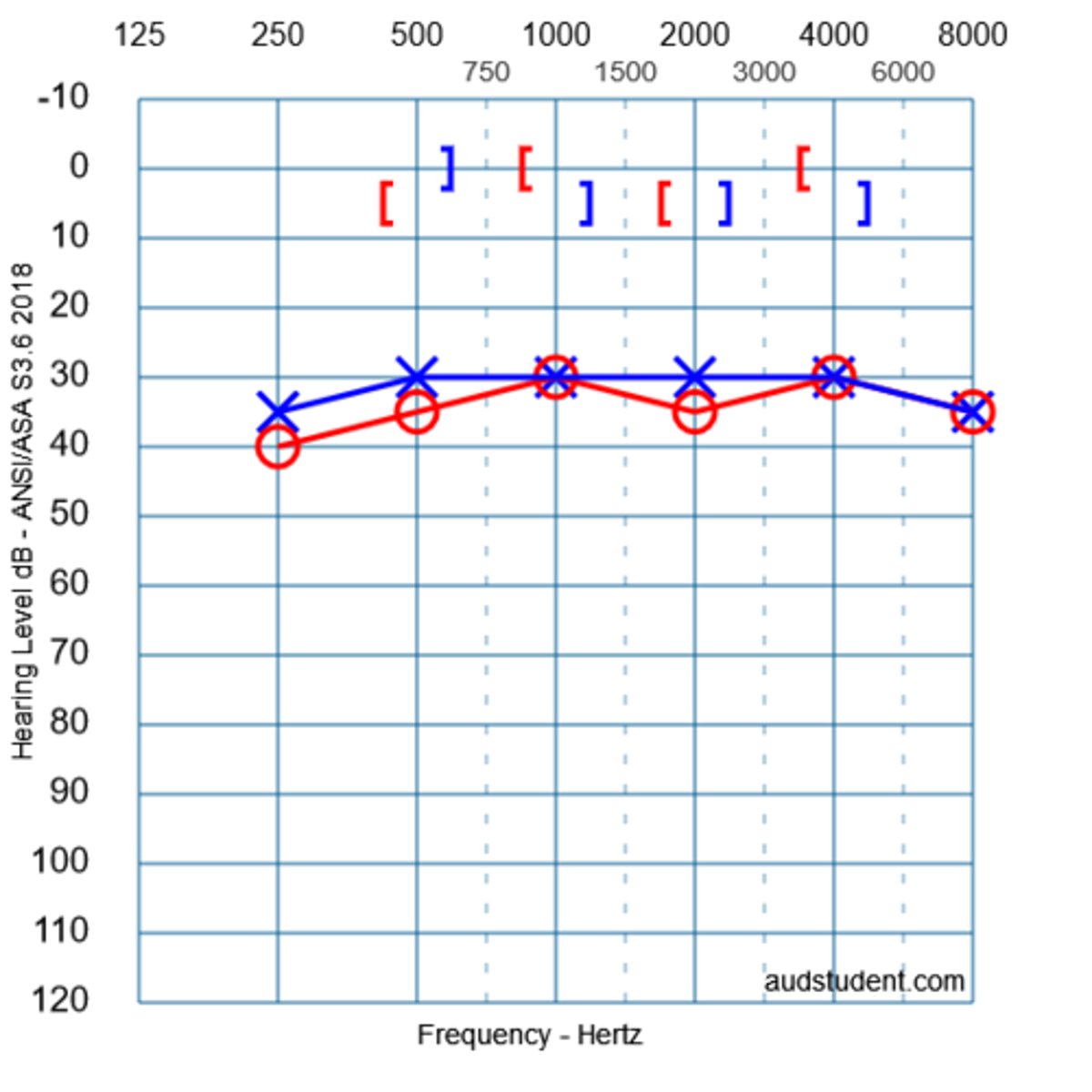
what type of hearing loss is shown in this audiogram?
sensorineural HL
3 multiple choice options
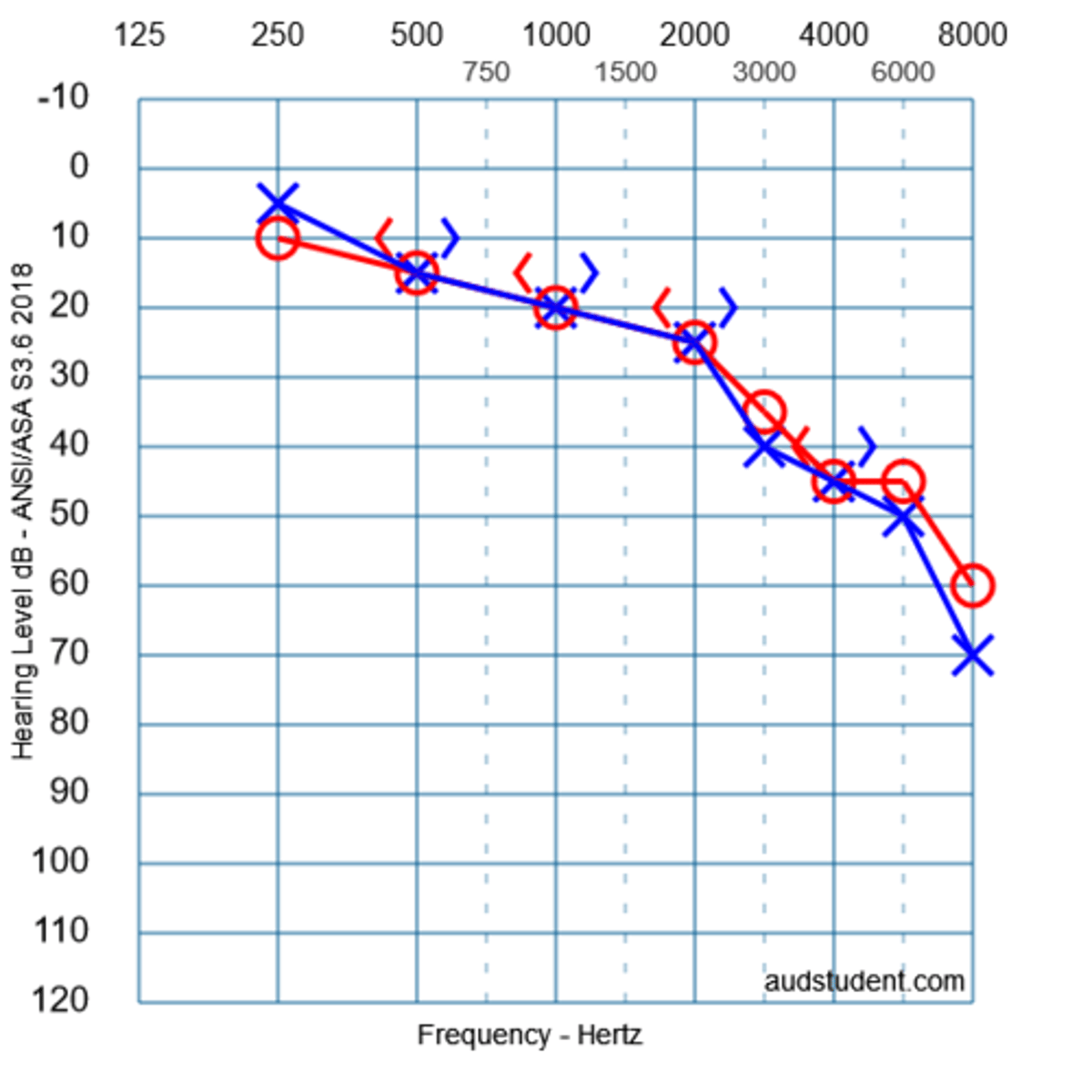
what type of hearing loss is shown in this audiogram?
mixed HL
3 multiple choice options
how many people have tinnitus?
50 million
how many people are regularly exposed to hazardous noise levels?
30 million
how many people are hard of hearing?
26 million
how many people have some degree of permanent noise induced hearing loss
10 million
how many people are classified as deaf
2 million
what percentage of school age children may fail a screening due to ear infections?
15%
what percentage of children before the age of 6, have had at least one ear infection?
90%
percentage of people with hearing loss _____ the older people get
increases
2 multiple choice options
Who is the father of audiology?
Raymond Carhart
styles of hearing aids
completely in the canal (CIC)
invisible in the canal (IIC)
in the canal (ITC)
in the ear (ITE)
half shell (ITE)
behind the ear (BTE)
receiver in the canal (RIC)
slim tube/open
customizable hearing aids
completely in the canal (CIC)
invisible in the canal (IIC)
in the canal (ITC)
in the ear (ITE)
half shell (ITE)
range of customizable hearing aids
mild - moderate - moderately severe
advantages to customizable hearing aids
less visible
disadvantages to customizable hearing aids
circuit inside ear
re-casing will be needed if weight changes
less power
behind the ear hearing aids
behind the ear (BTE)
receiver in the canal (RIC)
sim tube/open fit
range of behind the ear hearing aids
mild - profound
advantages of behind the ear hearing aids
power
no need for re-casing due to weight changes
circuit not inside ear
disadvantages of behind the ear hearing aids
visible
important factors when choosing hearing aids
age
dexterity
cost
steps for ear mold impression
1. perform an otoscopy
2. insert an otoblock
3. check otoblock placement
4. prepare the impression materiaal
5. inject impression material into the ear canal
6. let material harden
7. remove impression
parts of a hearing aid
microphone
amplifier
receiver
power supply
basic components of a hearing aid circuit
analog hearing aids
digital hearing aids
amplification
microphones
condensors
ear trumpet/ear cupping
1600-1899
carbon hearing aid
1899-1920
vacuum tube
1920-1940
transistor hearing aid
1940-1960
digital hearing aid
1960-1980
wireless hearing aid
2005
CROS vs BiCROS hearing aids
- Contralateral routing of signals (CROS): used when there is a dead ear and a normal ear
- Bi-contralateral routing of signals (BiCROS): used when there is a dead ear and a damaged ear
three levels of technology
1. high-end: used for people who are active and in frequency in noisy environments
2. mid-level: used for people who are somewhat active but dont need the advancements
3. low-end: used for people who are mainly at home
silicone ear mold material
advantages: durable and comfortable
disadvantages: shrinks over time, easy to modify
acrylic ear mold material
advantages: easy to clean, doesnt shrink over time, easy to modify
disadvantages: breaks easily
aural rehabilitation
helps rehabilitate the effects of hearing loss
aural habilitation
helps people who were born with hearing loss
participation restrictions
problems an individual may experience in involvement in life situations
activity limitations
difficulties an individual may have in executing activities
prelingual deafness
hearing loss acquired before the onset of language development
perilingual deafness
hearing loss is acquired while developing a first language
post-lingual deafness
hearing loss that occurs after the child has begun to learn language
hard of hearing
not able to hear well
deaf
unable to hear
discrimination
Behaving differently, usually unfairly, toward the members of a group.
dynamic range
the range of amplitudes that can be heard and discriminated; when applied to an individual auditory nerve fiber, the range of amplitudes over which the firing rate of the fiber changes
hearing aid
device used by persons with impaired hearing to amplify sound
acoustics
the study of sound
loudness scaling
occlusion effect
channels
directional microphone systems
digital noise reduction
feedback management
telecoil
datalogging
learning features
binaural processing
programs
gain
frequency responsive curve
output sound pressure
level 90
harmonic distortion
battery current
equivalent input noise level
attack and release times
telephone magnetic field response
compression circuitries
acoustic feedback
acclimatization process
troubleshooting
hearing aid outcome measure
functional gain
self-assessment
speech perception
real ear measures